Finance
When Does The IRS Extension Grace Period End?
Published: February 19, 2024
Find out the deadline for filing your taxes with the IRS extension grace period. Stay informed about important finance deadlines.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Understanding the IRS Extension Grace Period
As the tax filing deadline approaches, many individuals and businesses may find themselves in need of additional time to prepare and submit their returns. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) provides a solution in the form of an extension grace period, allowing taxpayers to request extra time to file their taxes. Understanding the nuances of the IRS extension grace period is crucial for avoiding penalties and ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
During this grace period, taxpayers have the opportunity to gather necessary documentation, organize their financial records, and accurately complete their tax returns. However, it’s essential to be aware of the specific deadlines associated with the extension grace period to avoid potential repercussions.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the IRS extension grace period, explore the important deadlines to keep in mind, and discuss the potential consequences of missing the extension deadline. Additionally, we will provide insights into the process of filing for an extension, empowering taxpayers to navigate this aspect of tax compliance with confidence.
Understanding the IRS Extension Grace Period
The IRS extension grace period offers taxpayers the opportunity to request additional time to file their tax returns. This extension, typically lasting for six months, provides valuable breathing room for individuals and businesses who require extra time to compile necessary financial information and complete their tax documentation accurately.
It’s important to note that while the extension grace period grants additional time to file, it does not extend the deadline for paying any taxes owed. Taxpayers must estimate their tax liability and pay any amount due by the original filing deadline, which is typically April 15th for most taxpayers. Failure to do so may result in penalties and interest on the unpaid amount.
Obtaining an extension does not exempt individuals from their tax obligations; rather, it serves as a mechanism to avoid late-filing penalties. By submitting the appropriate extension request to the IRS, taxpayers can mitigate the risk of incurring penalties for filing their returns after the original deadline.
Moreover, the extension grace period offers a strategic advantage for taxpayers who anticipate complexities in their tax situations. Whether dealing with intricate investment portfolios, business income, or other intricate financial matters, the extension provides the necessary time to ensure accurate reporting and compliance with tax laws.
Overall, understanding the IRS extension grace period empowers taxpayers to make informed decisions regarding their tax obligations. By leveraging this extension wisely, individuals and businesses can navigate the tax filing process with diligence and precision, thereby minimizing the risk of penalties and ensuring compliance with IRS regulations.
Important Deadlines for IRS Extension Grace Period
When considering the IRS extension grace period, it is crucial to be mindful of the associated deadlines to ensure compliance and avoid potential penalties. The following are key dates to remember:
- Original Filing Deadline: For most taxpayers, the original filing deadline is April 15th. It’s important to submit a request for an extension before this date to avoid late-filing penalties.
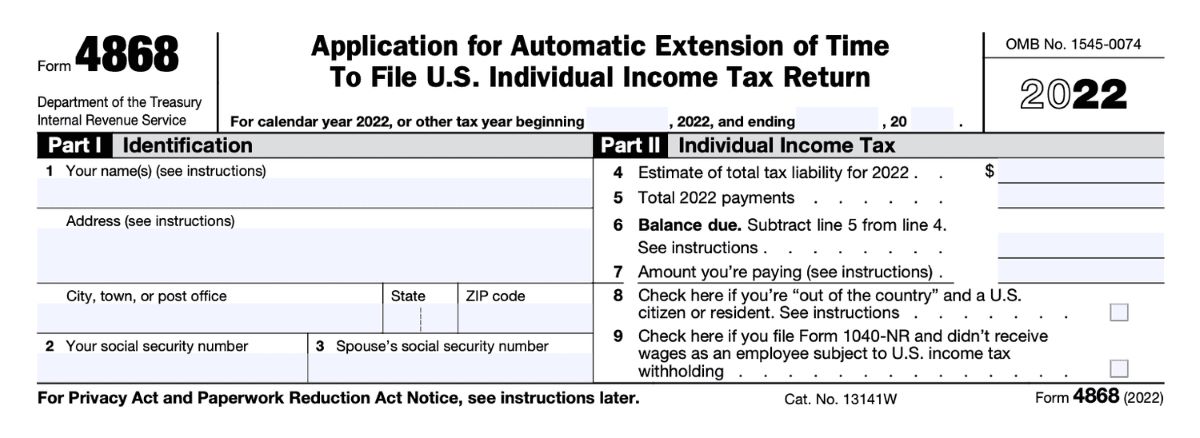
- Extension Request Deadline: Taxpayers must submit Form 4868, Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return, or utilize electronic filing options to request an extension by the original filing deadline. This typically falls on April 15th as well.
- Extended Filing Deadline: If an extension is approved, the new deadline for filing tax returns is usually October 15th. It’s imperative to complete and submit all required documentation by this extended deadline to avoid late-filing penalties.
Understanding and adhering to these deadlines is essential for a seamless and compliant tax filing process. Failing to request an extension or missing the extension request deadline can result in penalties, interest, and unnecessary stress. By staying informed about these important dates, taxpayers can proactively manage their tax obligations and navigate the extension process effectively.
Consequences of Missing the IRS Extension Grace Period
Missing the IRS extension grace period can have significant ramifications for taxpayers, potentially leading to financial penalties and added stress. It’s essential to be aware of the potential consequences of failing to request an extension or meet the associated deadlines:
- Late-Filing Penalties: If a taxpayer fails to request an extension and does not file their tax return by the original deadline, they may be subject to late-filing penalties. These penalties can accrue at a rate of 5% of the unpaid taxes for each month or part of a month that the return is late, up to a maximum of 25% of the unpaid taxes.
- Interest on Unpaid Taxes: In addition to late-filing penalties, individuals who fail to pay their taxes by the original deadline may be liable for interest on the unpaid amount. This interest accrues until the taxes are fully paid, compounding the financial burden over time.
- Impact on Refunds and Credits: Failing to file taxes within the extension grace period can delay the processing of refunds and the availability of tax credits. This delay can hinder individuals from accessing funds they are entitled to in a timely manner.
- Legal Ramifications: Persistent failure to file taxes and comply with IRS regulations can lead to legal repercussions, including potential audits and legal actions to compel compliance.
By understanding the potential consequences of missing the IRS extension grace period, taxpayers can take proactive measures to avoid these pitfalls. Requesting an extension in a timely manner and meeting the extended filing deadline can mitigate the risk of incurring penalties and alleviate unnecessary financial strain.
How to File for an Extension
Filing for an extension with the IRS is a straightforward process that provides taxpayers with the necessary breathing room to complete their tax returns accurately. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to request an extension:
- Evaluate the Need: Assess your situation to determine if an extension is necessary. If you anticipate challenges in gathering required documentation or need additional time to ensure accurate reporting, filing for an extension is a prudent decision.
- Complete Form 4868: For individual taxpayers, the most common method of requesting an extension is by completing Form 4868, Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return. This form requires basic personal information and an estimate of your total tax liability for the year.
- Submit Electronically: Utilize the IRS’s electronic filing options to submit Form 4868. Electronic filing provides a convenient and efficient way to request an extension, with immediate confirmation of receipt.
- Review State Requirements: If you are required to file state income tax returns, be sure to review the extension procedures and deadlines for your state of residence. Some states require a separate extension request, while others align with the federal extension timeline.
- Stay Informed: After submitting the extension request, mark the extended filing deadline on your calendar and stay informed about any updates or changes from the IRS. Keeping track of deadlines and requirements is essential for a smooth tax filing process.
By following these steps and proactively addressing the need for additional time, taxpayers can navigate the extension process with ease and ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
Conclusion
The IRS extension grace period serves as a valuable tool for taxpayers, offering the flexibility and time needed to fulfill their tax obligations accurately. By understanding the nuances of this extension and being mindful of important deadlines, individuals and businesses can navigate the tax filing process with confidence and diligence.
It is crucial to recognize that while the extension provides additional time to file tax returns, it does not extend the deadline for paying any taxes owed. Taxpayers must estimate their tax liability and make payments by the original filing deadline to avoid penalties and interest on unpaid amounts.
Missing the IRS extension grace period can lead to significant consequences, including late-filing penalties, interest on unpaid taxes, and potential delays in accessing refunds and credits. By proactively filing for an extension and meeting the extended deadline, taxpayers can mitigate these risks and ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
Filing for an extension is a straightforward process that empowers individuals to manage their tax obligations effectively. By evaluating the need for an extension, completing the necessary forms, and staying informed about deadlines, taxpayers can leverage this extension to their advantage and navigate the tax filing process with ease.
In conclusion, understanding the IRS extension grace period and adhering to its guidelines empowers taxpayers to fulfill their tax responsibilities conscientiously while avoiding unnecessary penalties and stress. By leveraging the extension wisely, individuals and businesses can approach tax filing with diligence and precision, ensuring compliance with IRS regulations and peace of mind.