Home>Finance>What Is The Difference Between Debt Consolidation And Credit Card Refinancing


Finance
What Is The Difference Between Debt Consolidation And Credit Card Refinancing
Modified: December 29, 2023
Find out the distinction between debt consolidation and credit card refinancing in the world of finance. Make informed decisions to manage your finances effectively.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Overview of Debt Consolidation
- Process of Debt Consolidation
- Pros and Cons of Debt Consolidation
- Overview of Credit Card Refinancing
- Process of Credit Card Refinancing
- Pros and Cons of Credit Card Refinancing
- Key Differences Between Debt Consolidation and Credit Card Refinancing
- Factors to Consider in Choosing Between Debt Consolidation and Credit Card Refinancing
- Conclusion
Introduction
When it comes to managing financial obligations, finding the right solution can make all the difference. Two popular options for individuals seeking to address their debt are debt consolidation and credit card refinancing. While both strategies aim to help individuals regain control of their finances, there are key differences between the two.
In this article, we will explore the differences between debt consolidation and credit card refinancing, as well as the pros and cons of each approach. By understanding the distinctions and advantages of these strategies, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their financial well-being.
Debt consolidation is a method of combining multiple debts, such as credit card balances, personal loans, and medical bills, into a single loan. This approach simplifies the repayment process by consolidating all the debts under one umbrella. On the other hand, credit card refinancing specifically focuses on transferring high-interest credit card balances to a new credit card or loan with a lower interest rate.
Both debt consolidation and credit card refinancing have their merits and drawbacks, and the most suitable choice depends on individual circumstances. Factors such as the amount of debt, interest rates, credit score, and personal preferences all play a role in determining which approach is best.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the processes, advantages, and disadvantages of debt consolidation and credit card refinancing. By examining these aspects, individuals can gain a comprehensive understanding of the options available and make informed decisions to improve their financial situations.
Overview of Debt Consolidation
Debt consolidation is a financial strategy that involves combining multiple debts into a single loan or credit line. The goal is to simplify repayment by merging all outstanding balances into one manageable monthly payment. This approach can be particularly beneficial for individuals with multiple debts, such as credit card balances, personal loans, and medical bills.
The primary objective of debt consolidation is to streamline the repayment process and potentially reduce overall interest rates. By consolidating debts, individuals can simplify their financial management, as they no longer have to keep track of multiple payment due dates and amounts. Instead, they make a single payment towards the consolidated debt, making it easier to budget and plan their finances.
There are several ways to consolidate debt. One common method is to obtain a debt consolidation loan from a financial institution or online lender. This loan is specifically designed to pay off existing debts, and the borrower then makes regular payments towards the consolidation loan. Another option is to transfer balances from multiple credit cards to a single credit card with a lower interest rate.
Debt consolidation can also involve utilizing a home equity loan or a line of credit secured by collateral, such as a property or vehicle. With these options, individuals can borrow against the value of their assets to pay off existing debts. However, it’s important to exercise caution when using collateral, as defaulting on payments could result in the loss of the asset.
Overall, the aim of debt consolidation is to make debt repayment more manageable and potentially reduce the overall interest burden. It simplifies financial management and can provide individuals with a clearer path towards becoming debt-free.
Process of Debt Consolidation
The process of debt consolidation involves several steps to effectively merge multiple debts into a single loan or credit line. Each step is essential in ensuring a successful consolidation strategy. Here is a breakdown of the typical process:
- Evaluate your debt: Start by assessing your current financial situation. List out all your debts, including credit cards, personal loans, or any other outstanding balances. Note down the interest rates, minimum monthly payments, and the total amount owed for each debt.
- Research your options: Next, explore different consolidation options available to you. This may include personal loans, debt consolidation loans, home equity loans, or balance transfer credit cards. Research the terms and conditions, interest rates, fees, and eligibility criteria for each option.
- Calculate your costs: Compare the total cost of your current debts with the potential consolidation options. Calculate the interest you would pay over the repayment period and factor in any fees associated with the consolidation method. This will help you determine if consolidating your debts would be more cost-effective in the long run.
- Select a consolidation method: Based on your research and cost analysis, choose the consolidation method that best suits your needs. Consider factors such as interest rates, repayment terms, monthly payments, and any potential impact on your credit score.
- Apply for consolidation: Once you have decided on a consolidation method, submit an application to the chosen lender or financial institution. Provide all necessary documents, such as proof of income, identification, and details of your existing debts. The lender will review your application and determine if you meet their criteria for approval.
- Consolidate and repay: If approved, the lender will disburse the funds to pay off your existing debts. Going forward, you will have one consolidated loan or credit line to manage. Make regular monthly payments according to the agreed-upon terms until the debt is fully repaid.
- Monitor and adjust: Continuously monitor your finances and track your progress towards debt repayment. Take steps to avoid accumulating additional debts and make adjustments to your budget if needed. Consult with a financial advisor if you need further guidance on managing your finances effectively.
Remember, debt consolidation is not a quick-fix solution and requires discipline, commitment, and responsible financial management. It is important to have a solid repayment plan in place and avoid taking on new debts while in the consolidation process.
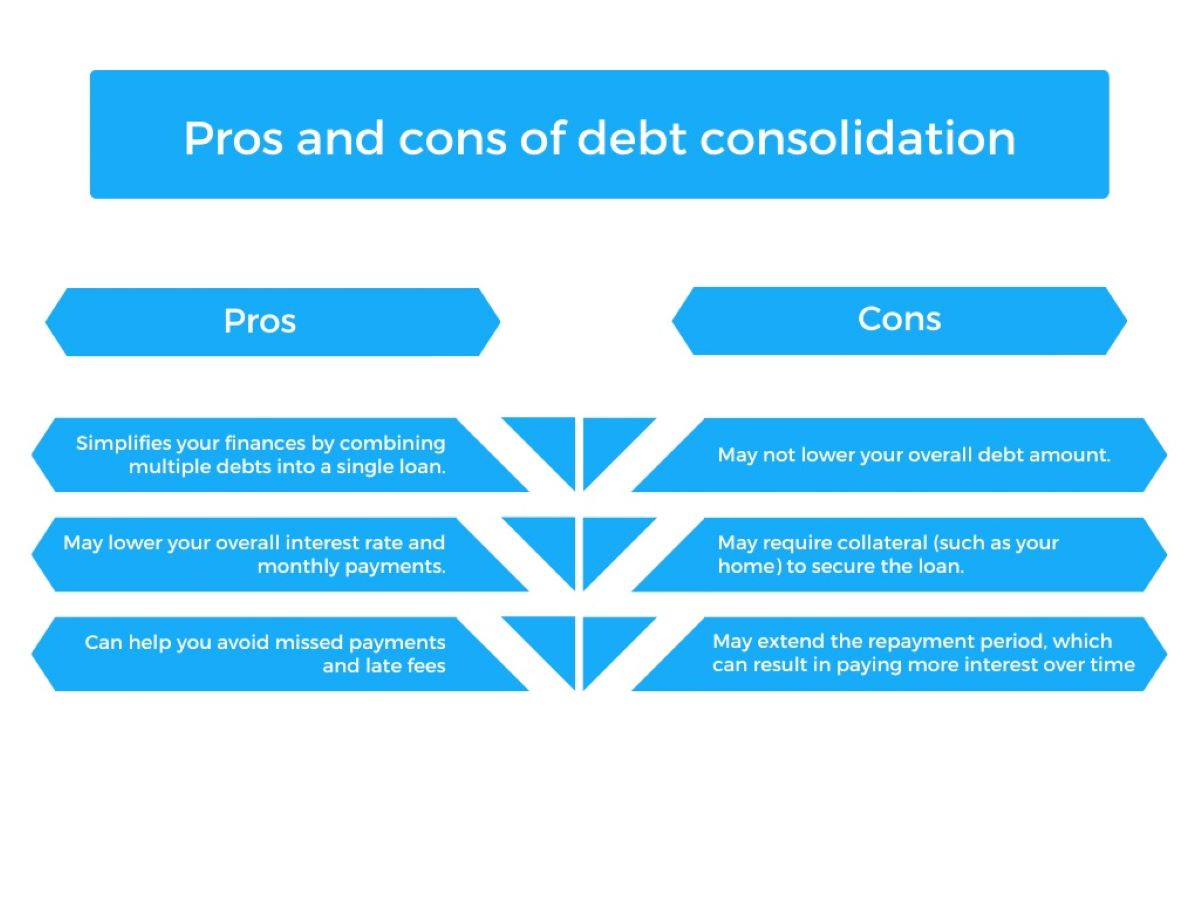
Pros and Cons of Debt Consolidation
Debt consolidation can be a useful financial strategy for individuals seeking to manage their debts more effectively. However, like any financial approach, it has both advantages and disadvantages. In this section, we will explore the pros and cons of debt consolidation to help you make an informed decision.
Pros of Debt Consolidation:
- Simplified repayment: Debt consolidation combines multiple debts into a single loan or credit line, resulting in one monthly payment. This streamlines your financial management, making it easier to keep track of payments and manage your budget.
- Potential for lower interest rates: Consolidating your debts can provide an opportunity to secure a lower interest rate compared to your existing debts. This can save you money in interest payments over the course of the consolidation loan.
- Reduced stress: Dealing with multiple debt payments can be overwhelming and stressful. Debt consolidation alleviates some of that stress by simplifying the repayment process and providing a clear path to becoming debt-free.
- Improved credit score: Successfully managing and repaying a consolidated debt can have a positive impact on your credit score. Timely repayments will demonstrate financial responsibility, potentially improving your creditworthiness over time.
- Ability to negotiate: When consolidating debts, there may be opportunities to negotiate with creditors to lower the outstanding balance or negotiate more favorable terms. This can help reduce the overall burden of your debt.
Cons of Debt Consolidation:
- Potential for fees and costs: Some consolidation methods may come with upfront fees, closing costs, or other charges. It is important to factor in these costs when evaluating the overall financial benefit of consolidation.
- Extended repayment period: Debt consolidation may result in a longer repayment period compared to your original debts. While this can lead to more manageable monthly payments, it also means paying more in interest over time.
- Risk of additional debt: Consolidating your debts does not eliminate the underlying financial issues that led to the debt accumulation. If you continue to rely on credit cards and loans without addressing spending habits, you may end up with even more debt.
- Potential impact on credit score: Applying for a debt consolidation loan or credit line may have a temporary negative impact on your credit score. However, making timely payments and responsibly managing your debt can help rebuild your credit over time.
- Loss of assets: Some consolidation methods, such as using home equity, involve putting assets at risk. If you default on payments, you could potentially lose the collateral used to secure the consolidation loan.
It is important to weigh these pros and cons carefully and consider your individual financial situation before deciding to pursue debt consolidation. Additionally, consulting with a financial advisor can provide valuable guidance and help you determine the best course of action.
Overview of Credit Card Refinancing
Credit card refinancing is a financial strategy that involves transferring high-interest credit card balances to a new credit card or loan with a lower interest rate. The primary objective of credit card refinancing is to reduce the amount of interest paid on outstanding credit card debt.
Many credit card issuers offer introductory promotional periods, during which they offer low or 0% interest rates on balance transfers. By taking advantage of these promotional rates, individuals can save money on interest and potentially pay off their credit card debt faster.
Refinancing credit card debt can be especially beneficial for individuals who are struggling to make minimum payments or are burdened by high-interest rates. Moving the balances to a lower interest rate card or loan can provide some relief and help individuals regain control of their finances.
It’s important to note that credit card refinancing is not a solution to eliminate debt completely. Rather, it is a strategy to make debt more manageable and potentially save on interest costs. Individuals should also be aware of any balance transfer fees or annual fees associated with the new credit card or loan.
Credit card refinancing can be done through various methods. One option is to apply for a new credit card that offers a low or 0% APR on balance transfers for an introductory period. Individuals can transfer their existing credit card balances to the new card and make payments towards the consolidated debt at a lower interest rate.
Another method of credit card refinancing is to take out a personal loan with a lower interest rate than the credit cards’ rates. This loan is used to pay off the credit card debt, leaving the individual with a single loan payment to manage with a potentially lower interest rate.
Ultimately, credit card refinancing provides an opportunity to save money on interest and make credit card debt more manageable. It can be a viable option for individuals looking to reduce their financial burden and take steps towards improving their overall financial health.
Process of Credit Card Refinancing
The process of credit card refinancing involves several steps to transfer high-interest credit card balances to a new credit card or loan with more favorable terms. Here is a breakdown of the typical process:
- Evaluate your credit card debt: Assess your current credit card balances, interest rates, and minimum monthly payments. Determine how much debt you want to refinance and calculate the total outstanding balance.
- Research credit card refinancing options: Compare different credit card issuers and financial institutions that offer refinancing options. Look for cards or loans that offer low or 0% introductory APRs specifically for balance transfers.
- Check your eligibility: Review the eligibility criteria for the credit card or loan you are considering. This may include factors such as credit score requirements, income verification, and any specific restrictions or limitations that may apply.
- Apply for credit card or loan: Once you have selected a refinancing option, submit an application with the chosen credit card issuer or financial institution. Provide the necessary information, including personal and financial details, to complete the application.
- Wait for approval: The credit card issuer or financial institution will review your application and determine if you meet their criteria for approval. This process typically involves a credit check to assess your creditworthiness.
- Transfer the balances: If your application is approved, you will receive the new credit card or loan. Contact the credit card issuer or financial institution to initiate the balance transfer process. Provide the necessary information to transfer your existing credit card balances to the new card or loan.
- Start making payments: Once the balance transfer is complete, start making payments towards the new credit card or loan. Follow the terms and conditions of the refinancing agreement, including monthly payment amounts and due dates.
- Monitor your progress: Keep track of your refinanced balances and payments. Set a repayment plan and make consistent payments to reduce your debt over time. Avoid adding new debts to the refinanced credit card to maximize the benefits of the lower interest rate.
It is important to read and understand the terms and conditions of the credit card or loan you choose for refinancing. Take note of any introductory APR periods, balance transfer fees, annual fees, or other charges that may apply. Additionally, be aware that failing to make timely payments may result in the loss of the promotional APR and potentially incur additional fees or penalties.
By following these steps and effectively managing your refinanced credit card debt, you can take control of your financial situation and potentially save money on interest payments. However, it is crucial to exercise responsible financial management and avoid racking up new credit card debt in the future.
Pros and Cons of Credit Card Refinancing
Credit card refinancing offers individuals the opportunity to transfer high-interest credit card balances to a new credit card or loan with more favorable terms. While this strategy can be beneficial for some, it is important to consider both the advantages and disadvantages before pursuing credit card refinancing. Here are the pros and cons:
Pros of Credit Card Refinancing:
- Lower interest rates: One of the primary benefits of credit card refinancing is the potential for lower interest rates. By transferring balances to a new credit card or loan with a lower APR, individuals can reduce the amount of interest they pay over time, potentially saving them money.
- Consolidated payments: Refinancing credit card debt allows individuals to consolidate multiple credit card balances into a single payment. This simplifies financial management by reducing the number of monthly payments to keep track of and potentially provides a clearer overview of overall debt.
- Opportunity to pay off debt faster: With lower interest rates, more of each payment goes towards the principal balance, allowing individuals to potentially pay off their credit card debt faster than if they remained on high-interest credit cards.
- Simplicity and convenience: Refinancing credit card debt can streamline the repayment process. By having only one credit card or loan to manage, individuals can avoid juggling multiple payments and due dates, making financial management more convenient.
- Potential for improved credit score: Responsible credit card refinancing and consistent repayment can positively impact an individual’s credit score. Making timely payments and reducing credit utilization can demonstrate financial responsibility and improve overall creditworthiness.
Cons of Credit Card Refinancing:
- Balance transfer fees: Some credit card issuers may charge balance transfer fees when transferring balances from one card to another. This fee is typically a percentage of the balance being transferred and can offset the potential savings from refinancing.
- Interest rate changes after the introductory period: Many credit cards offer low or 0% APR introductory periods for balance transfers as a promotional offer. However, once the introductory period ends, the interest rate may increase, potentially nullifying the initial savings if the balance is not paid off in full.
- Potential impact on credit score: Applying for a new credit card or loan for refinancing purposes may result in a temporary dip in credit score due to the credit inquiry. However, responsible management and consistent, on-time payments can help rebuild and improve the credit score over time.
- Risk of accumulating new debt: Refinancing credit card debt does not address the underlying financial behaviors that led to the accumulation of debt. If individuals continue to rely on credit cards without proper budgeting and spending habits, they may find themselves with even more debt in the future.
- Not suitable for everyone: Credit card refinancing may not be the best option for everyone. Factors such as creditworthiness, income stability, and personal financial goals should be considered before pursuing credit card refinancing as a debt management strategy.
It is crucial to carefully weigh the pros and cons of credit card refinancing before deciding to pursue this strategy. Consider your individual financial situation, goals, and preferences to determine if refinancing your credit card debt aligns with your needs. Consulting with a financial advisor can also provide valuable insights and guidance in making the right decision.
Key Differences Between Debt Consolidation and Credit Card Refinancing
While both debt consolidation and credit card refinancing aim to help individuals manage their debt, there are significant differences between the two approaches. Understanding these differences is crucial in determining the most suitable strategy for your financial situation. Here are the key distinctions:
Debt Consolidation:
- Debts included: Debt consolidation involves consolidating multiple debts, which can include credit card balances, personal loans, medical bills, and other outstanding obligations, into a single loan or credit line.
- Objective: The main purpose of debt consolidation is to simplify the repayment process by combining multiple debts into one, potentially reducing the overall interest rate and creating a clear repayment plan.
- Methods: Debt consolidation can be achieved through obtaining a debt consolidation loan, transferring balances to a low-interest credit card, or using a home equity loan or line of credit.
- Payment structure: With debt consolidation, individuals make a single monthly payment towards the consolidated debt, rather than multiple payments to different creditors.
- Impact on credit score: Debt consolidation may initially have a temporary negative impact on credit score due to the new loan application. However, making on-time payments can ultimately have a positive effect on credit score over time.
Credit Card Refinancing:
- Debts included: Credit card refinancing specifically focuses on transferring high-interest credit card balances to a new credit card or loan with more favorable terms.
- Objective: The primary goal of credit card refinancing is to lower the interest rate on credit card debt, potentially reducing the overall interest paid and making repayment more manageable.
- Methods: Credit card refinancing is typically done through balance transfers to a new credit card that offers a promotional low or 0% APR, or by obtaining a personal loan with a lower interest rate than the credit cards being refinanced.
- Payment structure: Credit card refinancing may result in a single monthly payment if all credit card balances are consolidated onto one card or loan. However, if multiple credit cards are refinanced individually, separate payments may still be required.
- Impact on credit score: Applying for new credit cards or loans for refinancing purposes may have a temporary impact on credit score due to the credit inquiry. However, responsible repayment can help rebuild and improve the credit score over time.
These key differences highlight that debt consolidation is a broader approach that encompasses multiple debts, while credit card refinancing specifically targets high-interest credit card balances. Debt consolidation can involve different methods and may have a greater impact on credit score, while credit card refinancing focuses on transferring balances to lower-interest options. Understanding these distinctions allows individuals to choose the most appropriate debt management strategy based on their unique financial circumstances.
Factors to Consider in Choosing Between Debt Consolidation and Credit Card Refinancing
When deciding between debt consolidation and credit card refinancing as debt management strategies, several factors should be taken into account to determine the most suitable approach for your financial situation. Consider the following factors before making a decision:
1. Types of Debts:
Assess the types of debts you have. If you have various debts beyond credit cards, such as personal loans, medical bills, or student loans, debt consolidation may be a more comprehensive solution. On the other hand, if the majority of your debt is specifically credit card balances, credit card refinancing may be a more targeted approach.
2. Interest Rates:
Compare the interest rates on your current debts with the potential rates offered through debt consolidation or credit card refinancing. If you can secure a significantly lower interest rate through refinancing, it may be a valuable opportunity to save money on interest costs.
3. Total Debt Amount:
Consider the total amount of debt you have. If you have a relatively small amount of debt that can be easily managed, you may not require the consolidation process. However, if you have a substantial amount of debt that is overwhelming to handle, debt consolidation or credit card refinancing may provide the structure needed to effectively manage and reduce your debt burden.
4. Credit Score and Credit History:
Assess your credit score and credit history. Debt consolidation and credit card refinancing may have different requirements and eligibility criteria. If your credit score is lower and you have a history of late payments or high credit utilization, debt consolidation may be more accessible. On the other hand, if your credit score is strong, credit card refinancing options with lower interest rates may be available.
5. Fees and Costs:
Consider any fees associated with debt consolidation or credit card refinancing. Balance transfer fees, origination fees, or annual fees could impact the overall savings or cost effectiveness of each option. Evaluate these fees alongside the potential interest savings to determine the true value of each approach.
6. Repayment Timeline:
Evaluate your desired repayment timeline. Debt consolidation loans typically have a fixed repayment term, whereas credit card refinancing can offer flexibility depending on the terms of the new credit card or loan. Consider whether a shorter or longer repayment timeline aligns better with your financial goals and capabilities.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision about whether debt consolidation or credit card refinancing is the best choice for your specific circumstances. It may also be helpful to consult with a financial advisor who can provide personalized guidance based on your financial goals and objectives.
Conclusion
Managing debt effectively is crucial for financial stability and peace of mind. Debt consolidation and credit card refinancing are two popular strategies that can help individuals regain control over their finances. While both approaches aim to simplify repayment and potentially reduce interest costs, they have distinct differences that should be carefully considered when choosing the best option for your situation.
Debt consolidation involves combining multiple debts into a single loan or credit line, streamlining repayment and potentially reducing overall interest rates. It is a comprehensive approach that can encompass various types of debt. On the other hand, credit card refinancing specifically focuses on transferring high-interest credit card balances to a new credit card or loan with lower interest rates.
When making a decision, it is important to consider factors such as the types and amounts of debt, interest rates, credit score, and repayment goals. Debt consolidation can be beneficial when dealing with diverse debts, while credit card refinancing may be more suitable for individuals with significant credit card balances. Understanding the fees, costs, and potential impact on credit scores is also crucial in making the right choice.
Ultimately, selecting the most suitable strategy requires a thoughtful assessment of your financial circumstances and goals. Each option has its advantages and disadvantages, and what works for one person may not work for another. It may be helpful to consult with a financial advisor to understand the implications and tailor the solution to your specific needs.
Regardless of the chosen approach, both debt consolidation and credit card refinancing should be complemented by responsible financial practices. It is essential to address the root causes of debt, develop a budget, and avoid incurring new debts. By taking proactive steps towards financial wellness, individuals can achieve lasting debt management success and pave the way for a brighter financial future.