Home>Finance>Non-GAAP Earnings: Definition And How They Work In Analysis


Finance
Non-GAAP Earnings: Definition And How They Work In Analysis
Published: December 31, 2023
Discover the definition and importance of Non-GAAP earnings in finance analysis. Learn how they impact financial decision-making and interpretation.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Unlocking the Secrets of Non-GAAP Earnings: A Comprehensive Guide
Welcome to the world of finance, where every number tells a story. As aspiring capitalists, we have all come across the mysterious term Non-GAAP earnings at some point. But what exactly does it mean? And how do these non-standard metrics fit into financial analysis? In this blog post, we will explore the definition of Non-GAAP earnings and delve into their significance in financial analysis. So, grab your calculators and let’s dive in!
Key Takeaways:
- Non-GAAP earnings are financial measures used by companies to present their financial performance excluding certain expenses or gains that they believe do not reflect the ongoing operations of the business.
- While Non-GAAP earnings can provide a clearer picture of a company’s financial health, investors should exercise caution and not solely rely on these measures when making investment decisions.
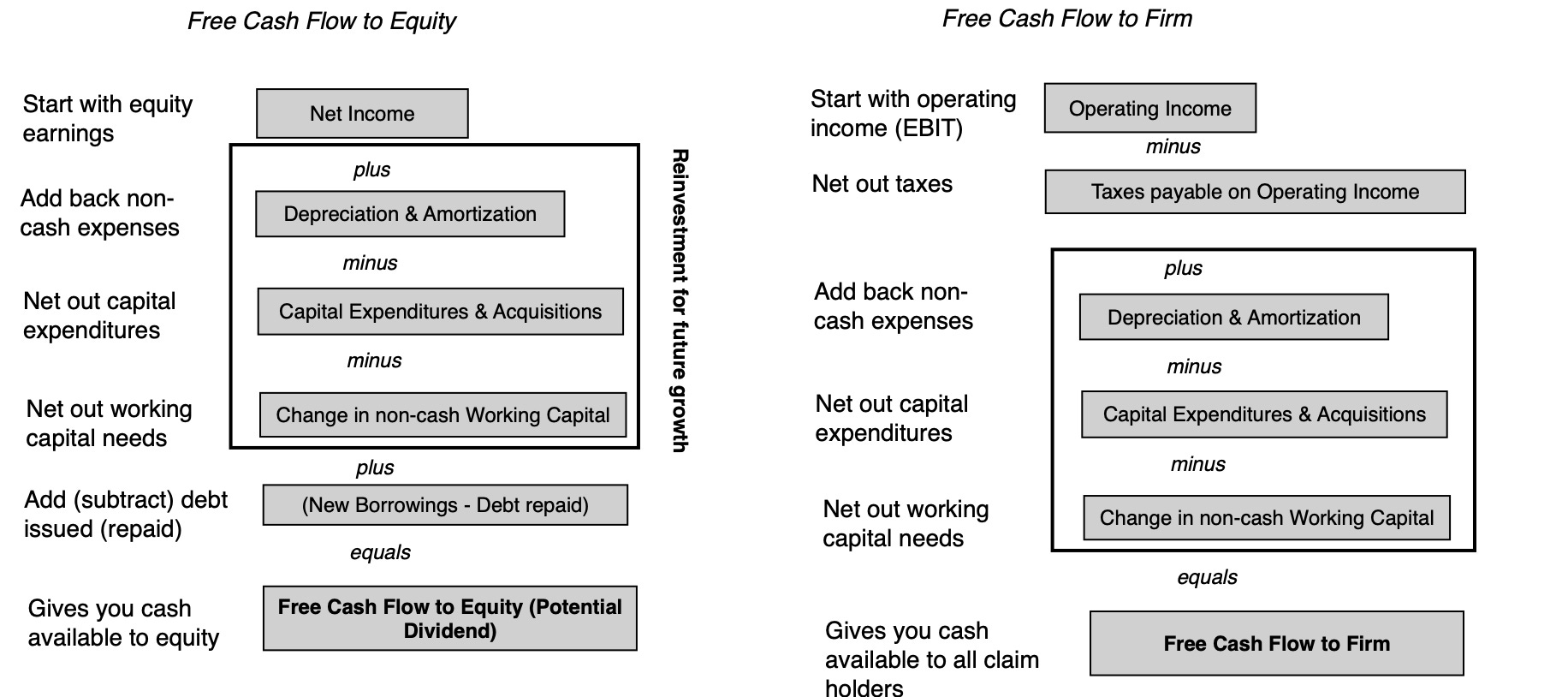
What are Non-GAAP Earnings?
Non-GAAP earnings, also known as adjusted earnings, are financial measures used by companies to present their financial performance excluding certain expenses or gains that they believe do not reflect the ongoing operations of the business. These non-standard measures provide a different perspective on a company’s profitability by excluding extraordinary or one-time events that may distort the true financial picture.
Companies often use Non-GAAP earnings to emphasize their operational performance or to better align with industry standards. By removing these non-recurring items from their financial statements, companies aim to provide investors with a clearer view of their underlying performance.
So, you might be wondering, what exactly gets excluded from Non-GAAP earnings? Well, common items that may be adjusted include restructuring charges, asset impairments, gains or losses from the sale of assets, stock-based compensation expenses, and expenses related to mergers and acquisitions. By eliminating these items, companies believe that Non-GAAP earnings provide a more useful metric for evaluating their ongoing financial health.
Why Do Non-GAAP Earnings Matter in Financial Analysis?
Non-GAAP earnings play a crucial role in financial analysis as they can provide valuable insights into a company’s performance, potentially beyond what the standard GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) measures offer. Here are a few reasons why Non-GAAP earnings matter:
- Comparability: Non-GAAP earnings can enable easier comparisons between companies within the same industry. By excluding non-recurring expenses or gains, investors can make more meaningful comparisons of operational performance.
- Long-term outlook: Non-GAAP earnings can help investors assess a company’s long-term potential by providing a clearer picture of its underlying profitability and cash flow generation capacity.
- Adjustments for key metrics: Non-GAAP earnings often serve as a basis for calculating critical financial ratios such as price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios. These adjusted ratios can provide a more accurate valuation of a company’s stock.
However, it is crucial to exercise caution when analyzing Non-GAAP earnings. While they can offer valuable insights, companies have some discretion in determining what gets excluded or adjusted. Investors should utilize these metrics as supplementary information alongside traditional GAAP measures, scrutinizing the company’s justifications for adjustments.
Conclusion
Non-GAAP earnings are an important tool in financial analysis, providing investors with additional insights into a company’s operational performance and long-term potential. By presenting financial information that excludes certain items, companies strive to convey a more accurate picture of their ongoing business operations. However, it’s essential to approach Non-GAAP earnings with a critical eye and not rely solely on them when making investment decisions. Understanding the context and rationale behind these adjusted metrics is crucial for conducting a comprehensive and insightful financial analysis.
Remember, in the complex world of finance, understanding the story behind the numbers is key. So, the next time you encounter Non-GAAP earnings, embrace the opportunity to extract valuable insights and make informed decisions.