Finance
What Is The Minimum Payment On A Perkins Loan
Published: February 27, 2024
Learn how to calculate and manage the minimum payment on a Perkins loan, and get your finances in order with expert guidance on finance. Discover the best strategies to handle your Perkins loan payments.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to managing student loans, understanding the minimum payment requirements is crucial for borrowers. Among the various types of student loans available, Perkins Loans stand out as a unique and beneficial option. These low-interest federal loans are designed to assist undergraduate and graduate students with exceptional financial need. However, comprehending the minimum payment on a Perkins Loan is essential for responsible financial planning.
Navigating the world of student loans can be daunting, especially for individuals who are new to the concept of borrowing money for education. The minimum payment on a Perkins Loan is a key aspect that directly impacts a borrower's financial obligations. By delving into the specifics of this requirement, borrowers can gain clarity on how to manage their loan effectively while maintaining their financial stability.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the intricacies of Perkins Loans, dissect the methods for calculating the minimum payment, and discuss various repayment options. By the end of this journey, borrowers will have a solid understanding of the minimum payment on a Perkins Loan and the available avenues for managing this financial commitment.
Understanding Perkins Loans
Perkins Loans, a federal student loan program, have been instrumental in providing financial assistance to students with exceptional financial needs. These loans are administered by the participating institutions, and the funds are provided by the federal government. One of the distinguishing features of Perkins Loans is their low fixed interest rate, currently set at 5%. This makes them an attractive option for students seeking financial aid to pursue their education.
Unlike other federal student loans, the Perkins Loan program is subject to the availability of funds at the participating institutions. Therefore, not all students who demonstrate financial need may receive a Perkins Loan. The amount awarded under this program varies based on the student’s financial need, the funding level at the institution, and other financial aid received. It’s essential for students to consult with their school’s financial aid office to determine their eligibility for Perkins Loans.
Another noteworthy aspect of Perkins Loans is the grace period, which is a nine-month period following graduation, leaving school, or dropping below half-time enrollment. During this grace period, borrowers are not required to make payments on their Perkins Loans. This provision offers students a transitional period to secure employment and establish their financial footing before entering the repayment phase.
Understanding the intricacies of Perkins Loans, including their eligibility criteria, fixed interest rate, and grace period, is crucial for students who are considering these loans as a means of financing their education. By grasping the unique features of Perkins Loans, borrowers can make informed decisions about their financial aid options and plan for the repayment phase effectively.
Calculating the Minimum Payment
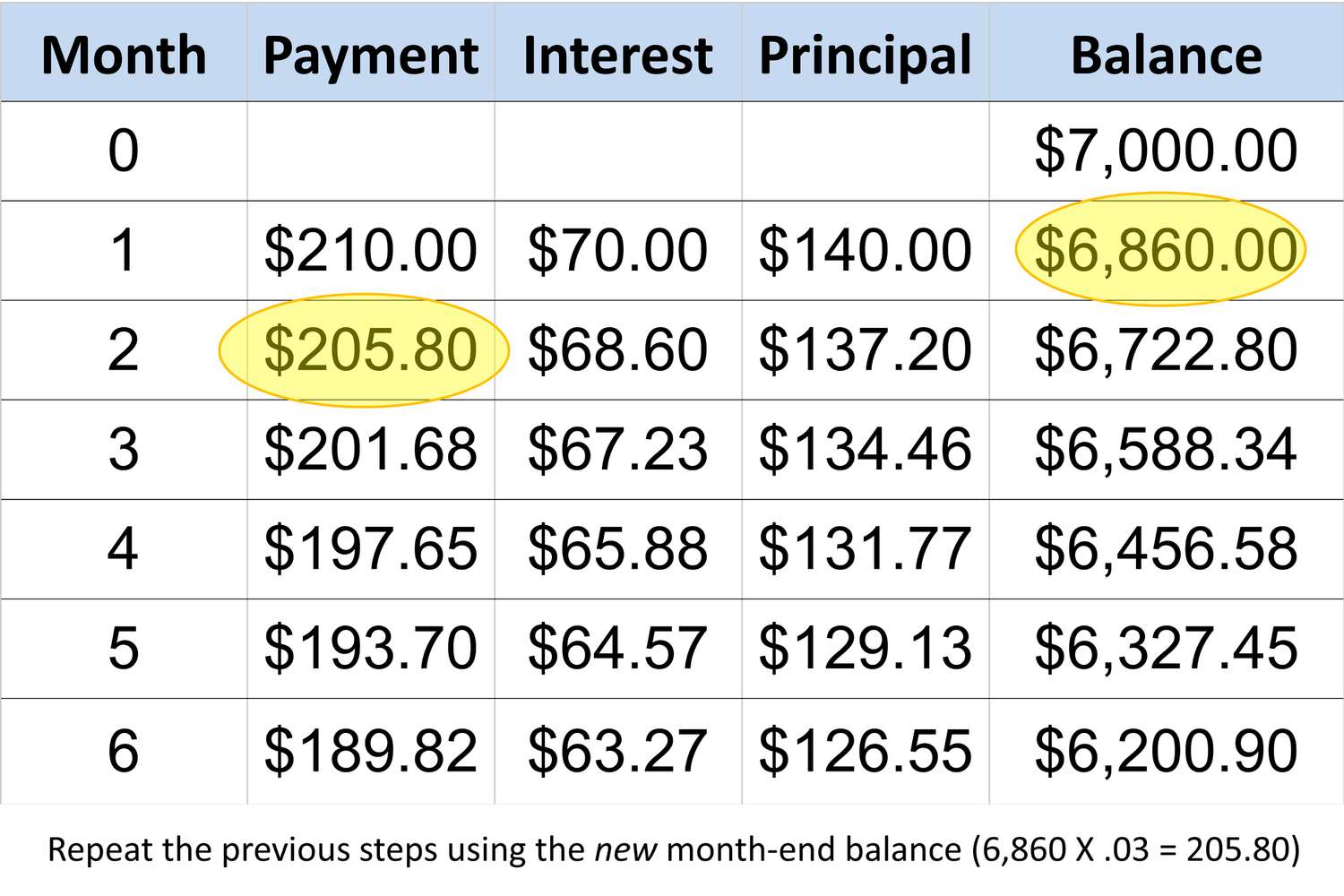
When it comes to managing student loan repayments, understanding how the minimum payment is calculated is essential for borrowers. The minimum payment on a Perkins Loan is determined based on various factors, including the total amount borrowed, the interest rate, and the chosen repayment plan. Unlike some other types of loans, Perkins Loans may have a different minimum payment requirement, and it’s crucial for borrowers to comprehend the calculation process.
The minimum payment on a Perkins Loan is typically calculated based on a 10-year standard repayment plan. Under this plan, the total amount borrowed, including interest, is divided by the number of months in the repayment period. This calculation method ensures that borrowers can fulfill their repayment obligations within a reasonable timeframe while managing their financial responsibilities effectively.
It’s important to note that the minimum payment on a Perkins Loan may also be influenced by the borrower’s income, family size, and other financial obligations. In some cases, borrowers may qualify for income-driven repayment plans, which adjust the minimum payment based on their income and family size. These plans provide flexibility and ensure that borrowers can manage their loan payments without experiencing financial strain.
Additionally, borrowers should be aware of the implications of deferment and forbearance on the minimum payment calculation. During periods of deferment or forbearance, the minimum payment may be temporarily suspended, allowing borrowers to address other financial priorities without defaulting on their loan obligations. However, it’s important to understand the impact of these options on the overall repayment timeline and the accrual of interest.
By understanding the intricacies of calculating the minimum payment on a Perkins Loan, borrowers can navigate the repayment process with confidence. Being well-informed about the factors that influence the minimum payment and the available repayment plans empowers borrowers to make sound financial decisions and effectively manage their student loan obligations.
Options for Repayment
When it comes to repaying Perkins Loans, borrowers have several options to consider, each tailored to accommodate their financial circumstances and preferences. Understanding these repayment options is crucial for borrowers as they navigate the process of managing their student loan obligations.
Standard Repayment Plan: The standard repayment plan for Perkins Loans involves fixed monthly payments over a 10-year period. This option is ideal for borrowers who can comfortably manage consistent payments and aim to pay off their loans within a reasonable timeframe.
Graduated Repayment Plan: Under the graduated repayment plan, borrowers make lower monthly payments initially, with the payments gradually increasing over time. This option is suitable for individuals who anticipate an increase in their income in the future and prefer to start with lower payments.
Income-Driven Repayment Plans: Income-driven repayment plans, such as Income-Based Repayment (IBR), Pay As You Earn (PAYE), Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE), and Income-Contingent Repayment (ICR), adjust the monthly payment based on the borrower’s income and family size. These plans offer flexibility and ensure that loan payments remain affordable, particularly for borrowers with lower incomes.
Deferment and Forbearance: Borrowers facing financial hardship or specific life circumstances may be eligible for deferment or forbearance, allowing them to temporarily suspend their loan payments. Deferment and forbearance options provide relief during challenging times, such as unemployment, economic hardship, or returning to school for further education.
Loan Consolidation: Consolidating Perkins Loans with other federal loans through a Direct Consolidation Loan can streamline the repayment process by combining multiple loans into a single loan with a single monthly payment. This option simplifies loan management and may extend the repayment period, resulting in lower monthly payments.
By exploring these repayment options, borrowers can select the most suitable approach based on their financial situation and long-term goals. It’s essential for borrowers to assess their individual circumstances and consult with their loan servicer to determine the most advantageous repayment strategy for their Perkins Loans.
Conclusion
Understanding the minimum payment on a Perkins Loan and the available options for repayment is pivotal for borrowers as they navigate the complexities of student loan management. By gaining insights into the unique features of Perkins Loans and the calculation of the minimum payment, borrowers can approach their loan obligations with clarity and confidence.
Perkins Loans, with their low fixed interest rate and grace period, offer valuable financial support to students with exceptional financial need. However, comprehending the minimum payment requirements and the various repayment options empowers borrowers to make informed decisions that align with their financial circumstances and long-term objectives.
As borrowers explore the standard, graduated, and income-driven repayment plans, as well as deferment, forbearance, and loan consolidation options, they can tailor their repayment strategy to suit their individual needs. This flexibility ensures that borrowers can manage their loan payments effectively while maintaining their financial stability.
Ultimately, the journey of repaying Perkins Loans is a significant aspect of a borrower’s financial life, and being well-informed about the minimum payment and repayment options is instrumental in achieving financial well-being. By leveraging the available resources and understanding the intricacies of Perkins Loans, borrowers can embark on a path toward successful loan repayment and long-term financial success.