Home>Finance>Property, Plant, And Equipment (PP&E) Definition In Accounting


Finance
Property, Plant, And Equipment (PP&E) Definition In Accounting
Published: January 13, 2024
Learn about the definition of Property, Plant, and Equipment (PP&E) in Accounting and its importance in the world of finance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Welcome to the World of Property, Plant, and Equipment (PP&E) in Accounting
Are you curious about the fascinating world of Property, Plant, and Equipment (PP&E) in accounting? Are you wondering what PP&E actually means and how it affects a company’s financial statements? Well, you’ve come to the right place! In this blog post, we’ll explore the definition of PP&E in accounting and its significance in financial reporting.
Key Takeaways
- Property, Plant, and Equipment (PP&E) refers to tangible assets that are long-term in nature and used in the normal course of business operations.
- PP&E assets include land, buildings, machinery, vehicles, and other physical assets.
What is Property, Plant, and Equipment (PP&E)?
Property, Plant, and Equipment (PP&E) is a category of tangible assets that a business owns and uses to generate income. These assets have a long-term nature, meaning they are expected to be used in the normal course of business operations for more than one year. PP&E assets are essential for a company’s day-to-day operations and are not easily converted into cash.
In the field of accounting, PP&E is also known as fixed assets or non-current assets. These terms are used interchangeably and represent the same concept. Let’s dive deeper into what constitutes PP&E assets:
1. Land
Land refers to the Earth’s surface and everything attached to it, such as buildings, natural resources, and improvements like fences or landscaping. Land is considered a non-depreciable asset, meaning its value remains stable over time.
2. Buildings
Buildings include structures owned by a company that are used for operational purposes, such as office spaces, factories, warehouses, or retail stores. The cost of buildings includes the purchase price, any additional construction or improvement costs, and legal fees associated with acquiring the property.
3. Machinery and Equipment
Machinery and equipment encompass a wide range of physical assets, including production machinery, vehicles, computer systems, furniture, and other tools necessary for business operations. These assets are subject to depreciation, as their value diminishes over time due to wear and tear or technological obsolescence.
4. Intangible Assets
Although intangible assets are not traditionally part of the PP&E category, they are worth mentioning. Intangible assets are non-physical assets, such as patents, copyrights, trademarks, or goodwill. While not included in PP&E, they are significant investments for many businesses.
Significance of PP&E in Financial Reporting
Now that we understand what PP&E assets are, let’s explore their significance in financial reporting:
1. Balance Sheet
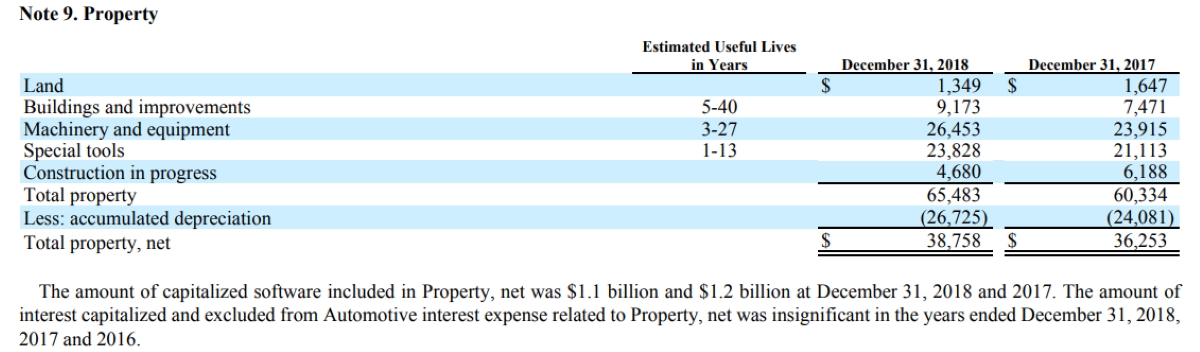
PP&E assets are reported on the balance sheet at their historical cost, which includes the original purchase price along with any costs directly attributable to bringing the asset to its intended use. As mentioned earlier, land is an exception as it is recorded at its acquisition cost, without depreciation.
2. Depreciation
Depreciation is a key concept related to PP&E assets. It represents the systematic allocation of the asset’s cost over its useful life. By recording depreciation expense on a periodic basis, businesses can reflect the wear and tear or obsolescence of their PP&E assets. Depreciation reduces the asset’s book value over time and has a significant impact on a company’s income statement and cash flows.
By accounting for PP&E assets and tracking their value over time, businesses can make informed decisions regarding repair, maintenance, replacement, or disposal of assets. Additionally, financial statement users, such as investors or creditors, can assess a company’s ability to generate future cash flows and its overall financial health.
So, the next time you come across the term Property, Plant, and Equipment (PP&E) in accounting, you’ll have a solid understanding of what it means and why it matters. PP&E assets are the backbone of many businesses, enabling them to carry out their operations, generate income, and contribute to their long-term success.