Home>Finance>How Much Of A Loan Can I Get With A 650 Credit Score


Finance
How Much Of A Loan Can I Get With A 650 Credit Score
Modified: February 21, 2024
Finance your dreams with a 650 credit score – find out how much you can borrow and take the next step towards your goals.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Credit Scores
- How Credit Scores Affect Loan Eligibility
- Factors to Consider for Loan Approval
- Loan Types and Credit Score Requirements
- Maximum Loan Amounts Based on Credit Score
- Improving Credit Score to Increase Loan Eligibility
- Alternative Options for Borrowing with a 650 Credit Score
- Conclusion
Introduction
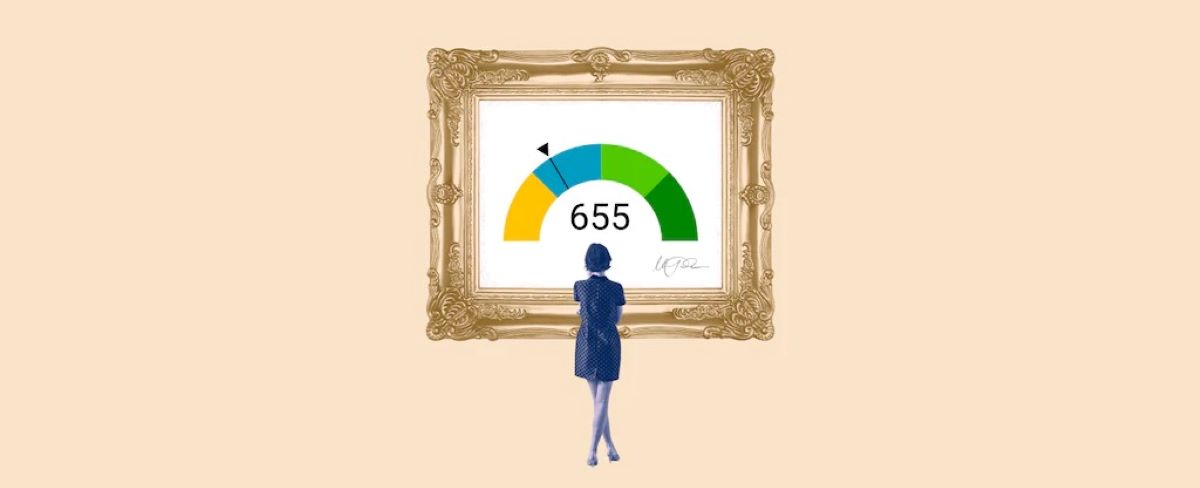
When it comes to borrowing money, your credit score can play a crucial role in determining the loan amount you can qualify for. A credit score is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness and serves as an indicator of how likely you are to repay a loan. Lenders use credit scores to assess the risk associated with lending money to individuals.
In this article, we will explore how much of a loan you can get with a credit score of 650. We will also delve into the factors that affect loan eligibility and discuss strategies to improve your credit score to increase your borrowing options.
It’s important to note that while credit scores are an essential factor in the loan approval process, they are not the only criteria considered by lenders. Other factors such as income, employment history, and debt-to-income ratio also play a significant role in determining your loan eligibility.
So, if you have a credit score of 650, let’s dive into the world of loans and find out what options are available to you.
Understanding Credit Scores
Credit scores are three-digit numbers that are calculated based on your credit history. They range from 300 to 850, with a higher score indicating a better creditworthiness. Credit scores are generated by credit reporting agencies, such as Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion, using a statistical algorithm that takes into account various factors.
The primary factors that influence your credit score include:
- Payment History: This accounts for the largest portion of your credit score. It reflects how consistently you make your debt payments, including credit cards, loans, and mortgages. A history of late payments can significantly impact your credit score.
- Credit Utilization: This refers to the amount of credit you are currently using compared to your total available credit. Keeping your credit utilization below 30% is generally recommended for maintaining a good credit score.
- Length of Credit History: The length of time you have been using credit also plays a role in determining your credit score. A longer credit history with responsible borrowing behavior is usually a positive indicator for lenders.
- Types of Credit: Your credit mix, including revolving accounts (credit cards) and installment loans (mortgages, auto loans), can impact your credit score. Having a diverse mix of credit can be beneficial for your score.
- New Credit Inquiries: Whenever you apply for new credit, such as a credit card or loan, it results in a hard inquiry on your credit report. Too many recent inquiries can temporarily lower your credit score.
It’s important to regularly monitor your credit score and credit report to keep track of any changes or potential errors. You can access your credit report for free once a year from each of the three credit reporting agencies. If you notice any inaccuracies, make sure to dispute them promptly to maintain an accurate credit profile.
Understanding these factors that contribute to your credit score is crucial in determining the loan options available to you. Now that we have a clear understanding of credit scores, let’s explore how they affect loan eligibility.
How Credit Scores Affect Loan Eligibility
Credit scores play a significant role in determining loan eligibility. Lenders rely on credit scores to assess the level of risk involved in lending money to borrowers. A high credit score indicates a lower risk, making it more likely for lenders to approve your loan application and offer favorable terms, such as lower interest rates and higher loan amounts.
On the other hand, a low credit score can make it more challenging to qualify for loans or result in higher interest rates and more limited loan options. Lenders may perceive individuals with lower credit scores as higher-risk borrowers, which can lead to stricter lending criteria or even loan denial.
When determining loan eligibility, lenders typically set minimum credit score requirements. These requirements vary depending on the type of loan and the lender’s risk tolerance. For example, a mortgage lender might require a minimum credit score of 620, while an auto lender might have a minimum requirement of 650.
In addition to meeting the minimum credit score requirement, lenders also consider other factors, such as income, employment history, and debt-to-income ratio. These factors provide lenders with a more comprehensive picture of your overall financial situation and your ability to repay the loan.
It’s important to note that while a credit score is a significant factor in loan eligibility, it is not the only factor. Lenders will assess your creditworthiness holistically, taking into account various aspects of your financial profile. So, even if you have a credit score that falls within the acceptable range, a lender may still decline your loan application if other aspects of your financial situation raise concerns.
Understanding how credit scores impact loan eligibility is crucial in managing your financial goals. In the next section, we will discuss key factors to consider for loan approval beyond credit scores.
Factors to Consider for Loan Approval
While credit scores play a significant role in loan approval, lenders consider several other factors when evaluating loan applications. Understanding these factors can help you prepare and increase your chances of securing a loan:
- Income and Employment History: Lenders want assurance that you have a stable income and a consistent employment history. A higher income and longer job tenure contribute to your loan eligibility, as they demonstrate your ability to repay the loan.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI): Your DTI ratio compares your monthly debt payments to your monthly income. Lenders prefer borrowers with lower DTI ratios as it indicates a lower risk of default. Aim to keep your DTI ratio below 43% to increase your chances of loan approval.
- Collateral: Secured loans, such as mortgages or auto loans, may require collateral. Collateral is an asset that you pledge to the lender as a guarantee for repayment. Having valuable collateral can improve your chances of loan approval and potentially allow you to borrow larger amounts.
- Loan Purpose: Some lenders may consider the purpose of your loan before approving your application. For example, if you’re borrowing for education or starting a business, they might evaluate the feasibility and potential for repayment.
- Cash Reserves: Lenders may want to see that you have sufficient cash reserves to cover unexpected expenses or emergencies. Having a solid savings account can increase your loan eligibility and demonstrate responsible financial management.
By considering these factors, lenders can assess your overall financial situation and determine the risk associated with lending to you. It’s essential to present a strong financial profile that showcases your ability to repay the loan and manage your financial obligations responsibly.
Now that we have explored the key factors for loan approval, let’s delve into different types of loans and their credit score requirements.
Loan Types and Credit Score Requirements
Various loan types have different credit score requirements. Here are a few common loan types and the typical credit score ranges lenders look for:
- Mortgages: To qualify for a conventional mortgage, lenders generally prefer a credit score of 620 or higher. However, certain government-backed loans like FHA loans may accept lower credit scores, sometimes as low as 500-580, with specific requirements.
- Auto Loans: For auto loans, credit score requirements can vary. Generally, a credit score of 650 or higher is considered good for securing favorable auto loan terms. However, it’s possible to get an auto loan with a lower credit score, albeit with higher interest rates.
- Personal Loans: Personal loans are unsecured loans, meaning they do not require collateral. Credit score requirements typically range from 600 to 700, depending on the lender. Some lenders specialize in providing personal loans to individuals with lower credit scores.
- Student Loans: Federal student loans typically do not have strict credit score requirements, making them accessible to most borrowers. However, private student loans may have more stringent credit score criteria, with lenders typically seeking credit scores of 650 or higher.
- Business Loans: Business loan credit score requirements can vary depending on the type of loan and the lender. Generally, a credit score of 650 or higher is preferred for conventional business loans, while alternative lenders may offer loans to borrowers with lower credit scores.
Keep in mind that these credit score requirements are general guidelines, and individual lenders may have their own specific criteria. It’s always a good idea to research and compare lenders to find the ones that are more flexible with credit score requirements and offer loan terms that suit your needs.
Next, we will discuss strategies to improve your credit score and increase your loan eligibility.
Maximum Loan Amounts Based on Credit Score
The maximum loan amount you can borrow is often influenced by your credit score. Lenders use credit scores as a factor in determining the level of risk associated with lending to you, which can impact the loan amount they are willing to offer. Here’s a general breakdown of how credit scores can affect maximum loan amounts:
- Excellent Credit (750+): Borrowers with excellent credit scores often have access to higher loan amounts. Lenders are more likely to offer larger loans to individuals with excellent credit due to their strong creditworthiness and lower perceived risk.
- Good Credit (700-749): Those with good credit scores still have access to competitive loan amounts. While the maximum loan amounts may not be as high as those with excellent credit, borrowers with good credit are still considered reliable and have a good chance of securing substantial loans.
- Fair Credit (650-699): Borrowers with fair credit scores may find that their loan options are more limited compared to those with higher scores. While it may be more challenging to obtain large loan amounts, there are still lenders who are willing to work with individuals in this credit score range.
- Poor Credit (below 650): Individuals with poor credit scores often face difficulties in obtaining large loan amounts from traditional lenders. However, alternative lending options such as online lenders or credit unions may offer more flexible terms and higher loan amounts for borrowers with poor credit.
It’s important to note that these credit score ranges are generalizations, and lenders may have varying policies and criteria when determining maximum loan amounts. Other factors such as income, employment stability, and debt-to-income ratio also influence the loan amount you can qualify for.
When considering the maximum loan amount, it’s crucial to assess your own financial situation and borrow within your means. Taking on too much debt can lead to financial strain and difficulty in making timely repayments.
Now that we have covered the maximum loan amounts based on credit score, let’s explore strategies to improve your credit score and increase your loan eligibility.
Improving Credit Score to Increase Loan Eligibility
If you have a credit score that may be hindering your loan eligibility, don’t fret. There are several strategies you can implement to improve your credit score and increase your chances of qualifying for better loan options:
- Pay Your Bills on Time: Consistently making your debt payments on time is one of the most effective ways to boost your credit score. Set up automatic payments or reminders to ensure you never miss a payment.
- Reduce Credit Card Balances: High credit card balances can negatively impact your credit utilization ratio. Aim to keep your balances below 30% of your credit limit for each card, or even better, pay them off in full each month.
- Limit New Credit Applications: Each time you apply for new credit, a hard inquiry is added to your credit report, which temporarily lowers your score. Minimize the number of credit applications you submit to avoid unnecessary inquiries.
- Keep Old Credit Accounts: Closing old credit accounts may seem like a good idea, but it can actually hurt your credit score. Keep your oldest accounts open to demonstrate a long credit history and responsible credit management.
- Diversify Your Credit Mix: Having a mix of different types of credit, such as credit cards, loans, and mortgages, can positively impact your credit score. However, only take on new credit if you genuinely need it and can manage it responsibly.
- Review Your Credit Report: Regularly review your credit report for any errors or inaccuracies. Dispute any incorrect information with the credit bureaus to ensure your credit score is based on accurate data.
- Manage Your Debt-to-Income Ratio: Paying down existing debt and avoiding taking on excessive new debt can improve your debt-to-income ratio. Lenders prefer borrowers with a lower DTI ratio, as it reflects a better ability to manage loan repayments.
Improving your credit score takes time and patience. Focus on implementing these strategies consistently and responsibly to see gradual improvements in your creditworthiness. As your credit score increases, you can become eligible for better loan terms and larger loan amounts.
If you need immediate financing and have limited loan options due to your credit score, exploring alternative borrowing options may be worth considering.
Next, we will discuss alternative options for borrowing with a credit score of 650.
Alternative Options for Borrowing with a 650 Credit Score
If you have a credit score of 650 and are unable to qualify for traditional loans or favorable terms, there are alternative options available to meet your borrowing needs:
- Peer-to-Peer Lending: Peer-to-peer lending platforms connect borrowers with individual investors who are willing to lend money. These platforms often have more flexible lending criteria and may consider individuals with lower credit scores.
- Credit Unions: Credit unions are non-profit financial institutions that operate similarly to banks. They generally offer more personalized service and may have more lenient lending criteria for their members, including those with lower credit scores.
- Secured Loans: If you have collateral, such as a vehicle or savings account, you may be able to secure a loan by offering it as security. Secured loans typically have lower credit score requirements and may offer more favorable interest rates.
- Co-Signer: Having a co-signer with a higher credit score can increase your chances of loan approval. A co-signer agrees to be equally responsible for the debt, providing additional assurance to the lender.
- Online Lenders: Online lenders often have more relaxed credit score requirements compared to traditional banks. They may consider a wider range of borrowers and offer loans with varying terms and interest rates.
- Building Credit with Small Loans: Taking out small loans and making consistent, on-time payments can help improve your credit score over time. Consider starting with smaller loan amounts and gradually working your way up as your credit score improves.
While these alternative borrowing options provide alternatives for individuals with a credit score of 650, it’s essential to be cautious and evaluate the terms and interest rates before committing to any loan. Ensure that the loan fits within your budget and that you can comfortably meet the repayment obligations.
It’s also worth noting that improving your credit score should still be a priority. As your credit score increases, you can qualify for better loan options with more favorable terms and interest rates.
Now that we have explored alternative borrowing options, let’s conclude our discussion.
Conclusion
Your credit score plays a crucial role in determining the loan amount you can qualify for and the terms you can secure. While a credit score of 650 may present some challenges in accessing traditional loans or favorable terms, there are still options available to you.
Understanding credit scores and the factors that affect loan eligibility is essential in navigating the borrowing landscape. By focusing on improving your credit score through responsible financial management, such as making timely payments, reducing credit card balances, and managing your debt-to-income ratio, you can gradually increase your loan eligibility.
If you need immediate financing or have difficulties qualifying for traditional loans, explore alternative options like peer-to-peer lending, credit unions, secured loans, having a co-signer, or working with online lenders. These alternatives may offer more flexibility in lending criteria and provide access to the funds you need.
Remember to consider the potential interest rates, terms, and repayment obligations of any loan before making a decision. It is crucial to borrow responsibly and within your means to avoid further financial strain.
In conclusion, a credit score of 650 does not need to hinder your borrowing options. By understanding the loan requirements, improving your credit score, and exploring alternative lending sources, you can increase your chances of securing the loan you need and achieving your financial goals.