Home>Finance>Bear Put Spread: Definition, Example, How It’s Used, And Risks


Finance
Bear Put Spread: Definition, Example, How It’s Used, And Risks
Published: October 14, 2023
Learn about a bear put spread in finance, including a definition, example, how it's used, and associated risks. Discover how this options strategy can help manage downside risk in your portfolio.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
The Bear Put Spread: Definition, Example, How It’s Used, and Risks
Welcome to our finance blog, where we delve into various investment strategies and financial concepts. In this post, we will be focusing on the Bear Put Spread, a popular options trading strategy used by investors to profit from downward price movements in a stock. In this article, we will define the Bear Put Spread, provide an example to help you better understand its mechanics, explain how it can be used effectively, and highlight the associated risks.
Key Takeaways:
- The Bear Put Spread is an options trading strategy
- It involves buying put options at one strike price and simultaneously selling put options at a lower strike price
The Bear Put Spread Defined
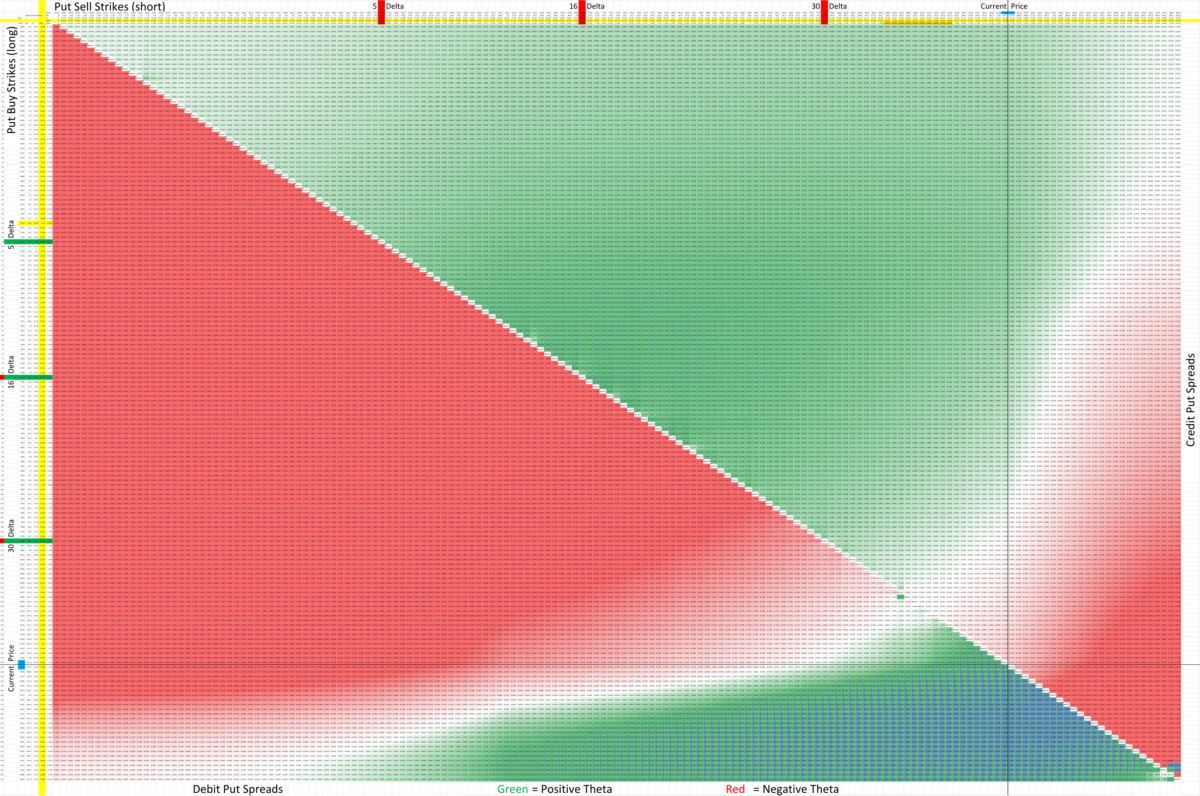
The Bear Put Spread is a strategy employed by investors who anticipate a decline in the price of a specific stock. It involves the purchase of put options at a higher strike price and the simultaneous sale of put options at a lower strike price. This strategy allows investors to profit from the potential downward movement in the stock’s price, while limiting their downside risk.
Example of a Bear Put Spread
Let’s say you are bearish on Company XYZ, and you believe its stock, currently trading at $50 per share, will decrease in value. To implement a Bear Put Spread, you could do the following:
- Buy 1 put option with a strike price of $55 for $3 per contract (the long put)
- Sell 1 put option with a strike price of $45 for $1 per contract (the short put)
In this example, you have a net cost of $2 per contract for implementing the Bear Put Spread.
How the Bear Put Spread Works
The Bear Put Spread works by combining a long put option and a short put option. The long put option provides downside protection, allowing you to profit if the stock price drops below the strike price of the long put. The short put option, on the other hand, generates income from the premium received by selling the put option.
By simultaneously buying and selling put options with different strike prices, the Bear Put Spread helps to offset the cost of the long put option. The profit potential of the strategy is limited to the difference between the two strike prices, minus the net cost of the spread. This limits potential gains but also lowers the breakeven point.
Using the Bear Put Spread Effectively
The Bear Put Spread can be used effectively in a bearish market environment or when you have a negative outlook on a particular stock. Some ways to use this strategy effectively include:
- When you expect a moderate decline in stock price
- When you want to limit your downside risk
- When you want to take advantage of the high premiums of out-of-the-money options
It’s important to conduct thorough research and analysis before implementing any options trading strategy. Understanding the risks associated with the strategy is crucial for managing your positions effectively.
Risks of the Bear Put Spread
While the Bear Put Spread offers a limited risk approach to profiting from a stock’s decline, it is essential to be aware of the potential risks:
- If the stock price rises above the strike price of the short put option, the strategy will result in a loss
- Changes in implied volatility can impact the profitability of the strategy
- Commissions and fees can eat into potential profits
It’s important to regularly monitor your positions and adjust your strategy if market conditions change.
In conclusion, the Bear Put Spread is an options trading strategy that allows investors to profit from downward price movements in a stock while limiting their downside risk. It offers a practical approach to bearish market scenarios and can be used effectively when a negative outlook on a specific stock exists. As with any investment strategy, understanding the risks involved and conducting thorough research is essential for successful implementation.
Stay tuned for more informative articles on various investment strategies and financial concepts in our finance blog category. Happy investing!