Home>Finance>How To Calculate Interest Rate Based On Monthly Payments With A Grace Period


Finance
How To Calculate Interest Rate Based On Monthly Payments With A Grace Period
Published: February 19, 2024
Learn how to calculate interest rates based on monthly payments in finance, including how to account for a grace period. Understand the formula and process to make informed financial decisions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Understanding the Basics of Interest Rates and Grace Periods
Welcome to the world of finance, where interest rates play a pivotal role in various transactions. Whether you’re considering a loan, mortgage, or credit card, understanding how interest rates are calculated is crucial for making informed financial decisions. Moreover, the concept of a grace period adds an additional layer of complexity to the calculation process. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of calculating interest rates based on monthly payments, taking into account the presence of a grace period.
Throughout this article, we will explore the fundamental principles of interest rates and grace periods, providing you with the knowledge and tools to navigate these financial aspects with confidence. By the end of this journey, you will have a clear understanding of how to calculate interest rates based on monthly payments, factoring in any grace period that may be applicable to your specific financial scenario.
So, let’s embark on this enlightening exploration of interest rates and grace periods, empowering you to make informed financial decisions and manage your monetary resources effectively.
Understanding Interest Rates and Grace Periods
Interest rates represent the cost of borrowing money and the return on invested funds. They are expressed as a percentage of the principal amount and can have a significant impact on the total amount repaid or earned over time. When it comes to loans, mortgages, or credit cards, the interest rate directly influences the monthly payments and the overall cost of borrowing.
Grace periods, on the other hand, refer to a specified period during which a borrower can delay making a payment without incurring penalties. This grace period is typically granted after the due date for a payment, providing a window of time during which the payment can be made without adverse consequences.
When calculating interest rates based on monthly payments, it is essential to consider both the nominal interest rate and the effective interest rate. The nominal interest rate is the stated rate before taking compounding into account, while the effective interest rate reflects the actual interest paid or earned after considering compounding within a specific time period.
Understanding the distinction between nominal and effective interest rates is crucial for accurately assessing the cost of borrowing or the return on investment. Additionally, being aware of the presence of a grace period allows borrowers to strategically manage their payments while optimizing their financial resources.
As we proceed, we will explore how to calculate interest rates based on monthly payments, integrating the concept of a grace period into the calculation process. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of these fundamental financial elements, you will be equipped to make informed decisions and navigate the intricacies of interest rates and grace periods with confidence and clarity.
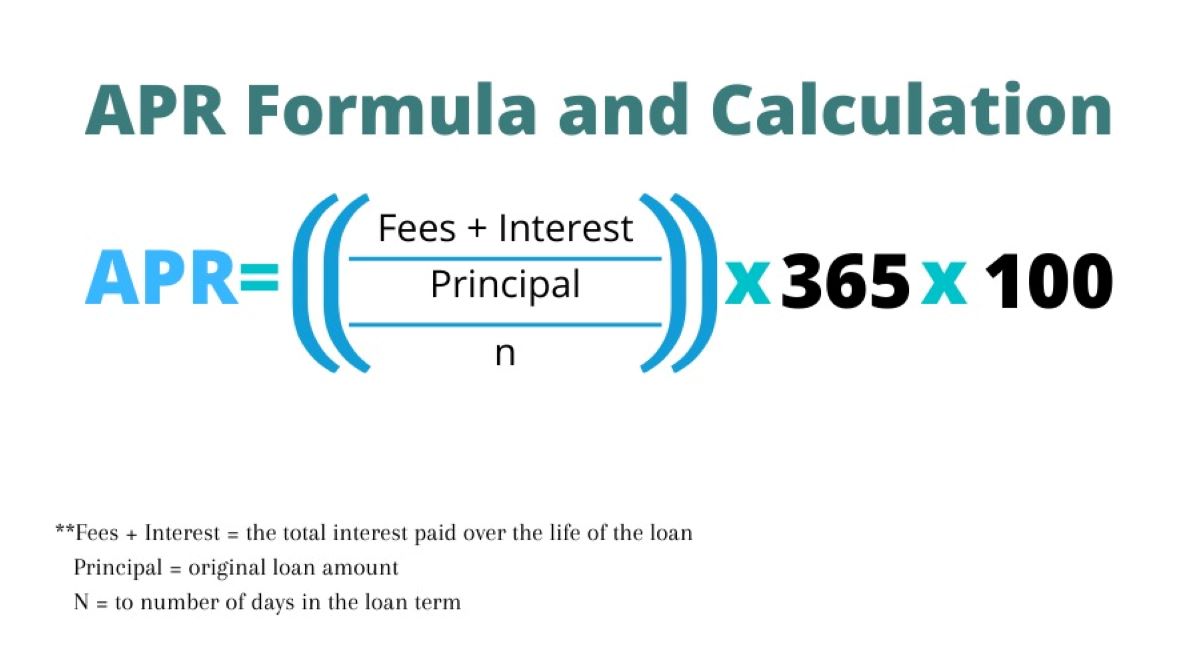
Calculating Interest Rate Based on Monthly Payments
When determining the interest rate based on monthly payments, several key factors come into play. The principal amount, the duration of the loan or investment, and the monthly payment amount are central to this calculation. By leveraging these variables, individuals can gain insights into the effective interest rate associated with their financial obligations or investments.
To calculate the interest rate based on monthly payments, one can utilize the formula for the present value of an annuity. This formula incorporates the monthly payment amount, the number of periods, and the present value to determine the interest rate. By rearranging the formula to solve for the interest rate, individuals can ascertain the rate at which their monthly payments accumulate to the given present value.
Moreover, understanding the concept of compounding is essential when calculating the interest rate based on monthly payments. Compounding refers to the process by which interest is calculated on the initial principal as well as the accumulated interest from previous periods. Consequently, the frequency of compounding, whether monthly, quarterly, or annually, can significantly impact the effective interest rate.
By comprehending the mechanics of interest accrual and compounding, individuals can make informed decisions regarding loans, investments, and other financial commitments. Armed with the ability to calculate the interest rate based on monthly payments, individuals can assess the affordability of loans, evaluate the potential returns on investments, and strategically manage their financial resources.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of interest rate calculation, we will explore how the presence of a grace period can influence the overall interest rate and the effective cost of borrowing. By integrating the concept of a grace period into the calculation process, individuals can gain a holistic understanding of their financial obligations and make well-informed decisions to optimize their financial well-being.
Taking Grace Period into Account
When factoring in a grace period while calculating interest rates based on monthly payments, it is essential to consider the impact of the grace period on the timing of payments and the overall cost of borrowing. The presence of a grace period can provide borrowers with a valuable opportunity to manage their payments strategically, potentially minimizing the accrual of interest and avoiding late payment penalties.
During a grace period, borrowers have the flexibility to make payments without incurring adverse consequences, offering a window of time to address financial obligations. By leveraging this grace period effectively, borrowers can align their payments with their cash flow, ensuring timely settlements while optimizing their financial resources.
From a calculation perspective, incorporating a grace period into the interest rate determination entails assessing the timing of payments and the corresponding impact on the total interest accrued. By adjusting the calculation to accommodate the grace period, individuals can gain a more accurate understanding of the effective interest rate and the total cost of borrowing.
Furthermore, the presence of a grace period can influence the frequency and timing of compounding, directly affecting the effective interest rate. By strategically timing payments within the grace period, borrowers can mitigate the impact of compounding and reduce the overall interest expense associated with their financial obligations.
As we navigate the realm of interest rate calculations, it is imperative to recognize the significance of the grace period and its potential implications for borrowers. By integrating the concept of a grace period into the calculation process, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their financial commitments, leveraging the flexibility offered by the grace period to optimize their financial well-being.
Examples of Calculating Interest Rate with a Grace Period
Let’s consider a practical example to illustrate the calculation of interest rates based on monthly payments, taking into account a grace period. Suppose an individual has a loan with a principal amount of $10,000, a monthly payment of $500, and an annual interest rate of 6%. The loan agreement includes a grace period of 15 days after the due date before late payment penalties are imposed.
When factoring in the grace period, the individual can strategically time their payments to optimize the effective interest rate. By making payments within the grace period, the impact of compounding and the total interest accrued can be minimized.
Utilizing the present value of an annuity formula, the individual can calculate the effective interest rate based on the monthly payments and the presence of the grace period. By considering the timing of payments within the grace period and the associated reduction in the total interest expense, the individual can gain insights into the true cost of borrowing and make informed financial decisions.
Furthermore, let’s explore a scenario involving a credit card with a grace period. A cardholder with a balance of $1,000 and a monthly payment of $100 benefits from a grace period of 25 days. By strategically managing payments within the grace period, the cardholder can optimize the effective interest rate and minimize the overall interest cost associated with the outstanding balance.
These examples highlight the practical application of factoring in a grace period when calculating interest rates based on monthly payments. By strategically leveraging the flexibility offered by the grace period, individuals can navigate their financial obligations with greater control and optimize the cost of borrowing or the returns on investments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the interplay between interest rates and grace periods significantly impacts the calculation of interest rates based on monthly payments. By understanding the fundamentals of interest rates, including nominal and effective rates, individuals can gain insights into the cost of borrowing and the returns on investments. Additionally, recognizing the value of a grace period empowers borrowers to strategically manage their payments and optimize their financial resources.
When calculating interest rates based on monthly payments, it is essential to consider the presence of a grace period and its potential implications for the timing of payments and the overall cost of borrowing. By factoring in the grace period, individuals can strategically align their payments to minimize the impact of compounding and reduce the total interest expense.
Furthermore, practical examples demonstrate how borrowers can leverage the flexibility offered by grace periods to optimize the effective interest rate and minimize the overall cost of borrowing. Whether it involves loans, mortgages, or credit card balances, integrating the concept of a grace period into interest rate calculations enables individuals to make informed financial decisions and manage their financial obligations with greater control.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of interest rates and grace periods, individuals are equipped to navigate the complexities of financial transactions with confidence and clarity. The ability to calculate interest rates based on monthly payments while considering the presence of a grace period empowers individuals to make informed decisions, optimize their financial well-being, and strategically manage their monetary resources.
Ultimately, the integration of grace periods into interest rate calculations serves as a valuable tool for borrowers, offering a strategic advantage in managing payments and minimizing the cost of borrowing. By embracing this holistic approach to interest rate calculations, individuals can enhance their financial literacy and make sound financial choices, ensuring a secure and informed financial future.