Home>Finance>What Does Liquidity Refer To In A Life Insurance Policy?


Finance
What Does Liquidity Refer To In A Life Insurance Policy?
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn what liquidity means in the context of a life insurance policy and how it relates to your financial situation. Understand the importance of having a liquid life insurance policy.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Liquidity
- Importance of Liquidity in Life Insurance Policies
- Types of Liquidity Options in Life Insurance Policies
- Cash Value
- Policy Loans
- Withdrawals
- Surrender Value
- Constraints and Limitations of Liquidity Options
- Factors to Consider when Assessing Liquidity in Life Insurance Policies
- Conclusion
Introduction
When considering life insurance policies, one important aspect to understand is liquidity. Liquidity refers to the ease with which you can access the cash value of your policy when needed. It plays a crucial role in providing financial flexibility and security. In this article, we will explore what liquidity refers to in a life insurance policy and why it is important.
Life insurance policies are designed to provide financial protection for your loved ones in the event of your passing. They offer death benefits to beneficiaries, which can help cover expenses such as funeral costs, outstanding debts, and ongoing living expenses. However, life insurance can also serve as an asset with potential benefits while you are still alive.
Liquidity in a life insurance policy refers to the ability to access the cash value within the policy during your lifetime. Unlike other forms of insurance, life insurance policies often accumulate cash value over time, which can be used for various purposes. This liquidity feature allows you to have a source of funds that can be accessed in times of financial need or opportunity.
Understanding the liquidity of a life insurance policy is essential as it can determine the flexibility and versatility in utilizing your policy’s cash value. Whether it’s for emergencies, education expenses, or supplementing retirement income, having the ability to access funds from your life insurance policy can be a valuable financial tool.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the definition of liquidity in life insurance policies, explore different types of liquidity options available, discuss their constraints and limitations, and provide guidance on factors to consider when assessing liquidity in a life insurance policy.
Definition of Liquidity
Liquidity, in the context of a life insurance policy, refers to the accessibility and convertibility of the cash value within the policy. It is the degree to which the policyholder can quickly and easily access funds when needed. When a life insurance policy has liquidity, it means that the policyholder can tap into the cash value without surrendering or terminating the policy.
The cash value of a life insurance policy represents the savings component that grows over time. It accumulates based on the premiums paid and any interest or investment gains. This cash value is separate from the death benefit, which is the amount paid to beneficiaries upon the insured’s death.
Liquidity provides the policyholder with flexibility, allowing them to use the cash value for various purposes such as emergency expenses, education costs, or supplementing retirement income. It serves as a financial safety net and can help navigate unexpected financial challenges or take advantage of opportunities.
It’s important to note that the level of liquidity in a life insurance policy can vary depending on the specific policy type, terms, and conditions set by the insurance company. Different policies and insurance providers may offer varying degrees of access to the cash value.
Understanding the liquidity of a life insurance policy is crucial because it allows you to have a clear picture of the financial resources available to you during your lifetime. Assessing the liquidity of a policy is an important step in making informed decisions about your financial planning and ensuring that your life insurance policy aligns with your current and future needs.
Importance of Liquidity in Life Insurance Policies
Liquidity plays a crucial role in the overall value and usefulness of a life insurance policy. It provides policyholders with financial flexibility and can serve as a valuable asset during their lifetime. Here are some key reasons why liquidity is important in life insurance policies:
1. Financial Security: Life is unpredictable, and unexpected expenses can arise at any time. Having liquidity in your life insurance policy enables you to access funds quickly to address emergency situations, such as medical expenses, home repairs, or car accidents. By having this financial security, you can protect yourself and your loved ones from the stress and burden of unforeseen financial challenges.
2. Supplement Retirement Income: Life insurance policies with liquidity options can be an effective tool for supplementing retirement income. As you near retirement age, the cash value in your policy can be accessed to provide additional funds for living expenses or to cover any income gaps. This can be especially beneficial if you have exhausted other retirement savings or investments.
3. Education Expenses: Liquidity in a life insurance policy can also be used to cover education expenses for yourself, your children, or grandchildren. Whether it’s funding college tuition, paying for specialized training, or financing other education-related costs, having access to the cash value can ease the financial burden and provide opportunities for educational advancement.
4. Business Needs: For business owners, liquidity in a life insurance policy can be invaluable. It can serve as a source of funding for business-related expenses, such as expanding operations, purchasing new equipment, or covering temporary cash flow shortages. The cash value can be accessed to provide necessary capital without the need for external financing or disrupting personal finances.
5. Flexibility for Policyholder’s Changing Needs: Life insurance policies with liquidity options allow policyholders to adapt to changing circumstances and financial goals. Whether it’s a new investment opportunity, a change in career, or unexpected life events, having the ability to access the cash value provides flexibility and peace of mind.
Overall, liquidity in life insurance policies provides policyholders with the means to address financial needs and seize opportunities without the need to surrender or cancel the policy. It adds an additional layer of versatility to life insurance, making it more than just a safety net in the event of death. Assessing and understanding the liquidity options within a life insurance policy is crucial for tailoring the policy to meet your specific financial needs and goals.
Types of Liquidity Options in Life Insurance Policies
Life insurance policies offer various options for accessing the cash value within the policy. These options provide policyholders with liquidity, allowing them to tap into the accumulated funds as needed. Here are the common types of liquidity options available in life insurance policies:
1. Cash Value Withdrawals: This is the most straightforward way to access the cash value in a life insurance policy. Policyholders can request a withdrawal of a specific amount from the cash value, which is then paid out to them. These withdrawals may be subject to income tax and potential surrender charges depending on the policy’s terms and conditions.
2. Policy Loans: Policy loans allow policyholders to borrow against the cash value of the policy. The insurance company lends the policyholder a certain amount based on the available cash value, and the policyholder is required to repay the loan with interest. Policy loans typically have lower interest rates compared to traditional loans, and the policyholder can use the loaned funds for any purpose.
3. Automatic Premium Loan (APL): The automatic premium loan is a feature in some life insurance policies that utilizes the cash value to pay any outstanding premiums if the policyholder fails to make the payment. The insurance company issues a loan against the cash value to cover the premium amount, effectively preventing the policy from lapsing. The loaned amount, including interest, will be deducted from the death benefit if it is not repaid during the policyholder’s lifetime.
4. Surrender Value: If a policyholder decides to terminate the life insurance policy prematurely, they can surrender the policy and receive the surrender value. The surrender value is the cash value minus any surrender charges or fees outlined in the policy. While surrendering a policy should be carefully considered, it provides an immediate lump sum of cash.
5. Partial Surrender: Some life insurance policies allow policyholders to make partial surrenders, where they can withdraw a portion of the cash value while keeping the policy in force. This option provides flexibility as it allows policyholders to access some of the funds without completely terminating the policy or losing the death benefit protection.
It’s important to note that each life insurance policy may offer different combinations of liquidity options. Some policies may offer all the options mentioned above, while others may have limited options. It is advisable to carefully review the terms and conditions of the policy and consult with your insurance provider or financial advisor to fully understand the specific liquidity options available.
Cash Value
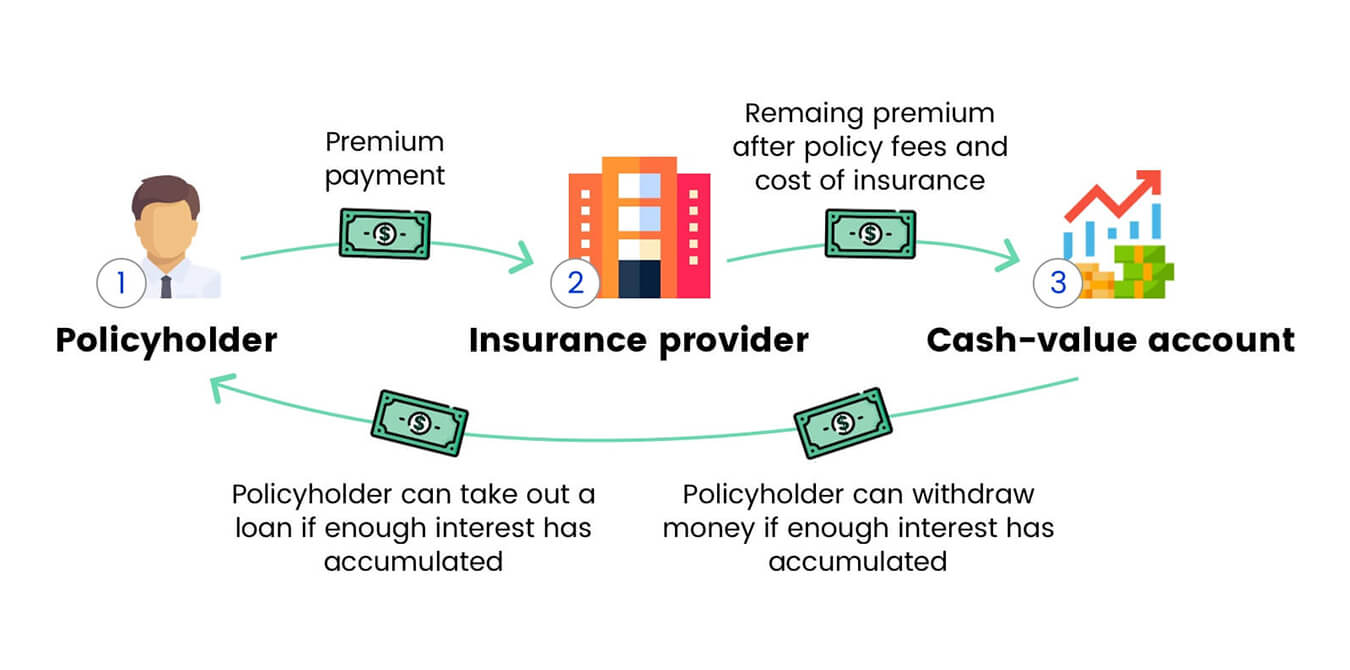
Cash value is a key component of many life insurance policies and refers to the savings portion that accumulates over time. It represents the funds that policyholders contribute through premium payments, as well as any interest or investment gains earned by the insurance company on those funds.
As policyholders continue to pay premiums, the cash value within the policy grows. The growth of the cash value is usually tax-deferred, meaning policyholders do not have to pay taxes on the accumulated funds until they are withdrawn.
One of the main benefits of the cash value is its liquidity. Policyholders can access the cash value in multiple ways, such as withdrawals, policy loans, or partial surrenders. The availability and terms of these liquidity options may vary depending on the specific life insurance policy.
Withdrawals from the cash value allow the policyholder to take out a specific amount of funds. These withdrawals may be subject to taxation if the accumulated cash value exceeds the total amount of premiums paid into the policy. However, policyholders should consult with a tax advisor to determine the tax implications specific to their situation.
Another option is to take out a policy loan against the cash value. The policyholder can borrow a certain amount from the insurance company, using the cash value as collateral. Policy loans typically have lower interest rates compared to traditional loans, making them an attractive option for accessing funds while still maintaining the policy’s death benefit protection.
In some cases, policyholders may choose to surrender the policy before its maturity date, in which they receive the surrender value. The surrender value is the cash value minus any applicable surrender charges or fees outlined in the policy. Surrendering the policy should be carefully considered, as it terminates the coverage and potentially leaves the policyholder without life insurance protection.
The cash value within a life insurance policy can serve various purposes. It can act as a financial safety net in the event of emergencies or unexpected expenses. It can also be used to supplement retirement income, fund education expenses, or provide capital for business needs. The flexibility and accessibility of the cash value make it a valuable asset that policyholders can tap into during their lifetime.
It’s important to note that the cash value accumulation may take time, especially in the early years of the policy when fees and expenses may offset the growth. The cash value also depends on the performance of the underlying investments, which can fluctuate. Policyholders should review their policy documents and consult with their insurance provider or financial advisor to get a clearer understanding of the cash value accumulation and the available liquidity options.
Policy Loans
Policy loans are a type of liquidity option available in many life insurance policies. They allow policyholders to borrow against the cash value of their policies and can provide a valuable source of funds when needed. Policy loans offer several advantages and considerations for policyholders.
When policyholders take out a policy loan, they are essentially borrowing from the accumulated cash value within their life insurance policy. The loaned amount is typically a percentage of the available cash value, which serves as collateral for the loan. The policyholder can use the loaned funds for any purpose, such as covering unexpected expenses, paying for education, or starting a business.
One of the significant advantages of policy loans is the relatively low interest rates compared to traditional loans. Insurance companies usually charge interest on policy loans, but these rates are typically lower than what borrowers would find through banks or credit cards. This can make policy loans an attractive borrowing option, especially for individuals who might have difficulty obtaining loans through traditional channels.
Furthermore, policy loans have flexible repayment terms. Policyholders have the option to repay the loan in installments or as a lump sum, depending on their financial situation. The repayment terms can be negotiated with the insurance company, providing convenience and flexibility for the policyholder.
An essential aspect of policy loans is that they do not require a credit check. Since the cash value serves as collateral for the loan, the insurance company does not consider the policyholder’s credit history or require extensive documentation for loan approval. This can be particularly advantageous for individuals who may have a less-than-perfect credit score.
Policy loans also provide policyholders with a degree of privacy since the loan transaction does not appear on credit reports. This can be beneficial for individuals who wish to maintain their financial privacy or avoid potential impacts on their credit score.
It’s important to note that policy loans are not without considerations. The loaned amount, including the interest charged, will be deducted from the death benefit if not repaid during the policyholder’s lifetime. Failure to repay the loan can reduce the overall payout to beneficiaries. Additionally, it’s essential to understand the impact of the loan on the policy’s cash value growth and potential tax implications. Policyholders should consult with their insurance provider or financial advisor to fully understand the terms, conditions, and potential consequences of taking a policy loan.
Policy loans can be a valuable liquidity option for policyholders, providing access to funds at relatively low interest rates and with flexibility in repayment. However, careful consideration should be given to the financial impact on the policy’s death benefit and the long-term effects on the policy’s cash value growth. Policyholders should evaluate their financial needs and consult with professionals to make an informed decision regarding policy loans and their overall life insurance strategy.
Withdrawals
Withdrawals are a common liquidity option available to policyholders in life insurance policies. They provide a straightforward and flexible way to access the cash value accumulated within the policy. Policyholders can withdraw a specific amount of funds from the cash value for various purposes, such as covering unexpected expenses, paying for education, or supplementing income during retirement.
When making a withdrawal, policyholders typically have the freedom to choose the amount they want to withdraw, up to the available cash value. The withdrawal amount is deducted from the cash value, reducing the overall value of the policy. The withdrawn funds can be used at the discretion of the policyholder, without any restrictions on how they are utilized.
It’s important to note that withdrawals may be subject to income tax. If the cash value withdrawn exceeds the total amount of premiums paid into the policy, the excess portion is generally considered taxable income. The taxation of withdrawals from life insurance policies can vary depending on factors such as the type of policy, the duration, and the specific tax laws applicable in the jurisdiction. Policyholders should consult with a tax advisor to understand the tax implications of withdrawals based on their individual circumstances.
Another consideration with withdrawals is the potential impact on the death benefit. When policyholders make a withdrawal, the death benefit of the policy is reduced by the amount withdrawn. This reduction can affect the intended financial protection for beneficiaries in the event of the policyholder’s death. Policyholders should carefully evaluate their financial needs and the impact of withdrawals on their desired level of coverage.
Policyholders also need to be aware of any surrender charges or fees associated with withdrawals. Some life insurance policies impose penalties for early withdrawals, especially within a certain time frame from the policy’s inception. These charges are designed to discourage policyholders from prematurely terminating the policy and may be applicable even for partial withdrawals. It’s essential to review the policy documents or consult with the insurance provider to understand the specific terms and conditions related to withdrawals and any associated charges.
Despite these considerations, withdrawals from the cash value in life insurance policies can provide policyholders with necessary liquidity. They allow individuals to access funds without the need to borrow or surrender the policy entirely. Withdrawals can be a valuable financial tool, providing flexibility and peace of mind during times of financial need.
Policyholders should carefully assess their financial situation, long-term financial goals, and the potential impact on the death benefit and cash value growth before making a withdrawal. Consulting with an insurance professional or financial advisor can help policyholders make informed decisions and ensure that withdrawals align with their overall financial strategy.
Surrender Value
The surrender value is an important component of a life insurance policy and refers to the cash value that policyholders receive if they decide to terminate or surrender their policy before its maturity date. It represents the amount of money that the insurance company pays to the policyholder when the policy is voluntarily surrendered.
When policyholders surrender a life insurance policy, they essentially cancel the coverage and forfeit the future death benefit protection. In return, they receive the surrender value, which is the cash value minus any applicable surrender charges or fees. Surrender charges are typically imposed to discourage policyholders from terminating the policy early and to offset any administrative costs incurred by the insurance company.
The surrender value can serve as a source of liquidity and provide policyholders with an immediate lump sum payment. It can be used for various purposes, such as covering financial obligations, investing in other opportunities, or addressing unexpected expenses. However, it’s important to carefully consider the implications of surrendering a policy, as it permanently terminates the coverage and may result in the loss of any potential future benefits.
Policyholders should be aware that surrendering a policy often triggers tax consequences. If the accumulated cash value exceeds the total premiums paid into the policy, the excess amount may be subject to income tax. The tax treatment of surrendering a life insurance policy can vary depending on factors such as the policy type, duration, and applicable tax laws. It is advisable to consult with a tax advisor to fully understand the tax implications specific to one’s individual circumstances.
It’s important to note that surrender charges are typically highest in the early years of the policy and gradually decrease over time. Many policies have a surrender charge period during which charges apply if the policy is terminated. As the policy continues, the surrender charges eventually decrease to zero, allowing policyholders to surrender the policy without incurring any charges.
The surrender value is influenced by various factors, including the duration of the policy, the premiums paid, the policy type, and the investment performance of the underlying assets. Policyholders should carefully review the policy documents, specifically the surrender value provisions, to understand how the surrender value grows over time and how any imposed charges may impact the amount received upon surrender.
Before deciding to surrender a life insurance policy and access the surrender value, policyholders should consider their long-term financial goals, the impact on their overall insurance coverage, and any potential tax implications. It’s advisable to consult with an insurance professional or financial advisor to evaluate the options available, weigh the pros and cons, and make an informed decision based on one’s unique financial circumstances.
Constraints and Limitations of Liquidity Options
While life insurance policies offer various liquidity options to policyholders, it’s important to be aware of the constraints and limitations that may apply. These factors can impact the accessibility and availability of the cash value within the policy. Here are some common constraints and limitations related to liquidity options:
1. Surrender Charges: Many life insurance policies impose surrender charges on early terminations or withdrawals. These charges are designed to discourage policyholders from surrendering the policy within a specific time frame, usually in the early years of the policy. Surrender charges can reduce the amount of cash value or surrender value received by the policyholder if they choose to terminate the policy.
2. Surrender Value Restrictions: Some policies may have restrictions on when the surrender value becomes available. For example, a policy may require a minimum number of years before the policyholder can access the full amount of the surrender value. These restrictions can limit the liquidity options and may require policyholders to keep the policy in force for a certain period to fully benefit from the cash value.
3. Loan Repayment Requirements: When policyholders take out a loan against the cash value, they are required to repay the loan with interest. Failure to repay the loan can have consequences, such as reducing the death benefit or potentially causing the policy to lapse. Policyholders need to carefully evaluate their ability to repay the loan and consider the impact on the policy’s coverage and future benefits.
4. Tax Implications: Liquidity options in life insurance policies can have tax implications. Withdrawals or surrenders that exceed the total amount of premiums paid into the policy may be subject to income tax. The tax treatment can vary based on factors such as the policy type, duration, and specific tax laws. It’s advisable to consult with a tax advisor to understand the potential tax consequences of utilizing liquidity options within a life insurance policy.
5. Impact on Death Benefit: Utilizing liquidity options, such as withdrawals or policy loans, can reduce the death benefit of the policy. Each withdrawal or loan decreases the cash value available to support the death benefit. It’s important for policyholders to consider the impact on the intended financial protection for beneficiaries and make informed decisions based on their long-term goals and priorities.
6. Policy Type Restrictions: The liquidity options available may vary depending on the type of life insurance policy. Some policies may offer more flexibility and ease of access to the cash value compared to others. For example, whole life insurance policies generally have more liquidity options than term life insurance policies. Policyholders should review their policy documents and consult with their insurance provider or financial advisor to fully understand the constraints and limitations specific to their policy.
Understanding the constraints and limitations of liquidity options is essential when evaluating the flexibility and usefulness of a life insurance policy. Policyholders should carefully consider their financial goals, risk tolerance, and the potential impact on coverage before utilizing any liquidity option. Consulting with a financial professional can provide guidance and help policyholders make informed decisions that align with their individual needs and circumstances.
Factors to Consider when Assessing Liquidity in Life Insurance Policies
Assessing the liquidity of a life insurance policy is crucial to determine the accessibility and usefulness of the cash value. When evaluating the liquidity options within a policy, there are several key factors to consider:
1. Policy Type: Different types of life insurance policies have varying levels of liquidity. Whole life insurance policies typically offer more liquidity options, such as withdrawals and policy loans, compared to term life insurance policies. Understanding the liquidity features specific to your policy type is important to assess the available options.
2. Cash Value Accumulation: The rate at which the cash value accumulates within the policy can impact liquidity. Policies that accumulate cash value more quickly offer policyholders greater access to the funds. It’s important to review the policy documents or consult with the insurance provider to understand the cash value growth and how it pertains to the liquidity options.
3. Surrender Charges and Restrictions: Take note of any surrender charges and restrictions that may apply when accessing the cash value. Surrender charges can reduce the amount received upon surrendering the policy, while restrictions may limit when and how the cash value can be accessed. Understanding these aspects helps weigh the costs and benefits of utilizing the available liquidity options.
4. Policy Loans: If the policy allows for loans against the cash value, evaluate the terms and conditions of the loans. Consider the interest rates, repayment requirements, and potential impact on the policy’s death benefit. Assessing the implications of taking a loan can help determine if it aligns with your financial objectives.
5. Tax Implications: Consider the potential tax consequences of utilizing liquidity options. Withdrawals or surrenders that exceed the total premiums paid into the policy may be subject to income tax. Consult with a tax advisor to understand the specific tax rules and implications based on your circumstances.
6. Long-Term Financial Goals: Assess your long-term financial goals and how liquidity options within the policy align with those objectives. Consider if accessing the cash value helps meet short-term needs without jeopardizing long-term financial security. Evaluate the impact on your overall financial plan and whether using liquidity options supports your goals.
7. Risk Tolerance: Evaluate your risk tolerance when considering liquidity options. Some options may involve potential risks, such as a decrease in the death benefit or policy lapsing if loans are not repaid. Assess the level of risk you are comfortable with and make decisions that align with your risk tolerance.
8. Professional Advice: Seek guidance from insurance professionals or financial advisors who have expertise in life insurance policies. They can help assess your specific financial situation, goals, and risk tolerance to provide personalized advice on utilizing liquidity options within your policy.
By considering these factors, you can make informed decisions about the liquidity options in your life insurance policy. Understanding the available options, their potential impact on the policy’s benefits, and how they align with your long-term goals will help ensure that you are maximizing the value and flexibility of your life insurance coverage.
Conclusion
Liquidity is a crucial aspect to consider when evaluating and utilizing life insurance policies. It refers to the accessibility and convertibility of the cash value within the policy, providing policyholders with financial flexibility during their lifetime. Understanding the liquidity options available is essential to make informed decisions that align with individual financial goals and circumstances.
Life insurance policies offer several liquidity options, including cash value withdrawals, policy loans, surrender value, and partial surrenders. Each option has its advantages, considerations, and potential impacts on the policy’s death benefit and tax implications. Assessing these options requires careful evaluation of factors such as policy type, cash value accumulation, surrender charges, loan terms, tax consequences, and long-term financial goals.
The importance of liquidity in life insurance policies lies in providing policyholders with a financial safety net, supplementing retirement income, covering educational expenses, or addressing business needs. Liquidity options offer flexibility and peace of mind during unexpected financial challenges or opportunities, allowing policyholders to access the accumulated cash value without surrendering or terminating the policy.
However, it is crucial to note the constraints and limitations that exist when utilizing liquidity options. Surrender charges, surrender value restrictions, loan repayment requirements, tax implications, and impact on the death benefit should be carefully considered to ensure the best use of the policy’s cash value while maintaining the desired coverage and benefits.
Policyholders should seek guidance from insurance professionals or financial advisors to navigate the complexities of liquidity options in life insurance policies. These experts can offer personalized advice based on individual financial situations, goals, and risk tolerance. They can help assess the available options and establish a comprehensive financial plan that maximizes the value and flexibility of the life insurance coverage.
In conclusion, understanding and assessing the liquidity options within a life insurance policy is vital to make informed decisions. By evaluating the various factors and seeking professional guidance, policyholders can effectively utilize the cash value in their policies to meet immediate financial needs, protect their long-term financial security, and achieve their unique financial goals.