Finance
What Is A Judgement On Your Credit Report
Published: October 20, 2023
Learn about the impact of a judgement on your credit report and how it can affect your finances. Understand the implications and strategies to minimize its impact.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to managing your personal finances, your credit score plays a crucial role. It determines your eligibility for loans, credit cards, and even rental agreements. One factor that can have a significant impact on your credit score is a judgment on your credit report. Understanding what a judgment is and how it affects your credit can help you take the necessary steps to improve your financial standing.
Your credit report is a snapshot of your financial history and behaviors. It includes information about your open accounts, payment history, and any negative entries that may exist. Lenders and creditors use this information to assess your creditworthiness and determine the risk associated with lending you money.
A credit judgment is a legal ruling against you in a court of law due to a debt that you owe. This ruling confirms that you are legally obligated to repay the debt and gives the creditor the right to take further action to collect what is owed. It is important to note that not all debts result in a judgment. It typically occurs when a creditor takes legal action after several unsuccessful attempts to collect the debt.
There are different types of judgments that can appear on your credit report, including monetary judgments and non-monetary judgments. A monetary judgment is when the court orders you to pay a specific amount of money to the creditor. On the other hand, a non-monetary judgment may involve actions like repossession of assets or eviction.
The presence of a judgment on your credit report can have significant consequences for your financial future. It serves as a red flag to potential lenders, indicating that you have a history of not repaying debts as agreed. This can result in higher interest rates, limited loan options, and even difficulties in securing housing or employment.
Understanding Credit Reports
A credit report is a detailed record of your financial history and activities. It is compiled by credit reporting agencies, which gather information from various sources such as lenders, creditors, and public records. The information in your credit report is used to calculate your credit score, which is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness.
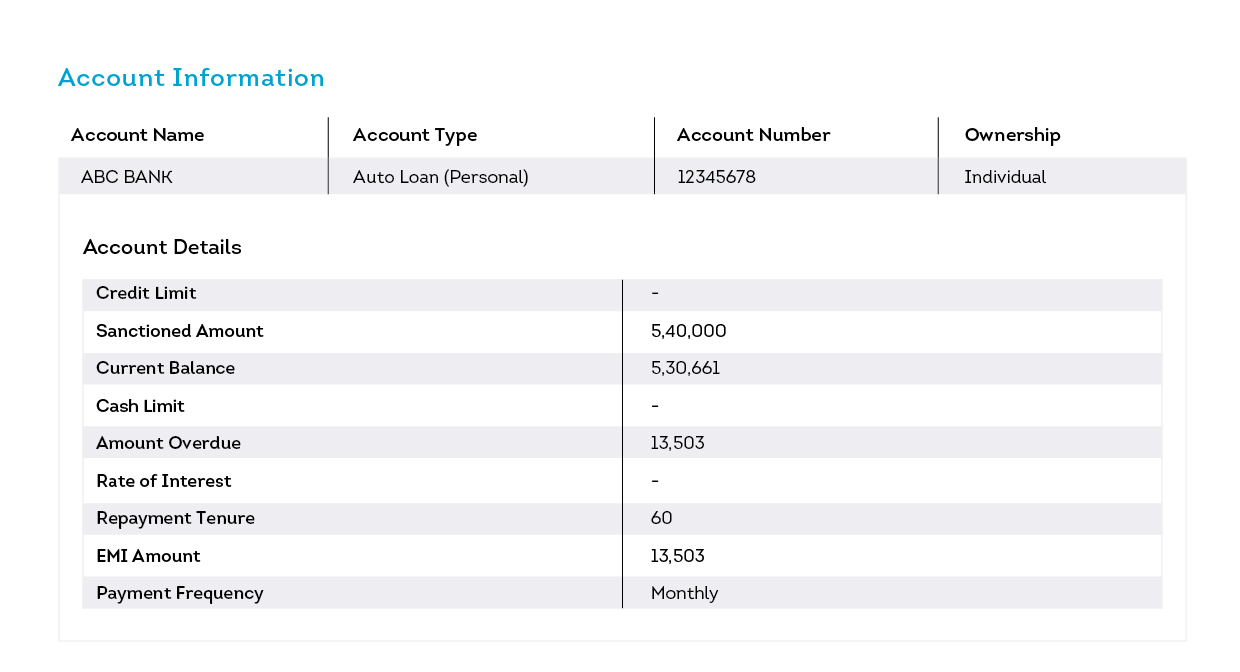
Your credit report includes several key components, including personal information, account information, payment history, and public records. Personal information includes your full name, address, social security number, and employment history. Account information lists all the credit accounts you have, such as credit cards, loans, and mortgages, along with details like account balances, credit limits, and payment history.
Payment history is one of the most important factors in determining your credit score. It shows whether you have paid your bills on time, have any late payments, or have gone into default on any debts. Public records section includes information about bankruptcies, liens, judgments, and other legal actions taken against you.
It’s important to regularly review your credit report to ensure that the information is accurate and up to date. Mistakes on your credit report can lower your credit score and negatively impact your ability to obtain credit in the future. By monitoring your credit report, you can identify any errors or fraudulent activity and take steps to correct them.
In the next section, we will delve into the specifics of what a credit judgment is and how it can affect your credit report.
What is a Credit Judgment?
A credit judgment is a legal ruling that occurs when a creditor takes legal action against you for non-payment of a debt. It is a decision made by a court of law that confirms your obligation to repay the debt and grants the creditor the authority to take further action to collect what is owed.
When you fail to make payments as agreed upon, the creditor may choose to file a lawsuit against you. This typically happens after other attempts to collect the debt, such as phone calls and collection letters, have been unsuccessful. The creditor will present evidence to support their claim in court, and if the judge rules in their favor, a judgment will be issued.
A credit judgment can have serious consequences for your financial well-being. It not only negatively impacts your credit report, but it also gives the creditor additional options for collecting the debt. They may be able to garnish your wages, place a lien on your property, or even seize your assets to satisfy the debt.
It’s important to understand that judgments can vary in terms of the amount owed and the actions that can be taken by the creditor. Monetary judgments require you to repay a specific amount of money to the creditor. Non-monetary judgments, on the other hand, may involve actions such as repossession of assets or eviction.
Having a credit judgment on your credit report can make it difficult for you to obtain new credit or loans. Lenders and creditors view judgments as a sign of financial irresponsibility, as it indicates a failure to meet your obligations. This can result in higher interest rates, lower credit limits, or even a denial of credit altogether.
In the next section, we will explore the different types of judgments that can appear on your credit report and how they can impact your financial situation.
Types of Judgments
There are various types of judgments that can appear on your credit report, each with its own implications for your financial situation. Understanding these different types can help you navigate the impact they may have on your creditworthiness and potential options for resolution.
1. Monetary Judgments: This type of judgment is the most common and occurs when the court orders you to pay a specific monetary amount to the creditor. The amount usually includes the original debt, interest, and any additional fees or court costs. Failure to satisfy a monetary judgment can result in wage garnishment, where a portion of your wages is deducted to repay the debt.
2. Non-Monetary Judgments: Non-monetary judgments involve actions other than a specific monetary payment. These can include repossession of assets, such as a vehicle or property, or eviction from a rental property. These judgments can significantly impact your financial stability and future prospects, as losing assets or being forced to find new housing can have long-term consequences.
3. Tax Liens: A tax lien is a judgment filed by the government against your property due to unpaid taxes. This lien gives the government a legal claim to your property and can hinder your ability to sell or refinance it until the tax debt is resolved. Tax liens can have a severe negative impact on your credit score and should be addressed promptly.
4. Child Support or Spousal Support Judgments: If you fail to meet your obligations for child support or spousal support, a judgment may be issued against you. These judgments are taken seriously by the courts, and failure to comply can result in consequences such as wage garnishment, suspension of driver’s licenses, or even imprisonment. It is crucial to address these judgments promptly and work towards a resolution.
5. Civil Judgments: Civil judgments encompass a wide range of disputes that go to court, including personal injury claims, contract disputes, or property disputes. These judgments can vary in nature and can have different implications depending on the specific circumstances of the case. It is essential to understand the terms of the judgment and any actions required on your part.
It’s important to note that the severity and impact of a judgment can vary depending on your jurisdiction and the specific circumstances of your case. If you have a judgment on your credit report, it is advisable to consult with a legal professional to understand your rights and options for resolution.
In the next section, we will explore how judgments can impact your credit report and why it is crucial to address them promptly.
How Judgments Impact Your Credit Report
Judgments can have a significant impact on your credit report and overall creditworthiness. When a judgment is entered against you, it becomes a public record and is typically reported by credit bureaus, which can negatively affect your credit score and make it more challenging to obtain new credit or loans.
1. Credit Score Impact: A judgment on your credit report can lower your credit score, making it more difficult to qualify for favorable interest rates or credit terms. It signals to lenders that you have a history of not fulfilling your financial obligations and can be considered a high credit risk. The decrease in your credit score can also impact other areas of your financial life, such as insurance premiums and rental applications.
2. Credit Report Entry: A judgment will be listed as a negative entry on your credit report. This can stay on your credit report for up to seven years, further damaging your creditworthiness during that time. Potential lenders reviewing your credit report will see this negative entry and may be hesitant to extend credit due to the higher risk associated with a judgment.
3. Difficulty Obtaining Credit: Lenders, credit card issuers, and other financial institutions may consider a judgment as a red flag when evaluating your creditworthiness. They may be more cautious in extending credit or may require higher interest rates, larger down payments, or additional collateral. Some lenders may even deny credit applications altogether due to the presence of a judgment.
4. Collection Actions: Once a judgment is issued, the creditor may have additional options for collecting the debt. This can include wage garnishment, where a portion of your wages is automatically deducted to repay the debt. The creditor may also be able to place a lien on your property or seize assets to satisfy the judgment. These collection actions can have further financial implications and disrupt your financial stability.
Given the negative impact that judgments have on your credit report, it’s crucial to address them promptly and take appropriate action to resolve the debt. In the next section, we will explore how long a judgment can stay on your credit report and what steps you can take to deal with it.
How Long Does a Judgment Stay on Your Credit Report?
When it comes to the duration of a judgment on your credit report, it’s essential to understand the limitations imposed by credit reporting laws. In general, a judgment can stay on your credit report for up to seven years from the date it was filed.
This seven-year timeframe is set by the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), which governs the reporting of consumer credit information. The clock starts ticking from the date of the judgment, not from the date the original debt was incurred.
However, it’s worth noting that some states have their own laws that may affect the reporting period for judgments. In certain states, it is possible for judgments to remain on your credit report for longer than seven years. It’s always a good idea to check the laws specific to your state to understand the timeframes applicable to your situation.
It’s important to remember that even if the judgment is removed from your credit report after the seven-year mark, it does not mean that you are no longer legally obligated to pay the debt. The creditor can still pursue collection efforts and take legal action to recover the outstanding amount. It’s in your best interest to address the judgment and make arrangements to resolve the debt, even after it is no longer visible on your credit report.
It’s worth noting that the impact of a judgment on your credit score will typically lessen over time as long as you are maintaining good financial habits. Positive actions, such as making consistent on-time payments and reducing your overall debt, can help improve your creditworthiness over time.
In the next section, we will discuss how you can deal with a judgment on your credit report and the steps you can take to resolve the debt.
How to Deal with a Judgment on Your Credit Report
Dealing with a judgment on your credit report can feel overwhelming, but there are steps you can take to address the situation and work towards resolution. Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Review the Judgment: Carefully review the details of the judgment, including the amount owed, the creditor’s information, and any accompanying legal documentation. Make sure the information is accurate and valid.
2. Verify the Statute of Limitations: Determine if the statute of limitations for collecting the debt has expired. The statute of limitations varies by state, and once it expires, the creditor may lose the legal right to collect the debt. If the statute of limitations has passed, you can challenge the judgment and have it removed from your credit report.
3. Negotiate a Settlement: Contact the creditor or their legal representative to discuss the possibility of settling the debt. You may be able to negotiate a lower lump-sum payment or set up a repayment plan that fits within your budget. Get any settlement agreement in writing before making any payments.
4. Consider Legal Assistance: If you feel overwhelmed or unsure about how to handle the judgment, it may be beneficial to seek legal counsel. An attorney with experience in debt resolution can provide guidance and represent your interests in negotiations or court proceedings.
5. Make Regular Payments: If you’re unable to negotiate a settlement, make regular payments towards the judgment. Demonstrating a consistent effort to repay the debt can improve your financial standing over time.
6. Monitor Your Credit Report: Continuously monitor your credit report to ensure that the judgment is being reported accurately. If there are any errors or inaccuracies, dispute them with the credit reporting agencies to have them corrected or removed.
7. Rebuild Your Credit: While a judgment may have a negative impact on your credit, you can start rebuilding your credit by making all other payments on time and keeping your credit utilization low. Over time, positive financial behaviors will help improve your credit score.
Dealing with a judgment on your credit report requires proactive steps and a commitment to resolving the debt. By taking the appropriate actions and seeking professional guidance when needed, you can work towards improving your financial situation and rebuilding your creditworthiness.
In the next section, we will explore the options available for removing a judgment from your credit report.
Removing a Judgment from Your Credit Report
Removing a judgment from your credit report is not an easy task, but it is possible to have it removed under certain circumstances. Here are some options to consider:
1. Validate the Debt: Request validation of the debt from the creditor or collection agency. They must provide proof that the debt is valid, including documentation of the original debt, the chain of ownership, and any agreements or contracts related to the debt. If they fail to provide adequate validation, you can dispute the judgment with the credit reporting agencies.
2. Dispute Errors and Inaccuracies: Carefully review your credit report for any errors or inaccuracies related to the judgment. If you find any discrepancies, file a dispute with the credit reporting agencies. They are obligated to investigate and correct any incorrect information on your credit report.
3. File a Motion to Vacate: If you believe that there were errors or irregularities in the legal process leading to the judgment, you can file a motion to vacate the judgment with the court. This essentially asks the court to set aside the judgment due to errors or noncompliance with legal procedures. It is recommended to consult with an attorney to guide you through this process.
4. Pay for Deletion: Negotiate with the creditor or collection agency to remove the judgment from your credit report in exchange for payment. This is known as a pay-for-deletion agreement. Ensure that you have a written agreement stating that the judgment will be removed from your credit report upon payment.
5. Wait for the Expiration Date: While judgments can stay on your credit report for up to seven years, they will eventually expire and be removed. Ensure that you make all other payments on time and maintain good credit habits during this time to rebuild your credit history.
It’s important to remember that removing a judgment from your credit report is not a guarantee, and it may require persistence and effort on your part. If you encounter difficulties, it’s advisable to consult with a legal professional who specializes in credit and collections laws.
Monitor your credit report regularly to track any changes and ensure that the judgment is accurately reported. By addressing the judgment and taking steps to improve your credit, you can work towards financial stability and a better credit standing.
Next, let’s conclude this article and summarize the key points discussed.
Conclusion
A judgment on your credit report can have a significant impact on your financial well-being. It serves as a warning sign to lenders and creditors, indicating that you have a history of not fulfilling your financial obligations. This can result in higher interest rates, limited access to credit, and difficulties in securing housing or employment.
Understanding credit reports, the different types of judgments, and how they can impact your credit is essential for taking control of your financial situation. It’s important to review your credit report regularly, address any inaccuracies or errors, and take steps to resolve outstanding debts.
Dealing with a judgment requires proactive action, whether it’s negotiating a settlement, making regular payments, or seeking legal assistance. While removing a judgment from your credit report can be challenging, it is possible under certain circumstances, such as proving errors or inaccuracies or entering into a pay-for-deletion agreement.
It’s crucial to be patient and diligent in rebuilding your credit. Make timely payments, maintain a low credit utilization ratio, and practice good financial habits to demonstrate your creditworthiness. Over time, positive actions will help improve your credit score and increase your chances of obtaining favorable credit terms in the future.
Remember, the presence of a judgment on your credit report is not the end of your financial journey. With determination and proper steps, you can overcome the challenges and take control of your credit and financial well-being.