Home>Finance>Leverage Items Are Typically Commodities. What Are Some Other Characteristics Of Leverage Items?

Finance
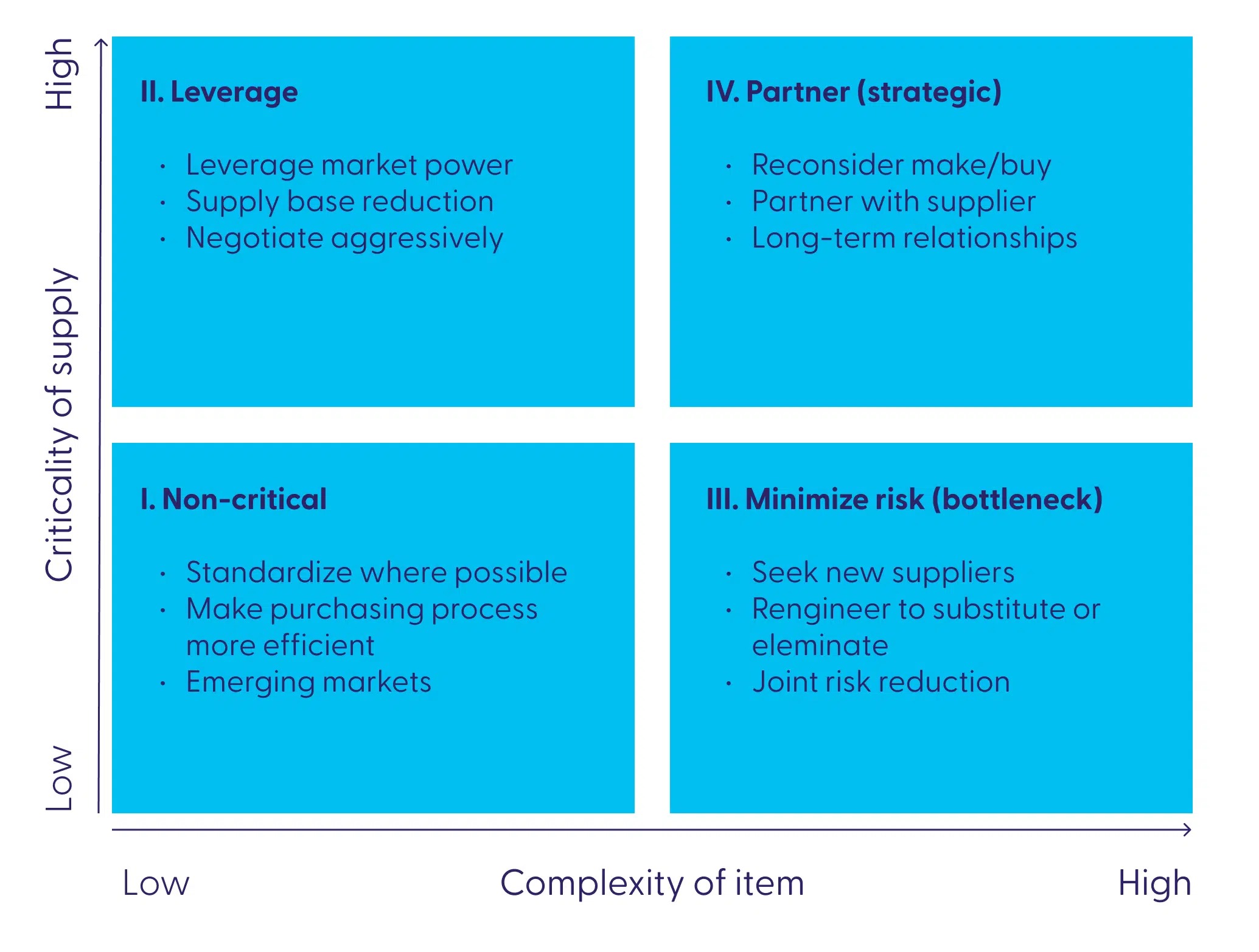
Leverage Items Are Typically Commodities. What Are Some Other Characteristics Of Leverage Items?
Published: October 27, 2023
Discover the key characteristics of leverage items in finance, including their potential for high profitability and volatility in the market. Gain insights into how these items are distinct from traditional commodities.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to the world of finance, leverage items play a crucial role in driving economic growth and investment opportunities. Leverage items are typically commodities that are used to increase the potential return of an investment or financial transaction. These items not only have a direct impact on the profitability of businesses but also influence the overall stability of the financial markets.
Understanding the characteristics of leverage items is essential for investors, businesses, and financial institutions alike. By analyzing these characteristics, one can make informed decisions when it comes to leveraging investments and managing financial risks.
In this article, we will explore the various characteristics of leverage items and how they impact the market dynamics. We’ll delve into the high demand, price sensitivity, availability, scalability, competitive market, standardization, substitute products, low differentiation, and cost efficiency that are commonly associated with these items. By gaining a deeper understanding of these characteristics, individuals and organizations can navigate the financial landscape more effectively while harnessing the potential of leverage items.
Definition of Leverage Items
Leverage items refer to commodities or assets that are used to enhance the potential return of an investment or financial transaction. These items act as a lever, amplifying the performance of the investment. By utilizing leverage, individuals and businesses can maximize their gains and potentially generate higher profits.
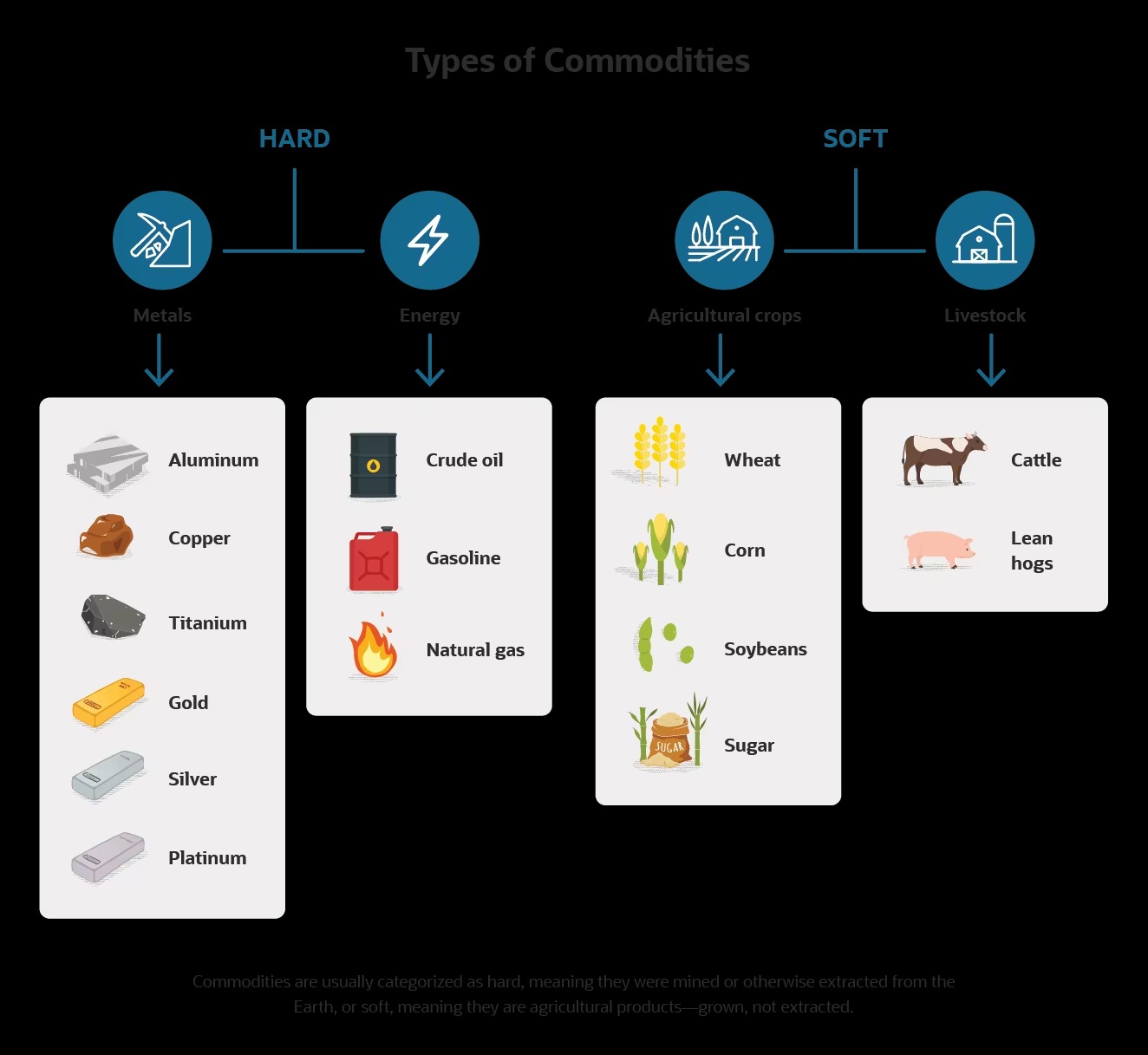
Common examples of leverage items include financial instruments such as options, futures contracts, and derivatives. These instruments allow individuals to take advantage of price movements in underlying assets without having to own the assets themselves. Additionally, leverage items can also include physical commodities such as gold, oil, or agricultural products, where investors can use leverage to participate in price fluctuations.
What sets leverage items apart from other types of assets or commodities is their ability to magnify the potential gains or losses. As leverage amplifies the performance, it also increases the level of risk involved. It is important to note that leverage items can be utilized by both individuals and institutions for various purposes, including speculative trading, hedging against market uncertainties, or as a means to access certain markets or assets that would otherwise be unaffordable.
The concept of leverage items stems from the principle of financial leverage, which refers to the use of borrowed funds or financial instruments to increase the potential return on investment. By using leverage, investors can allocate a relatively small amount of capital to control larger positions, thus increasing the potential profit.
It is crucial to recognize that leverage items and leverage itself carry inherent risks. The amplification of gains applies to losses as well, and improper use of leverage can lead to significant financial losses. Therefore, understanding the characteristics and dynamics of leverage items is vital for individuals and businesses to make informed decisions and mitigate risks effectively.
Characteristics of Leverage Items
Leverage items possess certain characteristics that differentiate them from other commodities or assets. These characteristics play a crucial role in shaping their market dynamics and impact the decision-making process of investors and businesses. Let’s explore some of the key characteristics of leverage items:
- High Demand: Leverage items are often in high demand due to their potential for generating significant returns. Investors are attracted to leverage items as they provide an opportunity to amplify their gains, especially in a bullish market.
- Price Sensitivity: Leverage items tend to be highly sensitive to price fluctuations. Small changes in the underlying asset’s price can have a magnified impact on the value of the leverage item. This price sensitivity adds an additional level of risk to investments in leverage items.
- Availability: Leverage items are typically readily available for trading or investing purposes. These items are actively traded in financial markets, allowing investors to easily access and utilize them in their investment strategies.
- Scalability: Leverage items offer scalability, allowing investors to control larger positions with a relatively small amount of capital. This scalability provides individuals and businesses with the flexibility to adjust their exposure to leverage items according to their risk tolerance and investment goals.
- Competitive Market: Leverage items are traded in highly competitive markets. Due to their popularity and potential for high returns, investors and traders actively participate in the buying and selling of these items. This competitive market environment can lead to increased volatility and liquidity, offering opportunities for profit as well as potential risks.
- Standardization: Many leverage items, such as futures contracts and options, follow standardized formats with predefined terms and conditions. This standardization allows for ease of trading and ensures transparency in the market. It also contributes to the overall efficiency of the trading process.
- Substitute Products: In some cases, leverage items have substitute products that offer similar exposure to the underlying asset. For example, options and futures contracts may have different expiration dates or strike prices, providing investors with choices and alternatives when it comes to leveraging their investments.
- Low Differentiation: Unlike some unique or specialized assets, leverage items often have low differentiation. They are designed to provide leverage to a specific underlying asset or market, and there may be multiple options available for investors to choose from. This low differentiation can impact pricing and competition among leverage items.
- Cost Efficiency: Leveraging investments through leverage items can offer cost efficiency. Instead of directly purchasing the underlying asset, investors can utilize leverage items to gain exposure at a fraction of the cost. This cost efficiency can make certain markets or assets more accessible to a broader range of investors.
Understanding the characteristics of leverage items is essential for individuals and businesses looking to incorporate them into their investment strategies. By considering these characteristics, investors can make informed decisions, manage risks effectively, and harness the potential of leveraging to optimize their investment outcomes.
High Demand
One of the key characteristics of leverage items is their high demand in the financial markets. Investors are attracted to leverage items due to their potential for generating significant returns. The allure of magnifying gains makes these items popular among traders and investors looking to maximize their profits.
Leverage items, such as options, futures contracts, and derivatives, offer individuals the opportunity to amplify their exposure to an underlying asset. This amplification allows investors to benefit from the price movements of the asset without having to invest a large capital amount. Instead, they can control a larger position with a relatively smaller upfront investment.
The high demand for leverage items reflects a desire to take advantage of market opportunities. Investors are constantly seeking ways to enhance their returns, and leverage items provide a means to do so. The potential for significant gains attracts a wide range of participants, including institutional investors, hedge funds, and individual traders.
Moreover, high demand for leverage items can be driven by market sentiment and prevailing market conditions. In a bull market, when prices are rising, investors may seek to capture and amplify those gains through leverage. The optimism and positive sentiment in the market drive increased demand for leverage items.
However, it is crucial to note that high demand for leverage items also comes with increased risks. While leverage magnifies potential gains, it also amplifies losses. Investors must carefully assess their risk tolerance and investment objectives before engaging in leverage trading.
In addition, regulation and market conditions can impact the demand for leverage items. Regulatory changes or restrictions on leverage trading in certain jurisdictions can influence the market participation and demand for these items. Economic factors, such as interest rates, market volatility, and geopolitical events, can also affect the demand for leverage items.
Overall, the high demand for leverage items underscores investors’ desire to increase their potential returns in the financial markets. By understanding the risks associated with leverage and carefully managing their positions, investors can make informed decisions and leverage their investments effectively to capitalize on market opportunities.
Price Sensitivity
Price sensitivity is a crucial characteristic of leverage items. These items are highly sensitive to price fluctuations in the underlying assets they are derived from or represent. Small changes in the price of the underlying asset can have a magnified impact on the value of the leverage item.
For example, in the case of options, the value of the option is directly influenced by the price movement of the underlying stock or asset. A slight increase or decrease in the underlying asset’s price can lead to a significant change in the option’s value. This price sensitivity is a key factor that attracts investors seeking to capitalize on potential market movements.
The price sensitivity of leverage items stems from their leverage factor. The leverage factor determines how much exposure an investor can have to the underlying asset with a given investment amount. Higher leverage factors result in higher price sensitivity, as the potential gains or losses are amplified by the leverage ratio.
It is important to note that while price sensitivity can amplify potential gains, it also increases the level of risk. The same leverage that magnifies profits can lead to substantial losses if the market moves against the investor’s position. Therefore, understanding and managing price sensitivity is crucial for investors utilizing leverage items.
Traders and investors must closely monitor the price movements of the underlying asset and be aware of the potential risks and rewards. Technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and market research can help in making informed decisions regarding the entry and exit points for leverage positions.
Moreover, the price sensitivity of leverage items can vary depending on factors such as the expiration date in the case of options or the contract specifications in the case of futures contracts. Different leverage items may have different price sensitivity profiles, providing investors with a range of options to suit their risk appetite and investment strategies.
Market conditions, volatility, and the liquidity of the underlying asset also influence the price sensitivity of leverage items. In times of heightened market volatility, leverage items tend to exhibit greater price sensitivity, as larger price swings occur more frequently. Conversely, in stable market conditions, price movements may be less pronounced, leading to lower price sensitivity.
In summary, price sensitivity is a defining characteristic of leverage items. Investors must recognize the potential gains and losses that come with price sensitivity, and conduct thorough analysis and risk management to effectively navigate leverage trading and investment strategies.
Availability
Availability is a key characteristic of leverage items. These items are typically readily available for trading or investment purposes, allowing investors to easily access and utilize them in their strategies.
Leverage items are actively traded in financial markets, such as stock exchanges, commodity markets, and derivative markets. They are widely accessible through various financial intermediaries, including brokerage firms, investment platforms, and online trading platforms. This accessibility enables investors to engage in leveraging their positions without significant barriers to entry.
The availability of leverage items provides investors with ample opportunities to participate in the market and capitalize on potential price movements or market trends. It allows both individual investors and institutional traders to implement their investment strategies effectively and efficiently.
Furthermore, the availability of leverage items gives investors the flexibility to adjust their exposure to different asset classes or markets. They can choose from a wide range of leverage items that provide exposure to various underlying assets, such as stocks, commodities, currencies, or indices. This flexibility allows investors to diversify their portfolios and manage risk by spreading their investments across different asset classes.
The availability of leverage items also contributes to market liquidity. As these items are actively traded, there is a constant flow of buyers and sellers, ensuring that there is usually a market for investors to enter or exit their positions. This liquidity enhances price transparency and efficiency in the market, enabling investors to execute their trades at competitive prices.
However, it is important for investors to exercise caution when accessing and utilizing leverage items. While the availability of these items provides opportunities for profit, it also exposes investors to the risks associated with leverage. It is crucial to understand the terms and conditions, associated costs, and the specific risks involved in trading or investing in leverage items.
In addition, the availability of leverage items can be influenced by regulatory policies and market conditions. Regulatory changes or restrictions on leverage trading in certain jurisdictions can impact the availability of leverage items to investors. Economic factors, such as market volatility or financial crises, can also affect market conditions and the availability of leverage items.
Overall, the availability of leverage items plays a significant role in enabling investors to implement leverage strategies and access a wide range of markets and assets. It offers flexibility, diversification, and liquidity, but investors should always conduct thorough research, understand the associated risks, and seek professional advice when using leverage items to make informed investment decisions.
Scalability
Scalability is a key characteristic of leverage items that provides investors with the ability to control larger positions with a relatively small amount of capital. It allows individuals and businesses to effectively amplify their exposure to underlying assets or markets.
When it comes to leverage items, their leverage factor determines the ratio of exposure to the invested capital. A higher leverage factor means that investors can control a larger position with a smaller upfront investment. This scalability is particularly appealing to investors looking to maximize their potential profits.
By utilizing leverage items, investors can potentially achieve higher returns compared to investing solely with their available capital. Leveraging enables individuals to participate in larger market movements and capitalize on price fluctuations without needing significant financial resources.
The scalability of leverage items offers investors the flexibility to adjust their exposure to different assets or markets according to their risk tolerance and investment objectives. It allows for the allocation of smaller capital amounts across a broader range of assets, diversifying the portfolio and potentially reducing risk.
Moreover, scalability also plays a crucial role in accessing markets or assets that would otherwise be unaffordable. For instance, trading futures contracts allows investors to gain exposure to commodities or financial instruments that might require substantial upfront capital if purchased outright.
However, it’s important to note that while scalability can amplify potential gains, it also increases the level of risk. Leveraged positions are vulnerable to larger losses if the market moves against the investor’s expectations. It is essential for investors to carefully assess their risk tolerance and use appropriate risk management techniques when employing leverage strategies.
Additionally, the scalability of leverage items may be subject to certain limitations or requirements set by financial institutions or regulatory authorities. Margin requirements, for example, may impose constraints on the amount of leverage that can be utilized or the types of assets that can be leveraged.
Market conditions and liquidity can also impact the scalability of leverage items. In highly liquid markets with deep order books, it may be easier to enter or exit leveraged positions, allowing for a greater degree of scalability. On the other hand, less liquid markets may pose challenges in executing larger leveraged trades.
In summary, the scalability of leverage items provides investors with the opportunity to control larger positions with a smaller upfront investment. It enables exposure to a broader range of assets, facilitates portfolio diversification, and offers access to markets that may have been otherwise unattainable. However, investors must carefully manage risk and consider the limitations and requirements associated with leveraging their investments.
Competitive Market
A competitive market is a characteristic often associated with leverage items. These items are traded in highly competitive markets, where investors actively participate in buying and selling to capitalize on potential opportunities.
Due to their potential for significant returns, leverage items attract a large number of investors, including both institutional and individual traders. The competitive market environment results in increased trading activity and liquidity, contributing to the efficiency and effectiveness of price discovery.
In a competitive market, prices of leverage items are determined by the forces of supply and demand. Multiple participants are constantly placing bids and offers, adjusting their prices based on market conditions and their respective strategies. This constant flow of trading activity creates a market that is both dynamic and responsive to changes in market sentiment and information.
The competitive nature of the market for leverage items can provide opportunities for investors to enter or exit positions at favorable prices. The presence of multiple buyers and sellers creates a more transparent and liquid market, facilitating smoother execution of trades.
Moreover, the competitive market for leverage items promotes market efficiency. As participants compete to buy or sell leverage items, prices adjust to reflect the underlying asset’s value. This process helps to ensure that the prices of leverage items accurately reflect the market conditions and provide fair value to investors.
However, it is important to recognize that the competitive market for leverage items also poses challenges for investors. The fast-paced nature of the market can lead to increased volatility and price fluctuations. Traders need to stay informed and adapt their strategies quickly to navigate the competitive environment.
Furthermore, the competitive market for leverage items can be influenced by external factors, such as economic events, geopolitical developments, or changes in regulatory policies. These factors can impact market sentiment and introduce additional risk and uncertainty into the competitive landscape.
Investors should also be aware of the impact of market competition on trading costs. In highly competitive markets, transaction costs, including bid-ask spreads and brokerage fees, tend to be lower due to increased competition between market makers and brokers. This can be beneficial for investors, as reduced trading costs can enhance overall investment returns.
In summary, leverage items are traded in a competitive market environment, attracting a diverse range of investors and facilitating active trading and price discovery. The competitive market promotes efficiency and transparency, providing opportunities for investors to enter and exit positions at favorable prices. However, investors must also stay vigilant and adapt to the fast-paced nature of the market, considering the impact of external factors and managing transaction costs.
Standardization
Standardization is a significant characteristic of leverage items. Many leverage items, such as options, futures contracts, and other derivatives, follow standardized formats with predefined terms and conditions. This standardization plays a crucial role in facilitating efficient trading and enhancing transparency in the market.
Standardization ensures that leverage items have consistent structures, contract sizes, expiration dates, and other relevant specifications. This consistency allows for seamless trading and enables investors to easily compare and evaluate different leverage items. It also reduces complexity and ambiguity, making it easier for market participants to understand and price these instruments.
The use of standardized leverage items fosters market transparency as it ensures that all market participants have access to the same information. The standardized terms and conditions of these items are publicly available, enabling investors to assess the risks and benefits associated with each instrument before making investment decisions.
Standardization also contributes to market liquidity by enhancing the tradability of leverage items. With standardized contracts, there is an established framework for matching buyers and sellers, ensuring that there is a ready market for these instruments. This facilitates efficient price discovery and allows for smooth execution of trades.
Moreover, standardization enables market participants to hedge their positions or manage risk more effectively. By having standardized leverage items, investors can easily offset their exposure to the underlying asset through opposite positions in the same or similar leverage items. This hedging mechanism helps investors to protect their portfolios and manage market volatility.
However, it is important to note that while leverage items follow standardized formats, there can still be flexibility and variations within these structures. For example, options may have different strike prices or expiration dates, allowing investors to choose different levels of leverage or timeframes for their positions.
Standardization is often implemented and overseen by regulatory bodies or exchanges to ensure fair and orderly markets. These entities establish guidelines and rules to govern the trading and usage of leverage items, maintaining market integrity and protecting the interests of investors.
Overall, standardization is a critical characteristic of leverage items that helps to streamline trading, enhance market transparency, and facilitate risk management. It provides a common framework for market participants, enabling efficient price discovery and ensuring a level playing field for all investors.
Substitute Products
Substitute products are an important aspect of leverage items. In some cases, leverage items have alternative products that offer similar exposure to the underlying asset. These substitute products provide investors with choices and alternatives when it comes to leveraging their investments.
For instance, in the case of options, there can be multiple options contracts available with different expiration dates or strike prices. Each option contract represents the right to buy or sell the underlying asset at a specified price within a certain timeframe. Investors can choose the option contract that best suits their investment objectives and risk appetite.
Similarly, futures contracts for commodities or financial instruments may have multiple expiration dates, allowing investors to select the contract that aligns with their trading strategy or investment horizon. These substitute contracts provide flexibility in terms of timing and enable investors to adapt their positions according to market conditions.
Substitute products in the market allow investors to compare and evaluate different leverage items based on their specific needs and market outlook. They can assess the advantages and disadvantages of each product, such as pricing, liquidity, and contract specifications, before deciding on the most suitable option.
Furthermore, the presence of substitute products encourages competition among market participants, leading to potential improvements in pricing and trading conditions. Market makers and liquidity providers strive to offer competitive prices and execution quality to attract investors to their particular substitute products.
However, it is important to note that while substitute products offer choices, they may also introduce complexity to the decision-making process. Investors need to carefully consider the characteristics, risks, and costs associated with each substitute product before initiating a leveraged position.
Moreover, the availability and liquidity of substitute products can vary. Some substitute products may have higher trading volumes and greater market depth, making them more attractive to investors. Others may have lower liquidity and thinner trading activity, which can impact the ease of entering or exiting positions.
Investors should also be aware of the unique features and trading mechanics of each substitute product. Different instruments may have distinct settlement procedures, margin requirements, or contract specifications, which can affect the overall trading experience and potential outcomes.
In summary, leverage items often have substitute products available, providing investors with choices and alternatives when it comes to leveraging their investments. These substitute products offer flexibility in terms of contract specifications, expiration dates, or strike prices, allowing investors to tailor their leveraged positions to their specific investment objectives and risk tolerance. Evaluating the characteristics and considering the potential risks associated with each substitute product is essential to make informed investment decisions.
Low Differentiation
Low differentiation is a notable characteristic of leverage items. Unlike some unique or specialized assets, leverage items often have low differentiation. They are designed to provide leverage to a specific underlying asset or market, and there may be multiple options available for investors to choose from.
For example, options contracts or futures contracts typically provide leverage to a particular stock, commodity, currency, or index. While there may be variations in contract specifications, such as expiration dates or strike prices, the underlying asset remains the same. This low differentiation means that investors can find similar leverage items with comparable characteristics in the market.
The low differentiation of leverage items can impact their pricing and competition among market participants. Since leverage items provide similar exposure to the underlying asset, investors have the ability to compare and evaluate different options based on factors such as pricing, liquidity, and contract terms.
Market participants, including market makers and liquidity providers, must compete to offer competitive pricing and favorable trading conditions to attract investors. This competition helps to drive efficiency in the market and ensures that pricing accurately reflects the underlying asset’s value and market conditions.
However, it is important to note that low differentiation does not imply that all leverage items are the same. While they provide leverage to the same underlying asset, their specific contract terms may differ. For example, options may have different expiration dates or strike prices, while futures contracts may have varying contract sizes or delivery requirements.
Investors should carefully consider the differences in contract specifications and how they align with their investment objectives and risk preferences. Evaluating the specific characteristics of different leverage items is crucial to make informed decisions and select the most suitable option.
Furthermore, low differentiation can also imply a lower level of uniqueness or exclusivity associated with leverage items. They are widely available in the market, and investors can readily access these instruments through various financial intermediaries.
While low differentiation may make it easier for investors to compare and evaluate leverage items, it is important to recognize that each instrument carries its own set of risks and considerations. Investors should educate themselves on the specific features of the leverage item they are interested in to fully understand its potential risks and rewards.
In summary, leverage items often have low differentiation, providing investors with similar exposure to a specific underlying asset or market. This characteristic allows for easy comparison and evaluation of different options in terms of pricing, liquidity, and contract terms. However, it is important for investors to consider the specific characteristics and risks associated with each leverage item when making investment decisions.
Cost Efficiency
Cost efficiency is a significant characteristic of leverage items that can make them attractive to investors. Leveraging investments through these items can offer cost efficiency compared to directly purchasing the underlying assets.
When investors use leverage items, they can gain exposure to the price movements of the underlying asset without needing to invest the full capital required to own the asset outright. This enables them to allocate a smaller amount of capital to control a larger position, thereby potentially magnifying their investment returns.
The cost efficiency of leverage items is particularly beneficial when the underlying assets have high market values. For instance, purchasing a physical commodity like gold or oil could require a substantial upfront investment. However, through leveraging, investors can gain exposure to these assets at a fraction of the cost, making them more accessible to a wider range of investors.
Leverage items also offer cost efficiency by reducing certain transaction costs. For example, instead of incurring brokerage fees and other expenses associated with direct asset ownership, investors can access leverage items through intermediary platforms, which often have lower transaction costs.
Furthermore, leverage items provide a means to enter and exit positions more efficiently compared to certain physical assets or specialized derivatives. The standardized nature of many leverage items allows for easy and seamless trading, reducing the time and costs associated with buying or selling assets directly.
However, it’s important to note that while leverage items may offer cost efficiency in terms of capital requirements and transaction costs, they are not entirely cost-free. Investors should be aware of other potential costs, such as financing charges and margin requirements, which can be associated with leveraging positions.
Moreover, investors should carefully assess the overall risk-reward balance and consider the potential costs and benefits associated with leveraging their investments. While leverage can amplify potential gains, it also magnifies losses. Investors must weigh the potential returns against the increased risk and associated costs to determine if leveraging is suitable for their investment objectives and risk tolerance.
In summary, leveraging investments through leverage items can offer cost efficiency by allowing investors to gain exposure to underlying assets at a fraction of the cost of direct ownership. This makes asset classes and markets more accessible to a broader range of investors. However, investors should carefully evaluate the overall costs, including transaction costs, financing charges, and the potential risks associated with leveraging, to determine the suitability of using these items in their investment strategies.
Conclusion
Leverage items play a vital role in the world of finance, offering investors the opportunity to enhance their potential returns and participate in the market with a smaller upfront investment. Understanding the characteristics of leverage items is essential for individuals and businesses looking to leverage their investments effectively and manage risks efficiently.
We have explored several key characteristics of leverage items throughout this article. High demand makes leverage items attractive to investors seeking to maximize their profits. Price sensitivity highlights the potential for amplified gains or losses due to small price fluctuations. The availability of leverage items allows investors to easily access and utilize them in their investment strategies. Scalability enables investors to control larger positions with a relatively small amount of capital, providing flexibility in portfolio management.
Furthermore, we examined the competitive market for leverage items, where market participants actively trade and compete to offer favorable terms and prices. Standardization ensures consistency and transparency, facilitating efficient trading and risk management. The presence of substitute products gives investors choices and alternatives when it comes to leveraging their investments. Low differentiation allows investors to compare and evaluate different leverage items effectively.
Finally, leveraging investments through leverage items can offer cost efficiency by providing exposure to assets at a fraction of the cost of direct ownership, reducing transaction costs, and enhancing overall market access.
While leverage items can present opportunities for enhanced returns, it is crucial for individuals and businesses to carefully manage their risk exposure. Understanding the dynamics and characteristics of leverage items empowers investors to make informed decisions, employ risk mitigation strategies, and optimize their investment outcomes.
In conclusion, leveraging investments through well-understood and carefully chosen leverage items can be a powerful strategy for individuals and businesses. By considering the characteristics discussed in this article, investors can harness the potential of leverage items while navigating the financial landscape with confidence.