Home>Finance>How Much Does A Stress Test Cost With Insurance?


Finance
How Much Does A Stress Test Cost With Insurance?
Published: November 12, 2023
Discover the cost of stress tests with insurance coverage. Find out how your finances can be affected by this medical procedure.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
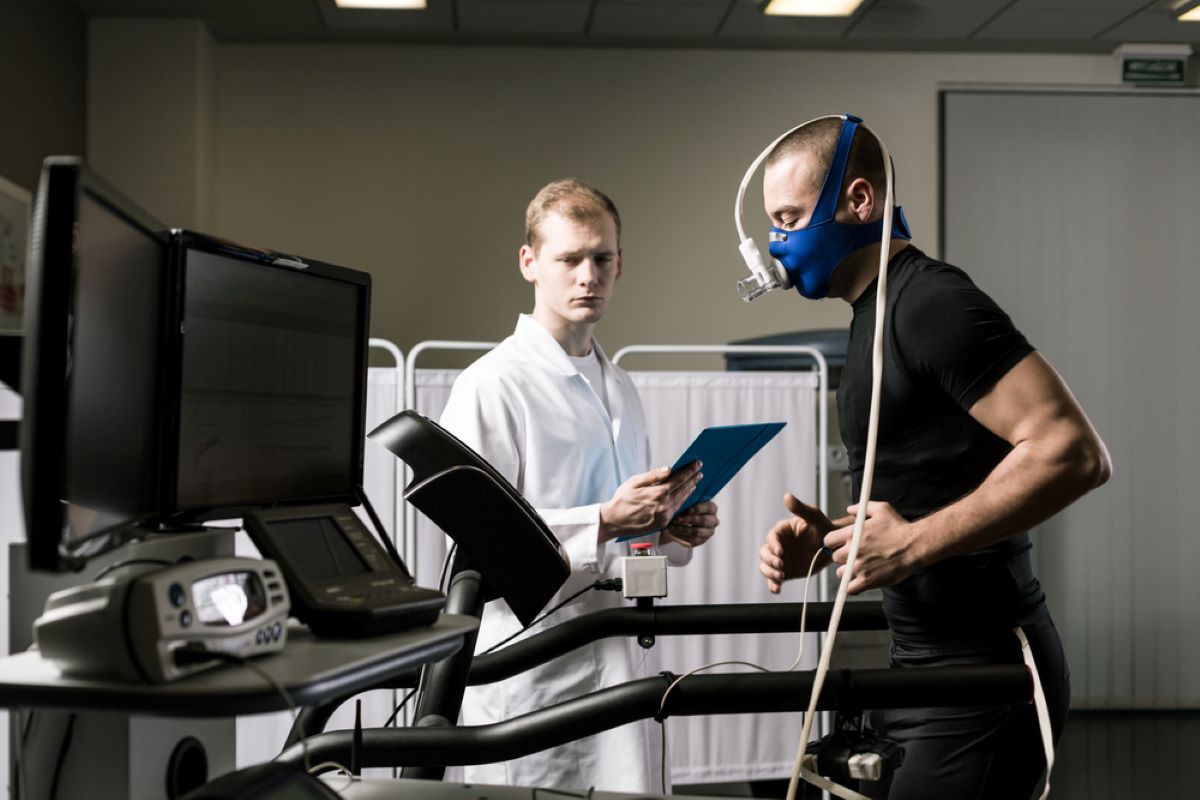
A stress test is a medical procedure used to evaluate how well your heart functions under physical stress. It helps doctors diagnose and monitor conditions such as coronary artery disease and assess the overall health of your cardiovascular system.
Stress tests are conducted in a controlled environment where you will be asked to exercise on a treadmill or ride a stationary bike. During the test, your heart rate, blood pressure, and electrocardiogram (ECG) will be monitored to observe any abnormalities that may indicate heart problems.
These tests play a crucial role in the early detection of heart disease, helping doctors develop appropriate treatment plans and interventions. However, many individuals are often concerned about the cost of stress tests, especially when insurance coverage comes into play.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of stress tests and discuss the factors that influence their cost. We will also explore how insurance coverage impacts the expense of stress tests and provide tips for minimizing costs.
Before we dive into the details, it is important to note that the cost of a stress test can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the type of test performed, the location of the healthcare facility, and the specific terms of your insurance plan. It is always a good idea to consult with your healthcare provider and insurance company to get a clear understanding of the costs involved.
Understanding Stress Tests
A stress test is a diagnostic procedure that evaluates how well your heart functions under physical stress. It is typically performed when your doctor suspects you may have coronary artery disease (CAD) or other heart-related conditions. Stress tests help determine how efficiently your heart pumps blood and if there are any abnormalities in its response to exercise.
There are different types of stress tests, including exercise stress tests and pharmacological stress tests. During an exercise stress test, you will be asked to walk on a treadmill or pedal a stationary bike while your heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG are monitored. This type of test allows doctors to observe how your heart responds to physical exertion.
Pharmacological stress tests, on the other hand, are performed on individuals who are unable to exercise due to physical limitations. In this type of test, medications are used to simulate the effects of exercise on the heart. The medications used dilate the blood vessels, increasing the workload on the heart and mimicking the effects of physical exertion.
The results of a stress test can provide valuable information about your heart’s health. The test helps identify potential blockages in the coronary arteries, assess the effectiveness of medications or treatments, and determine if any additional diagnostic tests, such as angiography, are necessary.
Stress tests are typically performed by trained medical professionals, such as cardiologists or technicians, in a hospital or outpatient facility. The procedure usually takes around 45 minutes to an hour, including the preparation time. It is a safe and non-invasive procedure that rarely causes complications.
If you are scheduled to undergo a stress test, it is important to follow any pre-test instructions given by your healthcare provider. These may include avoiding caffeine, nicotine, and certain medications prior to the test, as they can affect the results.
Overall, stress tests are a valuable tool in diagnosing and managing heart conditions. They help healthcare providers assess the functionality of your heart and develop appropriate treatment plans based on the results.
The Importance of Stress Tests
Stress tests play a critical role in the diagnosis and monitoring of various heart conditions, making them an essential tool in cardiovascular healthcare. They provide valuable information about the functionality and health of your heart, helping doctors make informed decisions regarding treatment and care. Here are some key reasons why stress tests are important:
1. Early Detection of Heart Diseases: Stress tests help in the early detection of coronary artery disease (CAD), a condition in which the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup. By identifying CAD early on, healthcare providers can initiate appropriate interventions and develop personalized treatment plans to prevent further complications.
2. Assessment of Heart Function: Stress tests evaluate how well your heart functions under physical stress, such as exercise or pharmacological stimulation. They provide important information about your heart rate, blood pressure, and electrocardiogram (ECG) changes during and after exertion, offering insights into the efficiency of your heart’s pumping function.
3. Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness: For individuals with existing heart conditions, stress tests can assess the effectiveness of medications and treatments. By monitoring changes in heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG during the test, doctors can gauge the impact of prescribed medications and make necessary adjustments to optimize treatment outcomes.
4. Determination of Exercise Capacity: Stress tests help determine your exercise capacity and fitness level. This information is particularly useful for individuals recovering from heart-related procedures or illnesses. It helps healthcare providers design customized exercise programs suitable for your specific needs and limitations.
5. Identification of Silent Ischemia: Silent ischemia refers to the lack of blood supply to the heart without causing noticeable symptoms, such as chest pain or discomfort. Stress tests can detect silent ischemia by revealing abnormal ECG changes during or after physical stress. Early detection allows doctors to take appropriate measures to manage the condition and prevent further damage to the heart.
6. Guidance for Further Diagnostic Tests: In some cases, stress tests may indicate the need for additional diagnostic tests, such as angiography or cardiac imaging. The results of a stress test can guide healthcare providers in determining the most appropriate next steps in the diagnostic process, ensuring the most accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan.
Overall, stress tests are an important tool in assessing the health of your heart and diagnosing or monitoring heart conditions. They provide crucial information that enables healthcare professionals to provide the best possible care and interventions tailored to your specific needs.
Insurance Coverage for Stress Tests
Understanding your insurance coverage for stress tests is crucial to avoid unexpected expenses and ensure you receive the necessary medical care without financial strain. Most health insurance plans provide some level of coverage for stress tests, but the specifics can vary depending on your insurance provider and plan. Here are important points to consider:
1. Coverage for Medically Necessary Stress Tests: Health insurance plans generally cover stress tests that are deemed medically necessary by your healthcare provider. This means that if your doctor orders a stress test to evaluate or diagnose a potential heart condition, your insurance will likely cover a portion of the cost.
2. Pre-authorization and Referral Requirements: Some insurance plans may require pre-authorization or a referral from your primary care physician before undergoing a stress test. It is important to check with your insurance company to determine if these requirements are necessary and to ensure you follow the proper procedures to ensure coverage.
3. In-Network vs. Out-of-Network Coverage: Insurance plans often have a network of preferred healthcare providers. To maximize coverage and minimize out-of-pocket expenses, it is important to choose a healthcare facility and providers that are in-network. Out-of-network providers may result in higher costs or limited coverage, so it is advisable to verify in advance.
4. Co-pays, Deductibles, and Coinsurance: Depending on your insurance plan, you may be responsible for certain out-of-pocket expenses for stress tests. These include co-pays, deductibles, and coinsurance. Co-pays are fixed amounts you pay for each visit or service, deductibles are the amount you must pay before insurance coverage kicks in, and coinsurance is the percentage of the cost you are responsible for after reaching your deductible.
5. Coverage Limits: Some insurance plans may have coverage limits or restrictions on the number of stress tests covered in a specific time period. It is important to review your policy to understand any limitations and ensure you have proper coverage for your specific healthcare needs.
6. Uncovered Services: There may be certain stress test services or components that are not covered by your insurance plan. This could include additional diagnostic tests, follow-up visits, or specific types of stress tests. It is important to discuss these aspects with your healthcare provider and insurance company to understand the potential costs.
Remember, every insurance plan is different, so it is essential to review your policy documents, contact your insurance provider, or consult with a healthcare professional to fully understand the coverage and potential costs associated with stress tests.
Factors Affecting Cost
The cost of a stress test can vary depending on several factors. Understanding these factors can help you anticipate the potential expenses and make informed decisions. Here are some key factors that can affect the cost of a stress test:
1. Type of Stress Test: The type of stress test you undergo can significantly influence the cost. Exercise stress tests, which involve physical exertion on a treadmill or stationary bike, are generally less expensive compared to pharmacological stress tests that require the administration of medications.
2. Healthcare Facility and Location: The cost of a stress test can vary depending on the healthcare facility and its location. Hospitals or specialized clinics in urban areas tend to have higher overhead costs, which can result in higher prices for the procedure.
3. Health Insurance Coverage: Your health insurance coverage plays a crucial role in determining the final cost of a stress test. The amount covered by insurance, including co-pays, deductibles, and coinsurance, can significantly impact your out-of-pocket expenses. It is important to understand your policy and the specific terms of coverage.
4. Provider Charges: Different healthcare providers may charge varying amounts for the same stress test. Charges can be influenced by factors such as the provider’s experience, reputation, and the specific facilities and technology utilized during the test.
5. Extra Diagnostic Testing: Depending on the results of the stress test and the specific circumstances, additional diagnostic tests, such as cardiac imaging or angiography, may be necessary. These additional tests can increase the overall cost of the diagnostic process.
6. Geographic Variation: The cost of medical procedures can vary significantly depending on geographic location. Factors such as local healthcare market competition, regional economic factors, and healthcare provider reimbursement rates can influence the price of a stress test in different areas.
7. Additional Services and Follow-up: Post-stress test services and follow-up visits could result in additional costs. This may include consultation fees, further testing, or visits with specialists or cardiologists for result interpretation and treatment planning, if necessary.
It is important to keep in mind that these factors can interact and affect the overall cost of a stress test. To get a clear estimate of the cost, it is recommended to consult with your healthcare provider and insurance company, as they can provide more specific information based on your individual circumstances.
Average Cost of Stress Tests With Insurance
It is challenging to provide an exact average cost for stress tests with insurance coverage, as it can vary significantly depending on various factors such as location, healthcare facility, and insurance plan. However, we can provide a general idea of the cost range based on available data and industry insights.
On average, the cost of a stress test with insurance coverage can range from around $500 to $3,000 or more. This range includes factors such as the type of stress test (exercise or pharmacological), the specific facility where the test is conducted, and the terms and coverage of your insurance plan.
Exercise stress tests typically tend to be less expensive, with costs ranging from approximately $500 to $1,500. This is because these tests involve physical exertion on a treadmill or stationary bike and do not require additional medications or specialized interventions.
Pharmacological stress tests, which involve the administration of medications to simulate the effects of exercise, are generally more expensive. The cost of pharmacological stress tests can range from around $1,000 to $3,000 or more.
It is important to remember that these figures are general estimates and can vary considerably based on individual circumstances. The final cost will depend on factors such as your specific insurance plan, deductibles, co-pays, and coinsurance percentages, as well as any additional diagnostic testing or services recommended based on the results of the stress test.
Additionally, it is crucial to confirm with your healthcare provider and insurance company to understand the exact cost and coverage details specific to your situation. The healthcare provider’s billing department or the insurance company’s customer service representatives can provide more accurate information and help you navigate the financial aspects of the stress test.
Remember, it is always advisable to be proactive and discuss the potential cost implications with your healthcare provider and insurance company to ensure you are well-informed and prepared for any out-of-pocket expenses associated with the stress test.
Variations in Cost Among Healthcare Providers
When it comes to the cost of stress tests, there can be significant variations among different healthcare providers. These variations can be influenced by several factors, including the provider’s location, reputation, facilities, and the specific terms negotiated with insurance companies. Understanding these variations is essential to make informed decisions regarding your healthcare expenses. Here are some key points to consider:
Geographic Location: The location of the healthcare provider can have a direct impact on the cost of a stress test. Prices can differ significantly between urban and rural areas due to variations in overhead costs, competition, and local economic factors. Providers located in areas with higher living expenses and operating costs generally tend to charge more for their services.
Provider Reputation and Expertise: The reputation and expertise of a healthcare provider can influence the cost of a stress test. Providers who are well-established, renowned, or have specialized expertise may charge higher fees for their services. They may also have access to advanced technologies and facilities, which can also impact the overall cost.
Facilities and Equipment: The quality and sophistication of the facilities and equipment used by a healthcare provider can affect the cost of a stress test. Providers with state-of-the-art facilities and advanced diagnostic technologies may charge higher fees to cover the expenses associated with maintaining and operating these resources.
Negotiated Rates with Insurance Companies: Healthcare providers negotiate rates with insurance companies for the services they offer. These negotiated rates can vary between different providers. As a result, the amount billed by a provider for a stress test may differ from one facility to another, based on the agreements they have established with insurance companies.
In-Network vs. Out-of-Network Providers: If you have health insurance, choosing an in-network provider can often result in lower out-of-pocket costs. In-network providers have agreements with insurance companies to provide services at negotiated rates, ensuring that your insurance coverage is maximized. Out-of-network providers, on the other hand, may charge higher fees, and you may be responsible for a greater proportion of the cost.
Considering these variations, it is vital to research different healthcare providers in your area, compare costs, and evaluate their reputation and facilities before undergoing a stress test. Consulting with your insurance company to determine their preferred providers and confirming coverage details can also help you make an informed decision and potentially save on expenses.
Keep in mind that while cost is an important factor, it is essential to balance it with other factors such as quality of care, provider expertise, and convenience when choosing a healthcare provider for your stress test.
Out-of-Pocket Costs for Stress Tests
When it comes to stress tests, there may be out-of-pocket costs that you are responsible for, even if you have insurance coverage. Understanding these potential expenses is crucial to avoid any surprises and effectively plan for your healthcare expenses. Here are some common out-of-pocket costs associated with stress tests:
Co-pays: A co-pay is a fixed amount that you are required to pay at the time of the stress test. The specific co-pay amount depends on your insurance plan and can vary from as low as $10 to $50 or more. It is important to check your insurance policy to determine the exact co-pay amount you may be responsible for.
Deductibles: A deductible is the amount you must pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage begins. For stress tests, you may have to meet your deductible first, and then insurance will start covering a portion or the full cost of the test. Deductibles can range from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars. Make sure to review your insurance policy to understand your deductible amount.
Coinsurance: Coinsurance is the percentage of the cost that you are responsible for after meeting your deductible. For example, if your coinsurance is 20%, you would be responsible for paying 20% of the cost of the stress test, while the insurance would cover the remaining 80%. The specific coinsurance percentage can vary depending on your insurance plan.
Out-of-Network Costs: If you choose to undergo a stress test at a healthcare provider that is out of network for your insurance, you may be subject to higher out-of-pocket costs. Out-of-network providers may not have negotiated rates with your insurance company, resulting in higher fees and potentially a larger portion of the cost being your responsibility.
Uncovered Services: It is important to understand that certain services or components of the stress test may not be covered by your insurance plan. This could include additional diagnostic testing, follow-up visits, or specific types of stress tests. You may be responsible for the full cost of these uncovered services.
Remember to review your insurance policy carefully to understand the specific out-of-pocket costs associated with stress tests. Contacting your insurance company or speaking with their customer service representatives can help you clarify any confusion and get a clearer idea of your financial responsibilities.
Additionally, considering the potential out-of-pocket costs can aid in comparing different healthcare providers and making informed decisions based on your budget and coverage. To minimize out-of-pocket expenses, it is advisable to choose in-network providers and facilities, when possible, and to discuss cost-saving options with your healthcare provider and insurance company.
Tips for Minimizing Stress Test Costs
Stress tests are vital diagnostic procedures, but they can come with expenses. However, there are several strategies you can employ to minimize the costs associated with stress tests. Consider the following tips when undergoing a stress test:
1. Review Your Insurance Coverage: Familiarize yourself with your insurance policy and specifically understand the coverage for stress tests. Take note of co-pays, deductibles, and coinsurance percentages. Understanding what your insurance covers will help you plan for potential expenses.
2. Choose In-Network Providers: Opt for healthcare providers and facilities that are in-network with your insurance plan. In-network providers have negotiated rates with your insurance company, resulting in lower out-of-pocket costs for you.
3. Seek Pre-Authorization: Some insurance plans require pre-authorization or referrals before undergoing a stress test. Be sure to follow the necessary procedures to avoid any potential claim denials or increased out-of-pocket expenses.
4. Compare Costs: Research and compare the costs of stress tests among different healthcare providers. Request estimates and compare the fees, taking into consideration factors such as reputation, quality of care, and location.
5. Ask About Cash or Self-Pay Discounts: Inquire if the healthcare provider offers cash or self-pay discounts. Some facilities may provide discounts for patients who pay out-of-pocket at the time of service.
6. Explore Financial Assistance Programs: Determine if you qualify for any financial assistance or payment plans offered by the healthcare provider or through local organizations. Some facilities have programs in place to help individuals manage medical expenses.
7. Consider Clinical Trials: Clinical trials for stress tests may offer the opportunity to undergo the procedure at reduced or no cost. Speak with your healthcare provider or explore research institutions to see if you qualify for any ongoing trials.
8. Discuss Alternative Testing Options: Engage in a conversation with your healthcare provider to explore alternative diagnostic tests that may be more cost-effective but still provide reliable results. In some cases, certain types of stress tests may be unnecessary, depending on your specific medical needs.
9. Review the Billing Statement: Carefully review the billing statement from your healthcare provider to ensure accuracy. Mistakes can happen, and you want to avoid being charged for services you did not receive.
10. Seek Financial Counseling: If you anticipate challenges in paying for a stress test, seek financial counseling from the healthcare provider’s billing department or consult with a financial advisor. They can guide you through potential options and help you manage the costs effectively.
Remember, it is crucial to balance cost considerations with the quality of care and expertise provided. Your health should always be the primary focus, but implementing these strategies can help you navigate the financial aspect of stress tests more efficiently.
Conclusion
Stress tests are valuable tools in diagnosing and monitoring heart conditions, allowing healthcare providers to assess the functionality and health of the cardiovascular system. While the cost of stress tests can vary based on factors such as the type of test, location, and insurance coverage, understanding the associated expenses is crucial for effective financial planning.
Insurance coverage plays a significant role in determining the cost of stress tests, with factors such as co-pays, deductibles, and coinsurance impacting the out-of-pocket expenses. Reviewing your insurance policy, choosing in-network providers, and seeking pre-authorization can help minimize costs.
It is also important to consider variations in costs among different healthcare providers due to factors such as location, reputation, and negotiated rates with insurance companies. Comparing costs and seeking out cash discounts or financial assistance programs can help reduce expenses.
To further minimize stress test costs, exploring alternative testing options and participating in clinical trials may be options worth considering. Additionally, maintaining open communication with your healthcare provider and reviewing billing statements can help ensure accuracy and prevent unnecessary charges.
In conclusion, while stress tests are essential for diagnosing and managing heart conditions, it is possible to take steps to minimize associated costs. By being proactive, understanding your insurance coverage, exploring cost-saving strategies, and seeking financial guidance, you can navigate the financial aspect of stress tests more effectively, allowing you to prioritize your cardiovascular health without undue financial burden.