Home>Finance>How To Get Health Insurance If Your Job Doesn’t Offer It


Finance
How To Get Health Insurance If Your Job Doesn’t Offer It
Published: October 30, 2023
Looking for health insurance options? Learn how to secure affordable coverage even if your job doesn't provide it. Find out more in our comprehensive finance guide.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding the Importance of Health Insurance
- Exploring Options for Health Insurance Coverage
- Researching Individual Health Insurance Plans
- Understanding the Affordable Care Act (ACA)
- Applying for Medicaid or CHIP
- Considering Short-Term Health Insurance Plans
- Joining a Spouse or Parent’s Health Insurance Plan
- Evaluating Health Insurance Marketplaces
- Seeking Assistance from Insurance Brokers or Agents
- Exploring Health Insurance Options for Freelancers or Self-Employed Individuals
- Conclusion
Introduction
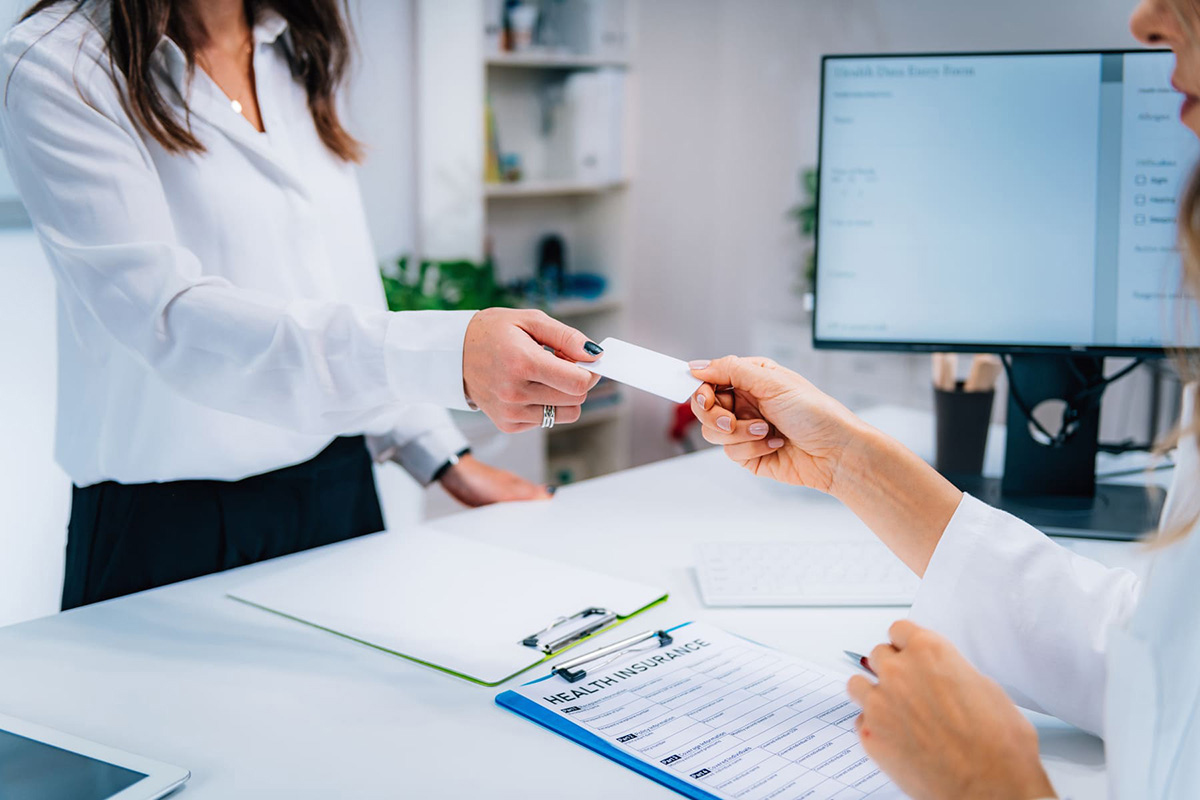
Health insurance is a crucial aspect of financial well-being, providing protection against unexpected medical expenses and ensuring access to quality healthcare. However, not everyone has the luxury of employer-provided health insurance coverage. If you find yourself in a situation where your job doesn’t offer health insurance, it’s essential to explore alternative options to safeguard your health and financial security.
Without health insurance, even routine medical expenses can quickly spiral out of control, leaving individuals and families vulnerable to significant financial hardship. According to the National Center for Health Statistics, nearly 30 million Americans were uninsured in 2019. If you are part of this statistic, don’t worry, there are several avenues you can pursue to obtain affordable health insurance coverage.
In this article, we will walk you through different options for obtaining health insurance when your job doesn’t offer it. From exploring individual health insurance plans to considering short-term coverage, applying for government assistance, or joining a spouse or parent’s plan, we will discuss the pros and cons of each option and provide practical guidance to help you make an informed decision.
It is important to note that obtaining health insurance is not just about meeting legal requirements. It is about protecting your health and financial well-being. Without adequate coverage, you may delay or even avoid necessary medical care due to cost concerns, which can lead to more significant health issues down the line.
Whether you are a recent college graduate, self-employed, or working part-time, it’s crucial to take steps to secure health insurance coverage. In the following sections, we will help you navigate the complex world of health insurance options and empower you to find the best solution to meet your unique circumstances and needs.
Let’s dive into the various alternatives and strategies you can explore to ensure access to quality healthcare and protect yourself from the high costs of medical treatments when your job doesn’t provide health insurance.
Understanding the Importance of Health Insurance
Health insurance is not just a luxury; it is a necessity. It serves as a financial safety net, protecting individuals and families from the exorbitant costs of medical treatments, hospital stays, and prescription medications. Without health insurance, even a minor illness or injury can lead to significant financial stress and potentially bankruptcy.
One of the key reasons health insurance is vital is the rising cost of healthcare. Medical expenses have been steadily increasing, and without insurance, these costs can quickly become unmanageable. A routine doctor’s visit, diagnostic tests, or prescription medications can add up to hundreds or even thousands of dollars. Health insurance helps mitigate these expenses by offering negotiated rates with healthcare providers and pharmacies, ensuring you pay a fraction of the actual cost.
Another critical aspect of health insurance is the access it provides to a network of healthcare providers. With insurance, you have the freedom to choose doctors, hospitals, and specialists within your plan’s network. This not only ensures optimal care but also provides a level of convenience and peace of mind.
Furthermore, health insurance promotes preventive care. Many insurance plans cover routine check-ups, vaccinations, and screenings at little to no cost. This enables individuals to detect and address health conditions at an early stage when they are more treatable and less costly. Regular preventive care helps individuals maintain overall well-being and reduces the risk of developing more severe health issues.
In addition to the financial and health benefits, having health insurance also brings the assurance of not having to worry about unexpected medical emergencies. Whether it’s a sudden illness, an accident, or a chronic condition, having insurance coverage means you can receive the necessary medical care without the fear of draining your savings or facing massive debts.
Finally, it’s essential to consider the legal requirements surrounding health insurance. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) mandates that most individuals have health insurance coverage or pay a penalty when filing taxes. Understanding and complying with these regulations is crucial to avoiding any financial consequences.
In summary, health insurance is essential for protecting your financial well-being, accessing quality healthcare, promoting preventive care, and providing peace of mind. It is an investment in your present and future health, and even if your job doesn’t offer it, there are various avenues to explore to secure the coverage you need. In the following sections, we will delve into these alternatives and help you navigate the complex landscape of health insurance options when your employer doesn’t provide it.
Exploring Options for Health Insurance Coverage
When your job doesn’t offer health insurance, it’s crucial to explore alternative options to ensure you have adequate coverage. Here are some avenues you can consider:
- Individual Health Insurance Plans: One option is to explore individual health insurance plans available in your area. These plans are purchased directly from insurance companies and offer coverage for individuals and families. Research different insurance providers, compare plans, and consider factors like premiums, deductibles, and coverage limits to find a plan that suits your needs and budget.
- Affordable Care Act (ACA) Marketplace: Under the ACA, individuals and families can purchase health insurance through the Health Insurance Marketplace. The Marketplace offers a range of plans with varying levels of coverage and costs. Depending on your income, you may be eligible for subsidies and tax credits to help make insurance more affordable.
- Medicaid or Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP): If your income falls within a certain threshold, you may qualify for Medicaid or CHIP. These government programs provide low-cost or free health coverage to eligible individuals and families. Eligibility criteria vary by state, so check your state’s Medicaid website or visit healthcare.gov to see if you qualify.
- Short-Term Health Insurance Plans: Short-term health insurance plans are designed to provide temporary coverage for individuals who are in between jobs, waiting for employer coverage to start, or need coverage for a limited period. These plans typically offer basic coverage and lower premiums but may come with limitations or exclusions, so carefully review the terms before enrolling.
- Spouse or Parent’s Health Insurance Plan: If you have a spouse or a parent who has health insurance coverage through their employer, you may be able to join their plan. Many employer-sponsored plans allow for dependents to be added to the coverage. However, there may be enrollment windows or eligibility criteria, so it’s important to understand the requirements and deadlines.
- Health Insurance Marketplaces: Some states have established their own health insurance marketplaces outside the federal marketplace. These state-run marketplaces may offer additional plan options or alternative enrollment processes, so check your state’s marketplace website for more information.
- Insurance Brokers or Agents: Another option is to seek assistance from insurance brokers or agents who specialize in health insurance. These professionals can help guide you through the process, explain different plan options, and assist in finding a plan that aligns with your needs and budget.
- Health Insurance for Freelancers or Self-Employed: If you are self-employed or work as a freelancer, there are specific health insurance options tailored to your unique situation. Look into professional organizations or industry associations that may offer group health insurance plans for members.
Remember to carefully review the terms and conditions of any health insurance plan you are considering. Pay attention to details such as coverage limits, out-of-pocket costs, and network providers to ensure you select a plan that provides comprehensive coverage and aligns with your healthcare needs.
Understanding and exploring these options will empower you to make an informed decision and secure the health insurance coverage necessary to protect your health and financial well-being.
Researching Individual Health Insurance Plans
When your job doesn’t offer health insurance, researching individual health insurance plans becomes essential. These plans are purchased directly from insurance companies and provide coverage for individuals and families. Here are some key steps to take when researching individual health insurance plans:
- Evaluate Your Coverage Needs: Start by assessing your healthcare needs and the needs of your family members if applicable. Consider factors such as prescription medications, existing medical conditions, and any anticipated medical procedures or treatments. This will help you determine the level of coverage required.
- Research Insurance Providers: Look into various insurance providers in your area and evaluate their reputation, financial stability, and customer reviews. Choose companies with a strong track record and positive customer feedback to ensure reliability in delivering healthcare benefits.
- Compare Plan Options: Insurance providers offer a range of plan options, each with its own coverage levels, premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket costs. Compare different plans to find one that aligns with your coverage needs and budget. Take note of limitations, exclusions, and benefits covered, such as preventive care, prescription medications, and specialist visits.
- Consider Network Providers: Ensure that the individual health insurance plan you are considering has a network of healthcare providers, including doctors, hospitals, and specialists, in your area. Having a wide network ensures convenient access to healthcare services and allows you to continue seeing your current healthcare providers if desired.
- Review Enrollment Periods: Individual health insurance plans typically have open enrollment periods during which you can enroll or make changes to your coverage. It’s important to be aware of these periods and plan accordingly. Outside of open enrollment, you may only be able to enroll or make changes if you experience a qualifying life event, such as marriage, birth or adoption of a child, or loss of other health coverage.
- Understand Costs and Financial Considerations: Evaluate the costs associated with individual health insurance plans, including monthly premiums, deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance. Consider your budgetary constraints and ensure you can comfortably afford the monthly premiums and any potential out-of-pocket expenses.
- Seek Expert Assistance: If you feel overwhelmed by the process, consider seeking assistance from insurance brokers or agents who specialize in health insurance. These professionals can provide guidance, answer questions, and help you navigate through the available options to find the best plan for your needs.
Remember to carefully review the policy documents and terms and conditions of any individual health insurance plan you are considering. Pay attention to details such as coverage limits, network restrictions, and pre-authorization requirements. It’s crucial to have a clear understanding of what is covered and what is not to avoid any surprises when it comes to utilizing your health insurance benefits.
By conducting thorough research and taking the time to understand your coverage needs, you can select an individual health insurance plan that provides comprehensive coverage and meets your healthcare needs. It’s an investment in safeguarding your health and ensuring financial peace of mind when your job doesn’t offer health insurance.
Understanding the Affordable Care Act (ACA)
The Affordable Care Act (ACA), also known as Obamacare, is a comprehensive healthcare reform law enacted in 2010. It aims to increase access to affordable health insurance and improve the quality and affordability of healthcare in the United States. Understanding the key components of the ACA can help you navigate the health insurance landscape when your job doesn’t offer coverage.
One of the primary features of the ACA is the establishment of Health Insurance Marketplaces, also known as Exchanges. These are online platforms where individuals and families can shop for and enroll in health insurance plans. The Marketplaces offer a range of plans with different levels of coverage and costs.
The ACA also introduced several important provisions aimed at protecting consumers and improving access to healthcare. These include:
- Prohibition of Pre-existing Condition Exclusions: The ACA prohibits insurance companies from denying coverage or charging higher premiums based on pre-existing conditions. This ensures that individuals with pre-existing conditions can obtain health insurance coverage.
- Essential Health Benefits: Under the ACA, health insurance plans are required to cover a set of essential health benefits. These benefits include preventive services, prescription medications, hospitalization, maternity care, mental health services, and more. This ensures that individuals have access to comprehensive coverage.
- Subsidies and Premium Tax Credits: The ACA provides subsidies and premium tax credits to help make health insurance more affordable for individuals and families with lower incomes. These financial assistance programs are available for those who purchase coverage through the Health Insurance Marketplace and meet certain income criteria.
- Individual Mandate and Penalties: Initially, the ACA included an individual mandate which required most individuals to have health insurance or pay a penalty when filing taxes. However, as of 2019, the penalty for not having health insurance was set to $0, effectively eliminating the individual mandate.
It is important to note that while the individual mandate no longer carries a penalty, having health insurance is still strongly encouraged. Health insurance provides vital financial protection and access to necessary healthcare services.
When exploring health insurance coverage options under the ACA, it’s important to be aware of the specific enrollment periods, which typically occur annually during the Open Enrollment Period. However, certain qualifying life events, such as marriage, birth or adoption of a child, or loss of other health coverage, may trigger a Special Enrollment Period, during which you can apply for coverage outside the standard enrollment period.
If you do not qualify for Medicaid and your income falls between 100% and 400% of the federal poverty level, you may be eligible for premium tax credits that can significantly reduce your monthly premiums. The exact amount of the tax credit is based on your income and the cost of the second-lowest cost Silver plan available in your area.
Understanding the ACA and its provisions can help guide you in selecting a health insurance plan that provides comprehensive coverage, meets your needs, and takes advantage of any available subsidies or premium tax credits. It’s important to stay informed about any changes or updates to the law and seek assistance if needed to navigate the ACA Marketplace and understand the options available to you.
Applying for Medicaid or CHIP
If your income falls within a certain threshold, you may be eligible for Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP). These government programs provide low-cost or free health coverage to individuals and families who meet specific income and other eligibility requirements. Applying for Medicaid or CHIP can be a viable option when your job doesn’t offer health insurance coverage:
Medicaid: Medicaid is a joint federal and state program that provides healthcare coverage to low-income individuals and families. Eligibility criteria for Medicaid vary by state, but they typically take into account factors such as income, assets, family size, disability status, and age. To determine if you qualify for Medicaid, visit the Medicaid website for your state or the healthcare.gov website.
Applying for Medicaid usually involves completing an application form, providing documentation, and undergoing an eligibility determination process. In some states, you may be able to apply online, while others may require in-person visits or assistance from a Medicaid enrollment center or social services office. Be prepared to provide information regarding income, household size, assets, and other personal details to facilitate the application process.
CHIP: The Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) is designed to provide healthcare coverage for children in low- to moderate-income families who do not qualify for Medicaid. Each state has its own CHIP program, and eligibility criteria may vary. In general, CHIP covers children up to a certain age, typically 18 or 19, and may also offer coverage for pregnant women in some states.
Applying for CHIP follows a similar process to applying for Medicaid. You will need to complete an application form, provide necessary documentation, and undergo an eligibility determination process. Many states allow online application submission, and assistance may be available through your state’s CHIP agency or healthcare.gov website.
It is important to note that Medicaid and CHIP enrollment periods are generally open year-round. However, it’s advisable to apply as soon as possible if you believe you may be eligible for these programs, as coverage can begin from the date of application.
Don’t hesitate to seek guidance from healthcare navigators, social workers, or enrollment counselors who can provide assistance and answer your questions during the application process. They can help ensure that you complete the necessary paperwork correctly and provide the required documentation, increasing your chances of a smooth and successful enrollment.
By exploring and applying for Medicaid or CHIP, you can secure affordable or free health insurance coverage for yourself and your family when your job doesn’t offer such benefits. These programs offer crucial support, ensuring you have access to essential healthcare services without incurring significant financial burdens.
Considering Short-Term Health Insurance Plans
If you find yourself in a temporary gap without health insurance coverage, or if you are in between jobs, considering a short-term health insurance plan can provide temporary coverage until you secure a long-term solution. Short-term health insurance plans are designed to bridge these gaps and offer basic coverage for a limited duration. Here are a few factors to consider when exploring short-term health insurance plans:
Duration: Short-term health insurance plans typically provide coverage for a short period, ranging from a few months to one year. It’s important to understand the specific duration and any limitations on renewability or portability of the plan.
Coverage: Short-term health insurance plans generally offer limited coverage compared to traditional health insurance plans. They often cover essential services, such as emergency care, hospitalizations, and some preventive care, but may not include coverage for pre-existing conditions, maternity care, mental health services, or prescription drugs. Review the plan details carefully to ensure it meets your specific healthcare needs.
Cost: Short-term health insurance plans typically have lower monthly premiums compared to comprehensive health insurance plans. However, they may come with high deductibles and out-of-pocket costs. Consider your budget and assess the overall affordability of the plan, taking into account both premiums and potential healthcare expenses.
Network and Provider Choice: Short-term health insurance plans may have limited networks of healthcare providers or may not cover out-of-network care at all. It’s important to understand the network restrictions and consider whether your preferred doctors, hospitals, and specialists are included in the plan’s network.
Pre-Existing Conditions: Short-term health insurance plans typically do not cover pre-existing conditions. If you have existing health conditions or anticipate the need for ongoing medical care, these plans may not provide adequate coverage. In these situations, it may be more beneficial to explore other insurance options.
Availability: Short-term health insurance plans are not available in all states, or they may have specific regulations and limitations depending on the state. Ensure that short-term plans are an option in your state and investigate any specific requirements or regulations that may apply.
Short-term health insurance plans can provide temporary coverage and serve as a reliable stopgap solution. However, it’s important to note that they are not a substitute for comprehensive health insurance. If you have ongoing healthcare needs or anticipate the need for extensive medical care, it’s advisable to explore other options, such as individual health insurance plans or government programs like Medicaid or CHIP.
Before enrolling in a short-term health insurance plan, carefully review the policy details, compare several options, and assess your specific healthcare needs. Remember that short-term plans are meant to provide temporary coverage, and it’s important to secure long-term health insurance as soon as possible to ensure continuous and comprehensive coverage for your health and well-being.
Joining a Spouse or Parent’s Health Insurance Plan
If your job doesn’t offer health insurance, one option to consider is joining a spouse or parent’s health insurance plan. Many employer-sponsored health insurance plans allow employees to include their eligible dependents, such as spouses or children, under their coverage. Here are some key considerations when exploring this option:
Eligibility: Understand the eligibility criteria set by the health insurance plan. Typically, spouses and dependent children are eligible for coverage. Ensure that you meet the plan’s requirements for being considered a dependent, such as age limits or marital status, if applicable.
Enrollment Periods: Employer-sponsored health insurance plans generally have specific enrollment periods during which you can add dependents to the coverage. These enrollment windows may be annual or occur within a certain timeframe after a qualifying life event, such as marriage or the birth or adoption of a child. Be aware of these enrollment periods and ensure you complete the necessary paperwork within the specified timeframe.
Coverage and Costs: Review the coverage and costs associated with joining a spouse or parent’s health insurance plan. Assess the benefits, such as the scope of coverage, access to preferred healthcare providers, and prescription drug coverage. Consider the premiums, deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance to evaluate the affordability of the plan for you and your spouse or parent.
Coordination of Benefits: If you are currently covered by a different health insurance plan, understand how the coordination of benefits works when joining a spouse or parent’s plan. This ensures that you maximize your coverage while minimizing out-of-pocket expenses. Coordination of benefits determines which plan is the primary payer and which is the secondary payer when you receive healthcare services.
Employer Contribution: If your spouse’s or parent’s employer contributes to the cost of the health insurance plan, factor in this benefit when evaluating the affordability of joining their plan. Employer contributions can significantly reduce the financial burden for you and your family.
Limitations: Be aware of any limitations or restrictions that may apply to dependent coverage. For example, some plans may have age limits for dependents or may not cover certain dependents, such as domestic partners. Check the plan’s policy documents or consult with the benefits administrator to fully understand the terms of dependent coverage.
Joining a spouse or parent’s health insurance plan can be a cost-effective option compared to obtaining an individual plan or other alternatives. It allows you to leverage the group coverage and benefits provided by the employer. It also ensures that you and your family have access to comprehensive healthcare coverage under one plan.
Before making a decision, it’s important to compare the benefits and costs of joining a spouse or parent’s plan with other available options, such as individual health insurance plans or government programs. Consider your specific healthcare needs and budget to choose the most suitable option for your circumstances.
Remember to liaise with your spouse or parent, and their employer’s benefits administrator, to obtain all the necessary information and complete the enrollment process within the specified timeframe. By joining a spouse or parent’s health insurance plan, you can ensure that you and your family have the healthcare coverage needed to protect your health and financial well-being.
Evaluating Health Insurance Marketplaces
Health Insurance Marketplaces, also known as Exchanges, are online platforms established under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) where individuals and families can shop for and enroll in health insurance plans. Evaluating health insurance marketplaces is important when your job doesn’t offer health insurance coverage. Here are some key factors to consider when assessing health insurance marketplaces:
Plan Availability: Determine which health insurance marketplaces are available in your state. Some states operate their own state-based marketplaces, while others use the federally facilitated marketplace. Research which marketplace options are accessible to you and review the plans offered, including the insurance providers and coverage options available.
Plan Options: Health insurance marketplaces offer a variety of plan options to choose from, typically categorized by metal tiers—bronze, silver, gold, and platinum. These tiers indicate the level of coverage and cost-sharing. Compare the plan options and consider your healthcare needs, budget, and preferred level of coverage to select the most suitable plan.
Premiums and Costs: Evaluate the premiums associated with the plans offered through the health insurance marketplace. Premiums vary based on factors such as age, location, and plan type. Consider your budget and ensure that the premiums are affordable for you. Also, assess other costs, including deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance, to have a complete picture of the potential financial obligations.
Network of Providers: Take into account the network of healthcare providers associated with the health insurance plans available through the marketplace. Ensure that the plans include your preferred doctors, hospitals, specialists, and other healthcare facilities. Additionally, consider the reach and accessibility of the network, especially if you live in a rural area or require specialized care.
Financial Assistance: Determine if you are eligible for financial assistance through the health insurance marketplace. Consider subsidies and premium tax credits that can help lower the cost of monthly premiums. Evaluate your income and household size to see if you qualify for these financial support options.
Customer Reviews and Satisfaction: Research customer reviews and satisfaction ratings of insurance companies offering plans through the marketplace. Look for feedback on customer service, claim processing, and overall satisfaction with the plan. This information can provide valuable insights into the experiences of others and help you make an informed decision.
Customer Support: Assess the availability of customer support services provided by the health insurance marketplace. Consider the ease of contacting customer service representatives, the availability of online resources and tools, and the responsiveness and helpfulness of the support team. Having access to reliable customer support can make the enrollment and claims process smoother.
Remember to review the policy details, terms, and conditions, and any limitations or exclusions of the plans offered through the health insurance marketplace. It’s important to have a clear understanding of what is covered, what is not covered, and any specific requirements or restrictions that may apply.
Evaluating health insurance marketplaces allows you to compare plan options, assess costs, and determine the best fit for your healthcare needs and budget. Take the time to research and weigh the available options, considering both the benefits and limitations of the marketplace plans. By making an informed decision, you can select a health insurance plan that provides the coverage and protection you need when your job doesn’t offer health insurance.
Seeking Assistance from Insurance Brokers or Agents
When your job doesn’t offer health insurance coverage and you find yourself overwhelmed by the complexities of the insurance market, seeking assistance from insurance brokers or agents can be incredibly helpful. These professionals specialize in navigating the world of health insurance and can provide valuable guidance and support. Here are some key reasons to consider working with insurance brokers or agents:
Expert Knowledge: Insurance brokers and agents have in-depth knowledge about different health insurance plans, coverage options, and regulations. They stay updated on changes in the industry and can provide valuable insights and advice to help you make informed decisions. Their expertise can save you time and ensure that you have a clear understanding of the options available.
Plan Comparison: Insurance brokers and agents can help you compare different health insurance plans. They have access to multiple insurance companies and can provide you with options tailored to your needs and budget. They can explain the benefits, costs, and limitations of each plan, making it easier for you to make an informed choice.
Budget Considerations: Insurance brokers and agents can help you find a health insurance plan that fits within your budget. They have the knowledge and experience to identify plans with affordable premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket costs. They can assess your healthcare needs and financial situation to guide you toward the most cost-effective options.
Navigating Complexities: The world of health insurance can be complex, with various terms and regulations. Insurance brokers and agents can help you navigate through the complexities, explaining industry jargon and simplifying the process for you. They can address any questions or concerns you may have, ensuring that you have a clear understanding of the health insurance options available to you.
Assistance with Enrollment: Insurance brokers and agents can assist you with the enrollment process. They can help you complete the necessary paperwork, gather required documentation, and ensure that your application is submitted correctly and on time. Their support can streamline the enrollment process and minimize the chances of errors or delays.
Advocacy and Support: Insurance brokers and agents act as advocates on your behalf. They can help resolve any issues that may arise with your health insurance, such as claim disputes or coverage questions. They have relationships with insurance companies and can navigate the system to address your concerns and ensure that you receive the benefits you are entitled to.
When seeking assistance from insurance brokers or agents, it’s important to work with reputable professionals. Ask for recommendations from friends, family, or colleagues, or research insurance brokerages in your area. Verify that the broker or agent is licensed and has a good reputation for providing quality service.
While insurance brokers and agents can provide valuable assistance, it’s important to stay engaged and ask questions during the process. Seek clarification on any doubts or uncertainties and make sure you fully understand the terms and conditions of the health insurance plan before making a final decision.
By working with insurance brokers or agents, you can tap into their expertise and experience to find the best health insurance coverage when your job doesn’t offer it. Their guidance can help simplify the process and ensure that you secure the coverage you need to protect your health and financial well-being.
Exploring Health Insurance Options for Freelancers or Self-Employed Individuals
Freelancers and self-employed individuals face unique challenges when it comes to obtaining health insurance coverage, as they don’t have the option of employer-sponsored plans. However, there are specific health insurance options designed to cater to the needs of this demographic. Here are some key options to explore:
Individual Health Insurance Plans: Freelancers and self-employed individuals can purchase individual health insurance plans directly from insurance companies. These plans offer coverage tailored to individual needs, with various options to choose from based on coverage levels, premiums, and deductibles. Research different insurance providers and compare plans to find one that suits your specific requirements and budget.
Health Insurance Marketplaces: Freelancers and self-employed individuals can also explore health insurance marketplaces, including state-based or federally facilitated marketplaces, authorized by the Affordable Care Act (ACA). These marketplaces offer a range of health insurance plan options, often with access to subsidies and premium tax credits to make coverage more affordable. Evaluate the plans available through the marketplace and consider the financial assistance options applicable to your income level.
Association Health Plans: Some professional associations and organizations offer group health insurance plans for their members. Freelancers or self-employed individuals who belong to such associations may be eligible to join these plans, leveraging the purchasing power of the group to access more affordable coverage. Research professional associations or industry groups in your field to explore any group health insurance options available.
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): Consider opening a Health Savings Account (HSA) to save for medical expenses while enjoying certain tax advantages. HSAs are paired with high-deductible health insurance plans, and contributions to the account are tax-deductible. The funds in the HSA can be used to pay for qualified medical expenses, offering a tax-efficient way to manage healthcare costs for self-employed individuals.
COBRA Coverage: If you recently left a job that provided health insurance and meet the eligibility criteria, you may have the option to continue your employer-sponsored health insurance coverage through COBRA. While COBRA can be more expensive since you’re responsible for the full premium, it can provide continuity of coverage as you explore other long-term options.
Healthcare Sharing Ministries: Healthcare sharing ministries are organizations where members share medical expenses. They are not traditional health insurance, but they can provide an alternative for certain self-employed individuals seeking a more cost-effective option. However, it’s important to carefully research and understand the limitations and requirements of each healthcare sharing ministry before considering this option.
When exploring health insurance options for freelancers or self-employed individuals, it’s important to consider factors such as coverage, costs, network of providers, and any specific requirements or limitations of each option. Assess your healthcare needs, budget, and preferences to identify the solution that best suits your situation.
Remember to review the policy details, terms, and conditions of any health insurance plan you are considering. Understand the coverage limits, deductibles, copayments, and any exclusions that may apply. Seeking assistance from insurance brokers or agents who specialize in serving self-employed individuals can also be beneficial, as they can provide guidance and help navigate the available options.
By exploring these health insurance options, freelancers and self-employed individuals can find coverage that meets their specific needs, protects their health, and ensures financial security in the face of medical expenses.
Conclusion
When your job doesn’t offer health insurance, it’s essential to take proactive steps to secure coverage and protect your health and financial well-being. Exploring various options can help you find the best solution based on your circumstances and needs.
In this article, we have discussed several alternatives for obtaining health insurance when your job doesn’t offer it. From researching individual health insurance plans to considering short-term coverage, applying for Medicaid or CHIP, joining a spouse or parent’s plan, evaluating health insurance marketplaces, seeking assistance from insurance brokers or agents, and exploring options for freelancers and self-employed individuals, each option comes with its own benefits and considerations.
Understanding the importance of health insurance is crucial, as it provides financial protection, access to healthcare, and promotes preventive care. It helps mitigate the rising costs of medical treatments and ensures that unexpected medical emergencies don’t lead to devastating financial consequences.
When researching individual health insurance plans, it’s important to evaluate your coverage needs, research insurance providers, compare plan options, and consider factors such as network providers, costs, and enrollment periods. Understanding the Affordable Care Act (ACA) is also important, as it provides essential provisions for access to affordable health insurance coverage and subsidies.
Applying for Medicaid or CHIP can be a viable option for those who meet the income threshold requirements. Short-term health insurance plans offer temporary coverage, bridging gaps in coverage, but it’s vital to assess their limitations. Joining a spouse or parent’s health insurance plan can provide affordable coverage, while health insurance marketplaces offer a wide range of plan options.
Seeking assistance from insurance brokers or agents can provide expert guidance, ensuring you make informed decisions about health insurance coverage. Exploring health insurance options for freelancers or self-employed individuals is essential, including individual plans, association health plans, health savings accounts (HSAs), COBRA coverage, or healthcare sharing ministries.
In conclusion, obtaining health insurance coverage when your job doesn’t offer it requires research, evaluation, and careful consideration. By exploring the options and understanding your healthcare needs and budget, you can find the right health insurance solution to protect your health and financial well-being.
Remember to thoroughly review plan details, seek assistance if needed, and stay informed about changes and updates in the insurance landscape. By taking the necessary steps, you can ensure access to quality healthcare and peace of mind in the face of unexpected medical expenses.