Finance
Stock Market Crash Definition
Published: February 2, 2024
Learn the definition of a stock market crash in the world of finance. Understand the impact and causes of this significant financial event.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Understanding the Stock Market Crash Definition: A Guide to Financial Turbulence
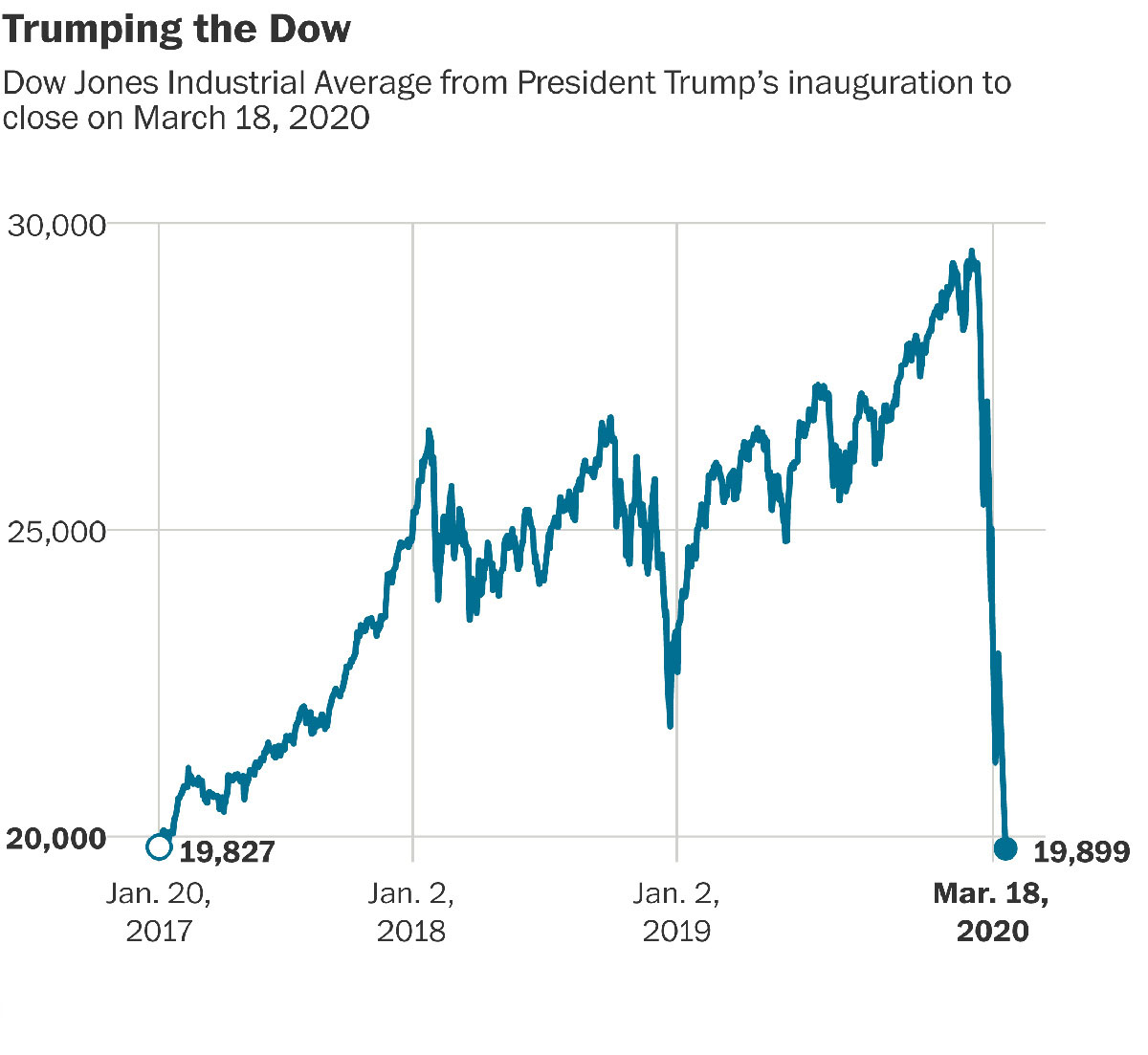
Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting to dip your toes into the world of finance, understanding the stock market crash definition is crucial. The history of financial markets is marked by significant downturns that have had a profound impact on economies around the globe. In this blog post, we will explore what constitutes a stock market crash, its causes, and the implications it can have for individuals and society as a whole.
Key Takeaways:
- A stock market crash refers to a sudden and severe decline in stock prices, often characterized by panic selling and a significant drop in market value.
- Stock market crashes are typically caused by a variety of factors, including economic recessions, geopolitical events, speculative bubbles, and investor fear and uncertainty.
So, what exactly is a stock market crash? In simple terms, a stock market crash occurs when there is a rapid and substantial decline in the value of stocks traded on the market. This decline is often accompanied by a widespread panic among investors, resulting in a frenzied selling spree that further exacerbates the downward spiral. While stock market fluctuations are a normal part of investing, a crash is characterized by its magnitude and speed, leading to substantial losses for investors.
Causes of stock market crashes: Stock market crashes can have various triggers, including:
- Economic recessions: A severe economic downturn can trigger a stock market crash as investors anticipate a decline in corporate earnings and react by selling their stocks.
- Geopolitical events: Wars, political instability, or trade disputes can create uncertainty and negatively impact investor confidence, leading to a market crash.
- Speculative bubbles: When prices of certain stocks or sectors become detached from their underlying value due to excessive speculation, a crash can occur when the bubble bursts, causing a swift and steep decline in prices.
- Investor fear and uncertainty: Market psychology plays a significant role in stock market crashes. Fear and uncertainty can quickly spread among investors, leading to panic selling and a market crash.
Implications of stock market crashes: The consequences of a stock market crash can be far-reaching and affect both individuals and society at large. Some of the implications include:
- Investor losses: Investors who fail to anticipate or react quickly enough to a market crash can suffer significant financial losses, eroding their wealth and impacting their long-term financial goals.
- Economic downturn: A severe stock market crash can have a ripple effect on the broader economy. It can lead to lower consumer spending, business closures, layoffs, and slower economic growth.
- Market volatility: A stock market crash often results in increased market volatility and uncertainty. This can make it challenging for businesses to raise capital, disrupt financial markets, and hinder economic progress.
- Policy interventions: Governments and central banks may intervene during a market crash to stabilize the situation. These interventions can include lowering interest rates, implementing stimulus measures, and introducing regulations to restore investor confidence and prevent further economic damage.
In conclusion, understanding the stock market crash definition is vital for investors and individuals interested in the world of finance. While stock market crashes can be disruptive and financially devastating, they also present opportunities for those who can navigate and capitalize on market volatility. By staying informed and employing sound investment strategies, you can mitigate the risks associated with stock market crashes and position yourself for long-term financial success.