Finance
What Is Swap In Forex Trading
Modified: February 21, 2024
Discover what swap is in forex trading and how it affects your finances. Learn how to use swap to your advantage in the volatile forex market.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, involves the buying and selling of different currencies in the global market. Traders engage in forex trading to profit from changes in exchange rates, aiming to buy currencies at a lower price and sell them at a higher price. However, forex trading is not solely about making profits from currency pairs; it also involves various financial instruments and strategies that traders can utilize to enhance their trading performance and mitigate risks.
One such financial instrument that plays a significant role in forex trading is the swap. In forex trading, a swap refers to the interest rate differential between two currencies that are being traded. It is essentially an agreement between two parties, usually the trader and the broker, to exchange interest payments on a specific date.
The concept of swap in forex trading can be complex, especially for beginners. Therefore, this article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of swaps and how they work in forex trading. You will learn about the different types of swaps, how to calculate swap points, the role of swaps in forex trading, as well as the advantages, disadvantages, and risks involved. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of swap in forex trading and explore its intricacies.
Definition of Swap in Forex Trading
In forex trading, a swap refers to the interest rate differential between two currencies that are being traded. It is a financial agreement between the trader and the broker to exchange interest payments on a specific date. The swap rate is calculated based on the difference in interest rates set by the central banks of the respective countries involved in the currency pair.
Swaps are primarily used to manage and adjust the positions held by traders overnight. In forex trading, positions are typically closed at the end of the trading day. However, if a position is left open overnight, it incurs an interest cost or gain, depending on the interest rate differentials between the currencies involved.
The interest rate differential is crucial in determining the swap rate. It represents the difference between the borrowing costs of one currency compared to another. The currency with a higher interest rate will generally carry a positive swap for long positions (buying) and a negative swap for short positions (selling).
For example, let’s consider a trader who holds a long position in a currency pair with an interest rate differential of 2%. In this scenario, the trader would earn 2% per year on the nominal value of the position if held overnight. Conversely, if the trader holds a short position in the same currency pair, they would incur a 2% interest cost per year.
It’s important to note that swap rates can be both positive and negative, depending on the interest rate differentials and the direction of the trade. Positive swaps provide traders with additional income, whereas negative swaps result in additional costs.
Swaps are typically applied to positions that are held overnight or over the weekend when markets are closed. The swap charges or credits are automatically debited or credited to the trader’s account at the end of each trading day.
Next, we will explore how swaps work and the process behind their calculation in forex trading.
How Swaps Work
Swaps in forex trading are typically carried out by brokers who act as intermediaries between traders and financial institutions. These brokers facilitate the exchange of interest rate differentials between currency pairs. When a trader enters into a position, either long or short, the broker will apply the appropriate swap rate based on the interest rate differential.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how swaps work in forex trading:
- Trader opens a position: The trader initiates a trade by buying or selling a specific currency pair, either in the spot market or through derivatives such as futures or options.
- Position is held overnight: If the trader decides to keep the position open overnight, a swap is applied. The broker determines the swap rate based on the interest rate differentials and the direction of the trade.
- Swap charges or credits: At the end of each trading day, the broker automatically applies the swap charge or credit to the trader’s account. The swap is typically debited or credited in the currency of the trading account.
- Accumulation of swaps: If the trader continues to hold the position for multiple days, the swap charges or credits accumulate. This means that the swap charges or credits will compound and affect the overall profitability of the trade.
- Swaps over weekends and holidays: Swaps are also applied during weekends and holidays when markets are closed. In these cases, the swap charges or credits may be multiplied to account for the additional days.
It’s important to note that while swaps are applied to open positions, they do not impact the actual profit or loss from the price movement of the currency pair. Swaps are separate from the net gain or loss derived from the trade’s performance.
Traders should also be aware that swap charges or credits can vary among brokers due to factors such as the broker’s liquidity providers, the interest rates offered by the central banks, and any additional fees charged by the broker.
Now that we understand the mechanics of how swaps work, let’s delve into the different types of swaps commonly used in forex trading.
Types of Swaps
In forex trading, there are two main types of swaps that traders encounter: interest rate swaps and currency swaps. These swaps serve different purposes and are applied based on specific trading strategies and market conditions.
1. Interest Rate Swaps:
Interest rate swaps involve the exchange of interest rate obligations between two parties. The swap is based on the difference between fixed and floating interest rates. In this type of swap, the parties agree to exchange cash flows based on a specified notional amount over a set period of time.
Interest rate swaps are commonly used by traders who want to mitigate interest rate risk or achieve more favorable financing terms. For example, a trader who anticipates an increase in floating interest rates on their loan can enter into an interest rate swap to convert it into a fixed interest rate, thereby reducing the risk of higher borrowing costs.
2. Currency Swaps:
Currency swaps involve the exchange of both the principal amount and the interest payments in different currencies. This type of swap is especially useful for traders who have exposure to multiple currencies and want to mitigate foreign exchange risk.
In a currency swap, two parties agree to exchange a specific amount of one currency for another at an agreed-upon exchange rate. The parties also agree to exchange interest payments in their respective currencies. Currency swaps are commonly used by multinational corporations to manage their currency exposure or by traders who want to take advantage of interest rate differentials between currencies.
It’s worth noting that while interest rate swaps and currency swaps are the most common types of swaps in forex trading, there are other specialized swaps such as equity swaps and commodity swaps that cater to specific trading needs.
Understanding the different types of swaps is essential for traders, as it allows them to implement appropriate hedging strategies or take advantage of opportunities presented by interest rate differentials and currency fluctuations.
Now that we have explored the types of swaps, let’s move on to understanding how swap points are calculated in forex trading.
Calculating Swap Points
In forex trading, swap points are used to calculate the swap rate applied to positions held overnight or over the weekend. Swap points represent the interest rate differentials between two currencies and are added or subtracted from the spot exchange rate to determine the forward exchange rate for the swap.
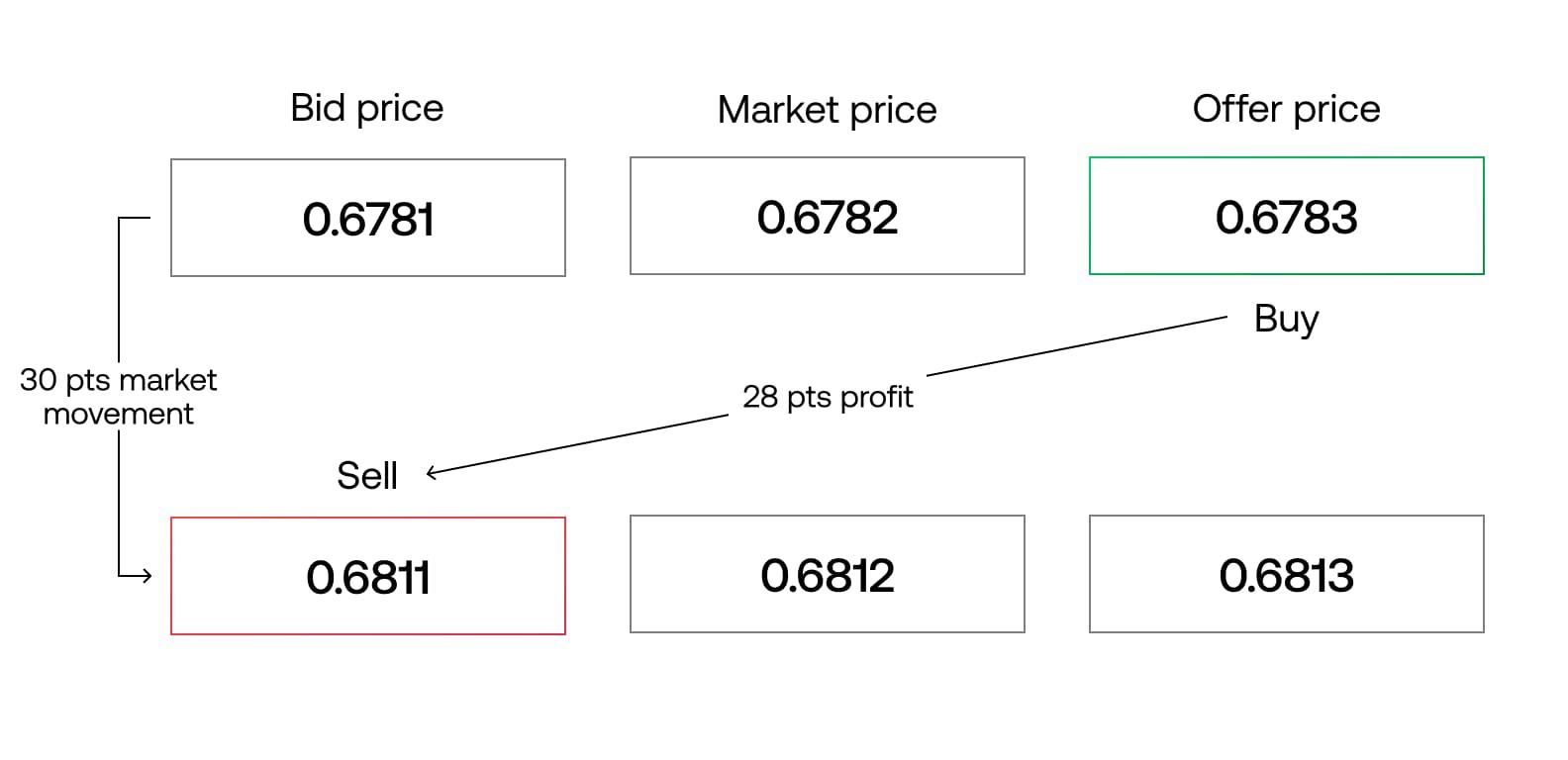
The calculation of swap points involves several factors, including the current spot rate, the interest rate differentials between the two currencies, and the number of days the position is held. Generally, swap points are expressed as pips and are added or subtracted from the fourth decimal place of the exchange rate.
Example:
Let’s consider a trader who holds a long position in the EUR/USD currency pair. The current spot exchange rate is 1.2000, and the interest rate differential between the Eurozone and the United States is 2%. The trader plans to keep the position open for one day.
To calculate the swap points, the trader needs to consider the interest rate differential and the number of days the position is held. In this case, the interest rate differential is 2% divided by 365 (number of days in a year), which is approximately 0.0055% per day.
Next, the trader multiplies the interest rate differential by the notional value of the position. For instance, if the trader’s position size is €100,000, the swap points would be calculated as follows:
Swap Points = (0.0055 / 100) * 100,000 = 5.5
The swap points of 5.5 would be added to the fourth decimal place of the spot exchange rate to calculate the forward exchange rate for the swap. If the spot rate is 1.2000, the forward exchange rate after considering the swap points would be 1.2005.
It’s important to note that swap points can vary based on market conditions, interest rate differentials, and the currency pair being traded. Traders should consult their broker or trading platform to determine the specific swap points for their positions.
Now that we understand how swap points are calculated, let’s explore the role of swaps in forex trading.
Role of Swaps in Forex Trading
Swaps play a significant role in forex trading and serve various purposes for traders and financial institutions. Understanding the role of swaps can help traders make informed decisions and manage their positions effectively. Here are some key roles that swaps fulfill in forex trading:
1. Financing Tool:
Swaps act as a financing tool for traders and investors. They allow market participants to borrow or lend currencies at different interest rates, providing access to capital and liquidity. Traders can leverage swaps to finance their positions in a more cost-effective manner compared to traditional borrowing methods.
2. Income Generation:
Swaps provide an opportunity for traders to generate additional income from their positions. Positive swap rates can lead to a credit in the trader’s account, effectively earning them interest on their open positions. Traders who hold positions for an extended period, especially those with positive interest rate differentials, can benefit from incremental income through swap credits.
3. Interest Rate Arbitrage:
Swaps enable traders to explore interest rate differentials between currencies and engage in interest rate arbitrage. By taking advantage of varying interest rates, traders can enter positions that offer potential profits beyond price movements. Interest rate arbitrage strategies involve borrowing a currency with a lower interest rate and investing in a currency with a higher interest rate, capturing the favorable interest rate differential.
4. Risk Management:
Swaps play a vital role in risk management for traders and financial institutions. Through swaps, traders can hedge against adverse currency movements or interest rate fluctuations. By entering into offsetting swap positions, traders can protect themselves from potential losses resulting from market volatility or unforeseen events.
5. Central Bank Policy Accommodation:
Swaps assist in aligning market interest rates with the monetary policy set by central banks. Central banks utilize swaps as a tool to alter domestic interest rates and manage their currency’s value in relation to foreign currencies. By adjusting swap rates, central banks can influence borrowing costs, stimulate economic growth, or stabilize exchange rates.
Overall, swaps contribute to the liquidity, stability, and functionality of the forex market. They serve as a mechanism for financing, income generation, risk management, and aligning market interest rates with central bank policies. Traders should be aware of the role that swaps play in the forex market to effectively utilize them in their trading strategies.
Next, we will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of utilizing swaps in forex trading.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Swaps
Utilizing swaps in forex trading can provide several advantages, but it is essential to consider the potential drawbacks as well. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of swaps can help traders make informed decisions and manage their positions effectively. Here’s a breakdown of the advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Income Generation: Swaps can offer traders an additional source of income through swap credits, especially when holding positions with positive interest rate differentials.
- Risk Management: Swaps provide a means of hedging against adverse currency movements or interest rate fluctuations, allowing traders to mitigate potential losses.
- Liquidity: Swaps contribute to the liquidity of the forex market as they facilitate borrowing and lending activities between market participants.
- Financing Flexibility: Swaps serve as a financing tool, offering traders an alternative to traditional borrowing methods, enabling them to fund their positions more cost-effectively.
- Interest Rate Arbitrage: Swaps enable traders to exploit interest rate differentials between currencies and engage in interest rate arbitrage strategies, potentially leading to additional profits.
Disadvantages:
- Additional Costs: Swaps can lead to additional costs if the trader holds a position with a negative swap rate or pays higher borrowing costs compared to alternative financing methods.
- Market Volatility: Swaps are subject to market volatility, which can result in fluctuations in the swap rates and potentially impact the profitability of a position.
- Counterparty Risk: Swaps involve an agreement between two parties, and there is a risk that one party may not fulfill its obligations, leading to potential financial loss or disruption.
- Complexity: Swaps can be complex financial instruments, and traders need to understand the mechanics, calculations, and potential risks associated with utilizing them.
- Regulatory Changes: Changes in regulatory policies or central bank actions can impact swap rates and their availability, potentially affecting trading strategies and costs.
Traders should carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages of utilizing swaps in their forex trading activities. It is important to consider factors such as interest rate differentials, market conditions, trading strategies, and risk tolerance when deciding to incorporate swaps into their trading approach. Consulting with a professional financial advisor or broker can also provide valuable insights and guidance.
Now that we have explored the advantages and disadvantages of swaps, let’s discuss the risks involved in utilizing swaps in forex trading.
Risks Involved in Swaps
While swaps can bring various benefits to forex trading, it is crucial for traders to be aware of the associated risks. Understanding the risks involved in swaps can help traders make informed decisions and manage their positions effectively. Here are some key risks to consider:
1. Interest Rate Risk:
Swaps are highly sensitive to changes in interest rates. If interest rates change in a manner that is unfavorable to the trader’s position, it can result in increased costs or decreased income from swap charges or credits. Interest rate movements are influenced by a wide range of factors, including central bank policies, economic indicators, and market conditions.
2. Foreign Exchange Risk:
Currency swaps expose traders to foreign exchange risk. Fluctuations in exchange rates between the two currencies involved in the swap can lead to gains or losses when converting the principal amount or the swap interest payments back to the trader’s base currency. Traders should consider currency risk management strategies to mitigate potential losses resulting from unfavorable exchange rate movements.
3. Counterparty Risk:
Swaps involve an agreement between two parties, and there is a risk that one party may default on their obligations. If the counterparty fails to fulfill their side of the swap agreement, it can result in financial losses or disruptions for the trader. It is essential to choose reputable and well-regulated counterparties to mitigate counterparty risk.
4. Liquidity Risk:
Swaps rely on the availability of liquidity in the market. In times of reduced market liquidity or extreme market volatility, the cost of entering into swaps may increase, and it may become more challenging to execute or exit positions. Traders should consider the liquidity of the instruments they are trading and plan accordingly to manage liquidity risk.
5. Regulatory Risk:
Regulatory changes and interventions can have an impact on swap rates, availability, and the overall market environment. Changes in regulations governing swaps or actions taken by central banks can influence interest rates and the profitability of swap positions. Traders should stay informed about potential regulatory changes and adapt their trading strategies accordingly.
It is essential for traders to assess their risk tolerance, carefully evaluate the risks associated with swaps, and incorporate risk management strategies into their trading plan. Diversification, proper position sizing, and regular monitoring of market conditions can help mitigate the risks involved in utilizing swaps in forex trading.
Next, let’s explore the factors that affect swap rates in forex trading.
Factors That Affect Swap Rates
Swap rates in forex trading are influenced by various factors that impact the interest rate differentials between currency pairs. Understanding these factors can help traders anticipate changes in swap rates and make informed decisions about their positions. Here are key factors that affect swap rates:
1. Central Bank Policies:
The monetary policies implemented by central banks have a significant impact on swap rates. Central banks adjust interest rates to manage inflation, stimulate economic growth, or stabilize their currency. Changes in central bank policies, such as interest rate hikes or cuts, can lead to fluctuations in swap rates as they affect the interest rate differentials between currencies.
2. Economic Data and Market Sentiment:
Economic indicators and market sentiment influence swap rates. Positive economic data, such as strong GDP growth, low unemployment rates, or rising consumer confidence, can lead to higher interest rates and potentially increase swap rates. Conversely, negative economic data or geopolitical uncertainties can lower interest rates and impact swap rates accordingly.
3. Liquidity and Market Conditions:
The availability of liquidity and general market conditions can affect swap rates. In times of increased market volatility or reduced liquidity, swap rates may become more volatile or subject to wider spreads. Traders should be aware of market conditions and consider potential impacts on swap rates, especially during events such as economic releases or geopolitical developments.
4. Interest Rate Differentials:
Interest rate differentials between currencies play a significant role in determining swap rates. The larger the interest rate differential, the greater the potential swap charges or credits. Traders should monitor changes in interest rate differentials, as they can result from shifts in central bank policies, economic developments, or market expectations.
5. Market Expectations and Forward Outlook:
Swap rates also reflect market expectations and forward outlook. Traders and investors consider future interest rate movements and potential changes in currency valuations when pricing swap rates. Market expectations, reflected through interest rate futures or other derivative instruments, can influence swap rates far in advance, allowing traders to anticipate potential changes.
It’s important for traders to stay updated on these factors and their potential impact on swap rates. By monitoring central bank policies, economic news, market sentiment, and interest rate differentials, traders can gain insights into swap rate movements and adjust their trading strategies accordingly.
Now that we have discussed the factors that affect swap rates, let’s summarize the key points covered in this article.
Conclusion
In conclusion, swaps play a crucial role in forex trading, allowing traders to manage positions overnight, generate additional income, hedge against risk, and take advantage of interest rate differentials. Swaps are agreements between traders and brokers to exchange interest rate payments on specific dates, based on the interest rate differential between the currencies involved in a currency pair.
Understanding the various types of swaps, such as interest rate swaps and currency swaps, is essential for traders to employ effective trading strategies. Additionally, calculating swap points accurately helps traders determine the forward exchange rate for the swap. Traders should be aware of the advantages, including income generation and risk management, as well as the disadvantages, such as additional costs and counterparty risks, associated with utilizing swaps in forex trading.
Risks involved in utilizing swaps include interest rate risk, foreign exchange risk, counterparty risk, liquidity risk, and regulatory risk. Traders should assess their risk tolerance and implement risk management strategies to mitigate potential losses. Furthermore, factors that affect swap rates include central bank policies, economic data, market sentiment, liquidity, interest rate differentials, and market expectations.
To navigate the world of swaps successfully, traders should remain informed about market conditions, stay updated on economic news and central bank actions, and adapt their trading strategies accordingly. Consulting with experienced professionals and studying the dynamics of swap rates can provide valuable insights to traders.
In essence, swaps offer opportunities for income generation, risk management, and financing flexibility in forex trading. By understanding how swaps work and the factors that influence swap rates, traders can effectively utilize swaps to enhance their trading performance and achieve their financial goals.