Home>Finance>How Much Is A Cancer Screening Without Insurance?

Finance
How Much Is A Cancer Screening Without Insurance?
Published: November 15, 2023
Discover how much a cancer screening costs without insurance and find financial options to help cover the expenses.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Cancer is a devastating disease that affects millions of people worldwide. Early detection and timely treatment significantly increase the chances of a successful outcome, making cancer screening an essential part of proactive healthcare. However, for those without insurance, the cost of cancer screening can be a major barrier to accessing these life-saving services.
Cancer screening refers to the process of detecting cancer or pre-cancerous conditions in individuals who do not have any symptoms. It involves various tests and procedures that can identify abnormalities and potential signs of cancer at an early stage. Early detection is crucial because it allows for early intervention and treatment, which can lead to better outcomes and potentially save lives.
The importance of cancer screening cannot be overstated. By detecting cancer in its early stages, when it is most treatable, screening can potentially prevent the disease from progressing to an advanced and more challenging stage. Regular screenings can help detect cancers such as breast, cervical, colon, lung, and prostate cancer, among others.
What is cancer screening?
Cancer screening refers to the use of tests and procedures to detect cancer in individuals who do not have any symptoms. The primary goal of screening is to identify cancer at an early stage when it is most easily treatable. This allows for prompt intervention and increases the chances of successful treatment outcomes.
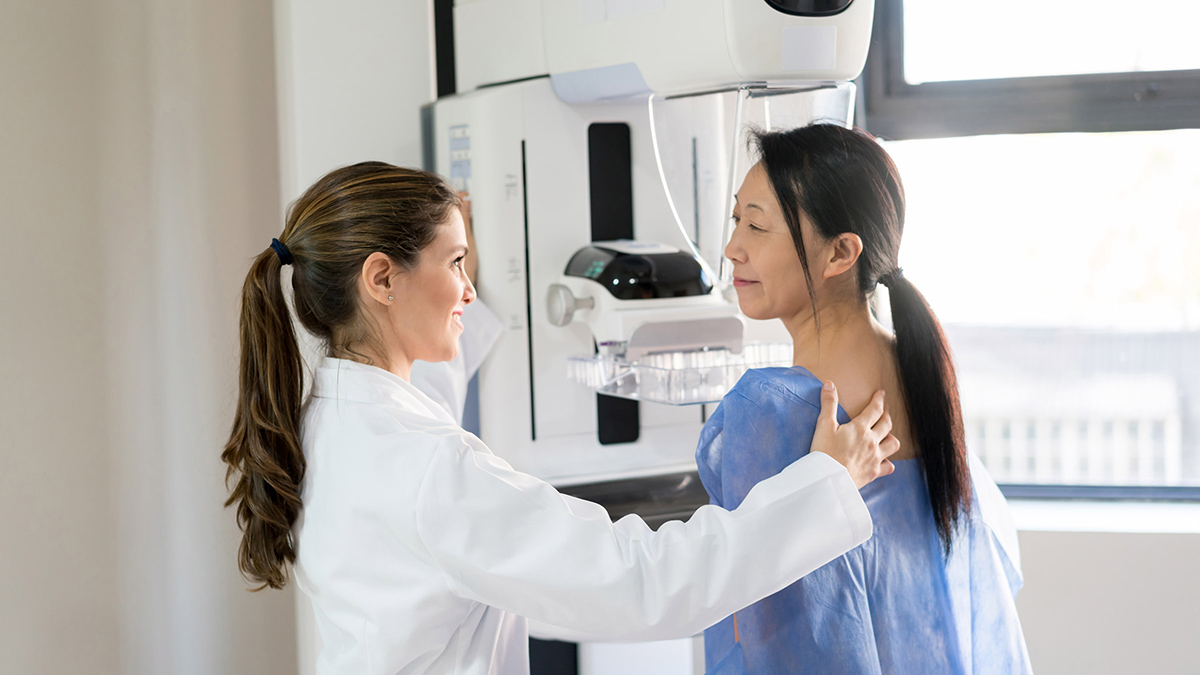
There are several types of cancer screening tests available, and the specific tests recommended may vary depending on factors such as age, gender, and family history. Common cancer screening procedures include mammography for breast cancer, Pap smears for cervical cancer, colonoscopy for colorectal cancer, and PSA tests for prostate cancer. These tests are designed to detect abnormalities or pre-cancerous conditions that may indicate the presence of cancer.
Cancer screening is not a diagnostic tool but rather a preventive measure. If screening tests detect any abnormality, further diagnostic tests, such as biopsies or imaging scans, may be recommended to confirm the presence of cancer. Early detection through screening can provide a window of opportunity for effective treatment and can significantly improve long-term outcomes.
It is important to note that not all cancers have effective screening tests available. Some cancers may not have reliable markers that can be easily detected through screening, while others may not have routine screening recommendations due to factors such as rarity or low incidence rates. In such cases, early detection may rely on recognizing symptoms and seeking medical attention promptly.
Regular cancer screening is typically recommended for individuals who are at an increased risk of developing certain types of cancer. This includes individuals with a family history of cancer, those with certain genetic mutations, and those exposed to known risk factors such as smoking or prolonged sun exposure.
Importance of cancer screening
Cancer is a complex disease that can often develop silently, without any noticeable symptoms in its early stages. This is why cancer screening plays a crucial role in identifying cancer at an early stage when treatment options are more effective and outcomes are generally better. Here are some key reasons why cancer screening is important:
- Early detection: The primary goal of cancer screening is to detect cancer in its early stages, before it has a chance to progress and spread. Finding cancer at an early stage offers a better chance of successful treatment and improves long-term outcomes.
- Increased chances of survival: When cancer is detected early, it is more likely to be localized and therefore easier to treat. This can significantly increase the chances of survival and reduce the need for aggressive treatments like surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy.
- Prevention: Some cancer screening tests can also detect pre-cancerous conditions, allowing for early intervention to prevent the development of cancer altogether. For example, regular Pap smears can detect abnormal cells in the cervix, which can be treated before they turn into cervical cancer.
- Peace of mind: Regular cancer screenings can provide individuals with peace of mind, knowing that they are taking proactive steps to monitor their health and detect any potential issues early on. This can help alleviate anxiety and promote overall well-being.
- Identifying high-risk individuals: Cancer screenings can identify individuals who may be at a higher risk of developing certain types of cancer. This information can prompt healthcare providers to provide personalized recommendations, such as increased surveillance or additional preventive measures.
It is important to keep in mind that cancer screening has its limitations. False-positive and false-negative results can occur, leading to unnecessary follow-up tests or possible missed diagnoses. Furthermore, not all cancers have effective screening methods, and individual risk factors should be considered when determining the need for specific screenings.
Despite these limitations, cancer screening remains an essential component of preventative healthcare. It is a proactive approach to identify cancer early, potentially saving lives and improving the overall well-being of individuals.
Cost of cancer screening without insurance
Accessing cancer screening services can be financially challenging for individuals without insurance coverage. The cost of cancer screenings can vary depending on several factors, including the type of test, the healthcare facility, and the geographic location. Here are some considerations regarding the cost of cancer screening without insurance:
- Screening test costs: Different cancer screening tests have varying costs. For example, mammograms for breast cancer screening can cost between $100 to $250, while colonoscopies for colorectal cancer screening may range from $1,000 to $3,000. It is important to research and understand the costs associated with specific screening tests.
- Doctor’s fees: In addition to the cost of the screening test, there may be fees associated with consulting a healthcare professional. These fees can vary depending on the physician’s specialization, experience, and location.
- Additional tests and procedures: If an abnormality or suspicious finding is detected during a screening test, additional diagnostic tests, such as biopsies or imaging scans, may be required. These can significantly increase the overall cost of cancer screening.
- Facility fees: The screening may be performed in a hospital, clinic, or imaging center, each with its own facility fees. These fees can contribute to the overall cost of the screening.
- Geographic variation: The cost of cancer screening can vary depending on the geographic location. Urban areas and regions with higher healthcare costs typically have higher screening costs compared to rural areas or regions with lower healthcare costs.
Without insurance, paying for cancer screening out-of-pocket can be a financial burden for many individuals. However, it is crucial to prioritize one’s health and consider available options for affordable cancer screening.
It is important to note that various organizations, such as community health centers and non-profit organizations, offer low-cost or free cancer screening programs. Additionally, some state-run programs provide screenings for individuals who meet specific criteria, such as income eligibility. Researching these programs and reaching out to local healthcare facilities can help individuals find more affordable options.
Furthermore, it may be possible to negotiate the cost of cancer screening with healthcare providers or inquire about payment plans to make the expenses more manageable. Exploring different options and discussing financial concerns with healthcare providers can help individuals without insurance access the necessary cancer screening services within their financial means.
Factors affecting the cost of cancer screening
There are several factors that can influence the cost of cancer screening. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions and navigate the financial aspects of accessing these important healthcare services. Here are some key factors that can affect the cost of cancer screening:
- Type of screening test: Different types of cancer screening tests have varying costs. For example, a simple blood test may be less expensive compared to a more complex imaging procedure or invasive test.
- Healthcare facility: The cost of cancer screenings can vary depending on the healthcare facility where the screening is performed. Hospitals, imaging centers, and private clinics may have different pricing structures and associated facility fees.
- Location: The geographic location of the healthcare facility can influence the cost of cancer screening. Areas with higher healthcare costs or densely populated regions may have higher screening costs compared to more rural or low-cost areas.
- Additional tests and procedures: If a cancer screening test detects any abnormalities or suspicious findings, further related tests or procedures may be necessary. These additional tests can contribute to the overall cost of the screening process.
- Healthcare provider fees: The fees charged by healthcare providers, such as radiologists, pathologists, or specialists, can impact the cost of cancer screening. The experience, expertise, and location of these providers can affect their fees.
- Insurance coverage: For individuals with insurance, the coverage and benefits provided by their policy can influence the cost of cancer screening. Insurance plans may cover certain screening tests fully or partially, reducing out-of-pocket expenses.
It’s important to note that these factors are interconnected and can vary depending on individual circumstances. For example, the same screening test can have different costs at different healthcare facilities or with different insurance plans.
To better understand the cost of cancer screening, individuals should research and compare pricing, inquire about available discounts or payment plans, and consult with healthcare providers to discuss options and potential financial assistance programs. Being proactive in exploring options can help individuals access the necessary screenings within their financial means.
Available options for affordable cancer screening
For individuals without insurance or facing financial constraints, there are several options available to access affordable cancer screening. While the cost of screening can be a barrier, it’s important to prioritize one’s health and explore alternative avenues. Here are some options to consider:
- Community health centers: Community health centers often provide affordable or low-cost healthcare services, including cancer screenings. These centers may offer discounted or sliding-scale fees based on income and provide comprehensive care.
- Non-profit organizations: Many non-profit organizations offer cancer screening programs and initiatives. These organizations may partner with healthcare providers to offer free or low-cost screenings to individuals in need. Research and reach out to local non-profit organizations to explore potential options.
- State-run programs: Some states have programs that provide cancer screenings for individuals who meet specific criteria, such as income eligibility. These programs may offer reduced or no-cost screening tests and diagnostic follow-ups. Check with the local health department or state-specific resources for information on available programs.
- Clinical trials: Clinical trials often provide access to cutting-edge cancer screening technologies at no cost or with reduced fees. Participating in clinical trials not only benefits the individual but also contributes to advancing medical research.
- Employer or community-sponsored health events: Keep an eye out for health fairs, wellness events, or screenings sponsored by employers or community organizations. These events may offer free or discounted cancer screenings as part of their outreach efforts.
- Negotiate costs and payment plans: If facing financial difficulties, it’s worth discussing concerns with healthcare providers. They may be willing to negotiate costs or provide payment plans to make the screenings more affordable.
Researching available resources, contacting community organizations, and speaking with healthcare providers are essential steps in finding affordable options for cancer screening. Remember that early detection can be life-saving, and exploring these avenues can help individuals access the necessary screenings within their financial means.
In addition to these options, it is crucial for individuals to be informed about their insurance coverage options. If eligible, obtaining health insurance can significantly reduce the cost burden of cancer screening and other healthcare services. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) in the United States provides insurance options through the Health Insurance Marketplace, and eligibility for Medicaid may vary by state.
Conclusion
Cancer screening is a vital component of proactive healthcare, as early detection can improve treatment outcomes and potentially save lives. However, for individuals without insurance, the cost of cancer screening can be a significant barrier. Understanding the factors that affect the cost and exploring available options for affordable screenings is crucial to ensure access to these life-saving services.
Cancer screening tests can vary in cost, and factors such as the type of test, healthcare facility, and geographic location can influence the overall expenses. However, there are options to make screenings more affordable. Community health centers, non-profit organizations, and state-run programs often offer low-cost or free screenings. Clinical trials and employer or community-sponsored health events can also provide access to screenings at little to no cost.
It’s important to research and explore these options, as well as engage in open discussions with healthcare providers about financial concerns. Negotiating costs or setting up payment plans can help make screenings more manageable for individuals without insurance. Additionally, obtaining health insurance coverage through options like the Health Insurance Marketplace or Medicaid can significantly reduce the financial burden of cancer screenings.
Remember, prioritizing one’s health is paramount. Regular cancer screenings, even if they come with a cost, can lead to early detection, better treatment outcomes, and improved long-term health. By being proactive and exploring affordable options, individuals can take charge of their healthcare and ensure they receive the necessary screenings to detect cancer early, ultimately increasing the chances of successful treatment and improving overall well-being.