Finance
How To Calculate Credit Hours Earned
Published: January 4, 2024
[How To Calculate Credit Hours Earned] - Learn the simple and effective methods for calculating credit hours earned in the field of finance. Master the credit hours calculation techniques now!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Understanding how to calculate credit hours earned is essential for students and professionals alike. Credit hours serve as a measure of the time and effort invested in a particular course or program. They determine the academic progress and completion requirements for students and play a significant role in various educational systems.
Whether you are a student navigating your way through college or a professional seeking to advance your career through continuing education, knowing how to calculate credit hours is crucial. This article will guide you through the process, providing you with a clear understanding of the factors to consider and the steps involved in calculating credit hours earned.
As you delve into the world of credit hours, keep in mind that different educational institutions and programs may follow slightly different guidelines for calculating credit hours. It is important to refer to your institution’s specific policies and consult with academic advisors or supervisors to ensure accuracy. However, the general principles discussed in this article will give you a solid foundation for understanding and calculating credit hours earned.
Now, let’s explore the concept of credit hours and the factors that come into play when determining their value.
Understanding Credit Hours
Credit hours are a standardized method used by educational institutions to quantify the amount of time and effort required to complete a course or program. They serve as a measure of the workload and are used to assess academic progress and determine requirements for degree completion.
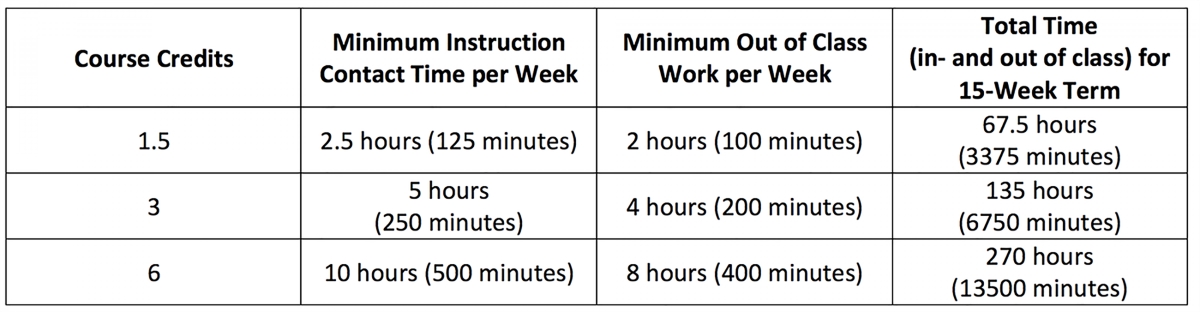
In most educational systems, one credit hour represents the equivalent of one hour of classroom or instructional time per week throughout a standard semester. This includes time spent in lectures, discussions, laboratories, and other structured learning activities. Additionally, credit hours account for the time spent outside of class on individual study, assignments, projects, and exams.
Typically, credit hours are assigned to courses based on a combination of factors, including the complexity and depth of the material covered, the number of contact hours with instructors, and the expected workload outside of class. Courses that require more rigorous academic engagement or involve specialized skill development are often assigned a higher number of credit hours.
It is important to note that credit hours are not solely based on the number of hours spent in class. Rather, they provide an overall estimate of the total time commitment required to successfully complete a course.
Furthermore, credit hours are cumulative and contribute to the total number of credit hours needed to fulfill graduation requirements. Each institution sets its own credit hour requirements for degree programs, typically ranging from 120 to 150 credit hours for undergraduate degrees. Graduate programs often have specific credit hour requirements as well, depending on the field of study and level of specialization.
Now that we have a basic understanding of credit hours, let’s explore the important factors to consider when calculating the credit hours earned for a particular course.
Factors to Consider
When calculating credit hours earned for a course, several factors need to be taken into consideration. These factors can vary depending on the educational institution and program. Here are some important factors to keep in mind:
- Course Duration: The length of the course, usually in terms of weeks or semesters, plays a significant role in determining the credit hours earned. Longer courses tend to have a higher credit hour value compared to shorter ones.
- Classroom/Instructional Time: The number of hours spent in direct instruction, including lectures, discussions, and labs, is an important factor. Institutions typically allocate a certain number of credit hours based on the amount of time students spend in the classroom.
- Out-of-Class Workload: Credit hours also account for the time students spend outside of the classroom on assignments, projects, readings, and studying. The complexity and extent of this workload will influence the credit hour value assigned to the course.
- Intensity of Study: Some courses require more intensive study and preparation, such as research-intensive projects, internships, or practical training. These factors may increase the credit hour value to reflect the additional effort required.
- Course Level: The level of the course also affects the credit hour value. Advanced or higher-level courses typically have a higher credit hour value compared to introductory or lower-level courses.
- Program Requirements: Different programs may have specific credit hour requirements for certain courses. Some programs, such as those in the STEM fields or professional programs like engineering or nursing, may require more credit hours for specialized coursework.
- Institutional Policies: It’s essential to consider the specific policies and guidelines set by your educational institution. Different institutions may have variations in their credit hour calculation methods, so it’s crucial to consult your academic advisors or refer to the institution’s guidelines for accurate calculation.
By carefully considering these factors, you can accurately calculate the credit hours earned for a course and ensure you are on track to meet your academic or professional goals. Now, let’s move on to the step-by-step process of calculating credit hours earned.
Remember that credits are designed to represent the amount of work required for a course and are consistent across institutions. However, individual courses may vary in their design, requiring different amounts of effort and time commitment. Understanding these factors will help you navigate the credit system effectively and make informed decisions relating to your education or professional development.
Calculating Credit Hours Earned
Calculating credit hours earned for a course involves considering the factors discussed previously and following a step-by-step process. By following these steps, you can accurately determine the credit hours earned. Let’s dive into the process:
Step 1: Determine the Credit Value of Each Course
The first step is to identify the credit value assigned to each course by your educational institution. This information can usually be found in the course catalog or on the institution’s website. The credit value represents the number of credit hours assigned to the course based on the factors mentioned earlier.
Step 2: Calculate the Total Credit Hours for Each Course
Once you have identified the credit value of the course, the next step is to calculate the total credit hours for that course. Consider the classroom or instructional hours per week, the expected workload outside of class, and any additional factors specific to the course.
For example, suppose a course has three hours of classroom instruction each week and requires an additional eight hours of study and assignments outside of class. If the institution has assigned this course a value of three credit hours, you would multiply the total hours (11) by the credit hour value to calculate the total credit hours (33) earned for that course.
Step 3: Summing Up the Credit Hours
The final step is to sum up the credit hours earned for all the courses you have completed. Add together the credit hours for each course, taking into account any elective or optional courses that may have been completed. This will give you the total credit hours earned for your program or degree.
It is important to note that the credit hours earned are cumulative, meaning they contribute to the overall total needed to fulfill the requirements of your program or degree. Keep track of your progress and make sure you are meeting the credit hour requirements set by your institution.
By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the credit hours earned for each course and ensure you stay on track towards your educational or professional goals. Remember to consult with your academic advisors or refer to your institution’s guidelines for any specific requirements or variations in the credit hour calculation process.
Now, let’s wrap up and conclude our discussion on calculating credit hours earned.
Step 1: Determine the Credit Value of Each Course
The first step in calculating credit hours earned for a course is to determine the credit value assigned to it by your educational institution. The credit value represents the number of credit hours that the course is worth and is based on various factors, including the complexity and workload of the course.
To find the credit value of a course, you can refer to the course catalog or the institution’s website. These resources provide detailed information about each course, including the number of credit hours awarded upon successful completion. The credit value may vary depending on the level of the course, such as undergraduate or graduate, and the specific requirements of your program.
When determining the credit value, consider the following factors:
- Course Level: Higher-level or advanced courses often have a higher credit value compared to introductory or lower-level courses. This is because advanced courses typically require more in-depth study and a greater time commitment.
- Course Intensity: Some courses, such as research-based or laboratory-intensive courses, may have a higher credit value due to the additional effort and time required. These courses may involve extensive hands-on work, data analysis, or research projects.
- Course Duration: The length of the course, usually measured in weeks or semesters, can influence the credit value. Longer courses typically have a higher credit value compared to shorter ones to account for the increased time and workload.
- Program Requirements: Your program of study may have specific credit hour requirements for certain courses or disciplines. For example, if you are pursuing a degree in a STEM field, there may be specific credit hour requirements for courses in mathematics or science.
It is important to note that the credit value assigned to a course represents the institution’s determination of the workload and academic value of the course. It serves as a standardized measure across different programs and institutions, ensuring consistency in credit hour calculations.
By determining the credit value of each course, you lay the foundation for accurately calculating the credit hours earned. In the next step, we will explore how to calculate the total credit hours for each course based on the credit value and other factors.
Step 2: Calculate the Total Credit Hours for Each Course
After determining the credit value of each course, the next step is to calculate the total credit hours earned for each individual course. This involves considering factors such as instructional time, out-of-class workload, and any additional course-specific requirements.
To calculate the total credit hours for a course, follow these steps:
- Identify the instructional hours per week: Determine the number of hours spent in direct instruction, including lectures, discussions, and labs, for the course. This information is often provided in the course syllabus or schedule.
- Evaluate the out-of-class workload: Consider the time spent on assignments, projects, readings, and studying outside of the classroom. This includes both individual and group work. The workload varies depending on the course and its requirements.
- Consider any additional factors: Some courses may have specific requirements that contribute to the total credit hours. For example, if there are fieldwork or practical components in the course, they should be considered in the calculation.
Once you have gathered these details, you can calculate the total credit hours for the course by summing up the instructional hours and the out-of-class workload. This reflects the overall time commitment required for the course.
For example, if a course has three hours of classroom instruction per week and an additional six hours of out-of-class work, the total time commitment for that course would be nine hours. If the course has been assigned a credit value of three credit hours, you would multiply the total hours (9) by the credit hour value to calculate the total credit hours earned (27) for that course.
Remember, the total credit hours earned for a course reflect the cumulative time and effort dedicated to it, both inside and outside the classroom. It is essential to accurately calculate these hours to ensure you meet the requirements of your program or degree.
By accurately calculating the total credit hours for each course, you can track your progress and ensure you are completing the necessary requirements for your educational or professional goals. In the next step, we will sum up the credit hours across all the completed courses to determine the overall credit hours earned.
Step 3: Summing Up the Credit Hours
In the final step of calculating credit hours earned, it’s time to sum up the credit hours for each individual course to determine the overall credit hours earned. This step provides an accurate representation of your progress towards completing the credit hour requirements for your program or degree.
To sum up the credit hours, follow these steps:
- Review completed courses: Take a comprehensive look at all the courses you have successfully completed. Ensure that you have recorded the credit value and total credit hours earned for each course accurately.
- Add up the credit hours: Sum up the credit hours earned for each course. Simply add together the total credit hours earned for all completed courses.
- Consider elective or optional courses: If you have taken elective or optional courses as part of your program, include the credit hours earned from those courses in the total calculation.
By following these steps, you will have a clear picture of the total credit hours earned towards your educational or professional goals.
It’s important to keep in mind that credit hours are cumulative, meaning they add up over time as you complete more courses. The total credit hours earned contribute to the overall credit hour requirements for your program or degree.
Monitoring your progress and ensuring you meet the required credit hours is vital for staying on track and fulfilling your educational or professional objectives. Regularly check with your academic advisor or program coordinator to ensure you are meeting the necessary credit hour requirements for graduation.
By following the step-by-step process outlined in this article, you can accurately calculate the credit hours earned for each course and for your overall program or degree. Understanding your progress in terms of credit hours will help you navigate your educational journey more effectively and strategically.
Now that you have a complete understanding of calculating credit hours earned, you can confidently navigate your academic or professional path while staying on track to achieve your goals.
Conclusion
Calculating credit hours earned is a fundamental aspect of the educational journey. It serves as a standardized measure of the time and effort invested in completing a course or program. By understanding how to calculate credit hours, students and professionals can effectively track their progress and ensure they meet the requirements of their academic or professional pursuits.
In this article, we explored the various factors to consider when calculating credit hours, such as course duration, instructional time, out-of-class workload, and program requirements. By taking these factors into account, individuals can accurately determine the credit value assigned to each course.
Additionally, we provided a step-by-step process for calculating credit hours earned. This involves determining the credit value of each course, calculating the total credit hours for each course based on instructional time and workload, and summing up the credit hours for all completed courses to determine the overall credit hours earned.
It’s important to note that credit hours are cumulative and contribute to the overall credit hour requirements for a program or degree. Regularly consulting with academic advisors and program coordinators ensures that individuals are on track to meet their academic goals.
By understanding and accurately calculating credit hours earned, students and professionals can make informed decisions about their course selections, track their progress, and ensure compliance with program requirements. This knowledge provides a clear road map to success in academia and professional development.
Remember, while the principles discussed in this article provide a general understanding of calculating credit hours, it is crucial to consult your educational institution’s specific guidelines and policies for accurate calculation and requirements.
Armed with this information, individuals can confidently navigate the educational landscape, advancing their knowledge, skills, and career prospects with a clear understanding of their credit hours earned.
So, take control of your educational journey, calculate your credit hours earned, and pave the way towards a successful future!