Home>Finance>Why Personal Finance Should Be Taught In High School?


Finance
Why Personal Finance Should Be Taught In High School?
Published: January 22, 2024
Learn why teaching personal finance in high school is crucial for students' financial literacy and future success. Discover the benefits of early financial education.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Personal finance is an essential aspect of life that significantly impacts an individual’s financial well-being and stability. However, the education system often overlooks this critical area, leaving young adults unprepared to manage their finances effectively. This article aims to explore the importance of integrating personal finance education into high school curriculums, shedding light on the current state of personal finance knowledge among students and the benefits of early financial literacy. Additionally, it will address the obstacles hindering the implementation of personal finance education and highlight successful models that have effectively incorporated financial education into high school programs.
As young adults transition into independence after high school, they are often confronted with financial decisions that can have long-term implications. From managing student loans and credit card debt to making informed investment choices, the need for financial literacy is evident. By introducing personal finance education in high school, students can gain the necessary knowledge and skills to navigate these financial challenges and make informed decisions that will shape their financial future.
Moreover, the lack of financial education in high schools has contributed to widespread financial illiteracy, leading to detrimental consequences such as high levels of debt, poor credit management, and inadequate retirement planning among young adults. By addressing this gap through formal education, we can empower students to develop responsible financial habits and make informed choices, ultimately fostering a financially savvy generation.
The Importance of Personal Finance Education
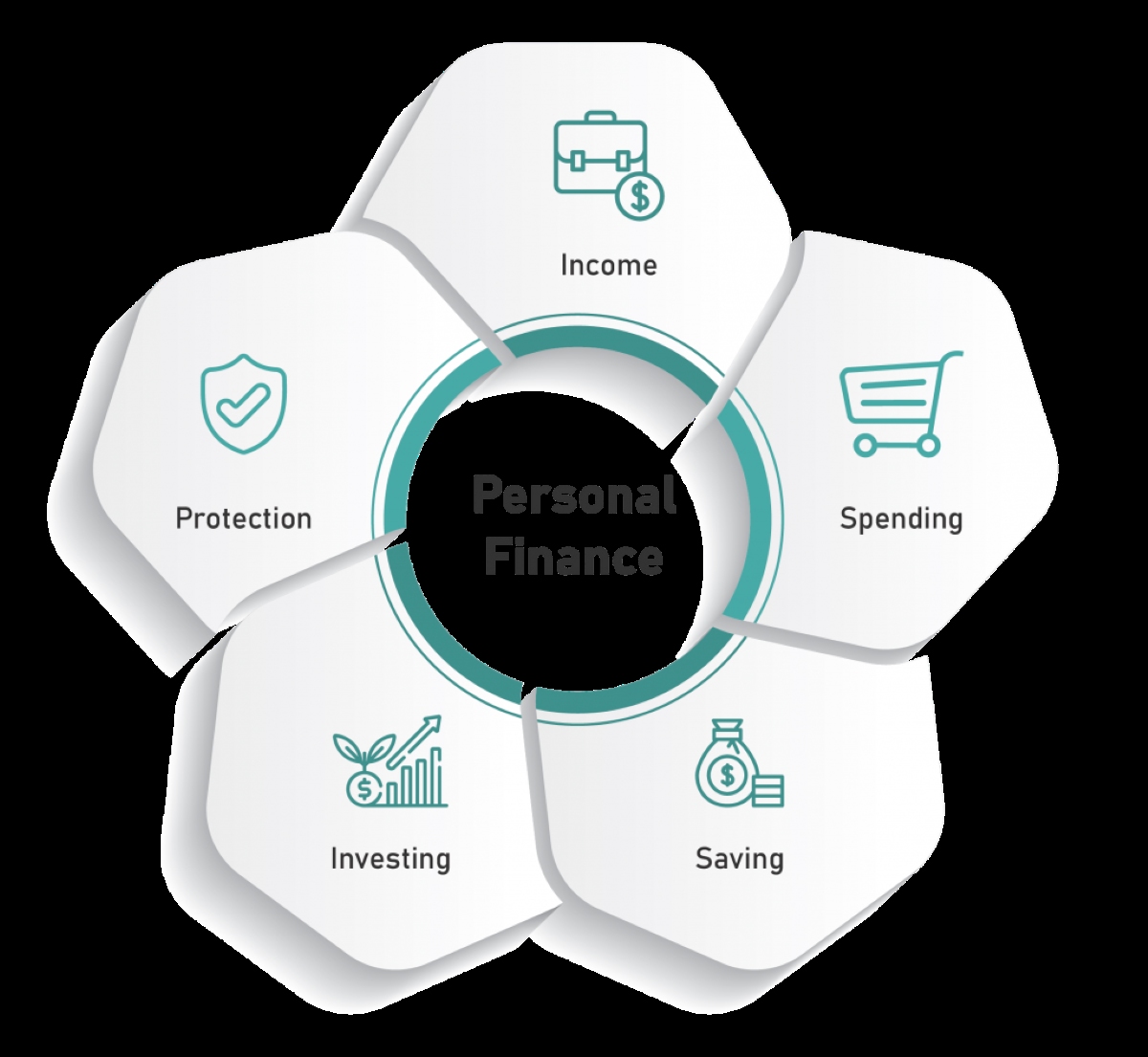
Personal finance education plays a pivotal role in equipping individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to make sound financial decisions throughout their lives. By integrating personal finance into high school curriculums, students can gain a comprehensive understanding of essential financial concepts, including budgeting, saving, investing, and managing debt. This early exposure to financial literacy sets the stage for responsible money management and fosters a sense of financial empowerment among young adults.
Furthermore, personal finance education instills a sense of financial responsibility and accountability, enabling students to develop a proactive approach towards their financial well-being. By understanding the implications of financial choices and learning to evaluate financial risks, students can make informed decisions that align with their long-term financial goals. Additionally, financial education empowers individuals to navigate complex financial products and services, such as loans, mortgages, and retirement plans, with confidence and prudence.
Moreover, integrating personal finance education into high school curriculums promotes economic stability at both individual and societal levels. Financially literate individuals are better equipped to contribute to the economy, make prudent investment decisions, and avoid falling into cycles of debt and financial hardship. This, in turn, fosters a more financially resilient and prosperous society, laying the groundwork for sustainable economic growth and stability.
Overall, the importance of personal finance education cannot be overstated, as it serves as a fundamental building block for financial well-being and economic prosperity. By empowering young adults with the knowledge and skills to navigate the intricacies of personal finance, we can cultivate a generation of financially savvy individuals capable of making informed decisions and securing their financial futures.
The Current State of Personal Finance Knowledge
The current state of personal finance knowledge among high school students is a cause for concern, as studies have consistently revealed low levels of financial literacy and understanding of basic financial concepts. Many students graduate from high school without the necessary skills to manage their finances effectively, leading to potential financial pitfalls and challenges as they enter adulthood.
Surveys and research studies have indicated that a significant percentage of high school students lack basic knowledge of budgeting, saving, investing, and managing credit. This lack of financial literacy leaves young adults vulnerable to making uninformed financial decisions, such as accumulating high-interest debt, falling victim to predatory lending practices, and failing to save for future goals.
Furthermore, the pervasive use of digital payment methods and online financial services has introduced new complexities to personal finance, requiring a deeper understanding of digital security, identity theft prevention, and responsible online financial management. Many high school students are navigating these digital financial landscapes without adequate education on safeguarding their financial information and making secure transactions.
It is evident that the current state of personal finance knowledge among high school students underscores the pressing need for comprehensive financial education within the school system. By addressing the gaps in financial literacy and equipping students with practical financial skills, we can empower them to make informed financial decisions and navigate the increasingly complex financial landscape with confidence.
The Benefits of Teaching Personal Finance in High School
Integrating personal finance education into high school curriculums offers a myriad of benefits that extend far beyond the classroom. By equipping students with essential financial knowledge and skills at an early age, we can empower them to make informed decisions and cultivate responsible financial habits that will shape their future financial well-being.
One of the primary benefits of teaching personal finance in high school is the capacity to instill a sense of financial responsibility and prudence among students. By providing education on budgeting, saving, and investing, students can develop a foundational understanding of money management, enabling them to make sound financial decisions as they transition into adulthood.
Moreover, early exposure to personal finance education fosters a proactive approach towards financial planning and goal setting. Students can learn to set realistic financial goals, such as saving for higher education, investing in their future, and planning for retirement, thereby laying the groundwork for long-term financial success.
Additionally, financial education in high school can help students avoid common financial pitfalls, such as excessive debt accumulation and impulsive spending. By understanding the implications of credit and debt, students can make informed decisions when managing their finances, mitigating the risk of falling into cycles of debt and financial distress.
Furthermore, teaching personal finance in high school promotes financial literacy and empowerment, enabling students to navigate the complexities of the modern financial landscape with confidence. From understanding the basics of banking and credit to evaluating investment opportunities, students can develop the skills necessary to make informed financial choices that align with their individual goals and values.
Overall, the benefits of teaching personal finance in high school extend to the broader societal and economic landscape, as financially literate individuals contribute to a more stable and prosperous society. By equipping young adults with the knowledge and skills to manage their finances responsibly, we can foster a generation of financially savvy individuals capable of making informed decisions and securing their financial futures.
Obstacles to Implementing Personal Finance Education
While the integration of personal finance education in high schools holds immense potential, several obstacles hinder its widespread implementation. These obstacles pose challenges to the comprehensive inclusion of financial literacy curriculums and require careful consideration and strategic solutions to overcome.
One significant obstacle is the crowded nature of existing high school curriculums, which often prioritize core academic subjects and standardized testing requirements. As a result, there may be limited room to incorporate additional coursework dedicated to personal finance education without sacrificing other essential areas of learning. Overcoming this obstacle requires a reevaluation of the existing curriculum structure and a concerted effort to integrate financial literacy into existing subjects or create dedicated space for financial education.
Furthermore, the availability of qualified educators proficient in personal finance and capable of delivering effective financial education presents a notable challenge. Many high schools may lack teachers with specialized expertise in personal finance, making it difficult to ensure consistent and high-quality instruction in this vital area. Addressing this obstacle entails investing in professional development opportunities for educators and collaborating with external experts to deliver comprehensive financial education programs.
Another obstacle to implementing personal finance education is the need for standardized curriculum guidelines and resources. Without established standards and resources for teaching personal finance, schools may struggle to develop cohesive and effective financial literacy programs. Overcoming this challenge involves the development of standardized curriculum frameworks, educational materials, and resources that can be readily adopted and implemented across diverse educational settings.
Moreover, the complex and evolving nature of financial topics, such as investment strategies, tax planning, and digital financial management, presents a challenge in designing age-appropriate and relevant curriculum content. Balancing the need for comprehensive financial education with the capacity to deliver accessible and engaging material requires ongoing adaptation and collaboration with industry experts and financial institutions.
Overall, addressing the obstacles to implementing personal finance education in high schools necessitates a multi-faceted approach that encompasses curriculum restructuring, educator training, resource development, and ongoing adaptation to meet the evolving needs of students in an increasingly complex financial landscape.
Successful Models of Personal Finance Education
Several successful models of personal finance education have emerged, providing valuable insights into effective approaches for integrating financial literacy into high school curriculums. These models showcase innovative strategies and best practices that have yielded positive outcomes in equipping students with essential financial knowledge and skills.
One successful model involves the integration of personal finance education across multiple subject areas, creating a holistic approach to financial literacy. By infusing financial concepts into subjects such as mathematics, economics, and social studies, students are exposed to real-world applications of financial principles within the context of their core academic coursework. This interdisciplinary approach fosters a deeper understanding of financial concepts and their relevance to various aspects of life, promoting a comprehensive and integrated understanding of personal finance.
Another successful model emphasizes experiential learning through practical applications of financial concepts. By incorporating simulations, interactive activities, and real-life case studies, students can engage directly with financial decision-making processes, gaining hands-on experience in managing budgets, making investment choices, and understanding the impact of financial decisions. This experiential approach not only enhances students’ practical financial skills but also cultivates critical thinking and decision-making abilities in the realm of personal finance.
Furthermore, successful models of personal finance education often leverage partnerships with financial institutions, community organizations, and industry professionals to provide students with access to real-world expertise and resources. Collaborations with local banks, credit unions, and financial advisors enable students to receive practical insights, mentorship, and exposure to financial services, enriching their educational experience and connecting classroom learning to the broader financial landscape.
Additionally, successful models prioritize the incorporation of digital financial literacy, addressing the evolving nature of financial management in the digital age. By integrating lessons on online banking, digital security, and responsible use of financial technology, students are equipped to navigate the digital financial landscape with confidence and security, preparing them for the realities of modern financial management.
Overall, these successful models of personal finance education exemplify diverse and innovative approaches that have effectively equipped students with essential financial knowledge and skills. By drawing inspiration from these models and embracing their core principles, educational institutions can establish comprehensive and impactful financial literacy programs that empower students to navigate the complexities of personal finance with confidence and competence.
Conclusion
The integration of personal finance education into high school curriculums holds immense significance in shaping the financial well-being and empowerment of young adults. By addressing the current gaps in financial literacy and equipping students with essential financial knowledge and skills, we can foster a generation of individuals capable of making informed decisions and navigating the complexities of the modern financial landscape with confidence.
From instilling a sense of financial responsibility and prudence to promoting proactive financial planning and goal setting, personal finance education in high schools offers a multitude of benefits that extend beyond the classroom. By empowering students to make sound financial decisions, avoid common financial pitfalls, and contribute to a more financially resilient society, we lay the groundwork for sustainable economic growth and stability.
While obstacles such as curriculum constraints, educator expertise, and evolving financial landscapes pose challenges to implementing personal finance education, successful models and best practices provide valuable insights into effective approaches. By leveraging interdisciplinary integration, experiential learning, industry partnerships, and digital financial literacy, educational institutions can establish comprehensive and impactful financial literacy programs that resonate with students and prepare them for the realities of managing their finances in the digital age.
In conclusion, the imperative to teach personal finance in high school is underscored by the transformative impact it can have on the financial well-being and future prospects of young adults. By embracing the importance of financial literacy and committing to comprehensive financial education, we can empower students to navigate their financial journeys with confidence, foresight, and responsibility, ultimately shaping a generation of financially savvy individuals capable of securing their financial futures.