Home>Finance>How Can Parents Teach Their Children About Money Management?


Finance
How Can Parents Teach Their Children About Money Management?
Published: February 28, 2024
Teach your kids valuable money management skills with these expert tips. Help them develop a healthy relationship with finance from an early age.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Teaching Children About Money Management
- Leading by Financial Example
- Instilling an Understanding of Financial Worth
- Empowering Children with Financial Planning Skills
- Fostering a Healthy Approach to Learning from Errors
- Cultivating a Habit of Financial Prudence
- Fostering Creativity and Financial Independence
- Fostering Financial Awareness and Responsibility
- Nurturing Financial Empowerment from an Early Age
Introduction
Teaching Children About Money Management
Teaching children about money management is a crucial aspect of their upbringing, yet it is often overlooked or underestimated. By instilling good financial habits from a young age, parents can empower their children to make informed decisions about money as they grow into adulthood. In this article, we will explore effective strategies for parents to teach their children about money management, setting the stage for a financially responsible future.
Understanding the value of money and learning how to manage it wisely are essential life skills that can positively impact a child's future. As children observe and absorb their parents' attitudes and behaviors toward money, it becomes evident that parental influence plays a pivotal role in shaping their financial mindset. Therefore, it is essential for parents to lead by example and actively engage their children in discussions about money matters.
By incorporating practical lessons and fostering a healthy relationship with money, parents can equip their children with the tools they need to navigate the complex world of personal finance. Let's delve into various approaches that parents can take to impart valuable financial knowledge to their children, laying a strong foundation for their financial well-being.
Setting a Good Example
Leading by Financial Example
One of the most powerful ways for parents to teach their children about money management is by setting a good example. Children are keen observers, and they often mimic the behaviors and attitudes they witness in their parents. Therefore, demonstrating responsible financial habits can have a profound impact on shaping a child’s perception of money.
Parents can start by openly discussing their financial decisions with their children, such as budgeting for household expenses, saving for future goals, and making thoughtful purchase choices. By involving children in age-appropriate discussions about money, parents can demystify financial concepts and instill a sense of financial responsibility from an early age.
Moreover, parents can lead by example through their own spending habits. By showcasing prudence and restraint when it comes to discretionary spending, parents can impart valuable lessons about prioritizing needs over wants and making informed purchasing decisions. Additionally, demonstrating the importance of regular saving and investment practices can underscore the significance of long-term financial planning.
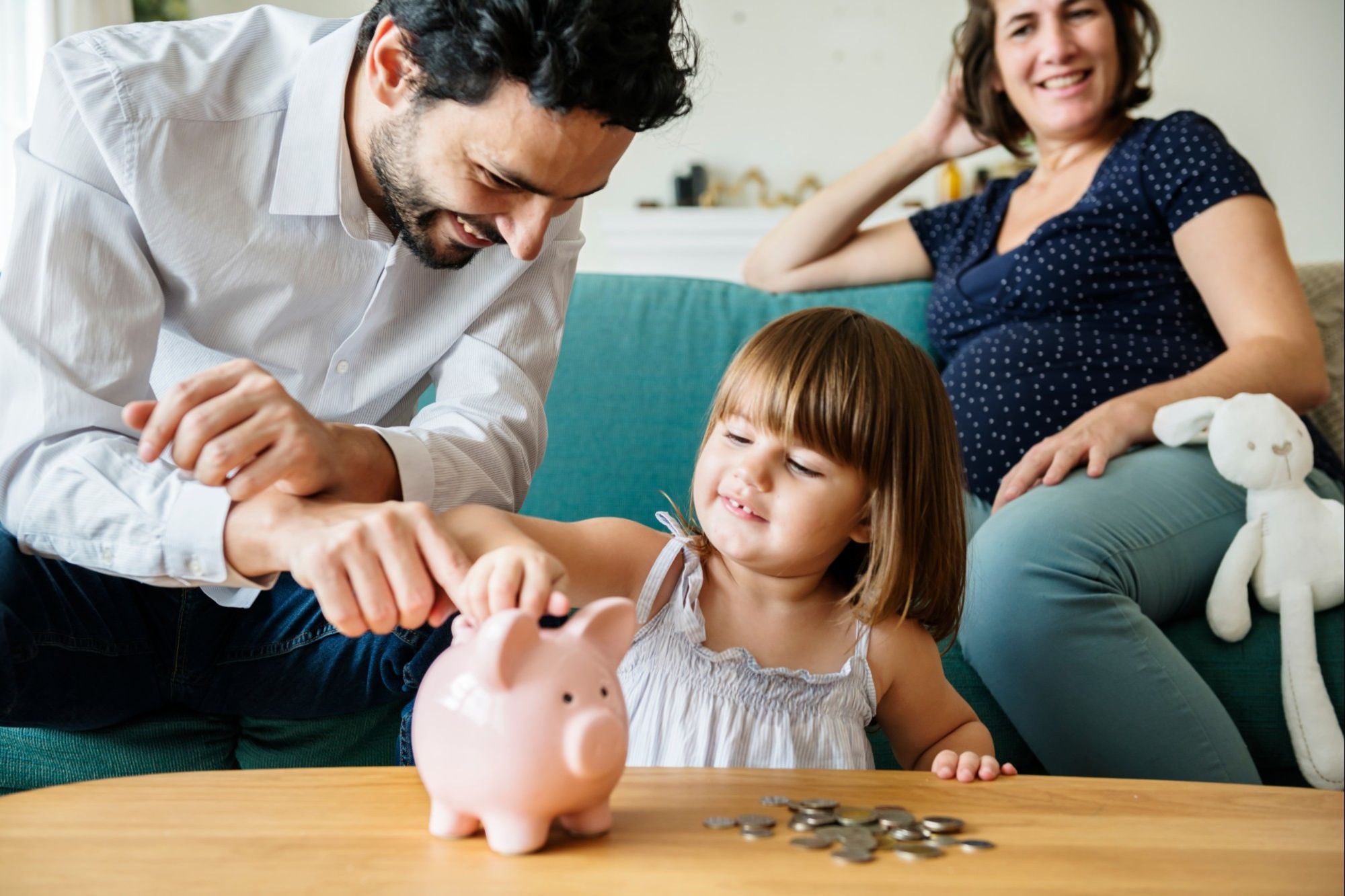
Furthermore, involving children in everyday financial activities, such as grocery shopping, comparing prices, and allocating a portion of their allowance to savings, can provide practical learning experiences that reinforce the value of money. By integrating financial discussions and activities into daily life, parents can effectively model positive financial behaviors, ultimately shaping their children’s attitudes toward money and instilling lifelong money management skills.
Teaching the Value of Money
Instilling an Understanding of Financial Worth
Instilling a deep understanding of the value of money is a fundamental aspect of teaching children about money management. Parents can convey this concept by introducing the notion that money represents the effort and time required to earn it. By emphasizing the connection between work and income, children can develop an appreciation for the resources at their disposal and comprehend the significance of making mindful financial choices.
One effective approach is to involve children in age-appropriate discussions about the family’s income sources and the effort it takes to earn money. By providing insights into the family’s financial dynamics, parents can help children recognize the correlation between work, income, and the ability to meet various needs and wants. This can foster a sense of empathy and gratitude, leading children to value the resources available to them.
Additionally, parents can encourage children to earn money through age-appropriate tasks or chores, allowing them to experience the satisfaction of earning their own income. This hands-on experience can instill a sense of pride and accomplishment, while also teaching the importance of hard work and diligence in financial matters.
Furthermore, teaching children the concept of delayed gratification can reinforce the value of money. By encouraging children to save for a desired item rather than instantly gratifying their wants, parents can impart the notion that money should be spent wisely and that patience can lead to more meaningful rewards. This practice cultivates a sense of discipline and prudence, shaping children’s attitudes toward spending and saving.
By instilling an understanding of the value of money, parents can lay the groundwork for children to develop a respectful and mindful approach to financial matters, setting the stage for responsible money management in the future.
Introducing Budgeting
Empowering Children with Financial Planning Skills
Introducing the concept of budgeting to children is a pivotal step in their financial education. By teaching children how to budget, parents can empower them with essential financial planning skills that will serve them well into adulthood. Budgeting instills the principles of prioritizing spending, setting financial goals, and making informed decisions with available resources.
Parents can introduce the concept of budgeting by explaining that it involves allocating money for different purposes, such as saving, spending, and sharing. By involving children in creating a simple budget for their allowance or earnings, parents can illustrate the importance of planning for various financial needs and wants. This hands-on approach allows children to visualize the allocation of funds and understand the trade-offs involved in financial decision-making.
Moreover, parents can encourage children to track their expenses and income, whether through a physical ledger or a digital tool. By recording their financial activities, children can gain a practical understanding of where their money goes and how their spending habits impact their financial resources. This practice promotes mindfulness and accountability, nurturing a sense of financial awareness from an early age.
Furthermore, parents can involve children in discussions about family budgeting, highlighting the considerations involved in managing household expenses, saving for the future, and addressing unexpected costs. By transparently sharing these financial aspects with children, parents can demystify the budgeting process and underscore its relevance in maintaining financial stability and pursuing financial goals.
By introducing budgeting as a foundational financial practice, parents equip their children with the skills to make informed financial decisions, prioritize their spending, and cultivate a mindset of proactive financial planning. This early exposure to budgeting lays the groundwork for prudent financial management and fosters a sense of financial responsibility in children.
Allowing for Financial Mistakes
Fostering a Healthy Approach to Learning from Errors
While it is important to instill sound financial principles in children, it is equally crucial for parents to create an environment where financial mistakes are viewed as valuable learning opportunities. Allowing children to make financial mistakes within a controlled setting can impart essential lessons that contribute to their overall financial literacy and decision-making skills.
Parents can encourage an open dialogue about financial decisions and their potential outcomes, emphasizing that mistakes are a natural part of the learning process. By fostering an environment where children feel comfortable discussing their financial choices and experiences, parents can provide guidance and support while allowing children to take ownership of their financial decisions.
Moreover, when children encounter financial setbacks or make less-than-ideal purchases, parents can engage them in reflective conversations rather than resorting to criticism. By asking open-ended questions that prompt children to evaluate their choices and consider alternative approaches, parents can guide children toward understanding the consequences of their actions and making more informed decisions in the future.
Furthermore, parents can introduce the concept of opportunity cost, illustrating that choosing to spend money on one item means forgoing the opportunity to use that money for something else. By highlighting the trade-offs involved in financial decisions, children can develop a deeper appreciation for the implications of their choices and become more discerning in their spending habits.
By allowing children to experience and learn from financial mistakes in a supportive and non-judgmental environment, parents can instill resilience, critical thinking, and adaptability in their children’s approach to money management. Embracing mistakes as valuable learning experiences fosters a healthy relationship with money and equips children with the skills to navigate financial challenges with confidence.
Teaching the Importance of Saving
Cultivating a Habit of Financial Prudence
Teaching children the importance of saving is a cornerstone of their financial education, laying the groundwork for responsible money management and future financial security. By instilling a habit of saving from a young age, parents can empower their children with the fundamental principle of setting aside money for future needs, goals, and unexpected expenses.
Parents can introduce the concept of saving by emphasizing the value of setting achievable financial goals. Whether it’s saving for a coveted toy, a special outing, or a long-term investment, children can learn the satisfaction of working toward and achieving their saving objectives. This practice instills a sense of discipline and purpose in managing financial resources.
Furthermore, parents can encourage children to allocate a portion of their allowance or earnings to a savings jar or account, reinforcing the habit of setting aside money before allocating funds for spending. By making saving a regular and non-negotiable practice, children internalize the importance of prioritizing long-term financial security over immediate gratification.
Moreover, parents can introduce the concept of earning interest on savings, illustrating how money saved in a bank account can grow over time. This serves as a valuable lesson in the potential benefits of saving and the concept of passive income, fostering an understanding of the rewards of prudent financial planning.
Additionally, parents can involve children in discussions about the purpose of emergency funds and the peace of mind that comes with having financial reserves for unexpected expenses. By highlighting the practical implications of saving for unforeseen circumstances, children develop a sense of financial preparedness and resilience.
By teaching the importance of saving, parents equip their children with the foundational skills of prudence, goal-setting, and delayed gratification, fostering a mindset of responsible financial stewardship. This early exposure to the value of saving establishes a strong financial foundation and cultivates a lifelong habit of mindful financial planning.
Encouraging Entrepreneurship
Fostering Creativity and Financial Independence
Encouraging entrepreneurship in children can be a transformative way to instill valuable financial skills and nurture their creativity and independence. By fostering an entrepreneurial mindset, parents can empower their children to explore innovative ideas, take calculated risks, and develop a proactive approach to financial opportunities.
One effective strategy is to encourage children to explore their interests and talents, identifying potential entrepreneurial ventures that align with their passions. Whether it’s starting a small business, offering a service, or creating and selling handmade products, children can learn the principles of entrepreneurship while honing their skills and pursuing their interests.
Moreover, parents can introduce the concept of budgeting and financial planning within the context of a child’s entrepreneurial endeavors. By involving children in the financial aspects of their ventures, such as calculating costs, setting prices, and managing profits, parents provide practical lessons in financial management and business acumen.
Furthermore, parents can facilitate discussions about the value of innovation, problem-solving, and adaptability in entrepreneurship. By highlighting real-world examples of successful entrepreneurs and their journeys, children gain insights into the diverse paths to financial success and the qualities that contribute to entrepreneurial achievement.
Additionally, parents can encourage children to allocate a portion of their earnings from entrepreneurial activities to savings or future investment opportunities. This practice instills the habit of prudent financial management and reinforces the notion of leveraging income for long-term financial growth.
By encouraging entrepreneurship, parents not only nurture their children’s creativity and resourcefulness but also instill a proactive and enterprising approach to financial opportunities. This entrepreneurial mindset equips children with the skills and mindset to navigate the evolving landscape of personal finance and pursue their aspirations with confidence and financial acumen.
Teaching the Dangers of Debt
Fostering Financial Awareness and Responsibility
Teaching children about the potential dangers of debt is a crucial aspect of their financial education, equipping them with the awareness and prudence to make informed decisions about borrowing and managing financial obligations. By instilling an understanding of the implications of debt, parents can empower their children to approach financial matters with caution and responsibility.
One effective approach is to introduce the concept of debt in age-appropriate terms, emphasizing that it involves borrowing money that must be repaid with interest. By illustrating the long-term impact of accumulating debt, parents can convey the importance of exercising prudence and restraint when considering borrowing as a financial option.
Moreover, parents can facilitate discussions about the various forms of debt, such as credit cards, loans, and mortgages, and the responsibilities and consequences associated with each. By providing insights into the terms and conditions of borrowing, children can develop a nuanced understanding of the commitments and potential risks involved in taking on debt.
Furthermore, parents can illustrate the implications of debt through relatable examples, such as the challenges of managing excessive debt and the impact it can have on financial stability and future opportunities. By fostering empathy and critical thinking, children can internalize the potential pitfalls of debt and develop a cautious approach to financial decision-making.
Additionally, parents can emphasize the importance of responsible borrowing and the value of maintaining a positive credit history. By discussing the factors that contribute to sound financial management, such as making timely payments and living within one’s means, children can grasp the significance of prudently managing financial obligations.
By teaching the dangers of debt, parents equip their children with the awareness and discernment to navigate the complexities of borrowing and financial commitments. This foundational knowledge fosters a mindset of financial responsibility and empowers children to make informed choices that contribute to their long-term financial well-being.
Conclusion
Nurturing Financial Empowerment from an Early Age
Teaching children about money management is a multifaceted endeavor that encompasses instilling essential financial principles, fostering practical skills, and nurturing a mindset of responsibility and prudence. By embracing various strategies, parents can lay a strong foundation for their children’s financial well-being and empower them to navigate the complexities of personal finance with confidence and acumen.
Setting a good example by modeling responsible financial behaviors and engaging children in age-appropriate discussions about money serves as a cornerstone for instilling valuable financial habits. By demonstrating prudence in spending, prioritizing saving, and engaging in open conversations about financial decisions, parents can shape their children’s attitudes toward money from an early age.
Introducing the value of money and the concept of budgeting equips children with practical financial skills that contribute to their financial literacy and decision-making abilities. By emphasizing the importance of saving, parents instill a habit of prudence and delayed gratification, nurturing a mindset of mindful financial planning and long-term goal setting.
Moreover, fostering an environment that allows for financial mistakes as learning opportunities cultivates resilience, critical thinking, and adaptability in children’s approach to money management. Encouraging entrepreneurship nurtures creativity, independence, and a proactive approach to financial opportunities, empowering children to explore innovative ideas and develop valuable business acumen.
Teaching the dangers of debt provides children with the awareness and discernment to approach borrowing and financial commitments with caution and responsibility. By instilling an understanding of the implications of debt and responsible borrowing practices, parents equip their children with the knowledge to make informed financial decisions.
Overall, by integrating these strategies into their parenting approach, parents can nurture financial empowerment in their children, setting the stage for a future where they can confidently navigate the intricacies of personal finance, make informed decisions, and pursue their financial aspirations with prudence and confidence.