Finance
How To Trade Credit Spreads
Modified: January 15, 2024
Learn how to trade credit spreads in the finance market and increase your profitability with our comprehensive guide on credit spread trading strategies.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of credit spreads! If you’re looking to enhance your trading portfolio and diversify your investment strategies, credit spreads can offer you a unique opportunity. In this guide, we will explore the world of credit spreads, discuss their benefits, and walk you through the process of trading them effectively. Whether you’re new to options trading or have some experience under your belt, understanding credit spreads can be highly beneficial.
Credit spreads are a popular options trading strategy that involves simultaneously buying and selling options contracts on the same underlying asset. The goal is to capitalize on the difference in premium prices between the two options. By creating a spread between the purchase and sale price, traders can generate income and limit their risk exposure.
The main advantage of credit spreads is that they allow you to take advantage of time decay, also known as theta, which erodes the value of options as they approach expiration. This means you can profit from the passage of time, regardless of the direction the market moves.
Another benefit of credit spreads is risk management. Unlike buying individual options, credit spreads provide built-in risk parameters. You know the maximum potential loss upfront, which allows for better risk management and portfolio protection.
Before diving into the intricacies of credit spreads, it is crucial to understand the basics of options trading, including calls, puts, and the concept of premium. Options give you the right to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price, known as the strike price, within a specified timeframe. The premium is the price paid for the option contract.
Now that we have covered the fundamentals, let’s explore the benefits of trading credit spreads and how they can fit into your trading strategy.
What are Credit Spreads?
Credit spreads are an options trading strategy that involves the simultaneous buying and selling of options contracts on the same underlying asset. Specifically, a credit spread refers to a type of options spread where the premium received from selling a higher-priced option is greater than the premium paid for buying a lower-priced option.
There are two main types of credit spreads: bull put spreads and bear call spreads. A bull put spread involves selling a put option with a higher strike price and simultaneously buying a put option with a lower strike price. On the other hand, a bear call spread involves selling a call option with a lower strike price and buying a call option with a higher strike price.
The intention behind trading credit spreads is to generate income by collecting the difference in premium between the options contracts. This income is credited to the trader’s account as soon as the trade is executed. The maximum profit potential of a credit spread is the difference in strike prices minus the net premium paid or received.
One of the key features of credit spreads is that they can be both bullish or bearish strategies. Bull put spreads are typically used when a trader expects the underlying asset’s price to rise or remain stable. Meanwhile, bear call spreads are employed when a trader anticipates the underlying asset’s price to decline or consolidate.
Credit spreads provide traders with a limited risk and potential reward structure. The maximum loss is limited to the difference between the strike prices minus the net premium received or paid. This predefined risk makes credit spreads an attractive strategy for risk-conscious traders who want to define and limit their downside exposure.
It’s important to note that credit spreads come with trade-offs. While you enjoy limited risk, the potential reward is also limited. The income received from the spread is the maximum profit attainable, and the underlying asset’s price must stay within a specific range for the trader to realize the maximum gain.
Now that we understand the concept of credit spreads and their basic structure, let’s explore the benefits of incorporating this strategy into your trading repertoire.
Benefits of Trading Credit Spreads
Trading credit spreads offers a range of benefits that make them an attractive strategy for options traders. By incorporating credit spreads into your trading repertoire, you can take advantage of the following advantages:
- Defined Risk: One of the key benefits of credit spreads is that they come with a defined risk. The maximum loss is limited to the difference in strike prices minus the net premium received or paid. This predefined risk allows traders to have better risk management and control over their positions, reducing the potential for catastrophic losses.
- Income Generation: Credit spreads allow traders to generate income upfront. By selling options with higher premiums and simultaneously buying options with lower premiums, traders receive a net credit to their account. This income is collected as soon as the trade is executed, providing traders with immediate cash flow.
- Time Decay advantage: Another advantage of credit spreads is the ability to profit from time decay, also known as theta decay. As time passes, the value of options contracts erodes, and credit spreads benefit from this decay. Traders can profit from the passage of time, regardless of the direction the underlying asset moves.
- Flexibility in market direction: Credit spreads can be employed in both bullish and bearish market conditions. Bull put spreads are used when traders expect an upward or stable movement in the underlying asset, while bear call spreads are utilized when traders anticipate a downward or sideways movement. This flexibility allows traders to adapt their strategies to various market scenarios.
- Lower margin requirements: Compared to other options strategies, credit spreads typically require lower margin requirements. This makes credit spreads more accessible to traders with limited capital or those who want to deploy their capital more efficiently.
- Portfolio diversification: Credit spreads provide an additional tool for diversifying an investment portfolio. By incorporating credit spreads alongside other trading strategies, traders can spread their risk and potentially enhance their portfolio returns.
These benefits make credit spreads a popular choice among options traders who seek income generation, risk management, and flexibility in their trading strategies. However, it’s important to remember that no strategy is foolproof, and adequate education, risk management, and analysis are still essential for successful trading.
Now that we understand the advantages of trading credit spreads, let’s move on to understanding how to choose the underlying assets for your credit spread trades.
How to Choose the Underlying Assets
Choosing the right underlying assets is a crucial step in trading credit spreads. The underlying asset refers to the security or instrument that the options contracts are based on. To increase the probability of success and maximize returns, consider the following factors when selecting underlying assets for your credit spread trades:
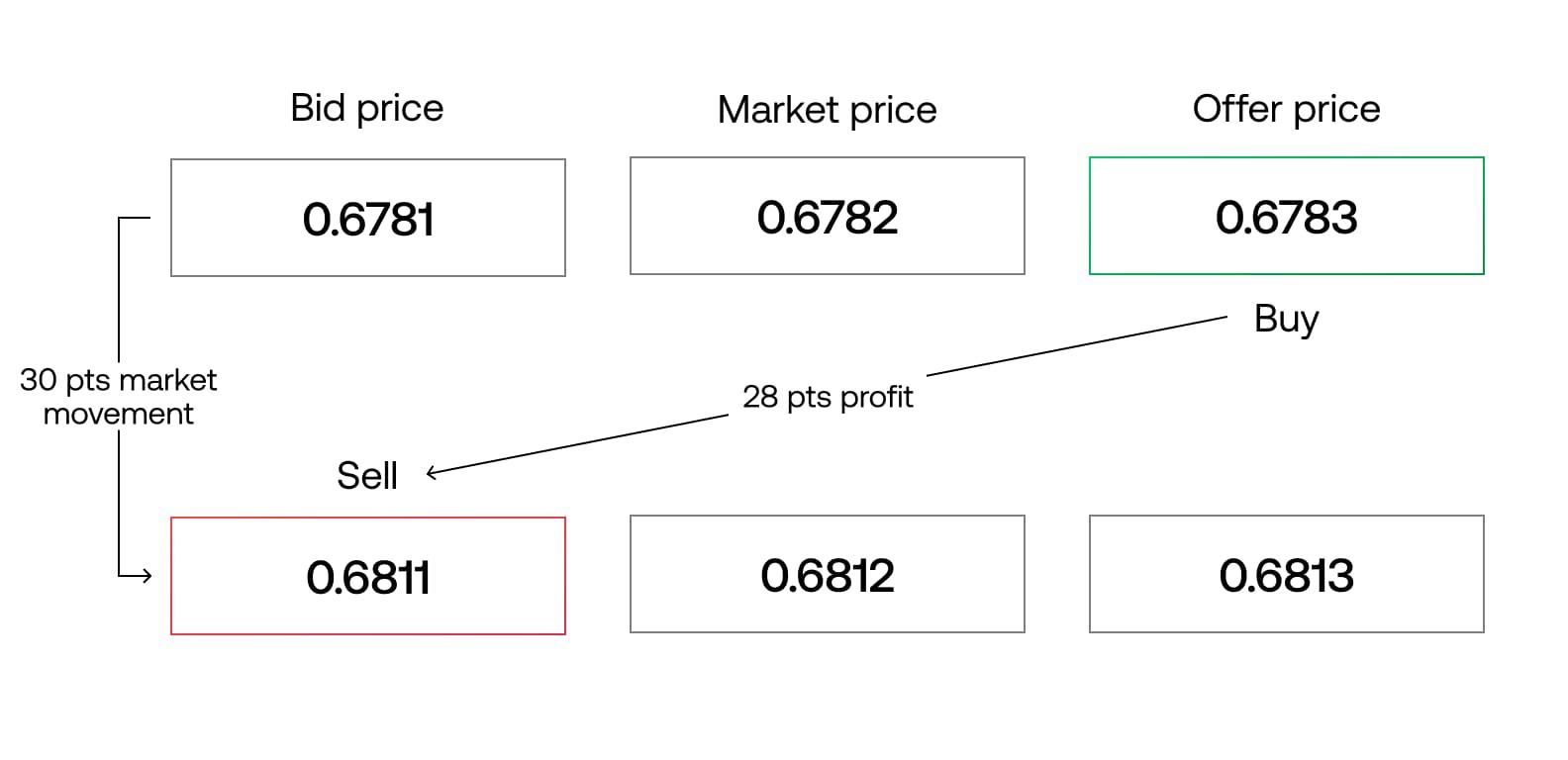
- Liquidity: It is important to choose underlying assets with sufficient liquidity. Higher liquidity ensures that there are enough buyers and sellers in the market to execute trades smoothly. Liquid assets typically have tighter bid-ask spreads, reducing transaction costs and minimizing slippage.
- Volatility: Volatility plays a crucial role in credit spread trading. Look for assets with a reasonable level of volatility, as it provides opportunities for larger price movements and potential profit potential. Higher volatility can result in wider options premiums, making credit spread trades more lucrative.
- Correlation: Consider the correlation between the underlying asset and the overall market or sector. Understanding the relationship can help gauge the potential impact of market movements on the asset’s price and improve trade selection.
- Earnings and News: Take into account significant upcoming events such as earnings releases, economic reports, or other market-moving news. These events can introduce additional volatility and unpredictability, which may affect the success of credit spread trades.
- Stock Selection Criteria: Develop a set of criteria for selecting individual stocks, such as fundamental analysis, technical analysis, or a combination of both. Factors to consider may include the company’s financial health, industry trends, historical price patterns, and analyst ratings.
- Diversification: Consider spreading your credit spread trades across different asset classes, sectors, and expiration dates. Diversification can help mitigate risk and reduce the impact of a single position or sector on your overall portfolio.
- Personal Knowledge and Interest: It can be beneficial to focus on assets that you have a strong understanding of or a personal interest in. Familiarity with the asset can aid in analyzing market trends, interpreting news, and making informed trading decisions.
Keep in mind that the selection of underlying assets will depend on your personal trading style, risk tolerance, and market conditions. It is essential to conduct thorough research, use technical analysis tools, and stay updated with market news to identify potential trading opportunities.
Once you have chosen the underlying assets for your credit spread trades, the next step is to understand the basic components of a credit spread. Let’s delve into that in the next section.
Basic Components of a Credit Spread
Understanding the basic components of a credit spread is essential for successfully executing these options trading strategies. A credit spread consists of two main components:
- Selling the Option: The first component involves selling an option contract. This can be either a put option or a call option, depending on whether you are using a bull put spread or a bear call spread. When you sell an option, you receive a premium, which represents the income generated from the trade.
- Buying the Option: The second component involves buying an option contract with a different strike price than the one you sold. This purchased option acts as a hedge and limits the potential loss in the trade. The premium paid for this option reduces the overall income generated from the trade but also defines the maximum loss.
Let’s break down these components further:
- Strike Prices: The strike price is the price at which the option can be exercised. In a credit spread, the sold option has a higher strike price, while the bought option has a lower strike price. The difference between the strike prices determines the maximum profit potential and the maximum loss of the credit spread.
- Premiums: The premium is the price of the option contract. When you sell an option, you receive a premium, which is credited to your trading account. When you buy an option, you pay a premium, which is subtracted from your account. The net premium received or paid is calculated by subtracting the premium of the bought option from the premium of the sold option.
- Breakeven Point: The breakeven point in a credit spread trade is the point at which the trade neither generates a profit nor incurs a loss. For a bull put spread, the breakeven point is the lower strike price minus the net premium received. For a bear call spread, the breakeven point is the higher strike price plus the net premium received.
- Maximum Profit: The maximum profit potential of a credit spread depends on the difference in strike prices and the net premium received. It is the net premium received minus any transaction costs. For the trade to realize the maximum profit, the price of the underlying asset must remain between the two strike prices at expiration.
- Maximum Loss: The maximum loss in a credit spread trade is limited to the difference in strike prices minus the net premium received. This is the worst-case scenario and occurs if the price of the underlying asset goes against the anticipated direction. The maximum loss is usually realized when the options are held until expiration.
Understanding these basic components is essential for managing risk, calculating potential gains, and setting up effective credit spread trades. In the next section, we will explore different strategies and factors to consider when identifying the right strategy for your trading goals.
Identifying the Right Strategy
When it comes to credit spread trading, there are various strategies to choose from, each with its own advantages and considerations. To identify the right strategy for your trading goals, it’s important to assess factors such as market conditions, risk tolerance, and profit objectives. Here are a few common credit spread strategies to consider:
- Bull Put Spread: This strategy is used when you have a bullish outlook on the underlying asset. It involves selling a put option with a higher strike price and buying a put option with a lower strike price. The goal is for the underlying asset to remain above the higher strike price by expiration, allowing the spread to expire worthless and the trader to keep the premium received.
- Bear Call Spread: This strategy is employed when you have a bearish view on the underlying asset. It involves selling a call option with a lower strike price and buying a call option with a higher strike price. The objective is for the underlying asset to stay below the lower strike price by expiration, causing both options to expire worthless and resulting in the trader keeping the premium received.
- Iron Condor: This strategy combines both a bull put spread and a bear call spread. It is used when you expect the underlying asset to remain within a specific range. The trader sells a put spread and a call spread simultaneously, with a gap between the strike prices. The goal is for the price of the asset to stay within the range defined by the strike prices of the spreads by expiration.
- Ratio Spreads: Ratio spreads involve an uneven ratio between the number of options contracts bought and sold. These strategies can be used in scenarios where the trader has a bias towards the direction of the underlying asset. Ratio spreads include ratio call spreads and ratio put spreads, and they aim to increase the potential profit through the asymmetric structure of the trade.
- Calendar Spreads: Calendar spreads, also known as time spreads, involve selling an option with a closer expiration date and buying a further out option with the same strike price. This strategy takes advantage of time decay and aims for the options to expire worthless, allowing the trader to keep the premium received. Calendar spreads are employed when you expect the underlying asset to have minimal price movement.
When identifying the right strategy, consider your outlook on the underlying asset, your risk tolerance, and the projected market conditions. It’s important to thoroughly analyze the potential risks and rewards associated with each strategy and select the one that aligns with your trading objectives.
Additionally, it’s crucial to stay updated with market news and perform technical analysis to identify potential entry and exit points. This will help you time your trades effectively and improve your chances of success.
Now that we’ve explored different credit spread strategies, let’s move on to the next step: setting up the trade.
Setting Up the Trade
Setting up a credit spread trade involves a few key steps to ensure a well-executed and strategically planned position. Let’s walk through the process of setting up a credit spread trade:
- Select the Strategy: Based on your market outlook and risk tolerance, choose the most suitable credit spread strategy. Consider factors such as bullish or bearish sentiment, volatility expectations, and potential profit objectives.
- Choose the Underlying Asset: Identify the underlying asset that meets your criteria for liquidity, volatility, and correlation. Conduct thorough research, analyze market trends, and use technical analysis tools to gauge potential price movements.
- Select the Strike Prices: Determine the strike prices for the options contracts in the credit spread. The sold option should have a higher strike price, while the bought option should have a lower strike price. Consider the desired risk-reward ratio and the probability of the underlying asset reaching those levels.
- Calculate the Premiums: Calculate the premiums for both the sold and bought options. The net premium is the difference between the two. Ensure that the net premium received is worth the risk taken and aligns with your profit objectives.
- Set the Trade Parameters: Establish the trade parameters, such as trade size, expiration date, and risk management rules. Determine the maximum loss you are willing to accept and set appropriate position sizing and stop-loss levels.
- Place the Trade: Execute the trade through your chosen brokerage platform. Ensure you review the order details and double-check the strike prices, premium amounts, and other trade parameters before confirming the trade.
- Monitor the Trade: Once the trade is placed, actively monitor the position. Keep an eye on market developments, such as earnings announcements or significant news events, as they might impact the trade. Regularly assess the position’s performance and make adjustments as needed.
It is crucial to have a well-defined trading plan and stick to it throughout the trade. Adhere to your risk management rules, follow a disciplined approach, and avoid emotional decision-making.
Remember that options trading involves risks, and no strategy guarantees success. It is essential to continuously educate yourself, stay informed about market trends, and adapt your trading strategies as needed.
Now that we have covered how to set up a credit spread trade, let’s move on to calculating the potential risk and reward of a trade.
Calculating Risk and Reward
Calculating the potential risk and reward of a credit spread trade is crucial for effective risk management and assessing the profit potential. Here are the key elements to consider when calculating the risk and reward of a credit spread trade:
- Maximum Loss: The maximum loss in a credit spread trade is determined by the difference between the strike prices of the options contracts and the net premium received. This is the maximum amount that can be lost if the trade goes against your expectations. It’s important to consider this maximum loss and ensure it aligns with your risk tolerance.
- Maximum Profit: The maximum profit potential of a credit spread trade is the net premium received. This is the initial credit collected when the trade is executed. To calculate your potential profit, subtract any transaction costs, such as commissions, from the net premium. It’s important to note that the maximum profit is only realized if the underlying asset closes at or above the higher strike price (for a bull put spread) or at or below the lower strike price (for a bear call spread) at expiration.
- Breakeven Point: Determine the breakeven point of the credit spread trade. This is the price at which the trade neither generates a profit nor incurs a loss. For a bull put spread, the breakeven point is the lower strike price minus the net premium received. For a bear call spread, the breakeven point is the higher strike price plus the net premium received. The breakeven point provides a reference point to assess the trade’s profitability.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: Evaluate the risk-reward ratio of the credit spread trade. This is calculated by dividing the potential profit by the maximum loss. A favorable risk-reward ratio indicates that the potential profit is greater than the potential loss, which suggests a more attractive trade setup. Traders often seek higher risk-reward ratios to ensure their potential profits outweigh the potential losses.
- Probability of Success: Assess the probability of the trade’s success based on your analysis and market conditions. Consider factors such as historical price action, technical indicators, and market sentiment. While it’s impossible to predict with certainty, evaluating the probability of success can help you make more informed trading decisions.
By calculating the potential risk and reward of a credit spread trade, you can make more educated decisions about position sizing, trade selection, and risk management. It’s crucial to ensure that the potential reward justifies the potential risk and that the trade aligns with your overall trading strategy and goals.
Remember, trading involves uncertainty, and past performance is not indicative of future results. Practice risk management, stay informed about market developments, and continuously review and adjust your trade strategies as necessary.
Now that we have covered risk and reward calculations, let’s explore the next step: exiting the trade.
Exiting the Trade
Knowing when and how to exit a credit spread trade is crucial for managing risk, capturing profits, and avoiding unnecessary losses. Here are some key considerations for exiting a credit spread trade:
- Expiration: One way to exit a credit spread trade is to let it expire naturally. If the trade is profitable and the underlying asset’s price remains within the desired range, the options contracts will expire worthless, allowing you to keep the premium received. However, it’s important to closely monitor the trade before expiration to ensure it is on track and the risk-reward profile remains favorable.
- Partial Profit Taking: Depending on your profit objectives, you may choose to take partial profits before expiration. If the trade has generated a significant portion of its potential profit and the underlying asset’s price is currently favorable, you can close a portion of the position to secure some profits while leaving a portion open to capture further gains.
- Adjustment or Rolling: In some cases, when the underlying asset’s price moves unfavorably but still within a manageable range, you may consider adjusting or rolling the credit spread. This involves closing one or both legs of the trade and opening new positions with different strike prices or expiration dates. Adjustments allow for potential profit opportunities or risk mitigation, depending on the market conditions.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Implementing stop-loss orders is another way to exit a credit spread trade. A stop-loss order is a pre-set order that automatically closes the trade if the underlying asset’s price reaches a specified level. This helps limit potential losses and protects your trading capital. Determine the appropriate stop-loss level based on your risk tolerance and the inherent volatility of the underlying asset.
- Market Assessment: Continuously assess the market conditions and reassess your trade’s viability. If there are significant changes in the underlying asset’s price action, market sentiment, or other factors that invalidate your initial trade rationale, it may be prudent to exit the trade and protect your capital.
- Profit Targets: Establish profit targets based on your trading plan and risk-reward ratio. If the trade reaches your predetermined profit target, consider closing the position to capture the profits. Keep in mind that setting realistic targets based on market conditions and the trade’s potential is essential.
Exiting the trade requires a combination of vigilance, discipline, and adherence to your trading plan. Regularly monitor the trade’s performance, reassess market conditions, and make informed decisions based on your strategy and risk management rules.
It’s worth noting that every trade is unique, and there is no one-size-fits-all approach to exiting credit spreads. Customizing your exit strategy to match your trading style, risk tolerance, and profit objectives is key to successful trading.
Now that we’ve discussed the process of exiting a credit spread trade, let’s explore some common pitfalls to avoid when trading credit spreads.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While credit spreads can be a valuable trading strategy, there are certain pitfalls that traders should be aware of and strive to avoid. Consider the following common pitfalls to ensure a more successful credit spread trading experience:
- Overleveraging: One of the biggest pitfalls is overleveraging your trades. It may be tempting to deploy a large portion of your capital in credit spreads, especially if the potential returns seem enticing. However, overleveraging increases the risk exposure and can lead to significant losses if the trades move against your expectations. Practice risk management and only allocate a reasonable portion of your capital to each trade.
- Ignoring Risk Management: Failing to implement proper risk management strategies is a major pitfall. Define your risk tolerance, set stop-loss orders, and stick to your predetermined risk-reward ratios. Without proper risk management, losses can quickly escalate, and it becomes challenging to recover from significant drawdowns.
- Trading Illiquid Options: Liquidity is crucial when trading credit spreads. Avoid trading illiquid options with wide bid-ask spreads as it may be difficult to execute trades at desired prices. Limited liquidity can lead to slippage, higher transaction costs, and challenges when exiting trades. Stick to effectively traded options with sufficient volume and tight spreads.
- Chasing Returns: Don’t fall into the trap of chasing high returns without considering the associated risks. Assess the potential profit against the potential loss and determine if the risk-reward ratio is favorable. It’s better to make consistent, controlled profits over time rather than seeking high-risk, high-return trades that can lead to significant losses.
- Ignoring Market Conditions: Failing to adapt to changing market conditions is a common pitfall. Market volatility, economic events, and other factors can impact the success of credit spread trades. Stay updated with market news, analyze market trends, and adjust your strategies accordingly to align with current conditions.
- Emotional Decision-making: Allowing emotions to drive your trading decisions is a pitfall that can lead to poor outcomes. Fear and greed often cloud judgment and can result in impulsive or irrational decisions. Stick to your trading plan, rely on thorough analysis, and avoid making impulsive trades based on emotions.
By being aware of these common pitfalls and actively working to avoid them, you can enhance your credit spread trading success. Consistency, discipline, and a focus on risk management are essential for long-term profitability in options trading.
Now that we’ve discussed the common pitfalls to avoid, let’s wrap up our discussion on credit spreads and their benefits.
Conclusion
Credit spreads offer options traders a versatile and effective strategy to generate income, manage risk, and capitalize on market conditions. With their defined risk, income generation potential, and flexibility in market direction, credit spreads can be a valuable addition to any trading repertoire.
In this guide, we covered the basic concepts of credit spreads, including their definition and benefits. We explored how to choose the underlying assets, the components of a credit spread, and the importance of identifying the right strategy based on market conditions and risk tolerance.
We discussed the process of setting up a credit spread trade, calculating the potential risk and reward, and the importance of proper risk management. We also highlighted the various methods for exiting a trade and the common pitfalls to avoid, such as overleveraging, ignoring risk management, and making emotionally-driven decisions.
Credit spread trading requires ongoing education, analysis of market trends, and disciplined execution. It’s important to continually refine your strategy and adapt to changing market conditions to maximize the potential for success. Remember to conduct thorough research, practice prudent risk management, and be mindful of the potential risks associated with options trading.
By being aware of the benefits, understanding the strategies, and avoiding common pitfalls, you can effectively incorporate credit spreads into your trading approach. Whether you are an experienced trader or new to options, credit spreads offer an opportunity to diversify your portfolio, generate income, and manage risk in an ever-changing market environment.
Remember, successful trading is a continuous journey of learning and adaptation. Keep honing your skills, staying informed, and practicing discipline in your trading decisions. With these strategies and a well-executed credit spread approach, you can strive for consistent profitability in the exciting world of options trading.