Home>Finance>Transaction Exposure: Definition, Example, Hedging Strategies


Finance
Transaction Exposure: Definition, Example, Hedging Strategies
Published: February 10, 2024
Learn about transaction exposure in finance, including its definition, examples, and effective hedging strategies to mitigate financial risks.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Transaction Exposure: Definition, Example, Hedging Strategies
Finance is a broad field that encompasses various aspects of managing money, investments, and financial risks. One crucial aspect of finance is transaction exposure, which refers to the financial risk a company faces due to fluctuations in currency exchange rates when conducting international transactions.
In this blog post, we will dive into the definition of transaction exposure, examine an example to understand its impact, and explore hedging strategies that companies can use to mitigate the associated risks.
Key Takeaways:
- Transaction exposure is the financial risk a company faces due to fluctuations in currency exchange rates.
- Companies can use hedging strategies to mitigate transaction exposure and protect themselves from potential losses.
What is Transaction Exposure?
Transaction exposure is a concept in international finance that refers to the potential impact on a company’s finances when a foreign currency exchange rate fluctuates between the time a transaction is initiated and the time it is settled. If a company operates internationally and engages in foreign transactions, they become vulnerable to transaction exposure.
When a company is exposed to transaction risk, the changing exchange rates can impact the value of their international payments, receivables, or payables. This can lead to unexpected gains or losses during the transaction settlement process.
An Example to Illustrate Transaction Exposure
Let’s consider a hypothetical example to better understand the impact of transaction exposure. Suppose Company A, based in the United States, imports goods worth €100,000 from Company B in Germany. The agreed exchange rate at the time of the transaction is $1.10 per euro, resulting in a total transaction value of $110,000.
However, due to currency fluctuations, the exchange rate changes to $1.20 per euro when the transaction is settled. As a result, Company A now has to pay $120,000 instead of the initially agreed $110,000, leading to an additional cost of $10,000.
In this scenario, Company A incurred a loss of $10,000 due to the adverse exchange rate movement. This illustrates the potential impact of transaction exposure for companies engaged in international transactions.
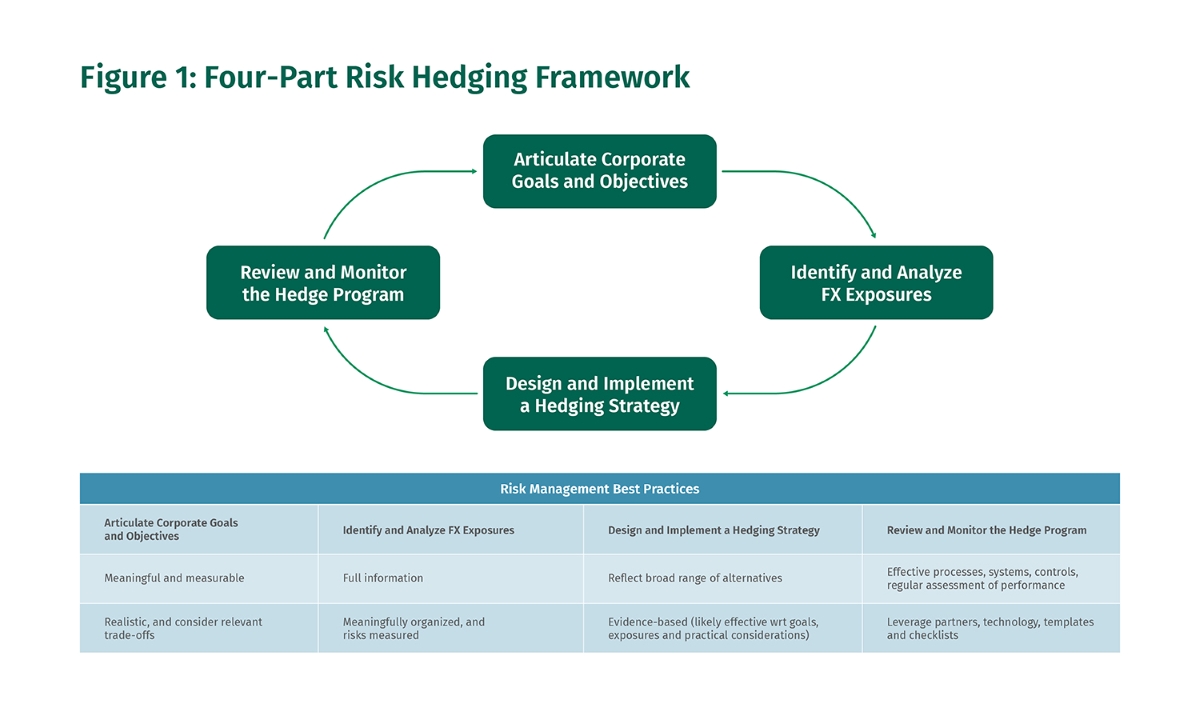
Hedging Strategies to Mitigate Transaction Exposure
Companies can employ various hedging strategies to mitigate transaction exposure and protect themselves from potential losses. Here are some commonly used hedging strategies:
- Forward Contracts: Companies can enter into forward contracts to lock in a specific exchange rate for future transactions. By doing so, they can hedge against potential adverse exchange rate movements.
- Options Contracts: Options contracts provide companies with the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specified amount of currency at a predetermined price within a specified timeframe. This flexibility allows companies to protect themselves from unfavorable exchange rate movements.
- Money Market Hedges: Money market hedges involve the borrowing or lending of foreign currencies at prevailing interest rates. This strategy helps to balance the exposure from the underlying transaction.
- Netting and Matching: Companies can offset their transaction exposure by matching inflows and outflows in the same currency or netting payments and receivables in different currencies.
By employing these hedging strategies, companies can effectively manage and reduce their transaction exposure, minimizing the potential impact of currency fluctuations on their financial performance.
Conclusion
Transaction exposure is an integral part of managing finances in the global marketplace. Companies engaging in international transactions must be aware of the risks associated with fluctuating exchange rates and take appropriate measures to mitigate their transaction exposure.
By utilizing hedging strategies such as forward contracts, options contracts, money market hedges, and netting, companies can protect themselves from potential losses and ensure smooth financial operations in an ever-changing international business landscape.
Remember, understanding transaction exposure and implementing effective hedging strategies will position your company for financial success in the global marketplace.