Home>Finance>What Would Be The Minimum Payment On A Credit Card With A $16,000 Balance


Finance
What Would Be The Minimum Payment On A Credit Card With A $16,000 Balance
Published: February 25, 2024
Learn how to calculate the minimum payment on a credit card with a $16,000 balance and manage your finances effectively. Explore expert tips and advice on credit card payments.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Credit cards are a ubiquitous financial tool in today's world, offering convenience and flexibility for making purchases and managing expenses. However, for many individuals, credit card debt can become a burden, especially when it comes to understanding and managing minimum payments. In this article, we will delve into the concept of minimum payments on credit cards, with a specific focus on a credit card carrying a $16,000 balance. Understanding how minimum payments are calculated and the factors influencing them is crucial for individuals seeking to effectively manage their credit card debt.
By shedding light on the intricacies of minimum payments, we aim to empower readers with the knowledge to make informed financial decisions and take control of their credit card debt. Additionally, we will explore practical tips for managing credit card debt, providing actionable strategies to alleviate financial stress and pave the way towards a more secure financial future.
Credit card debt can be a significant source of financial strain, but with the right information and strategies, individuals can navigate the complexities of minimum payments and work towards achieving financial stability. Let's embark on this insightful journey to unravel the mysteries of credit card minimum payments and discover actionable steps for managing credit card debt effectively.
Understanding Credit Card Minimum Payments
Credit card minimum payments represent the lowest amount that a cardholder must pay each month to keep the account in good standing. While making the minimum payment by the due date helps avoid late fees and negative marks on one’s credit report, it’s essential to recognize that this approach can lead to long-term financial challenges due to accruing interest and prolonged debt repayment.
Typically, a credit card’s minimum payment is calculated as a percentage of the outstanding balance, often ranging from 1% to 3% of the total amount owed. This percentage may also be subject to a minimum dollar amount, such as $25, ensuring that the minimum payment doesn’t fall below a certain threshold.
It’s crucial for cardholders to comprehend that while making only the minimum payment may offer temporary relief, it can result in substantial interest charges, leading to a significant increase in the overall cost of the debt. This can create a cycle of debt that becomes increasingly challenging to break free from, especially when additional charges are placed on the card, further compounding the balance and interest.
Understanding the implications of minimum payments is vital for individuals aiming to manage their credit card debt effectively. By grasping the relationship between minimum payments, interest accrual, and the long-term impact on financial well-being, cardholders can make informed decisions regarding their debt repayment strategies.
As we continue our exploration, we will delve into the factors that influence minimum payments on credit cards, shedding light on the dynamics that determine the amount cardholders are required to pay each month. This understanding will lay the groundwork for calculating the minimum payment on a credit card carrying a $16,000 balance, offering valuable insights into the practical implications of managing credit card debt.
Factors Affecting Minimum Payments
Several key factors influence the calculation of minimum payments on credit cards, playing a pivotal role in determining the amount that cardholders are required to pay each month. Understanding these factors is essential for individuals seeking to gain insight into the dynamics of credit card debt management and make informed decisions regarding their financial responsibilities.
1. Outstanding Balance: The outstanding balance on a credit card is a primary determinant of the minimum payment. Typically, the minimum payment is calculated as a percentage of the total amount owed, meaning that a higher balance will result in a larger minimum payment requirement.
2. Interest Rate: The annual percentage rate (APR) associated with a credit card directly impacts the minimum payment. Higher interest rates lead to increased interest charges, consequently raising the minimum payment to ensure the timely reduction of the outstanding balance.
3. Minimum Payment Calculation Method: Credit card issuers utilize various methods to calculate minimum payments, often incorporating a percentage of the outstanding balance, a minimum dollar amount, or a combination of both. Understanding the specific calculation method employed by the credit card issuer is crucial for predicting and managing minimum payment obligations.
4. Additional Charges and Fees: Any additional charges, such as late fees or over-limit fees, can contribute to an escalation in the minimum payment amount. It’s important for cardholders to be mindful of these potential charges and their impact on minimum payment requirements.
5. Credit Utilization Ratio: The credit utilization ratio, which represents the proportion of available credit being used, can influence minimum payments. Higher credit utilization ratios may prompt credit card issuers to require larger minimum payments to manage perceived risk.
By comprehending these influential factors, individuals can gain clarity on the mechanisms driving minimum payments on credit cards. This understanding forms the basis for effectively managing credit card debt and devising strategic approaches to mitigate financial challenges associated with outstanding balances and interest accrual.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of minimum payments, we will leverage this knowledge to calculate the minimum payment on a credit card carrying a $16,000 balance, offering practical insights into the real-world implications of these influential factors.
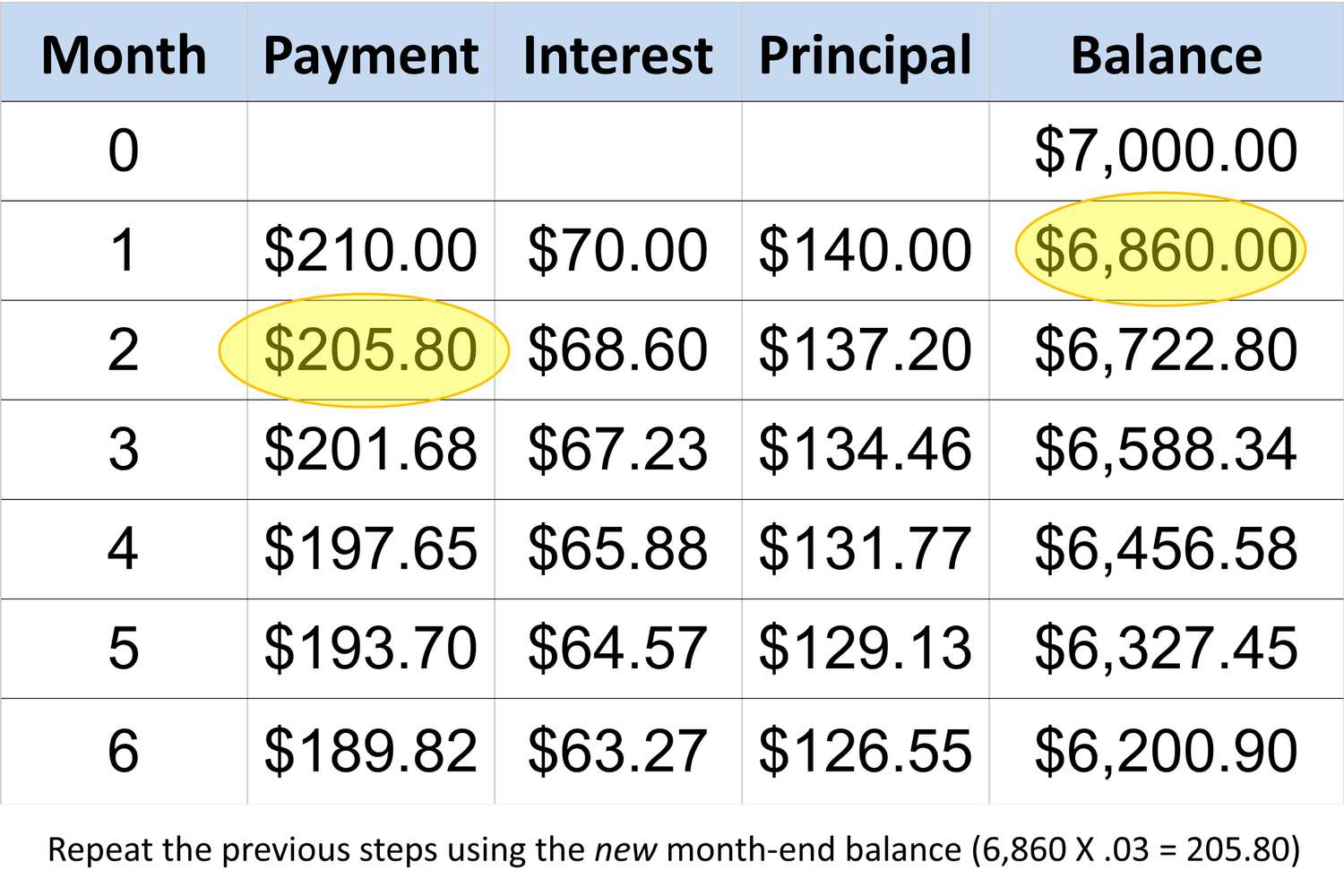
Calculating the Minimum Payment on a $16,000 Credit Card Balance
When faced with a substantial credit card balance, understanding how the minimum payment is calculated becomes crucial for effectively managing debt obligations. In the case of a $16,000 credit card balance, the calculation of the minimum payment involves several key considerations.
First and foremost, it’s essential to recognize that credit card issuers employ varying methods to determine minimum payments. While the most common approach involves a percentage of the outstanding balance, often around 1% to 3%, credit card agreements may also specify a minimum dollar amount to ensure that the minimum payment meets a certain threshold.
Considering a hypothetical scenario where a credit card issuer requires a minimum payment equivalent to 2% of the outstanding balance with a minimum payment floor of $30, the calculation for the minimum payment on a $16,000 balance would unfold as follows:
- Step 1: Calculate the percentage-based minimum payment:
- $16,000 (balance) x 2% = $320
- Step 2: Compare the percentage-based minimum payment to the minimum payment floor:
- $320 (calculated minimum payment) > $30 (minimum payment floor)
- Step 3: Determine the minimum payment:
- The minimum payment is the greater of the two amounts, resulting in a minimum payment of $320 in this scenario.
It’s important to note that this calculation is based on the specified percentage and minimum payment floor provided in the credit card agreement. Cardholders should refer to their individual credit card terms to ascertain the precise calculation method and minimum payment requirements applicable to their accounts.
By understanding the calculation process for minimum payments on a $16,000 credit card balance, individuals can gain valuable insight into the financial obligations associated with managing substantial debt on their credit cards. This knowledge serves as a foundation for making informed decisions regarding debt repayment strategies and taking proactive steps towards achieving financial stability.
As we proceed, we will explore practical tips for managing credit card debt, offering actionable strategies to empower individuals in navigating the complexities of debt repayment and fostering a more secure financial future.
Tips for Managing Credit Card Debt
Effectively managing credit card debt is essential for maintaining financial stability and working towards long-term financial goals. By implementing strategic approaches to debt repayment and cultivating responsible financial habits, individuals can mitigate the challenges associated with credit card debt and pave the way for a more secure financial future. Here are valuable tips for managing credit card debt:
- Create a Repayment Plan: Develop a structured repayment plan that outlines how you will tackle your credit card debt. Consider prioritizing high-interest balances and explore consolidation options to streamline repayment.
- Pay More Than the Minimum: Whenever possible, strive to pay more than the minimum payment to expedite debt reduction. By allocating additional funds towards your credit card balances, you can minimize interest charges and accelerate the path to debt freedom.
- Monitor Your Spending: Exercise prudence in your spending habits and strive to live within your means. By tracking your expenses and adhering to a budget, you can minimize the accumulation of additional credit card debt.
- Seek Lower Interest Rates: Explore opportunities to secure lower interest rates, such as negotiating with your credit card issuer or transferring balances to cards with introductory 0% APR offers. Lower interest rates can facilitate more efficient debt repayment.
- Explore Debt Relief Options: In cases of significant financial hardship, consider exploring debt relief options such as credit counseling, debt management plans, or debt settlement. These avenues can provide structured approaches to debt resolution.
- Avoid Accumulating New Debt: Exercise caution to avoid accumulating new debt while working towards repaying existing balances. Minimize credit card usage and focus on reducing outstanding balances to achieve financial progress.
- Build an Emergency Fund: Establishing an emergency fund can provide a financial safety net, reducing the reliance on credit cards for unexpected expenses and mitigating the risk of accruing additional debt.
- Seek Professional Guidance: If navigating credit card debt becomes overwhelming, seek the guidance of financial professionals who can provide personalized advice and assistance in managing debt effectively.
By incorporating these tips into your financial strategy, you can proactively address credit card debt and work towards achieving greater financial security. Empowering yourself with the knowledge and discipline to manage credit card debt effectively is a pivotal step towards realizing your broader financial aspirations and cultivating a solid foundation for long-term prosperity.
Conclusion
Understanding the dynamics of credit card minimum payments and the implications of managing credit card debt is paramount for individuals striving to achieve financial well-being. By unraveling the intricacies of minimum payments and exploring practical strategies for debt management, individuals can navigate the complexities of credit card debt with confidence and foresight.
Throughout this exploration, we have delved into the fundamental concepts of credit card minimum payments, shedding light on the factors influencing minimum payment calculations and providing a comprehensive understanding of the dynamics at play. From the impact of outstanding balances and interest rates to the calculation of minimum payments on a $16,000 credit card balance, we have equipped readers with valuable insights to inform their debt repayment strategies and financial decision-making.
Furthermore, the provision of actionable tips for managing credit card debt empowers individuals to take proactive steps towards debt reduction and financial stability. By embracing prudent financial habits, exploring debt relief options when necessary, and seeking professional guidance, individuals can chart a course towards alleviating the burden of credit card debt and fostering a more secure financial future.
Ultimately, the journey towards effective credit card debt management is rooted in knowledge, discipline, and strategic planning. By leveraging the insights and recommendations presented in this article, individuals can cultivate a proactive approach to debt repayment, minimize financial stress, and pave the way for long-term financial prosperity.
As you navigate your financial path, remember that each step taken towards managing credit card debt is a stride towards greater financial freedom and security. By embracing informed decision-making and proactive debt management strategies, you can embark on a journey towards achieving your financial aspirations and building a solid foundation for lasting prosperity.