
Finance
How Much Does An EEG Cost Without Insurance
Published: November 23, 2023
Find out the cost of an EEG without insurance and explore your financing options. Get the financial assistance you need for your neurological testing.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
An EEG (electroencephalogram) is a diagnostic procedure that measures the electrical activity of the brain. It is commonly used to diagnose and monitor various neurological conditions such as epilepsy, sleep disorders, and brain injuries. The test involves placing electrodes on the scalp to detect and record the brain’s electrical signals.
While an EEG is a valuable tool in assessing brain function, one consideration when undergoing this procedure is the cost, especially for individuals without insurance coverage. The cost of an EEG can vary depending on several factors, including the location, the healthcare provider, and the specific requirements of the patient.
In this article, we will explore the factors that influence the cost of an EEG without insurance, provide an estimation of the average cost, and discuss ways individuals can potentially reduce these expenses. Additionally, we will also touch upon government programs and assistance that may be available to help mitigate the financial burden of obtaining an EEG.
It is important to note that the information provided in this article serves as a general guide, and actual costs may vary depending on individual circumstances. It is always recommended to consult with healthcare providers and insurance providers for accurate cost estimates and coverage options.
Understanding EEG
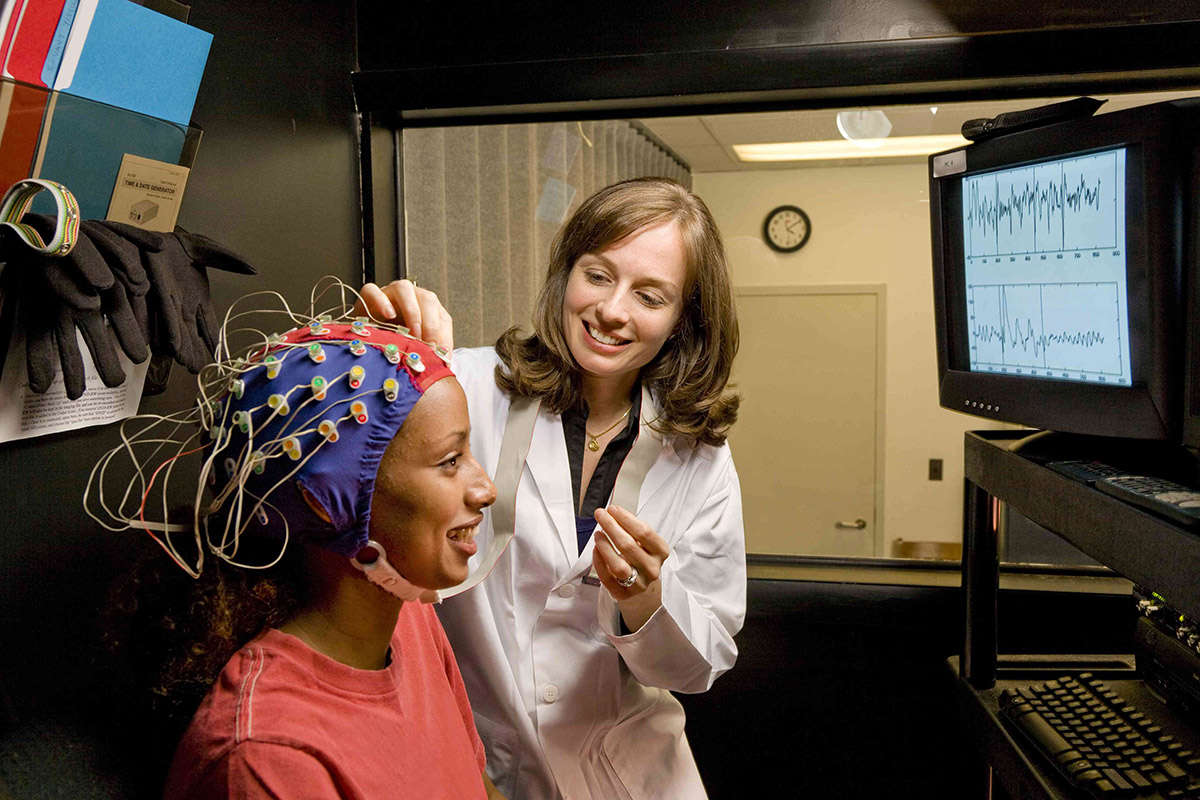
An EEG, or electroencephalogram, is a non-invasive procedure used to measure the electrical activity of the brain. The test records the brain’s electrical signals through small metal discs called electrodes, which are placed on the scalp. These electrodes detect and amplify the brain’s electrical activity, translating it into a visual representation known as an EEG waveform.
The EEG provides valuable information about the brain’s activity, allowing healthcare professionals to assess neurological conditions and monitor brain function. It is commonly used in the diagnosis and management of epilepsy, as well as other conditions such as sleep disorders, brain tumors, and cognitive disorders.
During an EEG, the patient lies down in a comfortable position while the electrodes are attached to their scalp using a conductive gel. The procedure itself is painless and typically takes about one hour to complete. It is important for patients to follow instructions regarding medication restrictions or fasting prior to the test, as these may impact the accuracy of the results.
The EEG results are interpreted by neurologists or other trained healthcare providers. They analyze the patterns and abnormalities in the brain’s electrical activity, which can help diagnose conditions such as epilepsy seizures, sleep disorders, or indicate the presence of abnormal brain activity caused by tumors or injuries.
Overall, the EEG is a valuable tool in understanding brain function and diagnosing neurological conditions. By providing insight into the electrical activity of the brain, it helps healthcare professionals make informed decisions regarding treatment options and management strategies for their patients.
Factors Affecting EEG Costs
The cost of an EEG can vary depending on a variety of factors. Understanding these factors can help individuals estimate and plan for the expenses associated with the procedure. Here are some key factors that influence the cost of an EEG:
- Location: The geographical location can have a significant impact on the cost of an EEG. Healthcare costs can vary between regions, with prices generally being higher in urban areas compared to rural locations.
- Healthcare Provider: The choice of healthcare provider also affects the cost. Larger medical institutions and specialty neurological centers may charge higher fees compared to smaller clinics or outpatient facilities.
- Type of Facility: The type of facility where the EEG is performed can impact the cost. EEGs performed in hospitals generally tend to be more expensive compared to those conducted in independent diagnostic centers or clinics.
- Additional Tests and Services: Depending on the patient’s condition and the healthcare provider’s recommendations, additional tests or services may be required alongside the EEG. These can include sleep-deprived EEGs, prolonged EEG monitoring, or video monitoring. Each additional test or service will contribute to the overall cost.
- Healthcare Provider’s Expertise: The expertise and reputation of the healthcare provider performing the EEG can also affect the cost. Providers with extensive experience and specialization in neurology may have higher fees compared to those with less experience.
- Insurance Coverage: For individuals with insurance coverage, the cost of an EEG will depend on the terms of their policy. Factors such as deductibles, co-pays, and in-network versus out-of-network providers can all play a role in determining the amount individuals will need to pay.
It is important to note that while these factors influence the cost of an EEG, they are not exhaustive or universally applicable. Prices can vary significantly, and it is essential to consult with healthcare providers and insurance companies for accurate cost estimates specific to individual circumstances.
Average Cost of EEG Without Insurance
The cost of an EEG without insurance coverage can vary depending on several factors previously mentioned. On average, the cost of a basic EEG without additional tests or services can range from $500 to $2,000 or more.
However, it is important to note that these figures are approximate and can vary significantly depending on location, healthcare provider, and individual circumstances. The cost can be higher in metropolitan areas or renowned medical institutions compared to smaller clinics or independent diagnostic centers.
Patients without insurance should also consider that the cost of an EEG may include additional expenses beyond the procedure itself. These may include consultation fees, the cost of the initial appointment with a neurologist, and the fees associated with interpreting the EEG results by a medical professional.
It is crucial for individuals without insurance coverage to inquire about self-pay or discounted rates. Some healthcare providers offer discounted rates for patients without insurance, or they may offer payment plans to make the cost more manageable. Exploring options such as these can help individuals without insurance access the necessary healthcare services at a more affordable price.
Moreover, it is worth mentioning that the cost of an EEG can be higher for individuals requiring additional tests or services beyond a basic EEG. For instance, a sleep-deprived EEG or a prolonged monitoring EEG can involve additional charges that should be factored into the overall cost.
As the cost of healthcare services can vary significantly, it is always advised to contact multiple healthcare providers to obtain cost estimates specific to individual circumstances. This will help individuals without insurance make informed decisions and plan for the financial aspects of undergoing an EEG.
Ways to Reduce EEG Costs
For individuals without insurance coverage or facing high out-of-pocket expenses for an EEG, there are several strategies to help reduce the overall cost. Consider the following options to make the procedure more affordable:
- Shop around for competitive prices: Contact different healthcare providers, clinics, and hospitals to compare the cost of an EEG. Prices can vary significantly, so it’s worth exploring multiple options to find the most affordable choice.
- Inquire about self-pay or discounted rates: Some healthcare providers offer discounted rates or self-pay options for individuals without insurance. Inquire about these options and negotiate the cost of the procedure to make it more affordable.
- Look into outpatient facilities: Consider having the EEG performed at an outpatient facility rather than a hospital. Outpatient centers often have lower overhead costs, which can translate into more affordable prices for patients.
- Ask about payment plans: Inquire with the healthcare provider about the possibility of setting up a payment plan. Spreading out the cost of the EEG over several installments can make it more manageable financially.
- Seek financial assistance programs: Research and inquire about financial assistance programs that may be available to help cover the cost of medical procedures. Some hospitals and charitable organizations offer assistance to individuals without insurance coverage.
- Consider clinical trials or research studies: Some research institutions conduct clinical trials or research studies involving EEGs. Participating in these studies may provide access to the procedure at a reduced cost or even free of charge.
- Explore government programs and assistance: Look into government programs such as Medicaid or Medicare that may provide coverage for EEGs or offer financial assistance. Eligibility and coverage can vary, so it is important to check the specific requirements.
Remember, it is essential to discuss these options and negotiate with healthcare providers to find the best solution to reduce EEG costs. Clear communication and thorough research can significantly impact the final expense of the procedure.
Government Programs and Assistance for EEG Costs
Individuals facing financial difficulties and unable to afford the cost of an EEG may be eligible for government programs and assistance that can help alleviate the financial burden. Here are some options to consider:
- Medicaid: Medicaid is a government healthcare program that provides coverage for low-income individuals and families. The eligibility requirements and coverage can vary depending on the state, but in certain cases, Medicaid may cover the cost of an EEG. Check with your state’s Medicaid program to determine if you qualify and what the coverage entails.
- Medicare: Medicare is a federal health insurance program primarily for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as certain younger individuals with disabilities. Medicare may cover the cost of an EEG if it is deemed medically necessary. However, coverage can vary depending on the specific Medicare plan you have.
- Charitable organizations: Some charitable organizations and foundations offer financial assistance for medical procedures, including EEGs. These organizations may have specific criteria for eligibility, so it is important to research and reach out to them to inquire about available assistance.
- State-specific healthcare programs: Some states have healthcare programs designed to assist individuals without insurance coverage. These programs may provide options for low-cost or free EEG services. Research the healthcare programs in your state to see if they offer any assistance for EEG costs.
- Veterans Affairs (VA) benefits: Veterans may be eligible for healthcare benefits through the Department of Veterans Affairs. The VA may cover the cost of an EEG for eligible veterans. Veterans should reach out to their local VA facility to inquire about coverage and eligibility.
It is important to note that eligibility requirements and coverage for government programs can vary, and there may be waiting periods or limitations associated with these programs. It is advisable to contact the relevant program or agency directly for detailed information on eligibility and coverage.
If you are unsure about which government program or assistance option is available to you or whether you qualify, consider contacting a local healthcare navigator, social worker, or patient advocacy organization. These resources can guide you through the process and provide information specific to your situation.
Remember, government programs and assistance options are designed to help individuals access necessary healthcare services, so it’s worth exploring these avenues if you are in need of financial support for an EEG.
Conclusion
The cost of an EEG without insurance coverage can be a significant concern for individuals seeking neurological diagnostics. It is essential to understand the factors that influence the cost and explore various avenues to reduce expenses. By shopping around, inquiring about self-pay or discounted rates, and considering outpatient facilities, individuals can potentially find more affordable options for their EEG.
It is also important to explore government programs and assistance options that may provide financial relief. Medicaid, Medicare, state-specific healthcare programs, and charitable organizations can offer support to individuals without insurance coverage. Additionally, veterans may have access to EEG coverage through the Department of Veterans Affairs.
While the cost of an EEG can vary depending on factors such as location, healthcare provider, and additional tests or services required, it is crucial for individuals to proactively research and seek cost estimates from multiple sources. Communication with healthcare providers, negotiating payment plans, and exploring financial assistance programs can make the overall cost of an EEG more manageable.
Ultimately, the goal is to ensure that individuals have access to the necessary diagnostic procedures without facing excessive financial burden. It is recommended to consult with healthcare providers, insurance companies, and local resources to fully understand the options available for EEG cost reduction and financial assistance.
Remember, your brain health is invaluable, and seeking proper diagnosis and treatment is crucial. By exploring different options, individuals can find affordable ways to obtain an EEG and receive the neurological care they need.