Home>Finance>What Does A Life Insurance Blood Test Look For?

Finance
What Does A Life Insurance Blood Test Look For?
Published: October 15, 2023
Learn what a life insurance blood test entails and what it looks for in order to secure your financial future.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When applying for a life insurance policy, it is common for insurance companies to request a blood test as part of the underwriting process. This blood test provides valuable information about your health and helps insurers assess the risk involved in providing you with coverage. By analyzing your blood, insurers can gain insights into various aspects of your health, such as your cholesterol levels, blood sugar levels, liver function, and genetic predispositions.
The life insurance blood test is typically performed by a licensed medical professional who will draw a small sample of blood from your body. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where a range of tests is conducted to evaluate your overall health and identify any potential red flags that may affect your eligibility or premium rates.
While the idea of a life insurance blood test may seem daunting, it is important to understand that its purpose is not to invade your privacy but rather to assess your health accurately. The results of these tests are crucial for insurers to determine the appropriate amount of coverage and the risk associated with insuring you.
It is essential to be transparent and honest while applying for life insurance. Trying to hide or misrepresent your medical conditions can lead to the denial of coverage or the cancellation of your policy in the future. Therefore, it is beneficial to have a clear understanding of what the life insurance blood test looks for and how it may impact your policy.
In this article, we will explore the common tests conducted during a life insurance blood test, their purposes, and what potential areas of concern insurers may have. By understanding the significance of these tests, you can be better prepared and ensure a smooth and successful application process.
Overview of Life Insurance Blood Tests
Life insurance blood tests play a vital role in determining your eligibility for coverage and calculating your premium rates. These tests provide insurers with valuable information about your overall health and help them assess the level of risk associated with insuring you.
During a life insurance blood test, a number of different components in your blood are analyzed, including cholesterol levels, blood sugar levels, liver and kidney function, genetic markers, and the presence of any infectious diseases or drug use. By examining these factors, insurance companies can gain insight into your overall health and identify any potential red flags that may impact your policy.
The results of these tests are a significant factor in determining the type and amount of coverage you qualify for. If your test results indicate good health, you may be eligible for standard or preferred rates. However, if any abnormalities or health issues are detected, you may be classified as a higher risk and offered coverage at a higher premium.
It is important to note that the specific tests conducted during a life insurance blood test may vary depending on factors such as your age, gender, and the insurance company’s underwriting guidelines. Insurance companies may also request additional tests or medical exams, such as a urine test or a physical examination, to gather a comprehensive picture of your health.
While the idea of a life insurance blood test can be intimidating, it is important to remember that its purpose is not to pass judgment on your health but rather to accurately assess the risk for the insurer. The results of these tests help insurance companies make informed decisions and ensure they can provide coverage to individuals at an appropriate risk level.
Next, we will take a closer look at the specific purposes of life insurance blood tests and the common tests conducted during the process.
Purpose of Life Insurance Blood Tests
Life insurance blood tests serve several important purposes for insurance companies. These tests provide insurers with valuable information about your health and help them assess the risk involved in providing you with coverage. The results of these tests are used to determine your eligibility for coverage, as well as to calculate your premium rates. Let’s explore the main purposes of life insurance blood tests:
- Evaluating overall health: Life insurance blood tests provide a comprehensive view of your health by analyzing various markers in your blood. This allows insurers to assess your overall health and identify any underlying medical conditions that could affect your coverage or rates.
- Assessing risk: The results of blood tests help insurers gauge the level of risk associated with insuring you. By analyzing factors such as cholesterol levels, blood glucose levels, and liver function, insurers can determine the likelihood of future health complications and adjust your premium rates accordingly.
- Detecting pre-existing conditions: Life insurance blood tests can uncover pre-existing medical conditions that you may not be aware of. These conditions can range from high cholesterol or diabetes to liver or kidney problems. Identifying these conditions allows insurers to accurately assess the risk involved in providing coverage.
- Verifying applicant information: Life insurance blood tests also serve as a means of verifying the information provided on your application. Insurers use blood test results to ensure that the information you provided about your medical history and lifestyle is accurate and complete. Inaccurate or incomplete information can impact your coverage and may even result in the denial of your application.
- Preventing fraud: Blood tests help insurance companies identify any attempts to deceive or manipulate the application process. By analyzing your blood, insurers can check for the presence of drugs or alcohol, which can indicate risky behaviors or undisclosed habits that may affect your policy.
It is important to understand that the purpose of life insurance blood tests is not to discriminate against individuals based on their health status. Instead, these tests are used to accurately assess the risk involved in providing coverage and to ensure fairness in the pricing of insurance policies.
Next, we will delve into the common tests conducted during a life insurance blood test and what they reveal about your health.
Common Tests Conducted
During a life insurance blood test, several common tests are conducted to assess your overall health and identify any potential risk factors. These tests provide insurers with important information about your blood composition and organ function. Let’s explore some of the most common tests conducted during a life insurance blood test:
- Blood Pressure: A blood pressure test measures the force of blood against the walls of your arteries. High blood pressure (hypertension) can indicate an increased risk of heart disease and other health complications.
- Cholesterol Levels: Cholesterol is a fatty substance found in your blood. High levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol or low levels of HDL (good) cholesterol can increase the risk of heart disease.
- Blood Glucose: Blood glucose (sugar) levels are measured to assess the risk of diabetes. High levels of glucose can indicate impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes.
- Liver Function Tests: Liver function tests check for levels of enzymes and proteins in the blood that indicate liver health. Abnormal results may indicate liver disease or damage.
- Kidney Function Tests: Kidney function tests measure levels of various substances in the blood to assess how well the kidneys are functioning. Abnormal results may indicate kidney disease or malfunction.
- Hepatitis and HIV: Blood tests may also screen for infectious diseases such as hepatitis or HIV. These tests help identify any potential risks for insurers and ensure appropriate coverage.
- Drug and Alcohol Testing: Some life insurance blood tests include screenings for drugs and alcohol. These tests can reveal any substance use that may impact your policy eligibility.
- Genetic Testing: Genetic tests may be conducted to identify specific genetic markers linked to certain diseases or conditions. This information helps insurers assess the risk of developing hereditary conditions.
These are just a few examples of the many tests that may be conducted during a life insurance blood test. The specific tests performed will depend on various factors, including your age, gender, and the insurance company’s underwriting guidelines.
It is important to note that the results of these tests are used to assess risk and determine your eligibility for coverage. If any abnormalities or health issues are detected, it doesn’t automatically mean that you won’t be able to obtain life insurance. However, it may affect the type of policy you qualify for and the premium rates you are offered.
Now that we have explored the common tests conducted during a life insurance blood test, let’s discuss some of the key areas insurers focus on when assessing your health.
Blood Pressure and Heart Health
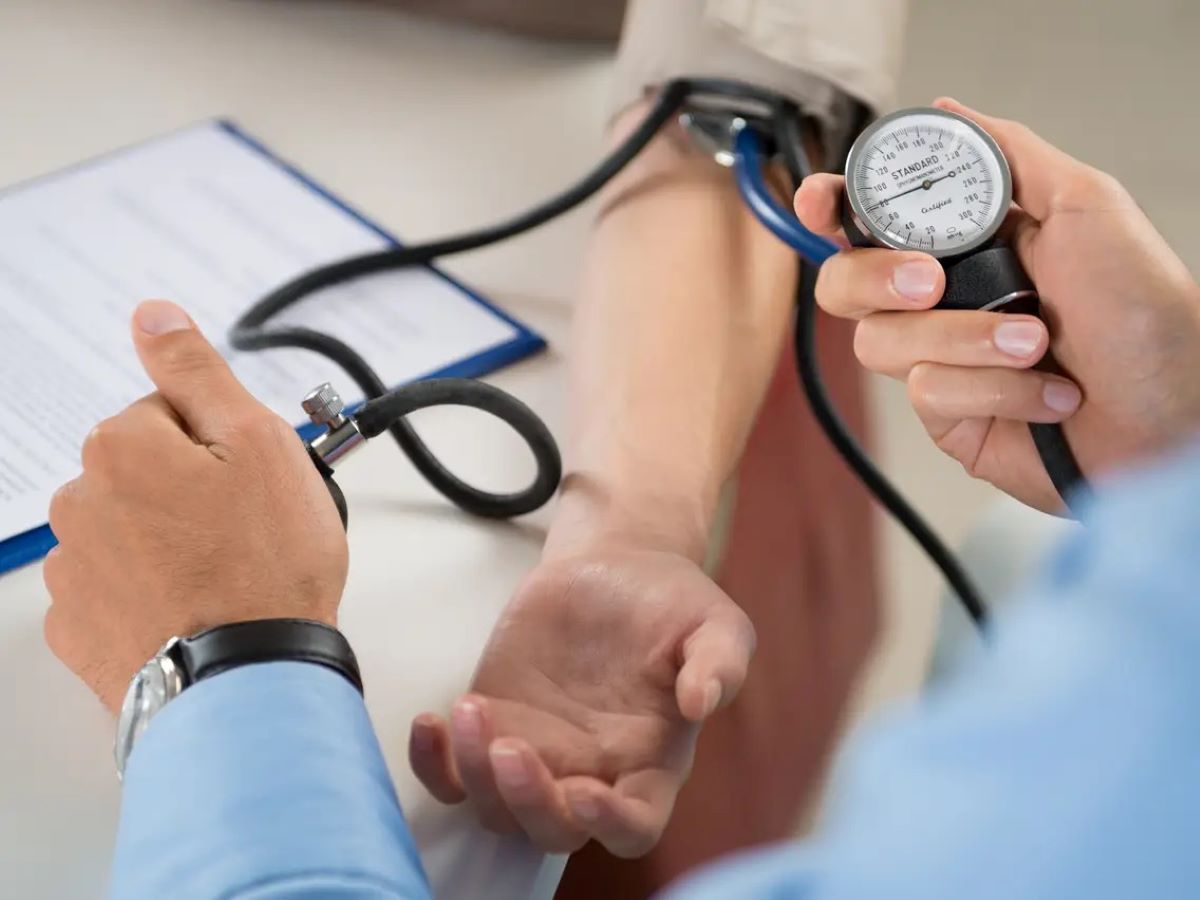
Blood pressure is a key indicator of heart health and is a crucial component of a life insurance blood test. High blood pressure, or hypertension, can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications. Since heart disease is a leading cause of death, insurance companies pay close attention to blood pressure levels when assessing an applicant’s health and risk profile.
During a life insurance blood test, your blood pressure is measured using a device called a sphygmomanometer. The measurement is given in two numbers: systolic pressure over diastolic pressure. The systolic pressure represents the force exerted on the arteries when the heart beats, while the diastolic pressure measures the force when the heart is at rest.
Normal blood pressure is typically around 120/80 mmHg. Insurance companies consider blood pressure readings within this range as an indication of good heart health. However, if your blood pressure is consistently elevated, it may suggest an increased risk of cardiovascular complications and may result in higher premiums or limited coverage.
It is important to note that a single high blood pressure reading during a life insurance blood test may not necessarily disqualify you from coverage. Insurers typically take multiple readings and consider your average blood pressure over time. If your blood pressure is only slightly elevated during the test, insurers may request a follow-up reading or request additional tests to ensure accuracy.
If you have been diagnosed with high blood pressure, it is crucial to manage your condition and follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations. Taking steps to control your blood pressure through lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and potentially prescribed medication, can significantly improve your overall health and reduce the associated risks.
When applying for life insurance, it is important to be upfront about any pre-existing conditions, including high blood pressure. Providing accurate and complete information helps insurance companies better assess your risk and determine appropriate coverage options for you.
In summary, blood pressure is a key component of a life insurance blood test and an important indicator of heart health. Maintaining healthy blood pressure levels through lifestyle modifications can not only improve your overall health but may also positively impact your insurance rates and eligibility for coverage.
Cholesterol Levels
Cholesterol levels are a crucial aspect of a life insurance blood test as they provide insight into your cardiovascular health. Cholesterol is a waxy substance produced by your liver and obtained from certain foods. It plays an essential role in your body’s normal functioning, but high levels of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, also known as “bad” cholesterol, can increase the risk of heart disease.
A life insurance blood test typically measures three types of cholesterol:
- Total cholesterol: This represents the sum of all types of cholesterol in your blood.
- HDL cholesterol: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol, often referred to as “good” cholesterol, helps remove LDL cholesterol from your arteries, reducing the risk of heart disease.
- LDL cholesterol: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol is considered “bad” cholesterol because it contributes to the formation of plaque in your arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease.
An elevated level of total cholesterol or LDL cholesterol can indicate an increased risk of cardiovascular complications, while a higher level of HDL cholesterol is generally considered favorable for heart health.
Insurance companies use cholesterol levels as an important factor in assessing an applicant’s overall health and potential risk. If your blood test reveals higher cholesterol levels, it may result in higher premiums or additional screenings to get a comprehensive understanding of your health status before determining your eligibility for coverage.
If your cholesterol levels are found to be elevated during a life insurance blood test, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider. They can provide guidance on lifestyle changes, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, increasing physical activity, and potentially prescribing medications, to help you manage your cholesterol levels and reduce the associated health risks.
When applying for life insurance, it is essential to be honest about your cholesterol levels and any related medical conditions. Providing accurate and complete information allows insurance companies to accurately evaluate your risk profile and offer appropriate coverage options.
In summary, cholesterol levels play a significant role in a life insurance blood test. Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels through lifestyle modifications and medical interventions can not only improve your overall well-being but may also positively impact your insurance rates and eligibility for coverage.
Blood Glucose and Diabetes
During a life insurance blood test, one of the measurements taken is your blood glucose level. This test is used to assess your risk of diabetes and your overall management of blood sugar levels. Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood glucose levels, and it can have significant health implications.
The blood glucose test provides valuable information about your body’s ability to regulate sugar levels. There are two main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes: This is an autoimmune disease where the body does not produce enough insulin, a hormone that allows glucose to enter the cells for energy. Type 1 diabetes is typically diagnosed earlier in life and requires insulin injections.
- Type 2 diabetes: This is a chronic condition that occurs when the body becomes insulin resistant or doesn’t produce enough insulin. Type 2 diabetes is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, and poor diet.
Insurance companies are interested in your blood glucose levels during a life insurance blood test because diabetes can lead to various health complications. High blood glucose can increase the risk of heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and other serious health issues.
If your blood glucose level is within a normal range during the blood test, it is an indication of good sugar regulation. However, if your blood glucose level is consistently elevated, it may suggest impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes. Insurance companies may view this as a higher risk factor, resulting in higher premiums or additional medical underwriting before offering coverage.
If you have been diagnosed with diabetes, it is important to manage your condition effectively by following your healthcare provider’s recommendations. This may include monitoring your blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, taking prescribed medications, and managing any related health complications.
When applying for life insurance, it is crucial to be transparent about your diabetes diagnosis and provide accurate information about your management and treatment. Insurance companies assess this information to determine appropriate coverage options and premium rates based on your health status.
In summary, blood glucose levels are an essential component of a life insurance blood test. Managing your blood sugar levels effectively through proper diabetes management can not only improve your overall health but may also positively impact your eligibility for coverage and insurance rates.
Liver and Kidney Function
A life insurance blood test often includes measuring liver and kidney function to assess the health of these vital organs. The liver and kidneys play crucial roles in maintaining overall well-being and removing toxins from the body. By evaluating liver and kidney function, insurance companies can gain insights into an individual’s overall health status and potential risk factors.
The liver function tests (LFTs) check for the levels of enzymes and proteins in the blood that indicate liver health. Abnormal levels can be indicators of liver disease or damage. Some common liver function tests include:
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) tests, which assess liver enzyme levels.
- Bilirubin test, which measures a pigment produced from the breakdown of red blood cells and helps detect liver or bile duct complications.
- Albumin and total protein tests, which evaluate liver protein production.
Similarly, kidney function tests assess how well the kidneys are functioning by measuring levels of various substances in the blood. Some common kidney function tests include:
- Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) test, which measures the amount of nitrogen in the blood produced from the breakdown of proteins during kidney filtration.
- Creatinine test, which evaluates waste product levels in the blood and provides an indication of kidney function.
- Glomerular filtration rate (GFR), which estimates the kidneys’ ability to filter waste from the blood.
Abnormal liver or kidney function test results may indicate underlying health conditions or potential risks. Insurance companies consider these results when assessing an applicant’s overall health and determining coverage eligibility and premium rates.
If the blood test reveals liver or kidney abnormalities, insurers may request further testing or medical evaluations to gain a better understanding of your health status. It is important to note that a single abnormal test result does not automatically disqualify an individual from receiving life insurance coverage. Further investigation is typically required to make an accurate assessment of risk.
It is crucial to be honest about any pre-existing liver or kidney conditions when applying for life insurance. Providing accurate information allows insurers to properly evaluate your risk profile and offer appropriate coverage options.
In summary, liver and kidney function tests are essential components of a life insurance blood test. Monitoring and managing the health of these organs through regular medical check-ups and following healthcare provider recommendations can contribute to overall well-being and potentially affect insurance rates and eligibility for coverage.
Drug and Alcohol Testing
Drug and alcohol testing is a common component of a life insurance blood test. Insurance companies conduct these tests to assess an applicant’s lifestyle and potential health risks associated with substance use. The results of drug and alcohol testing play a significant role in determining coverage eligibility and premium rates.
During a life insurance blood test, several substances may be screened, including illicit drugs and alcohol. The purpose of this testing is to identify any drug or alcohol use that may pose a potential risk to an applicant’s health or raise concerns about their ability to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
The accuracy and types of substances tested may vary depending on the insurance company’s underwriting guidelines. Common substances that may be screened during a life insurance blood test include:
- Marijuana
- Opiates
- Cocaine
- Amphetamines
- Benzodiazepines
- Alcohol
If the test detects the presence of drugs or higher-than-acceptable levels of alcohol, it may raise concerns for insurers. Substance use can contribute to a variety of health issues, including liver damage, heart problems, and mental health disorders. Insurers may view applicants with substance use issues as higher risk, resulting in higher premiums or potential limitations on coverage.
It’s important to note that occasional or moderate use of alcohol or legally-prescribed medications is typically not a concern for insurers. However, it is crucial to be transparent and provide accurate information about any substance use when applying for life insurance. Withholding or providing false information about substance use can lead to policy denial or even cancellation in the future.
If an applicant tests positive for drugs or alcohol during a life insurance blood test, insurers may request additional medical documentation or request a follow-up test to confirm the results. In some cases, individuals who have successfully overcome substance use disorders and can provide evidence of their recovery may still be eligible for coverage, albeit potentially at higher premium rates.
In summary, drug and alcohol testing is part of a life insurance blood test process to evaluate an applicant’s substance use and associated health risks. Being honest about substance use and following any necessary treatment or recovery programs can help ensure accurate underwriting and potentially impact insurance rates and eligibility for coverage.
Infectious Diseases
As part of a life insurance blood test, screening for infectious diseases is a critical aspect of the assessment process. Insurance companies conduct these tests to identify any potential risks associated with infectious diseases, which can impact an applicant’s health and increase the likelihood of future medical complications.
During a life insurance blood test, several infectious diseases may be screened, depending on the insurance company’s underwriting guidelines and regional considerations. Common infectious diseases that may be tested for include:
- HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)
- Hepatitis B and C
- Syphilis
- Tuberculosis (TB)
Detecting the presence of these infectious diseases helps insurance companies assess an applicant’s overall health and determine the level of risk they pose for future claims. It is important to note that testing positive for an infectious disease does not automatically disqualify an individual from obtaining life insurance. The severity and management of the disease, as well as the individual’s overall health status, are taken into consideration.
In some cases, insurance companies may request additional medical documentation or consultations with healthcare providers to gain a better understanding of the disease’s impact on the applicant’s health. This allows insurers to make informed decisions about coverage eligibility and premium rates.
It is crucial to provide accurate and truthful information regarding any infectious diseases during the life insurance application process. Attempting to hide or misrepresent this information can result in denial of coverage or policy cancellation in the future.
If an individual tests positive for an infectious disease, it is important to consult with healthcare professionals and follow the recommended treatment plans. Proper medical management can help control and/or reduce the impact of the disease on overall health, potentially improving eligibility for life insurance coverage.
In summary, infectious disease screening is an important component of life insurance blood tests to evaluate an individual’s health risks. Providing accurate information about infectious diseases and following appropriate medical guidance can contribute to a fair assessment of risk and potential impact on insurance rates and eligibility for coverage.
Genetic Testing
In recent years, genetic testing has become increasingly common in the field of life insurance underwriting. Genetic testing involves analyzing an individual’s DNA to identify inherited genetic mutations or variations that may be associated with certain diseases or conditions.
The purpose of genetic testing during a life insurance blood test is to assess an individual’s potential risk for developing hereditary conditions. Insurance companies are interested in genetic testing as it provides valuable insights into an applicant’s health profile and potential future health risks.
Genetic testing can reveal information about a wide range of conditions, including but not limited to:
- Breast and ovarian cancer (BRCA mutations)
- Cardiovascular diseases (such as familial hypercholesterolemia)
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Cystic fibrosis
- Huntington’s disease
Insurance companies use genetic testing results to assess the risk of an applicant developing these hereditary conditions. Depending on the specific genetic mutations or variations identified, insurers may adjust premium rates or determine eligibility for coverage.
It is important to note that genetic testing results alone do not lead to an automatic denial of coverage. Insurance companies consider the overall health profile of applicants, including genetic information, and often factor in additional medical and lifestyle information.
Disclosure of accurate and complete genetic testing information is crucial during the life insurance application process. Providing thorough and honest answers allows insurance companies to make fair and informed decisions based on an applicant’s health and risk factors.
Lastly, it is essential to be aware of privacy concerns surrounding genetic testing. Insurance companies adhere to strict privacy regulations and are not allowed to require individuals to undergo genetic testing. However, if an individual has already undergone genetic testing, voluntarily providing the results during the underwriting process may be necessary.
In summary, genetic testing plays a role in life insurance underwriting by providing insights into an individual’s potential risk for hereditary conditions. Accuracy and transparency when disclosing genetic testing results help insurers make fair assessments of risk and determine appropriate coverage options and premium rates.
Conclusion
A life insurance blood test is an integral part of the underwriting process and allows insurance companies to assess an individual’s health and potential risks associated with coverage. The tests conducted during this process provide valuable information about various aspects of an individual’s health, including blood pressure, cholesterol levels, blood glucose, liver and kidney function, genetic markers, drug and alcohol use, and infectious diseases.
Understanding the purpose of the life insurance blood test and the significance of the results can help individuals navigate the application process more effectively. It is crucial to provide accurate and complete information about one’s medical history and lifestyle to ensure a fair evaluation by insurance companies.
If tests reveal any abnormalities or health concerns, individuals can take proactive steps to improve their health. This may involve managing conditions such as high blood pressure or cholesterol, diabetes, or liver and kidney issues through lifestyle modifications and following healthcare provider recommendations.
It is important to remember that the results of a life insurance blood test are used to assess an individual’s risk profile and determine appropriate coverage options and premium rates. Even if an individual has certain health conditions, it does not automatically disqualify them from obtaining life insurance. Insurance companies take various factors into consideration when evaluating an applicant’s eligibility.
Transparency and honesty during the application process are key. Attempting to hide or misrepresent information, including pre-existing conditions or substance use, can have serious consequences, including denial of coverage or policy cancellation in the future.
In conclusion, a life insurance blood test provides insurers with important information about an individual’s health and potential risks. By understanding the purpose of these tests and offering genuine and accurate information, individuals can navigate the application process with confidence and potentially secure the coverage that suits their needs.