Finance
What Is A Teller Transaction Credit
Published: January 9, 2024
Learn about teller transactions and how they can impact your credit. Discover the importance of financial literacy and managing your finances effectively.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to managing financial transactions, the role of a teller is vital. Tellers play a crucial role in ensuring that daily transactions are recorded accurately and efficiently. One of the key aspects of this responsibility is handling teller transaction credits.
Teller transaction credits refer to the process of recording and tracking the inflow of funds into a customer’s account. This can include deposits, transfers, loan payments, and other forms of credit transactions. It is essential for banks and financial institutions to properly manage and document these credits to maintain accurate records and ensure customer satisfaction.
In this article, we will explore the definition of a teller transaction credit, the different types of credits, why they are important, how they are recorded, common challenges associated with them, and best practices for managing them effectively.
Understanding the ins and outs of teller transaction credits is essential for tellers, as well as bank managers and other finance professionals. So, let’s dive into the world of teller transaction credits and discover the crucial role they play in the financial industry.
Definition of a Teller Transaction Credit
A teller transaction credit refers to the process of recording and documenting the inflow of funds into a customer’s account. It involves crediting the customer’s account with the amount of money deposited or transferred into it. These credits can come from various sources, including cash deposits, checks, electronic transfers, or loan payments.
When a customer makes a deposit or receives money into their account, the teller is responsible for accurately processing the transaction and updating the customer’s account balance accordingly. This ensures that the customer’s records are up to date and that any interest or fees are calculated correctly.
In a teller transaction credit, the funds received are added to the customer’s available balance, increasing the overall amount of money they have in their account. This allows customers to access these funds for future use, such as making withdrawals, paying bills, or making purchases.
Teller transaction credits are not limited to just individual customers. They also play a crucial role in business banking, where companies receive payments from their customers or clients. The teller must accurately record these transactions to ensure that the business’s account reflects the correct amount of funds received.
Overall, a teller transaction credit is the process of updating a customer’s account balance by adding funds received through various channels. It is a fundamental part of the teller’s role in maintaining accurate financial records and providing excellent customer service.
Types of Teller Transaction Credits
There are several types of teller transaction credits that occur in the banking industry. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common types:
- Cash Deposits: Cash deposits are one of the most straightforward types of teller transaction credits. Customers bring physical currency to the bank and the teller records the amount and credits it to the customer’s account. These deposits can be made at the teller window or through self-service machines.
- Check Deposits: Check deposits involve customers depositing checks into their accounts. The teller verifies the information and ensures that the check is valid. The credited amount is based on the face value of the check and any applicable holds or restrictions.
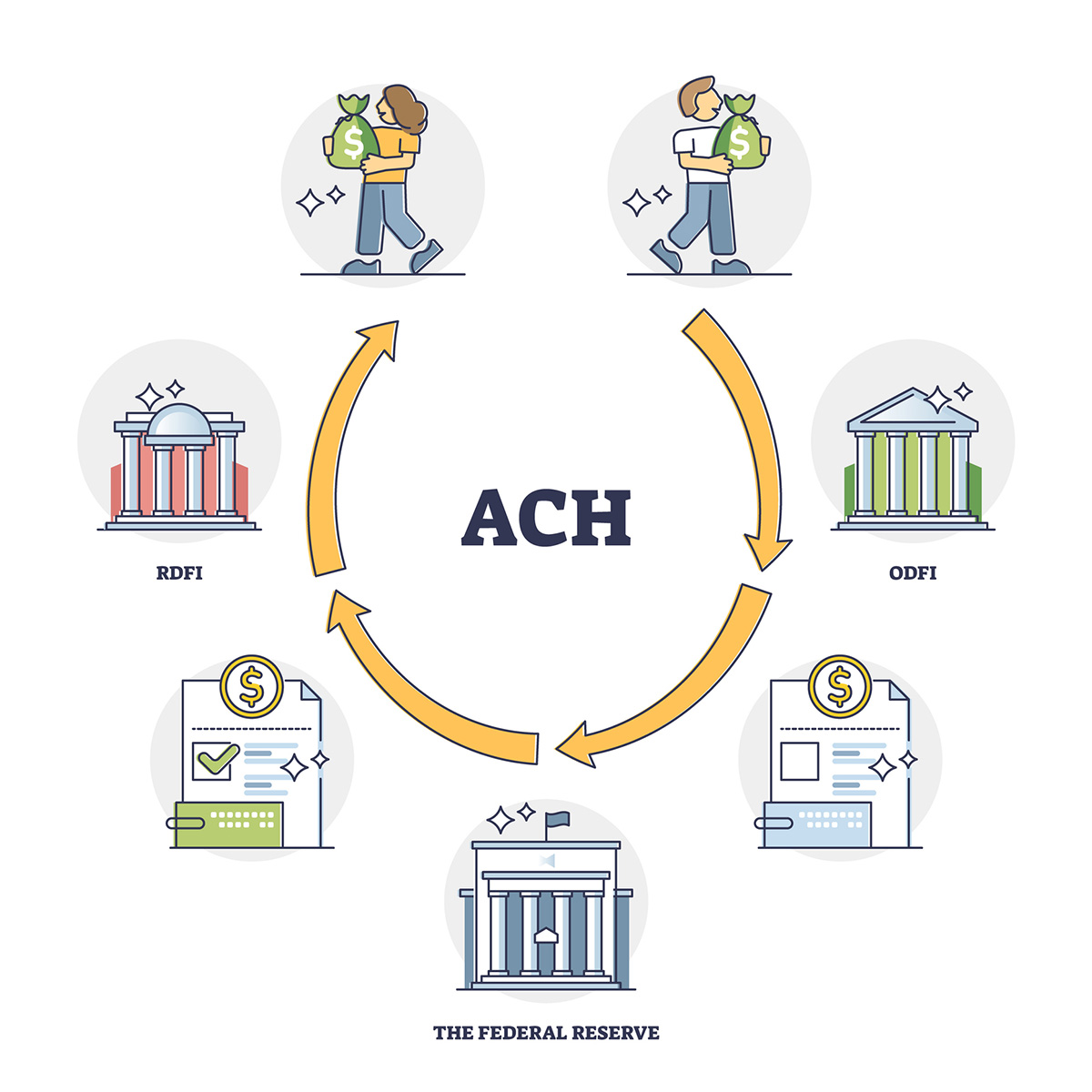
- Electronic Transfers: With the increasing popularity of online banking, electronic transfers have become a common type of teller transaction credit. Customers can transfer funds from one account to another electronically, either within the same financial institution or to another bank. The teller ensures that the transfer is processed accurately and updates the account balances accordingly.
- Loan Payments: Loan payments are another type of teller transaction credit. Customers make payments towards their loans, such as mortgages, auto loans, or personal loans. The teller records the payment and credits it towards the outstanding balance of the loan.
- Wire Transfers: Wire transfers involve the movement of funds from one bank to another through a secure electronic network. Customers can initiate wire transfers for various purposes, such as sending money to family members, making international payments, or settling business transactions. The teller plays a crucial role in verifying the transfer details, ensuring the accuracy of the transaction, and crediting the funds to the appropriate accounts.
These are just a few examples of the types of teller transaction credits that occur in the banking industry. Each type requires the teller’s attention to detail and accuracy to ensure that the customer’s account is credited correctly and the financial records are maintained accurately.
Importance of Teller Transaction Credits
Teller transaction credits play a crucial role in the banking industry. Let’s explore why they are important:
- Accurate Financial Records: Teller transaction credits are essential for maintaining accurate financial records. By properly recording and documenting the inflow of funds, banks can ensure that the customer’s account balances are up to date. This allows for accurate interest calculations, fee assessment, and overall financial reporting.
- Customer Satisfaction: Accurate and efficient handling of teller transaction credits contributes to customer satisfaction. When customers see that their deposits and other credits are promptly and accurately reflected in their accounts, it enhances their trust in the bank and its services. It also provides a seamless banking experience for customers who need to access their funds for withdrawals or other financial transactions.
- Risk Management: Teller transaction credits are an integral part of managing risk in the banking industry. Properly recording transactions helps identify any potential fraudulent activities or errors. By promptly detecting and resolving discrepancies, banks can mitigate risks and maintain the integrity of their financial operations.
- Compliance and Audit: Teller transaction credits are subject to regulatory compliance and are crucial during audits. Banks need to demonstrate that they have accurate and transparent financial records. Properly documenting teller transaction credits ensures that banks adhere to regulatory requirements and enables smooth auditing processes.
- Financial Analysis: Accurate teller transaction credits provide valuable data for financial analysis. Banks rely on these records to analyze deposit trends, customer behavior, and liquidity management. The data derived from teller transaction credits helps banks make informed decisions and develop effective business strategies.
Overall, teller transaction credits are vital for maintaining accurate financial records, enhancing customer satisfaction, managing risk, ensuring compliance, and enabling financial analysis. Banks and financial institutions rely on these credits to maintain the stability and integrity of their operations in an ever-evolving financial landscape.
Process of Recording Teller Transaction Credits
The process of recording teller transaction credits involves several steps to ensure accuracy and maintain proper documentation. Let’s explore the typical process:
- Verification: The teller begins by verifying the customer’s identification and confirming their account information. This step ensures that the transaction is being credited to the correct account.
- Transaction Entry: Once the customer’s identity is verified, the teller enters the transaction details into the bank’s computer system. This includes the type of credit, such as a cash deposit, check deposit, electronic transfer, or loan payment.
- Amount Calculation: If the transaction involves a specific amount of money, such as a cash or check deposit, the teller accurately calculates the total amount being credited to the account. They verify the currency denominations and ensure that the amount matches the customer’s deposit.
- Verification of Supporting Documents: Depending on the type of credit, the teller may need to verify supporting documents, such as a deposit slip, check, or wire transfer confirmation. This step ensures that the transaction is legitimate and can be properly documented.
- Entry Confirmation: Once all the necessary information is entered, the teller confirms the transaction details with the customer. This allows for any necessary corrections or clarifications to be made before finalizing the credit.
- Finalization and Account Update: After confirming the transaction details, the teller finalizes the credit by submitting it for processing. The customer’s account is then updated to reflect the credited amount, increasing their available balance. The teller may issue a receipt or provide a confirmation number to the customer as proof of the transaction.
Throughout the entire process, tellers must exercise attention to detail and accuracy. Any errors or discrepancies can have significant implications for the customer’s account and overall financial records.
It is worth noting that with the advancements in technology, teller transaction credits can now be processed digitally, reducing the need for manual entry and allowing for faster and more efficient transactions. However, the verification and accuracy checks remain crucial regardless of the medium used for recording teller transaction credits.
By following these steps and ensuring the accuracy of each credit, tellers contribute to the maintenance of accurate financial records and provide excellent customer service.
Common Challenges in Handling Teller Transaction Credits
While handling teller transaction credits is an essential part of a teller’s role, there are several challenges that can arise in the process. Let’s explore some common challenges:
- Human Error: Human error is one of the most common challenges in handling teller transaction credits. Teller’s might accidentally enter incorrect amounts or make mistakes during the verification process. These errors can lead to discrepancies in the customer’s account balance and require manual corrections.
- Technical Issues: Another challenge is dealing with technical issues or system downtime. If the computer system or software used for recording transaction credits malfunctions or experiences downtime, it can disrupt the normal flow of processing credits. This can result in delays in updating account balances and cause inconveniences for both tellers and customers.
- Transaction Discrepancies: Transaction discrepancies can occur when there is a mismatch between the customer’s records and the bank’s records. This can happen due to various reasons, such as delays in processing, incorrect data entry, or failure to document a credit properly. Resolving these discrepancies requires thorough investigation and coordination among tellers, supervisors, and the bank’s back-office staff.
- Handling Large Volumes: Teller’s may face challenges when handling large volumes of teller transaction credits, especially during peak times. The influx of customers and transactions can create pressure and increase the risk of errors. Proper time management, multitasking skills, and efficient workflow management are crucial in handling the volume effectively.
- Counterfeit or Fraudulent Transactions: One of the significant challenges in handling teller transaction credits is dealing with counterfeit or fraudulent transactions. Teller’s must be vigilant in verifying the authenticity of checks, cash, and electronic transfers to prevent the acceptance of fraudulent funds. They need to stay up to date with the latest security features and detection methods.
- Customer Disputes: Teller’s may encounter challenges when handling customer disputes related to transaction credits. Customers may dispute the credited amount, question the accuracy of the transaction, or claim that a credit was not properly processed. Communicating effectively and resolving customer disputes in a professional manner is essential for maintaining good customer relationships.
Dealing with these challenges requires continuous training, attention to detail, effective communication, and the ability to adapt to changing situations. By understanding and addressing these common challenges, teller’s can ensure the smooth handling of teller transaction credits and provide excellent service to customers.
Best Practices for Managing Teller Transaction Credits
Managing teller transaction credits effectively is crucial for both accurate financial records and excellent customer service. Here are some best practices to ensure the smooth handling of teller transaction credits:
- Attention to Detail: Paying close attention to every detail is essential in managing teller transaction credits. Teller’s should double-check the accuracy of entered amounts, verify supporting documents, and confirm the transaction details with the customer before finalizing the credit. This helps minimize errors and ensures that the customer’s account is credited correctly.
- Adherence to Policies and Procedures: Teller’s should be well-versed in the bank’s policies and procedures regarding teller transaction credits. They should follow standardized protocols for verifying customer identities, recording transactions, and resolving discrepancies. Adhering to established guidelines ensures consistency and reduces the risk of errors or non-compliance.
- Continuous Training and Education: Keeping teller’s updated with the latest industry trends, regulatory requirements, and technological advancements is crucial. Regular training sessions and educational programs help enhance their skills in managing teller transaction credits efficiently. It also ensures they are knowledgeable about new security features and fraud prevention techniques.
- Effective Communication: Communication is key in managing teller transaction credits. Teller’s should communicate clearly and effectively with customers, explaining the transaction process, addressing any concerns, and providing necessary documentation or receipts. Timely and accurate communication also helps manage customer expectations and resolves disputes promptly.
- Collaboration with Back-Office Staff: Teller’s should work closely with the bank’s back-office staff, such as the operations team or the fraud prevention department. Maintaining open lines of communication and collaboration ensures the seamless handling of transaction credits, resolves discrepancies efficiently, and maintains the integrity of the bank’s financial records.
- Regular Reconciliation: Regular reconciliation of teller transaction credits is essential to ensure that the bank’s records align with the actual transactions. Teller’s should compare the recorded credits with the corresponding supporting documents and investigate and correct any discrepancies promptly. This helps maintain accurate financial records and identify any inconsistencies or potential fraud.
By implementing these best practices, banks and financial institutions can achieve efficient management of teller transaction credits. This leads to accurate financial records, reduced errors, enhanced customer satisfaction, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
Managing teller transaction credits is an integral part of a teller’s role in the banking industry. Accurately recording and documenting the inflow of funds into customer accounts is essential for maintaining accurate financial records, ensuring customer satisfaction, and mitigating risks.
In this article, we explored the definition of teller transaction credits and the various types of credits that occur, such as cash deposits, check deposits, electronic transfers, loan payments, and wire transfers. We discussed the importance of teller transaction credits, including accurate financial records, customer satisfaction, risk management, compliance, and financial analysis.
We also discussed the process of recording teller transaction credits, which involves verification, transaction entry, amount calculation, verification of supporting documents, entry confirmation, and finalization with an account update. Attention to detail, adherence to policies and procedures, continuous training, effective communication, collaboration with back-office staff, and regular reconciliation were identified as best practices for efficiently managing teller transaction credits.
While there are common challenges in handling teller transaction credits, such as human error, technical issues, transaction discrepancies, handling large volumes, counterfeit or fraudulent transactions, and customer disputes, these challenges can be mitigated through proper training, attention to detail, effective communication, and collaboration.
Ultimately, the effective management of teller transaction credits is crucial for the smooth operation of banks and financial institutions. By following best practices and overcoming challenges, tellers can ensure accurate financial records, enhance customer satisfaction, and contribute to the overall success of the organization.