Finance
What Are Exempt Commodities
Published: October 27, 2023
Discover what exempt commodities are in the world of finance and how they may impact your investment strategies. Learn the ins and outs of this important financial term today.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of exempt commodities! In the realm of finance, exempt commodities play a crucial role in shaping markets and providing investors with unique opportunities. From agricultural products to precious metals, exempt commodities encompass a wide range of goods that are exempt from certain regulations and oversight.
Exempt commodities refer to goods that are excluded or exempted from specific financial regulations, such as the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) regulations in the United States. These regulations are in place to monitor and regulate the trading of futures contracts, options, and other derivative instruments.
The rationale behind exempting certain commodities from these regulations is to foster liquidity, promote innovation, and reduce barriers to entry for market participants. By allowing exemptions for select commodities, the market can operate more efficiently, giving traders and investors greater flexibility in managing their portfolios.
Exempt commodities often have unique characteristics that differentiate them from regulated commodities. These characteristics may include physical features, market liquidity, or specific uses in various industries. Understanding the distinctions between exempt and regulated commodities is essential for investors looking to diversify their portfolio and explore alternative investment options.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the world of exempt commodities, exploring their definition, examples, regulations, market trends, and key players in the industry. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or someone new to the world of finance, this article will provide you with valuable insights into the fascinating realm of exempt commodities.
Definition of Exempt Commodities
Exempt commodities are a subset of the broader commodity market that are excluded or exempted from specific financial regulations. These regulations typically pertain to trading, reporting, and transparency requirements imposed by regulatory bodies such as the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) in the United States.
The purpose of exempting certain commodities from regulation is to encourage market liquidity, innovation, and efficiency. By exempting these commodities, regulators aim to reduce barriers to entry and foster a more dynamic and competitive environment.
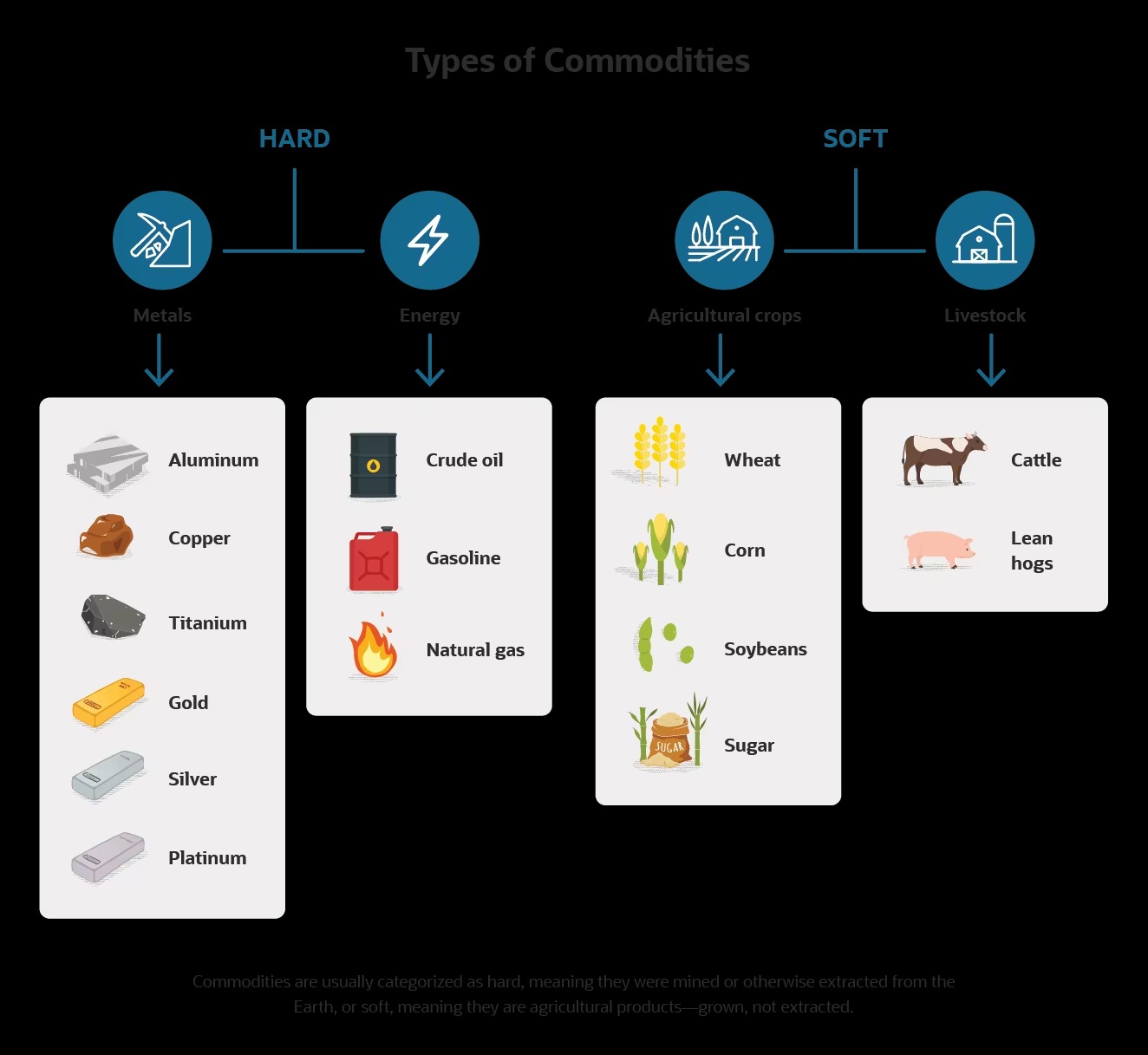
Exempt commodities can include a wide variety of goods and assets. Some common examples include agricultural products, such as crops and livestock, precious metals like gold and silver, energy resources such as natural gas and crude oil, and even certain types of financial instruments like foreign currency or certain types of derivatives.
What sets exempt commodities apart from regulated commodities is the level of oversight and reporting requirements imposed upon them. While regulated commodities are subject to strict regulations and monitoring, exempt commodities enjoy a greater degree of flexibility and freedom in terms of trading and market operations.
It’s important to note that exempt commodities are not completely unregulated. While they may be exempt from certain regulations, they are still subject to general laws and regulations governing financial transactions and contracts. Additionally, although exempt commodities may be less regulated, their trading activities are expected to adhere to fair market practices and ethical conduct.
The classification of a commodity as exempt can vary across jurisdictions. Different countries may have different regulations or exemptions in place for specific commodities. Therefore, it’s crucial for market participants to familiarize themselves with the regulations and exemptions applicable to their respective jurisdictions.
In the next section, we will explore some examples of exempt commodities to provide a clearer understanding of the diverse range of goods that fall under this category.
Examples of Exempt Commodities
Exempt commodities encompass a wide range of goods and assets that are exempt from specific financial regulations. Here are a few examples of exempt commodities:
- Agricultural Products: Agricultural commodities such as corn, wheat, soybeans, and livestock are often considered exempt commodities. These products are crucial to the global food supply chain and are heavily traded in commodity markets.
- Precious Metals: Precious metals like gold, silver, platinum, and palladium are popular exempt commodities due to their historical and intrinsic value. Investors often turn to these metals for diversification and as a hedge against inflation or economic uncertainty.
- Energy Resources: Commodities in the energy sector, including crude oil, natural gas, and gasoline, are frequently classified as exempt commodities. These resources are vital for various industries and play a significant role in global economic activities.
- Foreign Currencies: Foreign currencies, such as the Euro, Japanese Yen, or British Pound, are often exempt commodities. Investors and companies engage in currency trading to manage currency risks and take advantage of fluctuations in exchange rates.
- Financial Instruments: Some financial instruments, particularly certain types of derivatives, are considered exempt commodities. Examples include certain types of options, swaps, and futures contracts that do not fall under strict regulatory oversight.
It’s important to note that the list above is not exhaustive, and the classification of exempt commodities can vary across jurisdictions. Different countries may have different regulations in place, leading to variations in the commodities considered exempt.
Exempt commodities offer investors and traders unique opportunities and diversification benefits. Their exemption status allows for greater flexibility in trading, potentially leading to increased market liquidity and efficiency.
Now that you have a better understanding of the different types of commodities that fall under the exempt category, let’s explore the regulations and laws governing exempt commodities in the next section.
Regulations and Laws Governing Exempt Commodities
While exempt commodities enjoy certain exemptions from specific financial regulations, they are still subject to general laws and regulations governing financial transactions and contracts. Additionally, the classification and regulation of exempt commodities can vary across jurisdictions. Let’s take a closer look at the regulations and laws that govern these commodities:
General Financial Regulations: Exempt commodities, like any other financial instrument, are subject to general financial regulations that ensure fair and transparent market practices. These regulations include anti-fraud provisions, insider trading laws, and regulations regarding market manipulation and abusive trading practices.
Commodity Exchange Act (CEA) (United States): In the United States, the CEA provides the regulatory framework for commodities trading, including both regulated and exempt commodities. While certain commodities may be exempt from specific regulations under the CEA, they are still subject to the overall provisions of the act.
Reporting Requirements: In some cases, exempt commodities may have reduced reporting requirements compared to regulated commodities. However, market participants are still expected to maintain proper records and provide necessary disclosures as mandated by applicable laws and regulations.
International Regulations: For commodities that are traded internationally, global organizations like the International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) and the Financial Stability Board (FSB) may establish guidelines and principles to ensure consistency and harmonization in the regulation of exempt commodities across different jurisdictions.
National Regulatory Bodies: Each country has its own regulatory bodies responsible for overseeing commodity markets and enforcing regulations. These bodies may have specific guidelines and exemptions applicable to exempt commodities within their jurisdiction.
It’s important for market participants, including investors and traders, to stay informed about the regulations and laws governing exempt commodities. Understanding the regulatory landscape not only helps ensure compliance but also enables participants to make informed decisions and mitigate risks.
Next, let’s explore the benefits and drawbacks of engaging in exempt commodities trading.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Exempt Commodities
Engaging in exempt commodities trading offers various benefits and drawbacks for investors and traders. Let’s explore some of the key advantages and considerations:
Benefits:
- Diversification: Exempt commodities provide an opportunity to diversify investment portfolios beyond traditional asset classes like stocks and bonds. Adding commodities to a portfolio can help spread risk and potentially increase returns.
- Inflation Hedge: Certain exempt commodities, such as precious metals, have historically served as a hedge against inflation. Investing in these commodities can help protect against the erosion of purchasing power during times of rising prices.
- Potential for Profit: Exempt commodities, like any other investment, have the potential for profit. The fluctuating prices in commodity markets can provide opportunities for savvy investors to capitalize on price movements and generate returns.
- Market Liquidity: The exempt commodities market often benefits from increased liquidity due to reduced regulatory barriers. This liquidity can enhance market efficiency, allowing for smoother transactions and easier entry and exit points for market participants.
- Portfolio Hedging: Exempt commodities can be used as a hedging tool to manage risks associated with other investments. For example, investors may use commodities to offset potential losses in other asset classes during market downturns.
Drawbacks:
- Price Volatility: Exempt commodities are known for their price volatility, which can create significant fluctuations in value. The inherent unpredictability of commodity markets can pose risks and require careful monitoring for investors.
- Commodity-Specific Risks: Different exempt commodities come with their own unique risks. For example, agricultural commodities can be affected by weather conditions, while energy commodities can be influenced by geopolitical events. Understanding these risks is crucial for effective risk management.
- Regulatory Changes: While exempt commodities enjoy certain exemptions from regulations, changes in laws and regulations can impact their trading environment. Market participants should stay informed about regulatory developments and adapt their strategies accordingly.
- Complexity: Commodities trading can be complex, requiring a good understanding of the underlying market dynamics and factors that influence prices. In-depth research and analysis are necessary to make informed decisions and mitigate risks.
As with any investment, it’s important to carefully assess the benefits and drawbacks of engaging in exempt commodities trading. A thorough understanding of the market, risk tolerance, and investment goals is crucial in determining if exempt commodities align with one’s investment strategy.
Now, let’s explore the current market trends related to exempt commodities.
Current Market Trends for Exempt Commodities
The exempt commodities market is constantly evolving, influenced by various factors such as economic conditions, geopolitical events, and shifts in supply and demand dynamics. Here are some current market trends for exempt commodities:
- Green Commodities: With the growing focus on sustainability and renewable energy, green or eco-friendly commodities have gained traction in the market. Examples include carbon credits, renewable energy certificates, and sustainable agricultural products. Investors are increasingly looking to incorporate these environmentally conscious commodities into their portfolios.
- Digital Commodities: The rise of digital technologies has given rise to a new class of commodities known as digital or virtual commodities. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are prime examples of these assets, providing alternative investment opportunities with unique market dynamics.
- Commodities and Emerging Markets: Emerging markets play a significant role in the global commodities market. Increased industrialization and urbanization in countries like China and India have fueled demand for commodities such as metals, energy resources, and agricultural products. Monitoring the trends and developments in emerging markets can provide insights into the potential growth of various exempt commodities.
- Supply Chain Transparency: There is a growing emphasis on transparency and ethical sourcing in commodity markets. Consumers and investors are increasingly demanding greater transparency in the supply chain of commodities, particularly in sectors such as agriculture and precious metals. This trend has led to the development of certification programs and increased focus on responsible sourcing practices.
- Technological Advancements: Technological advancements have significantly impacted the exempt commodities market. The use of advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and blockchain technology has improved efficiency, transparency, and risk management in commodity trading. These advancements continue to reshape the market and offer new opportunities for investors and traders.
It’s important to note that market trends can be dynamic and subject to change. Staying informed about the latest developments and trends in the exempt commodities market is crucial for market participants to make informed decisions and capitalize on potential opportunities.
Next, let’s explore the key players in the exempt commodities industry.
Key Players in the Exempt Commodities Industry
The exempt commodities industry involves a diverse range of participants who play vital roles in the trading, production, and distribution of these commodities. Let’s take a look at some of the key players in this industry:
- Producers and Suppliers: Producers and suppliers are the primary source of exempt commodities. They include farmers, miners, energy companies, and other entities involved in the extraction, cultivation, and production of commodities. These players have a significant impact on the overall supply and pricing of exempt commodities.
- Commodity Exchanges: Commodity exchanges act as centralized marketplaces where buyers and sellers can trade exempt commodities. Examples of prominent commodity exchanges include the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME), New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX), and London Metal Exchange (LME). These exchanges provide a transparent and regulated platform for price discovery and trading.
- Financial Institutions: Banks, investment firms, and other financial institutions play an important role in the exempt commodities market. They provide financing, hedging services, and investment products related to commodities. These institutions often have dedicated commodity trading desks and offer derivative products to investors and hedgers.
- Hedgers and Speculators: Hedgers and speculators are crucial participants in the exempt commodities market. Hedgers, such as farmers or energy companies, use commodity futures contracts to hedge against price volatility and protect their business operations. Speculators, on the other hand, buy and sell commodities with the intention of profiting from price fluctuations.
- Traders and Brokers: Traders and brokers facilitate the buying and selling of exempt commodities. They act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, executing trades on behalf of their clients. Trading firms and brokerage houses play a vital role in providing liquidity to the market and ensuring efficient price discovery.
- Regulatory Bodies: Regulatory bodies, such as the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) in the United States, oversee and regulate the exempt commodities industry. These agencies enforce rules and regulations to ensure fair and transparent market practices, protect investors, and maintain market integrity.
It’s worth noting that the exempt commodities industry is highly interconnected, with various players working collaboratively to shape the market. Their roles and interactions contribute to the overall functioning and dynamics of the exempt commodities market.
Now that we have explored the key players in the industry, let’s conclude our article.
Conclusion
In conclusion, exempt commodities provide investors and traders with unique opportunities to diversify their portfolios and navigate the dynamic world of finance. These commodities, which are exempt from certain financial regulations, encompass a wide range of goods and assets, including agricultural products, precious metals, energy resources, foreign currencies, and financial instruments.
While exempt commodities enjoy certain exemptions, they are still subject to general financial regulations and laws governing financial transactions and contracts. It is important for market participants to stay informed about the regulatory landscape and comply with applicable laws to ensure fair and transparent market practices.
Engaging in exempt commodities trading offers both benefits and drawbacks. On the positive side, investing in exempt commodities allows for portfolio diversification, potential hedging against inflation, and the potential for profit. However, they also come with considerations such as price volatility, commodity-specific risks, and the need for a deep understanding of the underlying market dynamics.
Current market trends reflect the evolving landscape of exempt commodities, including the rise of green and digital commodities, the impact of emerging markets, the emphasis on supply chain transparency, and advancements in technology. Staying updated on these trends is crucial for making informed investment decisions and capitalizing on potential opportunities.
The exempt commodities industry involves a variety of key players, such as producers and suppliers, commodity exchanges, financial institutions, hedgers and speculators, traders and brokers, and regulatory bodies. Their roles and interactions shape the functioning and dynamics of the market, contributing to its overall liquidity and efficiency.
In the dynamic world of finance, exempt commodities continue to play a critical role. Whether you are a seasoned investor or someone exploring alternative investment options, understanding exempt commodities and the opportunities they present can be valuable in building a robust and diversified investment portfolio.