Finance
Exempt Commodity Definition
Published: November 20, 2023
Get a clear understanding of the definition of exempt commodities in the field of finance. Explore key insights and learn more about this crucial concept.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
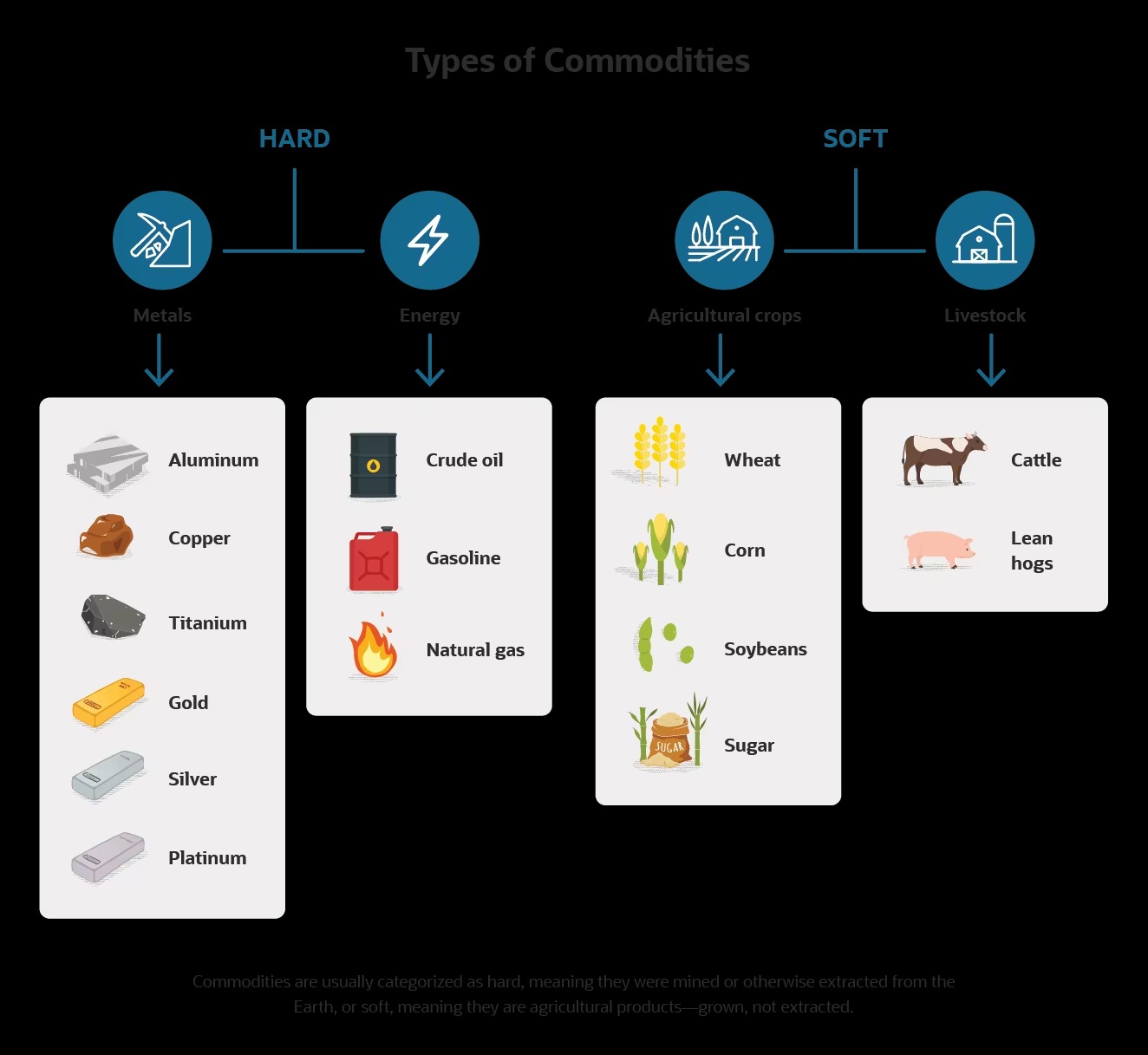
Exempt Commodity Definition: Understanding the Basics
When it comes to navigating the complex world of finance, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of various terms and definitions. In the realm of commodities, one such term that often arises is “exempt commodity.” But what exactly does it mean? In this blog post, we’ll delve into the definition of exempt commodities and explore why they hold significance in the financial landscape.
Key Takeaways:
- An exempt commodity is a type of financial product that is exempt from certain regulations imposed by financial authorities.
- This exemption allows market participants to trade these commodities without the same level of scrutiny and oversight as other financial products.
So, what exactly is an exempt commodity?
Put simply, an exempt commodity refers to a specific financial product that is exempted from certain regulatory requirements imposed by financial authorities. This exemption means that market participants can trade these commodities without facing the same level of scrutiny and oversight as other financial products. By exempting certain commodities, regulators aim to foster innovation and provide opportunities for market growth.
When a commodity is deemed exempt, it falls outside the purview of certain regulations, such as those outlined in the Commodity Exchange Act (CEA) in the United States. As a result, market participants enjoy certain advantages when trading exempt commodities, including reduced reporting requirements, less stringent compliance measures, and potentially lower transaction costs.
It’s important to note that exempt commodities regulations may vary from country to country. In the U.S., for instance, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) provides specific criteria for a commodity to qualify as exempt. These criteria may include factors such as the commodity’s underlying asset, trading volume, or the nature of market participants.
Why do exempt commodities matter?
Exempt commodities play a crucial role in fostering innovation and liquidity in financial markets. By exempting certain commodities from stringent regulations, authorities aim to encourage the development of new and unique financial products. This, in turn, can attract more market participants, increase trading volumes, and enhance market liquidity.
Furthermore, exempt commodities can offer investors and traders an avenue for diversification. With fewer regulatory burdens, market participants have the flexibility to explore alternative investment options beyond traditional financial products. This can help spread risk and potentially enhance portfolio performance.
In conclusion, exempt commodities provide a unique opportunity for market participants to engage in trading with reduced regulatory requirements. By understanding the exempt commodity definition and its implications, investors and traders can better navigate the financial landscape and explore new avenues for growth and diversification.