Home>Finance>How Much Does A Cancer Screening Cost Without Insurance?

Finance
How Much Does A Cancer Screening Cost Without Insurance?
Modified: December 29, 2023
Discover the cost of cancer screening without insurance and learn about financing options. Protect your health and your finances with affordable solutions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to this comprehensive guide on the cost of cancer screening without insurance. Cancer screening plays a crucial role in early detection and treatment, significantly improving the chances of successful outcomes. Regular screenings are recommended for individuals at risk or to detect cancer in its early stages.
However, one of the key concerns that many people face when considering cancer screening is the cost, especially if they do not have health insurance. Without insurance coverage, the financial burden of cancer screening can be significant, potentially deterring individuals from seeking these life-saving tests.
In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of cancer screening costs without insurance. We will explore the importance of cancer screening, how it can impact your financial well-being, and highlight the factors that influence the cost of screenings. Additionally, we will discuss the different types of cancer screening tests available and offer potential options for financial assistance.
Understanding the cost implications of cancer screenings without insurance is vital in making informed decisions about your healthcare. Whether you are uninsured or have limited coverage, this guide aims to provide you with valuable insights to navigate the financial challenges of cancer screening.
Understanding Cancer Screening
Cancer screening refers to the process of testing individuals for the presence of cancer even in the absence of symptoms. The objective of cancer screening is to detect cancer at an early stage when it is more easily treatable and before it has spread to other parts of the body.
Screening tests are designed to identify abnormalities or warning signs that may indicate the presence of cancer. These tests can help healthcare professionals diagnose the disease at an early stage, promote better treatment outcomes, and potentially save lives.
It is important to note that cancer screening is different from diagnostic tests. While screening tests are conducted on individuals without symptoms, diagnostic tests are performed when there are noticeable symptoms or for further evaluation after an abnormal screening result.
The types of cancer screenings recommended can vary based on factors such as age, gender, personal and family medical history, and lifestyle choices. Some common cancer screening tests include mammograms for breast cancer, Pap smears for cervical cancer, colonoscopies for colorectal cancer, and PSA tests for prostate cancer.
Regular cancer screenings are particularly important for individuals who are at a higher risk due to factors such as family history, genetic predispositions, certain lifestyle choices, or exposure to carcinogens. By proactively undergoing cancer screenings, individuals can identify potential cancerous changes early on, enabling the initiation of timely treatment.
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate cancer screening tests based on your personal circumstances and risk factors. They can provide guidance on when to initiate screenings, how often to undergo them, and which specific tests are most appropriate for you.
Why is Cancer Screening Important?
Cancer screening plays a vital role in the early detection and prevention of cancer. Here are several key reasons why cancer screening is important:
- Early Detection: One of the primary goals of cancer screening is to detect the presence of cancer at an early stage. Early-stage cancer is typically more treatable and has a higher chance of successful outcomes. Regular screenings can help identify cancer before symptoms become apparent, leading to earlier intervention and potentially life-saving treatments.
- Reduced Mortality: Studies have shown that certain cancer screenings, such as mammography for breast cancer and colonoscopy for colorectal cancer, can significantly reduce mortality rates. By detecting cancer in its early stages, when it is more localized and easier to treat, the chances of survival and long-term remission are greatly increased.
- Preventive Measures: Some cancer screenings, such as Pap smears for cervical cancer or HPV testing, can help identify pre-cancerous conditions. This early identification allows for preventive measures to be taken, such as vaccination or the removal of abnormal cells before they develop into cancer.
- Peace of Mind: Undergoing regular cancer screenings can provide individuals with peace of mind, knowing that they are taking proactive steps to monitor their health and detect any potential issues early on. This can alleviate anxiety and promote a sense of control over one’s health.
- Family History Awareness: Cancer screenings can be particularly crucial for individuals with a family history of specific cancers. Identifying familial risk factors can help healthcare professionals develop personalized screening plans and implement preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of developing cancer.
- Public Health Impact: Widespread adoption of cancer screening can have a significant impact on public health by reducing the incidence and mortality rates of various cancers. Screening programs can help identify high-risk populations and implement targeted interventions to detect and treat cancer early.
It is important to remember that cancer screenings are not foolproof, and false-positive or false-negative results can occur. However, they remain an essential tool in the fight against cancer, providing opportunities for early intervention, reducing the burden of the disease, and improving overall health outcomes.
The Financial Implications of Cancer Screening
The cost of cancer screening can be a significant concern for individuals, particularly those without health insurance coverage. It is important to understand the financial implications of undergoing cancer screening, as it can impact your overall financial well-being. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Screening Costs: The cost of cancer screening tests can vary depending on various factors, including the type of test, the healthcare facility, and geographical location. Some tests, such as mammograms or colonoscopies, may require additional procedures or follow-up tests, which can further increase costs.
- Out-of-Pocket Expenses: Without insurance, individuals are typically responsible for paying the full cost of cancer screenings out of their own pockets. This can include fees for the test itself, facility charges, healthcare provider fees, and any necessary laboratory or pathology tests.
- Diagnostic Procedures: In some cases, if an abnormality or potential cancerous lesion is detected during a screening test, additional diagnostic procedures may be required for further evaluation. These procedures can add significant costs to the overall screening process.
- Follow-Up Treatments: If cancer is detected through screening, individuals may be faced with additional expenses related to follow-up treatments, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, medications, and ongoing monitoring. These costs can accumulate over time.
- Travel and Accommodation: Depending on your location and the availability of specialized healthcare facilities, there may be additional costs associated with travel, accommodation, and transportation to undergo cancer screenings or receive follow-up treatments.
- Financial Stress: The financial burden of cancer screenings and treatments can cause significant stress and anxiety for individuals and their families. The fear of incurring high medical bills or the inability to afford necessary screenings may lead to delayed or avoided healthcare, potentially impacting health outcomes.
It is important to be proactive and explore potential financial assistance options if you are concerned about the cost of cancer screening without insurance. There may be programs, grants, or resources available through government agencies, non-profit organizations, or healthcare facilities that can help alleviate some of the financial burdens.
Remember, the cost of cancer screening should not deter you from prioritizing your health. Discussing your concerns with healthcare providers and exploring all available options can help you make informed decisions and take the necessary steps to undergo screenings that can potentially save lives.
Factors Affecting the Cost of Cancer Screening
The cost of cancer screening can vary based on several factors. Understanding these factors can help you anticipate and manage the expenses associated with undergoing screenings. Here are some key factors that can influence the cost of cancer screening:
- Type of Test: Different types of cancer screening tests have varying costs. Some tests, like mammograms or Pap smears, are generally more affordable compared to others, such as MRI or CT scans. The complexity and technology involved in performing the test can impact the overall cost.
- Healthcare Facility: The choice of healthcare facility can significantly impact the cost of cancer screening. Larger hospitals or specialized cancer centers may charge higher prices compared to smaller clinics or community health centers. It is important to research and compare the costs at different facilities.
- Geographical Location: The cost of cancer screening can also vary depending on your geographic location. Healthcare costs can be higher in certain regions, particularly in large cities or areas with higher living costs. Consider exploring options in nearby areas or researching low-cost clinics or screening programs.
- Healthcare Provider Fees: The fees charged by healthcare providers, such as radiologists or pathologists, can impact the overall cost of cancer screening. These fees may vary between providers, so it is important to inquire about the costs associated with each step of the screening process.
- Additional Tests and Procedures: Depending on the results of the initial screening, additional tests or procedures may be necessary. These can include biopsies, follow-up imaging, or genetic testing. Each additional procedure incurs extra costs, so it is essential to discuss potential follow-up tests with your healthcare provider beforehand.
- Insurance Coverage: If you have health insurance, the extent of coverage can greatly impact the out-of-pocket expenses associated with cancer screening. Insurance plans vary, and some may cover certain screenings in full or at a reduced cost. Review your insurance policy to understand what screenings are covered and if any deductibles or co-pays apply.
- Financial Assistance Programs: Various financial assistance programs may be available to help individuals who are uninsured or underinsured. These programs can provide subsidies or discounts on screening tests. Research local, state, and national resources that offer financial assistance specifically for cancer screenings.
It is important to keep in mind that while cost is a significant consideration, the primary focus should be on prioritizing your health and well-being. Discussing the cost concerns with healthcare providers, exploring affordable options, and seeking potential financial assistance can help ensure that you receive the necessary cancer screenings without undue financial hardship.
Types of Cancer Screening Tests
There are various types of cancer screening tests available, each designed to detect specific types of cancer or abnormalities. The choice of screening test depends on factors such as age, gender, personal and family medical history, and lifestyle choices. Here are some common types of cancer screening tests:
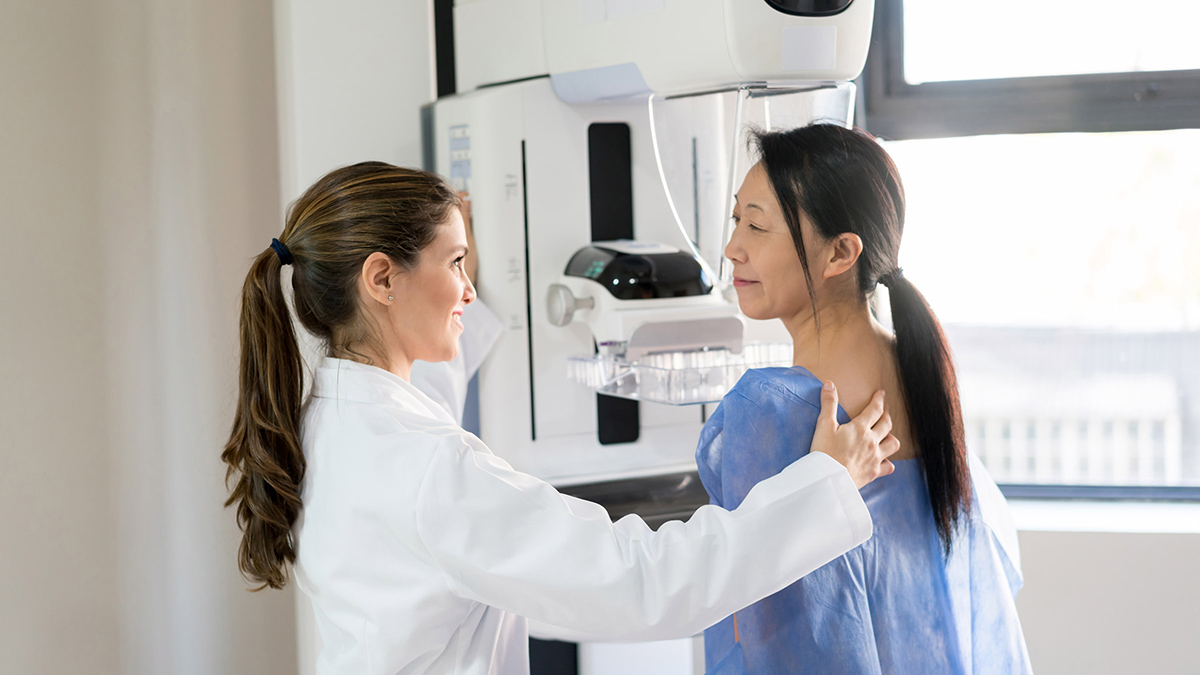
- Mammogram: Mammography is a common screening test for breast cancer. It involves low-dose X-rays to examine breast tissue for any abnormalities or signs of cancer. Mammograms are recommended for women starting at a certain age or for those with an increased risk of breast cancer.
- Pap Smear: A Pap smear, also known as a Pap test, is a screening procedure for cervical cancer. It involves collecting cells from the cervix to check for any potentially cancerous or precancerous changes. Regular Pap smears are recommended for women starting at a certain age, usually beginning in their late teens or early twenties.
- Colonoscopy: Colonoscopy is a screening test for colorectal cancer. It involves inserting a thin, flexible tube with a camera into the rectum and colon to examine the lining for any abnormal growths or signs of cancer. Colonoscopies are generally recommended for individuals over a certain age or those with an increased risk of colorectal cancer.
- PSA Test: The Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) test is a blood test used for prostate cancer screening. It measures the levels of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate gland. Elevated PSA levels can be an indication of prostate health issues, including cancer. PSA testing is typically recommended for men over a certain age or those with risk factors.
- Skin Examination: Skin examinations involve a visual inspection of the skin by a healthcare professional to identify any potential signs of skin cancer. Regular self-examinations and professional skin checks are essential, especially for individuals with risk factors such as a history of sun exposure or a family history of skin cancer.
- Lung Cancer Screening: Low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) scans are used for lung cancer screening in individuals at high risk, such as heavy smokers or those with a history of lung cancer. Regular screenings with LDCT can help detect lung cancer at an early stage when treatment options are more effective.
It is important to note that these screening tests are specific to certain types of cancer. There are also other types of cancer screenings available for different types of cancers, such as oral, prostate, ovarian, or pancreatic cancer. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate screening tests based on your risk factors and personal circumstances.
Remember, cancer screenings are an essential tool in detecting cancer early, but they have limitations. No screening test is 100% accurate, and false-positive or false-negative results can occur. Regular screenings, along with other preventive measures such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle and following recommended guidelines, can significantly contribute to early detection and improved outcomes.
Average Costs of Cancer Screening Without Insurance
The cost of cancer screening tests without insurance can vary depending on several factors, including the type of test, the healthcare facility, and geographical location. While it is challenging to provide precise figures, here are some average costs for common cancer screening tests:
- Mammogram: The average cost of a mammogram without insurance can range from $100 to $250.
- Pap Smear: The average cost of a Pap smear without insurance can range from $50 to $200.
- Colonoscopy: The average cost of a colonoscopy without insurance can range from $800 to $3,000, depending on the location and additional procedures required.
- PSA Test: The average cost of a PSA test without insurance can range from $30 to $100.
- Skin Examination: The average cost of a professional skin examination without insurance can range from $50 to $200.
- Lung Cancer Screening (LDCT Scan): The average cost of a LDCT scan without insurance can range from $200 to $700.
It is important to note that these are general average costs and can vary significantly depending on factors such as the specific healthcare facility, geographical region, and any additional procedures or tests required based on the initial screening results.
If you are concerned about the cost of cancer screening without insurance, consider exploring options for financial assistance. Some healthcare facilities offer discounted or sliding-scale fees for individuals without insurance. Additionally, non-profit organizations, government programs, or local community health centers may provide financial assistance or free screenings for eligible individuals.
Being proactive in researching cost-effective options, discussing your concerns with healthcare providers, and exploring available resources can help you find affordable options for cancer screenings, ensuring that you prioritize your health without facing undue financial strain.
Options for Financial Assistance
If you are unable to afford the cost of cancer screening without insurance, there are several options available for financial assistance. These resources can help alleviate the financial burden and ensure that you receive the necessary screenings. Here are some options to consider:
- Government Assistance Programs: Depending on your income level and eligibility, you may qualify for government assistance programs such as Medicaid or Medicare. These programs can provide coverage for cancer screenings and related healthcare services. Additionally, some state-specific programs offer assistance for uninsured or underinsured individuals.
- Non-Profit Organizations: Numerous non-profit organizations dedicated to cancer awareness and support provide financial assistance for screenings. Examples include the American Cancer Society, CancerCare, and The Prevent Cancer Foundation. These organizations may offer grants, vouchers, or financial aid programs specifically for cancer screenings.
- Local Community Health Centers: Community health centers often provide low-cost or free healthcare services to individuals without insurance. These facilities may offer discounted rates or payment plans for cancer screenings. Contact your local community health center to inquire about their services and financial assistance options.
- Hospital Financial Assistance Programs: Many hospitals and healthcare systems have financial assistance programs in place to support individuals who are uninsured or facing financial hardship. These programs may offer discounts or sliding-scale fees based on your income and financial situation.
- Cancer Screening Programs: Some states and local communities offer cancer screening programs that provide free or low-cost screenings for eligible individuals. These programs aim to increase access to screenings for underserved populations. Research programs in your area and determine if you meet the criteria for participation.
- Patient Assistance Programs: Pharmaceutical companies and drug manufacturers may have patient assistance programs in place to help individuals who cannot afford the cost of medications or treatment. While these programs may not directly cover the cost of cancer screenings, they can be helpful if follow-up treatments or medications are necessary.
It is important to note that eligibility criteria, availability, and the level of financial assistance may vary for each resource. Contact the specific organization or healthcare facility to inquire about the application process and requirements for financial assistance.
Remember, early detection through cancer screenings can save lives. If you are concerned about the cost of cancer screening without insurance, do not hesitate to reach out and explore these financial assistance options to ensure that you receive the necessary screenings and prioritize your health.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost of cancer screening without insurance is essential in making informed decisions about your healthcare. While the financial implications can be a concern, it is crucial not to let cost deter you from prioritizing your health and undergoing these life-saving tests.
Cancer screening plays a vital role in the early detection and prevention of cancer. By detecting cancer at an early stage, treatment options are usually more effective, leading to better outcomes and improved chances of survival.
Although the average costs of cancer screenings without insurance can vary, several options exist to help alleviate the financial burden. Government assistance programs, non-profit organizations, local community health centers, hospital financial assistance programs, and cancer screening programs can provide support and financial resources for individuals who are uninsured or facing financial hardship.
It is essential to research and explore these resources, discuss your concerns with healthcare providers, and be proactive in finding affordable options for cancer screenings. Do not hesitate to reach out for financial assistance if needed to ensure that you receive the necessary screenings and take care of your overall health and well-being.
Remember, early detection through cancer screenings can greatly improve outcomes and potentially save lives. Prioritize your health, explore your options, and take the necessary steps to undergo regular screenings. By staying informed and proactive, you can navigate the financial challenges of cancer screening and make choices that positively impact your health and future.