Home>Finance>What Is The Purpose Of A Suicide Provision Within A Life Insurance Policy?


Finance
What Is The Purpose Of A Suicide Provision Within A Life Insurance Policy?
Published: November 24, 2023
The purpose of a suicide provision in a life insurance policy is to protect insurers against intentionally self-inflicted deaths, ensuring the policy remains financially viable. Learn more about this important aspect of life insurance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Life Insurance Policies
- What is a Suicide Provision?
- Purpose of the Suicide Provision
- Protecting the Insurance Company
- Protecting the Policyholder’s Beneficiaries
- Preventing Moral Hazard
- Examining Suicide Provisions in Different Policies
- Exceptions to the Suicide Provision
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the purpose of a suicide provision within a life insurance policy. Life insurance is a vital financial tool that provides financial protection to individuals and their loved ones in the event of their untimely death. While it may seem morbid to discuss suicide within the context of life insurance, it is an important aspect to consider as it directly impacts the policy coverage and benefits.
In this article, we will delve into the concept of a suicide provision, also known as a suicide clause, within a life insurance policy. We will explore the purpose behind its inclusion, the rationale behind protecting both the insurance company and the policyholder’s beneficiaries, and its role in preventing moral hazards.
Life insurance policies come in various types, including term life insurance, whole life insurance, and universal life insurance. Regardless of the type, most policies include a suicide provision. This provision outlines specific conditions and limitations related to suicides that occur within a certain timeframe after the policy’s inception. It is crucial to understand the implications of this provision to ensure your loved ones receive the intended financial support in the event of your unfortunate demise.
Though the topic may be sensitive, it is vital to shed light on the importance and significance of a suicide provision within a life insurance policy. By understanding its purpose and the various aspects associated with it, you can make informed decisions regarding your life insurance needs while ensuring the financial well-being of your beneficiaries.
Understanding Life Insurance Policies
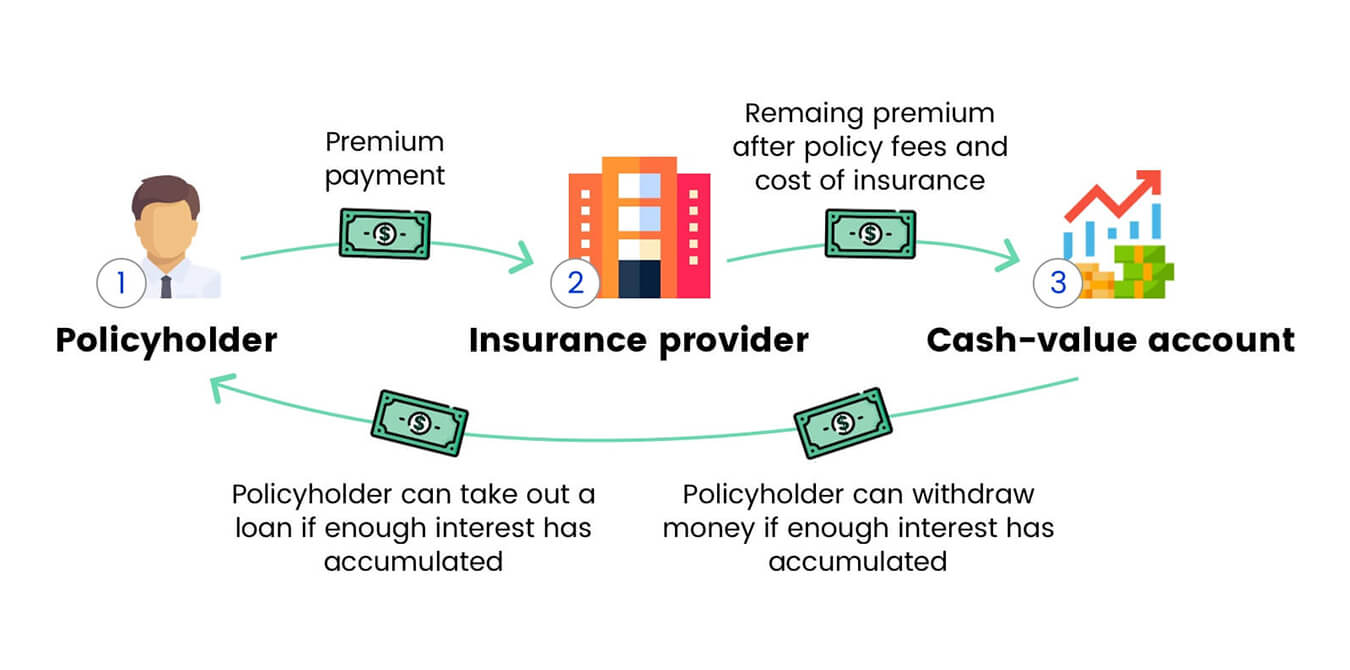
Before delving into the concept of a suicide provision within a life insurance policy, it is essential to have a basic understanding of how life insurance works. Life insurance is a contract between an individual (the insured) and an insurance company (the insurer). The insured pays regular premiums to the insurer, and in return, the insurer promises to provide a designated sum of money, known as the death benefit, to the policyholder’s beneficiaries upon the insured’s death.
Life insurance policies come in different types, including term life insurance, whole life insurance, and universal life insurance. Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, such as 10, 20, or 30 years. Whole life insurance, on the other hand, provides coverage for the insured’s entire life and also accumulates cash value over time. Universal life insurance combines the benefits of both term and whole life insurance.
Life insurance policies play a crucial role in ensuring financial security for the insured’s dependents, such as their spouse, children, or other loved ones. The death benefit provided by the policy can be used to cover various expenses, including funeral costs, outstanding debts, mortgage payments, and ongoing living expenses.
Insurance companies assess the risk involved in providing life insurance coverage by considering various factors, including the insured’s age, health condition, occupation, lifestyle choices, and medical history. These factors help determine the premium amounts and the extent of coverage offered by the policy.
Now that we have established a foundation of understanding life insurance policies, let us explore the concept of a suicide provision and its significance within these policies.
What is a Suicide Provision?
A suicide provision, also known as a suicide clause, is a common feature found in most life insurance policies. It is a provision that specifies the conditions and limitations regarding suicides that occur within a certain timeframe after the policy’s inception. Essentially, it defines how the policy will respond in the unfortunate event of the insured taking their own life.
The suicide provision typically states that if the insured dies by suicide within a specific period, often within the first two years of the policy, the death benefit will not be paid out to the beneficiaries. Instead, the insurance company will generally refund the premiums paid by the insured, minus any expenses incurred by the insurer.
The specific details of the suicide provision can vary depending on the insurance company and the policy type. Some policies may exclude suicide as a cause of death entirely, while others may have longer waiting periods before the provision is no longer applicable.
It’s important to note that the suicide provision applies to intentional self-inflicted deaths only. If the insured dies due to reasons beyond their control, such as natural causes or accidents, the suicide provision does not apply, and the death benefit will be paid out to the beneficiaries.
Insurance companies include the suicide provision in policies to mitigate the risk of adverse selection. Adverse selection refers to the situation where individuals who have a higher probability of dying soon or who are at a higher risk of suicide are more likely to purchase life insurance. By having a suicide provision in place, insurance companies can protect themselves from potential losses caused by individuals intentionally taking out a policy with the intent to commit suicide.
While the presence of a suicide provision may initially seem harsh or insensitive, it is crucial to understand its purpose within the broader context of life insurance policies. It serves to strike a balance between providing financial protection to the policyholder’s beneficiaries while protecting the financial interests of the insurance company.
Purpose of the Suicide Provision
The inclusion of a suicide provision within a life insurance policy serves several important purposes. Let’s explore these purposes in detail:
Protecting the Insurance Company: One of the primary purposes of a suicide provision is to protect the financial interests of the insurance company. Suicides are considered high-risk events for insurers, as intentional self-inflicted deaths are within the control of the insured. By including a suicide provision, insurance companies can mitigate the risk of adverse selection, ensuring that individuals with a higher probability of intentionally causing harm to themselves do not exploit the policy for financial gain.
Protecting the Policyholder’s Beneficiaries: Another crucial purpose of the suicide provision is to safeguard the interests of the policyholder’s beneficiaries. Life insurance is designed to provide financial support to dependents in the event of the insured’s death. However, if an individual purchases a policy with the intention of committing suicide shortly after, it could be seen as an attempt to defraud the insurance company. By including a suicide provision, the insurer ensures that the financial benefits are provided to beneficiaries who are not involved in the intentional act of self-harm.
Preventing Moral Hazard: The suicide provision also serves as a deterrent to individuals who might be contemplating suicide simply to provide a financial windfall for their loved ones. The provision’s presence encourages individuals to seek help and prioritize their mental health rather than viewing life insurance as a solution to their financial problems. It promotes responsible decision-making and discourages the idea of intentionally causing harm to oneself for monetary gain.
The suicide provision should be seen as a balance between protecting the insurance company from adverse selection and safeguarding the interests of the policyholder’s beneficiaries. While it may seem harsh or insensitive, it ensures that life insurance policies fulfill their intended purpose of providing financial security to dependents in tragic circumstances.
In the next sections, we will examine the specifics of the suicide provision across different types of life insurance policies, as well as the exceptions that may apply under certain circumstances.
Protecting the Insurance Company
The suicide provision within a life insurance policy plays a significant role in protecting the financial interests of the insurance company. Let’s explore how it serves this purpose:
Managing Risk: Suicides are considered high-risk events for insurance companies because they are intentional acts within the control of the insured. Actuarial calculations and underwriting processes are crucial for insurance companies to assess the risks associated with providing life insurance coverage. By including a suicide provision, insurers can manage this risk by excluding intentional self-inflicted deaths during a specific timeframe after the policy’s inception.
Preventing Adverse Selection: Adverse selection is a phenomenon where individuals with a higher probability of dying soon or those who are at a higher risk of suicide are more likely to purchase life insurance policies. By including a suicide provision, insurance companies protect themselves from adverse selection by discouraging those with suicidal tendencies from taking out policies primarily to benefit their loved ones financially. This helps maintain a fair and balanced risk pool among policyholders.
Mitigating Financial Losses: Suicides can have a significant financial impact on insurance companies, as they may result in large death benefit payouts. By including a suicide provision, insurers can minimize potential losses caused by individuals intentionally taking out policies with the intent to commit suicide. The provision ensures that insurance benefits are provided to beneficiaries based on a fair assessment of the insured’s intent at the time of policy creation.
Ensuring Long-Term Viability: Insurance companies aim to maintain long-term viability and ensure the continued delivery of financial protection to policyholders. By incorporating a suicide provision, insurers establish a measure of risk management that contributes to the stability and sustainability of the insurance industry. This protection ultimately benefits policyholders as it helps ensure the availability of life insurance products at affordable rates.
It’s important to note that the suicide provision is not a blanket exclusion. Many life insurance policies still provide coverage for suicides after the specified waiting period has passed, typically within the first two years of the policy. This demonstrates the balance insurance companies aim to strike between managing risk and fulfilling their commitment to support beneficiaries in tragic circumstances.
By protecting their financial interests through the inclusion of a suicide provision, insurance companies can maintain stability in the industry, support long-term viability, and ensure the availability of life insurance products that meet the needs of individuals and their loved ones.
Protecting the Policyholder’s Beneficiaries
The suicide provision within a life insurance policy also serves to protect the interests of the policyholder’s beneficiaries. Let’s explore how it fulfills this purpose:
Fair Distribution of Benefits: Life insurance policies are designed to provide financial support to the policyholder’s loved ones in the event of their untimely death. By including a suicide provision, insurance companies ensure that the death benefit is distributed fairly to beneficiaries who are not involved in the intentional act of self-harm. This protects the integrity of the policy and ensures that the intended financial protection reaches those who truly rely on it.
Prevention of Fraudulent Claims: In some unfortunate cases, individuals may purchase life insurance policies with the intention of committing suicide shortly after, in an attempt to provide a financial windfall for their beneficiaries. The suicide provision acts as a deterrent to such fraudulent claims. By excluding coverage for intentional self-inflicted deaths within a certain timeframe, insurance companies minimize the risk of policyholders exploiting the system for personal gain at the expense of the insurer and other policyholders.
Encouraging Mental Health Support: The inclusion of a suicide provision encourages individuals who may be struggling with suicidal thoughts to seek help and prioritize their mental health. Insurance companies recognize the importance of addressing mental health issues appropriately rather than relying on life insurance as a solution to financial problems. By promoting responsible decision-making, the provision helps policyholders understand the significance of seeking professional help in times of distress.
Stability and Accessibility of Life Insurance: Protecting the interests of policyholder beneficiaries through the suicide provision contributes to the stability of the life insurance industry. By managing risks associated with intentional self-inflicted deaths, insurance companies can maintain financial stability and continue to offer life insurance products at affordable rates. This ensures that policyholders’ loved ones have access to necessary financial protection in times of need.
While the suicide provision may seem restrictive, it is put in place to uphold the purpose of life insurance – to provide genuine support to policyholder beneficiaries during difficult times. By protecting the interests of beneficiaries, insurance companies ensure that the death benefit is allocated fairly and responsibly, fostering trust and maintaining the integrity of the life insurance industry.
Next, we will explore exceptions to the suicide provision and circumstances in which the provision may not apply within certain life insurance policies.
Preventing Moral Hazard
The inclusion of a suicide provision within a life insurance policy serves an important role in preventing moral hazard. Let’s explore how it accomplishes this:
Encouraging Responsible Decision-Making: By incorporating a suicide provision, insurance companies aim to discourage individuals from viewing life insurance as a means to intentionally cause harm to themselves for monetary gain. The provision sends a clear message that life insurance is intended to provide financial protection for dependents in the event of an unforeseen tragedy, rather than as a tool for self-inflicted harm. This encourages responsible decision-making and discourages individuals from contemplating suicidal acts solely for financial reasons.
Prioritizing Mental Health: The inclusion of a suicide provision underscores the importance of prioritizing mental health and seeking professional help when facing emotional distress. Insurance companies recognize that life insurance should not be seen as a solution to underlying mental health issues or financial problems. Rather, it serves as a safety net for loved ones in the event of an unforeseen tragedy. By promoting the importance of seeking help, the suicide provision encourages individuals to prioritize their well-being and addresses the root causes of distress rather than relying solely on insurance benefits.
Maintaining Fairness Among Policyholders: Without a suicide provision, there would be a significant moral hazard as individuals with suicidal intentions could secure life insurance policies with the intent of benefiting their loved ones through intentionally self-inflicted death. This would unfairly burden the insurance company and policyholders who play by the rules. By including a suicide provision, insurers ensure that policyholders who genuinely seek financial protection for their beneficiaries are not unfairly impacted by the actions of those seeking to exploit the system for personal gain.
By incorporating a suicide provision within life insurance policies, insurance companies strike a balance between providing financial protection to beneficiaries and discouraging morally hazardous behavior. It encourages responsible decision-making, helps to prioritize mental health, and ensures fairness among policyholders.
Next, we will examine the specific details of suicide provisions in different types of life insurance policies, including the waiting periods and exceptions that may apply.
Examining Suicide Provisions in Different Policies
While suicide provisions are a common feature in most life insurance policies, the specific details can vary depending on the policy type and the insurance company. Let’s explore how suicide provisions are structured in different types of life insurance policies:
Term Life Insurance: Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, typically ranging from 10 to 30 years. Suicide provisions in term life insurance policies usually include a waiting period, typically two years from the policy’s effective date. If the insured dies by suicide during this waiting period, the death benefit may be excluded, and the premiums paid by the policyholder are typically refunded.
Whole Life Insurance: Whole life insurance provides coverage for the insured’s entire life and accumulates cash value over time. Suicide provisions in whole life insurance policies generally follow a similar waiting period structure as term life insurance. If the insured dies by suicide within the waiting period, the death benefit may be excluded. However, after the waiting period elapses, typically two years, the suicide provision typically no longer applies, and the full death benefit is paid out to the beneficiaries.
Universal Life Insurance: Universal life insurance is a flexible policy that combines the benefits of term and whole life insurance. Like other policy types, universal life insurance generally includes a suicide provision with a waiting period. The specific details of the provision can vary across different insurers and policies, but the general principle remains the same: the death benefit may be excluded if the insured dies by suicide within the waiting period, typically two years.
It’s important to review the specific terms and conditions of the policy to understand the exact provisions and waiting periods that apply. Additionally, different insurance companies may have variations in their suicide provisions. Some may have shorter waiting periods or additional requirements, so it’s crucial to read the policy documentation carefully and consult with an insurance professional if there are any questions or concerns.
Exceptions to the suicide provision may exist in certain circumstances, such as if the suicide occurs due to the insured’s mental illness or if the policy was in force for an extended period. These exceptions can vary among insurance companies, so it’s important to verify the specific conditions under which the suicide provision may be waived.
Understanding the suicide provision within different life insurance policies helps policyholders and their beneficiaries have a clear perspective on the coverage and benefits they can expect. It emphasizes the importance of reviewing policy details and seeking clarification from insurance providers to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the suicide provision’s specific terms.
In the next section, we will wrap up our discussion by summarizing key aspects related to suicide provisions within life insurance policies.
Exceptions to the Suicide Provision
While suicide provisions are a common feature in life insurance policies, there are exceptions under which the provision may not apply. These exceptions vary depending on the insurance company and the policy type. Let’s explore some common exceptions to the suicide provision:
Mental Illness: In some cases, if the insured’s suicide is a result of a documented mental illness, the suicide provision may be waived. Insurance companies recognize that mental health issues can significantly impact an individual’s state of mind and decision-making. In such circumstances, the policy may still provide the full death benefit to the beneficiaries, even if the death is ruled a suicide.
Extended Waiting Period: While most suicide provisions have a waiting period of typically two years, some policies may have longer waiting periods. If the suicide occurs after the waiting period has elapsed, the provision may no longer apply, and the full death benefit will be paid out to the beneficiaries. It is important to review the policy terms to understand the specific waiting period and its impact on the suicide provision.
Reduced Death Benefit: In certain cases, instead of excluding the entire death benefit, the suicide provision may stipulate that a reduced death benefit will be paid out if the insured dies by suicide within the waiting period. The specific reduction can vary, but typically it is a percentage of the death benefit, such as 50%. After the waiting period, the full death benefit would be paid out, provided the death is not due to suicide.
Material Misrepresentation: If it is discovered that the insured made material misrepresentations or withheld crucial information during the application process that would have affected the insurer’s underwriting decision, the suicide provision may be invoked. In such cases, the insurer may deny the claim, including cases where the death is ruled a suicide.
It is important to note that the exceptions to the suicide provision can vary among insurance companies and policies. It is essential to carefully review the specific policy terms and consult with the insurance provider to understand the circumstances under which the suicide provision may be waived or modified.
These exceptions demonstrate that insurance companies recognize unique situations and circumstances that may warrant the exclusion of the suicide provision. These exceptions provide additional protection to policyholders and their beneficiaries when faced with tragic circumstances related to suicide.
In the next section, we will conclude our discussion by summarizing the main points covered in this article.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the inclusion of a suicide provision within a life insurance policy serves several important purposes. It protects the financial interests of the insurance company, ensuring long-term viability and stability within the industry. Additionally, it safeguards the interests of the policyholder’s beneficiaries by promoting fairness and discouraging fraudulent claims. Moreover, the suicide provision acts as a deterrent, encouraging responsible decision-making and emphasizing the importance of prioritizing mental health over financial gain.
By understanding the specific details of the suicide provision in different types of life insurance policies, individuals can make informed decisions and ensure their loved ones are appropriately protected. While suicide provisions typically include waiting periods and exclusions, exceptions may exist under certain circumstances, such as mental illness or extended policy durations.
It’s crucial to carefully review the terms and conditions of a life insurance policy, including the suicide provision, to have a comprehensive understanding of the coverage and benefits. Consulting with an insurance professional can provide further clarity and guidance in navigating the complexities of the suicide provision.
Ultimately, the suicide provision is designed to strike a balance between protecting the interests of the insurance company and ensuring financial support for policyholder beneficiaries in the event of an unforeseen tragedy. It is a necessary component of life insurance policies that ensures the industry’s stability, fairness, and availability of financial protection.
Remember, life insurance should be seen as a valuable tool to provide peace of mind and financial security to loved ones. If you or someone you know is struggling with mental health issues, it is important to seek help from professionals who can provide the necessary support and guidance.
By understanding the purpose and significance of a suicide provision within a life insurance policy, individuals can make informed choices that align with their financial goals and the well-being of their beneficiaries.