Home>Finance>Money Market Hedge: Definition, Strategy, Process, And Example


Finance
Money Market Hedge: Definition, Strategy, Process, And Example
Published: December 26, 2023
Learn about the finance strategy known as money market hedge, its definition, process, and see a practical example. Enhance your financial knowledge now!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Unlocking the Power of Money Market Hedge in Your Financial Strategy
When it comes to managing your finances, it’s important to have a variety of tools in your arsenal to protect against market fluctuations and exchange rate risks. One effective strategy that can help you mitigate these risks is the money market hedge. In this blog post, we will dive into the definition, strategy, process, and provide an example of how a money market hedge can be used to safeguard your financial assets.
Key Takeaways:
- Money market hedge is a financial strategy used to protect against exchange rate fluctuation risks.
- It involves offsetting exposure to foreign currency by taking an equal and opposite position in the money market.
What is Money Market Hedge?
A money market hedge is a financial technique that allows individuals and businesses to protect themselves from potential losses caused by changes in exchange rates. This strategy involves using forward contracts, short-term investments, or borrowing and lending in a foreign currency market to offset the risk of currency fluctuations.
Essentially, a money market hedge aims to establish an equal and opposite position in the money market to the underlying foreign currency exposure. By doing so, any potential gains or losses from the foreign currency are effectively offset by the gains or losses in the money market investment.
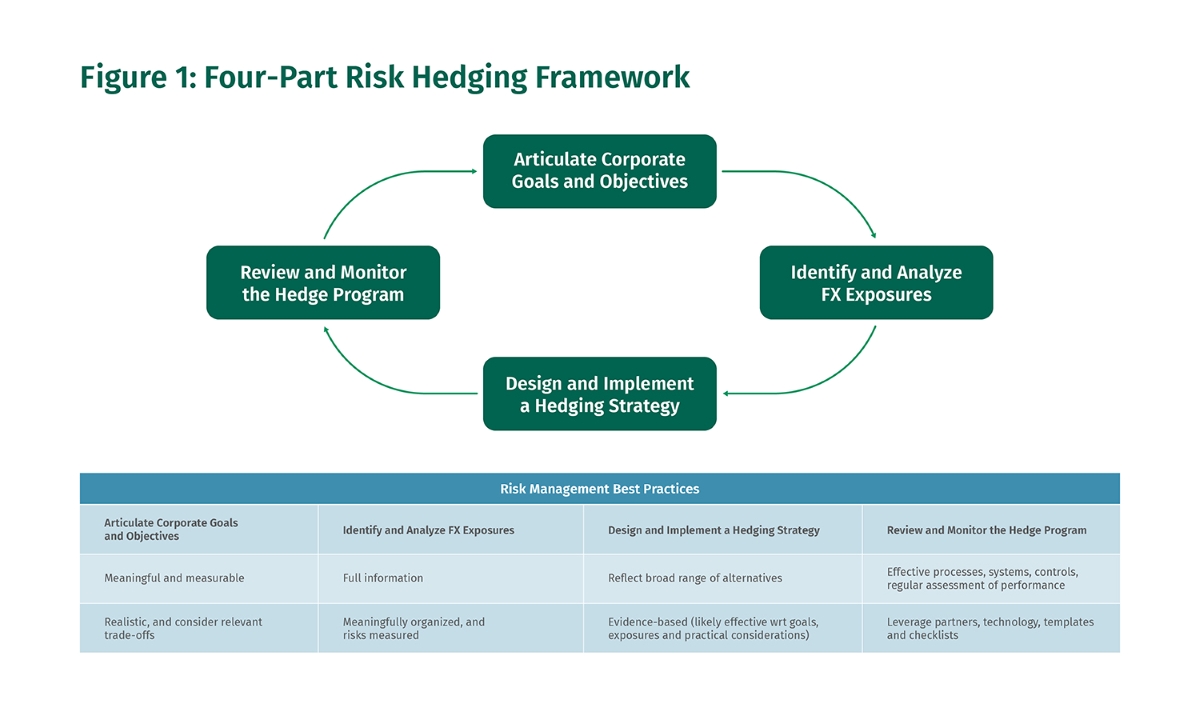
The Money Market Hedge Process:
- Identify the foreign currency exposure: Determine the amount and timing of the foreign currency that needs to be hedged.
- Select the appropriate money market instrument: Choose the money market instrument that aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
- Calculate the hedge ratio: Determine the ratio between the amount of foreign currency exposure and the money market instrument.
- Execute the money market hedge: Establish the required positions in both the foreign currency and the money market instrument.
- Monitor and manage the hedge: Continuously assess and adjust the hedge as needed to account for any changes in market conditions.
Money Market Hedge Example:
Let’s say Company A, a US-based firm, has a contract to receive €100,000 in six months. The current exchange rate is 1 USD to 0.85 EUR. Worried about potential fluctuations in the exchange rate, Company A decides to implement a money market hedge.
Following the money market hedge process, Company A identifies its foreign currency exposure as €100,000. They decide to use a forward contract to hedge their position. The forward contract has an exchange rate of 1 USD to 0.90 EUR, which is more favorable than the current rate.
Company A calculates the hedge ratio by dividing the amount of foreign currency exposure (€100,000) by the exchange rate in the forward contract (0.90). The hedge ratio is approximately €111,111 (€100,000 / 0.90).
Next, Company A executes the money market hedge by entering into a forward contract to sell approximately €111,111 for USD at the established exchange rate. This creates an offsetting position in the money market, protecting the value of the expected future cash flows.
If the exchange rate moves unfavorably to 1 USD to 0.80 EUR at the end of six months, Company A would receive €88,889 (€111,111 * 0.80) from the forward contract. However, they would have lost value on the original €100,000. The money market hedge helps mitigate this loss, as the gains from the forward contract offset the losses from the foreign currency exposure.
Conclusion
A money market hedge is a valuable financial strategy that can protect individuals and businesses against exchange rate fluctuations. By employing a money market hedge, you can minimize the risk of potential losses and safeguard your financial assets. Remember to carefully understand the process and seek professional advice when implementing a money market hedge to ensure it aligns with your specific financial goals and risk tolerance.
Key Takeaways:
- Money market hedge is a financial strategy used to protect against exchange rate fluctuation risks.
- It involves offsetting exposure to foreign currency by taking an equal and opposite position in the money market.