
Finance
What Is IRS Schedule 2?
Published: October 30, 2023
Learn about IRS Schedule 2 and how it affects your finances. Understand its role in calculating your tax liability and managing your deductions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to managing your finances, understanding your tax obligations is essential. As a taxpayer, you are required to report various sources of income and pay applicable taxes to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). To facilitate this process, the IRS has developed various forms and schedules to capture specific types of income or deductions.
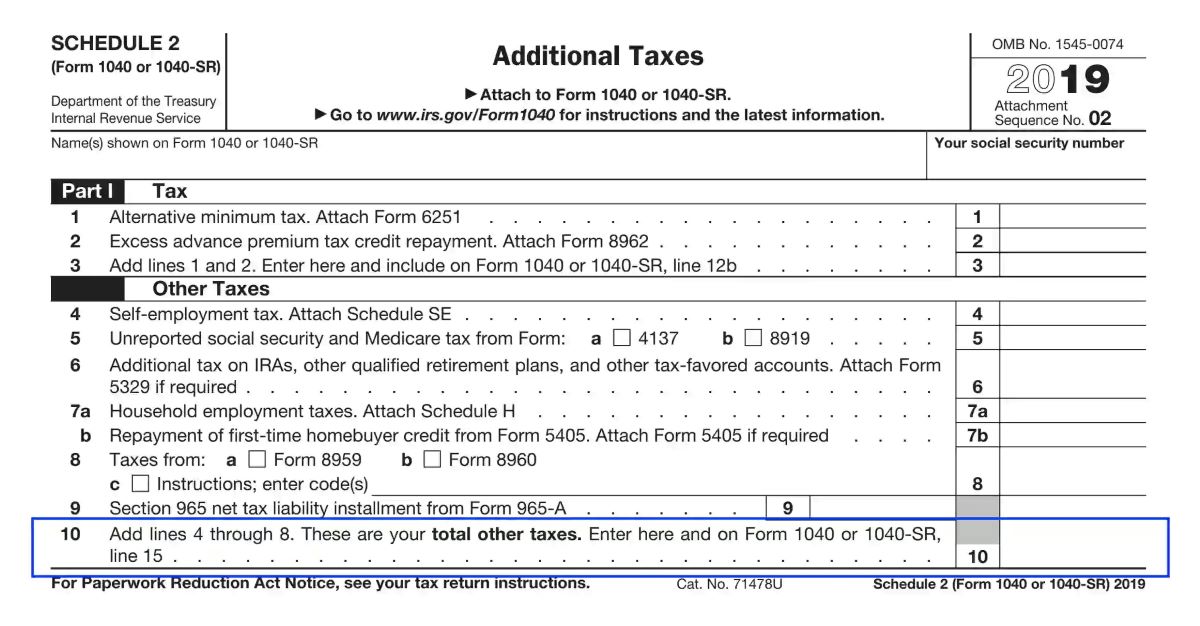
In this article, we will focus on IRS Schedule 2, which is used to report additional taxes that may not be reported on the main tax form, such as Form 1040. Schedule 2 serves as a supplementary schedule to provide detailed information on these additional tax obligations.
Schedule 2 is typically filed alongside your other tax forms when you have specific types of income or deductions that require additional reporting. While it may sound daunting, understanding and completing Schedule 2 correctly can help you avoid potential penalties and ensure compliance with the IRS.
In the following sections, we will explore the purpose of Schedule 2, the types of taxes it covers, instructions for completing the form, and the repercussions of incorrectly filing Schedule 2.
Purpose of IRS Schedule 2
The primary purpose of IRS Schedule 2 is to report additional taxes that may not be captured on the main tax form, such as Form 1040. These additional taxes typically arise from specific types of income or deductions that require separate reporting.
Schedule 2 enables taxpayers to provide detailed information about these additional tax obligations. By separating these taxes into a supplementary schedule, the IRS can effectively track and verify the accuracy of reported amounts.
One of the common reasons for the need to fill out Schedule 2 is to report additional taxes related to certain types of income, such as self-employment income, alimony received, or rental income. These incomes are subject to separate tax calculations and may have additional reporting requirements beyond what is captured on the main tax form. Schedule 2 ensures that these additional taxes are properly accounted for.
In addition to income-related taxes, Schedule 2 also covers other types of taxes that may arise from specific deductions or credits. For example, if you need to report the Additional Medicare Tax or the Net Investment Income Tax, you will use Schedule 2 to provide the necessary details.
The purpose of Schedule 2 is not only to ensure accurate reporting but also to help taxpayers understand their overall tax liability. By breaking down the taxes into separate categories, Schedule 2 provides transparency and clarity regarding which income sources or deductions contribute to your overall tax obligation.
It is important to note that not all taxpayers will need to fill out Schedule 2. If your tax situation is relatively straightforward and does not involve any additional taxes beyond what is captured on the main form, then Schedule 2 may not be necessary for you. However, if you have specific types of income or deductions that require separate reporting, it is crucial to familiarize yourself with Schedule 2 and ensure its proper completion.
Reporting Additional Taxes
When it comes to reporting additional taxes, the IRS Schedule 2 plays a crucial role. This supplementary schedule allows taxpayers to provide detailed information about various types of taxes that may not be covered on the main tax form.
The process of reporting additional taxes begins with identifying whether you have any specific income or deductions that require separate reporting. This could include self-employment income, alimony received, rental income, additional Medicare tax, or net investment income tax, among others.
Once you have determined that you need to report additional taxes, you will need to complete Schedule 2 accordingly. The form provides specific sections and lines for reporting each type of tax. You will need to enter the relevant amounts and details for each category.
It is important to note that accurate reporting is essential when completing Schedule 2. Ensure that you have the necessary documentation and records to support the reported amounts. This will help you avoid any potential discrepancies or issues during the IRS’s review process.
When reporting additional taxes, it is crucial to pay close attention to the instructions provided by the IRS. The instructions will guide you on which specific taxes to report and how to calculate the corresponding amounts. You may also need to refer to other forms or schedules to ensure accurate reporting.
When completing Schedule 2, it is important to keep in mind that the IRS requires you to report all income, even if it is not subject to federal income tax. This includes income that may be exempt or excluded from taxation. By providing a comprehensive view of your income, you help the IRS ensure the accuracy and integrity of your tax return.
Lastly, always double-check your completed Schedule 2 for accuracy before filing it along with your other tax forms. Even a small error in reporting additional taxes can have consequences, leading to potential penalties, delays, or additional scrutiny from the IRS.
By diligently reporting additional taxes on Schedule 2, you demonstrate your compliance with tax laws and contribute to the overall transparency and fairness of the tax system.
Types of Taxes Reported on Schedule 2
IRS Schedule 2 is used to report various types of additional taxes that may not be captured on the main tax form. These additional taxes cover a range of income sources and deductions. Let’s explore some of the common types of taxes reported on Schedule 2:
- Self-Employment Tax: If you are self-employed or operate a small business, you are responsible for paying the self-employment tax. This tax covers Social Security and Medicare taxes for self-employed individuals.
- Additional Medicare Tax: The Additional Medicare Tax is an extra tax that applies to high-income earners. If your income exceeds certain thresholds, you may need to report and pay the Additional Medicare Tax.
- Net Investment Income Tax: The Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT) is a tax on certain investment income. If you have investment income from sources such as interest, dividends, capital gains, or rental income, you may be subject to the NIIT.
- Alimony Recapture: Alimony recapture is applicable when certain conditions are met for alimony payments. If there are significant fluctuations in the amount of alimony paid or received over a three-year period, you may need to report alimony recapture and calculate any applicable taxes.
- Recapture of Federal Mortgage Subsidy: If you received a federal mortgage subsidy for a home and later sold or disposed of the property, you may need to report the recapture of that subsidy as taxable income.
- Health Care Individual Responsibility Penalty: Although the Health Care Individual Responsibility Penalty is no longer in effect as of 2019, some taxpayers may still need to report and pay this penalty if they were uninsured for part or all of the year.
These are just a few examples of the types of taxes reported on Schedule 2. It is important to carefully review the instructions provided by the IRS to determine if any other specific taxes apply to your situation and need to be reported on Schedule 2.
By accurately reporting and paying these additional taxes on Schedule 2, you fulfill your tax obligations and contribute to the funding of important government programs and services.
Instructions for Completing Schedule 2
Completing IRS Schedule 2 requires careful attention to detail and familiarity with the specific instructions provided by the IRS. Here are some general guidelines to help you navigate through the process:
- Download the form: Start by downloading Schedule 2 from the IRS website or obtain a copy from your tax preparation software. Make sure you have the most recent version of the form to ensure accuracy.
- Fill in your personal information: Enter your name, Social Security number, and any other requested personal information at the top of the form. This will help identify your tax return and ensure accurate processing.
- Identify the types of taxes to report: Review the instructions and identify the specific types of taxes that apply to your situation. Carefully read through each line item and determine which taxes require reporting on Schedule 2.
- Gather supporting documents and records: Collect all relevant documentation and records related to the additional taxes you are reporting. This includes income statements, expense receipts, and any other supporting documentation that you may need to refer to when completing Schedule 2.
- Enter the amounts on the appropriate lines: For each type of tax you need to report, find the corresponding line on Schedule 2 and enter the relevant amounts. Be sure to follow the specific instructions provided by the IRS for each line item.
- Calculate and summarize the total: After entering the amounts for each tax on Schedule 2, calculate the total for all additional taxes. This will give you an overall view of the additional tax liability that needs to be reported.
- Transfer the total to the main tax form: Once you have completed Schedule 2, transfer the total additional tax amount to the appropriate section on the main tax form you are filing, such as Form 1040.
- Review and double-check for accuracy: Before submitting your tax return, thoroughly review Schedule 2 for accuracy. Check that all amounts are entered correctly, and double-check that you have reported all required additional taxes.
It is important to note that these instructions are general guidelines. Always refer to the specific instructions provided by the IRS for the most accurate and up-to-date information on completing Schedule 2.
By carefully following the instructions and accurately completing Schedule 2, you can ensure compliance with the IRS and avoid potential penalties or issues with your tax return.
Filing Schedule 2
Once you have completed IRS Schedule 2 as part of your tax return, it is important to know how to properly file it. Here are some key steps to follow when filing Schedule 2:
- Attach Schedule 2 to your tax return: After completing Schedule 2, you will need to attach it to your main tax form, such as Form 1040. Ensure that Schedule 2 is securely attached and easily accessible.
- File electronically or by mail: You have the option to file your tax return electronically or by mail. If you choose to e-file, you can typically submit Schedule 2 along with your main tax form electronically through your chosen tax software or online platform. If you choose to file by mail, make sure to include Schedule 2 in the envelope along with your tax return.
- Double-check for accuracy: Before filing, carefully review your entire tax return, including Schedule 2, for accuracy. Check that all amounts are entered correctly and that you have reported all required additional taxes. This will help minimize potential errors or issues that could arise during the IRS’s processing of your return.
- Keep a copy for your records: It is important to keep a copy of your completed tax return, including Schedule 2, for your records. This will serve as a reference in case any questions or inquiries arise in the future regarding your tax filing.
- Submit payment, if applicable: If your additional taxes reported on Schedule 2 result in a tax liability, ensure that you submit the payment to the IRS by the designated deadline. The IRS provides various payment options, such as electronic payment methods or mailing a check or money order.
- Track your filing: After submitting your tax return and Schedule 2, it is a good practice to keep track of your filing. You can use the IRS’s online tracking tools or contact the IRS directly to confirm that your tax return, including Schedule 2, has been received and processed.
It is important to file Schedule 2 and your tax return accurately and on time to avoid potential penalties or issues with the IRS. Filing in a timely manner ensures that your additional taxes are properly reported and that you are in compliance with IRS regulations.
By following these steps, you can successfully file Schedule 2 along with your tax return and fulfill your tax obligations to the IRS.
Penalties for Incorrectly Filing Schedule 2
As with any aspect of tax filing, it is crucial to accurately complete and file IRS Schedule 2. Incorrectly filing this supplementary schedule can have serious consequences, including potential penalties imposed by the IRS. It is important to understand these penalties to ensure compliance and avoid unnecessary financial repercussions.
The specific penalties for incorrectly filing Schedule 2 vary depending on the nature and severity of the error. Here are some penalties that may apply:
- Accuracy-related penalties: If the IRS determines that the information reported on Schedule 2 is inaccurate or misleading due to negligence or disregard for tax rules, it may impose an accuracy-related penalty. This penalty is typically a percentage of the underpayment of taxes resulting from the error.
- Fraudulent filing penalties: If the IRS finds evidence of intentional fraud or willful intent to deceive on Schedule 2, it may impose penalties that are more severe than accuracy-related penalties. Fraudulent filing penalties can result in substantial financial penalties and even criminal charges in severe cases.
- Late filing penalties: Failing to file Schedule 2 by the specified deadline can result in late filing penalties. These penalties are usually calculated as a percentage of the additional tax due for each month or part of a month that the return is late, up to a maximum percentage.
- Underpayment penalties: If reported taxes on Schedule 2 are significantly lower than the actual tax liability, the IRS may impose underpayment penalties. These penalties are typically based on the amount of underpaid tax and the length of time it remains unpaid.
- Interest on unpaid taxes: In addition to the penalties mentioned above, the IRS will also charge interest on any outstanding tax liabilities resulting from incorrectly filed Schedule 2. The interest rate is determined by law and is compounded daily.
To avoid these penalties, it is crucial to diligently complete Schedule 2 with accurate information. Double-check all entries, seek professional assistance if needed, and utilize the resources provided by the IRS to ensure that you meet the requirements for filing Schedule 2 correctly.
If you realize that you have made an error on Schedule 2 after filing, it is important to promptly address the issue. You can file an amended return using Form 1040X to correct the error and minimize potential penalties. However, it is essential to consult a tax professional or contact the IRS for guidance on the proper procedures for amending your return.
By understanding the potential penalties for incorrectly filing Schedule 2 and taking the necessary steps to file accurately and on time, you can avoid unnecessary financial consequences and maintain compliance with the IRS.
Conclusion
Understanding and correctly filing IRS Schedule 2 is vital for taxpayers who have additional taxes that need to be reported. By following the specific instructions provided by the IRS, you can accurately report these additional taxes and avoid potential penalties or issues with your tax return.
IRS Schedule 2 serves as a supplementary schedule to capture specific types of income or deductions that require separate reporting. It covers various types of taxes such as self-employment tax, additional Medicare tax, net investment income tax, alimony recapture, and more. Familiarizing yourself with the types of taxes and their reporting requirements ensures that you fulfill your tax obligations.
When completing Schedule 2, it is important to gather all the necessary documentation and records to support the reported amounts. Pay close attention to detail, follow the instructions provided by the IRS, and double-check for accuracy before filing.
Filing Schedule 2 involves attaching it to your main tax form, whether you choose to file electronically or by mail. Make sure to keep a copy of your completed tax return, including Schedule 2, for your records.
Incorrectly filing Schedule 2 can lead to various penalties, including accuracy-related penalties, fraudulent filing penalties, late filing penalties, underpayment penalties, and interest on unpaid taxes. To avoid these penalties, take the time to complete Schedule 2 accurately and promptly address any errors or inconsistencies.
In conclusion, by understanding the purpose of IRS Schedule 2, familiarizing yourself with the types of taxes it covers, following the instructions for completion, and filing it correctly, you can navigate the tax filing process with confidence. Being diligent and accurate when reporting your additional taxes on Schedule 2 ensures compliance with the IRS and contributes to the transparency and integrity of the tax system.














