Home>Finance>What Is The Difference Between Credit Card Refinancing And Debt Consolidation


Finance
What Is The Difference Between Credit Card Refinancing And Debt Consolidation
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn about the key distinctions between credit card refinancing and debt consolidation in the realm of finance. Discover which option is the right fit for your needs.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Overview of Credit Card Refinancing
- Overview of Debt Consolidation
- Key Differences Between Credit Card Refinancing and Debt Consolidation
- Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Credit Card Refinancing and Debt Consolidation
- Pros and Cons of Credit Card Refinancing
- Pros and Cons of Debt Consolidation
- Conclusion
Introduction
When it comes to managing your finances, credit card debt can be a significant burden. High interest rates, multiple payments, and mounting bills can make it challenging to get ahead. Fortunately, there are options available to help you regain control of your financial situation. Two popular methods for tackling credit card debt are credit card refinancing and debt consolidation.
In this article, we will explore the differences between credit card refinancing and debt consolidation and outline the key factors to consider when choosing between the two. By understanding these options, you can make an informed decision about the best approach for your unique financial circumstances.
Before delving into the specifics, it’s important to have a clear understanding of the objectives of credit card refinancing and debt consolidation. Both methods aim to simplify your financial obligations and potentially reduce your overall debt burden. However, they achieve this through different means.
Credit card refinancing involves transferring your credit card balances to a new credit card with a lower interest rate. This can be done through balance transfer offers or by obtaining a personal loan specifically designed for debt consolidation. The goal of credit card refinancing is to secure a more favorable interest rate, allowing you to save money on interest payments and potentially pay off your debt faster.
Debt consolidation, on the other hand, involves combining multiple debts into a single loan. This loan is often secured using collateral, such as your home or a valuable asset. The objective of debt consolidation is to streamline your payments by consolidating multiple debts (including credit card debt) into one monthly payment, ideally with a lower interest rate and extended repayment terms.
Now that we have a basic understanding of credit card refinancing and debt consolidation, let’s dive into the key differences between the two methods and explore the factors you should consider when deciding which option is right for you.
Overview of Credit Card Refinancing
Credit card refinancing is a strategy that allows you to transfer your existing credit card balances to a new credit card with more favorable terms. The primary objective of credit card refinancing is to reduce your interest rate, potentially saving you money on interest payments and accelerating your debt repayment.
There are a few different methods you can use to refinance your credit card debt. One option is to take advantage of balance transfer offers. Many credit card issuers offer promotional periods where they provide low or 0% interest rates on balance transfers for a specified period, typically ranging from 6 to 18 months. By transferring your balances to one of these cards, you can save on interest charges during the promotional period and focus on paying down your debt.
Another approach to credit card refinancing is to obtain a personal loan specifically designed for debt consolidation. These loans typically carry lower interest rates compared to credit cards, making them an attractive option for refinancing. With a personal loan, you can pay off your high-interest credit card debt in one lump sum and then make fixed monthly payments on the loan at a lower interest rate. This allows you to simplify your payments and potentially save on interest charges over time.
When considering credit card refinancing, it is important to evaluate the terms and conditions of any balance transfer offers or personal loan options. Look for factors such as the length of the promotional period, any fees associated with the transfer or loan origination, and the interest rate that will apply after the promotional period ends. It’s also crucial to assess your ability to make consistent payments and pay off the debt within the designated timeframe.
While credit card refinancing can be an effective strategy for tackling credit card debt, there are some potential downsides to consider. Transferring balances to a new credit card may come with balance transfer fees, and if you are unable to pay off the debt within the promotional period, you could be subjected to higher interest rates. Additionally, if your credit score is not in good standing, you may not qualify for the best refinancing options.
Despite these considerations, credit card refinancing can provide an opportunity to save money on interest payments and expedite your path to debt freedom. It is crucial to carefully evaluate your financial situation and consider the potential risks and benefits before pursuing credit card refinancing as a debt management strategy.
Overview of Debt Consolidation
Debt consolidation is a method of combining multiple debts, including credit card debt, into a single loan with the aim of simplifying payments and potentially reducing your interest rate. Debt consolidation can be an effective tool for managing your finances and regaining control over your debt.
There are several ways to consolidate your debts. One common approach is to obtain a debt consolidation loan from a financial institution or lender. This loan allows you to pay off your existing debts in full and then make a single monthly payment on the consolidation loan. The advantage of a debt consolidation loan is that it often comes with a lower interest rate compared to the rates on your credit card balances, potentially saving you money on interest charges over time.
Another option for debt consolidation is to use a home equity loan or a home equity line of credit (HELOC). These loans are secured by the equity you have in your home and can provide you with a significant amount of money to pay off your debts. By using a home equity loan or HELOC for debt consolidation, you may benefit from lower interest rates and longer repayment terms.
Debt consolidation can also be accomplished through a debt management plan (DMP) offered by credit counseling agencies. With a DMP, the agency negotiates with your creditors to lower your interest rates and consolidate your payments. You make a single monthly payment to the agency, and they distribute the funds to your creditors according to the agreed-upon plan. This option can be particularly beneficial if you are struggling to manage your debt on your own.
When considering debt consolidation, it is crucial to assess the terms and conditions of the loan or program. Look for factors such as the interest rate on the consolidation loan, any fees associated with the loan or program, and the length of the repayment period. It’s important to ensure that the consolidation option you choose aligns with your financial goals and capabilities.
While debt consolidation can provide a streamlined approach to debt repayment, it is important to recognize that it may not be suitable for everyone. Consolidating your debts can extend the length of time it takes to repay them, and you may end up paying more in interest over the long run. Additionally, if you use a home equity loan or HELOC for debt consolidation, you are putting your home at risk if you are unable to make the payments.
Debt consolidation can be a helpful tool for managing your debts and simplifying your financial obligations. However, it is essential to carefully consider the terms of the consolidation option, assess your ability to make consistent payments, and weigh the potential advantages and disadvantages before proceeding with a debt consolidation strategy.
Key Differences Between Credit Card Refinancing and Debt Consolidation
While credit card refinancing and debt consolidation both aim to help individuals manage their debt, there are key differences between the two approaches. Understanding these differences can help you determine which option is best suited for your financial situation. Let’s explore these differences:
- Method of consolidation: Credit card refinancing involves transferring your credit card balances to a new card or obtaining a personal loan specifically designed for debt consolidation. Debt consolidation, on the other hand, involves combining multiple debts into a single loan, often through a debt consolidation loan or program.
- Collateral: Credit card refinancing typically does not require collateral, as it involves transferring balances to another credit card or obtaining an unsecured personal loan. Debt consolidation, on the other hand, often requires collateral, such as your home or a valuable asset, to secure a debt consolidation loan.
- Interest rates: In credit card refinancing, the primary goal is to obtain a new credit card or loan with a lower interest rate than your current credit cards. This can help reduce the amount of interest you pay and accelerate your debt repayment. Debt consolidation also aims to lower interest rates, but the specific interest rate will depend on the type of consolidation loan or program you choose.
- Repayment terms: With credit card refinancing, the repayment terms will depend on the new credit card or personal loan you obtain. Debt consolidation loans often come with longer repayment terms, which can result in lower monthly payments but potentially more interest paid over time.
- Impact on credit score: Both credit card refinancing and debt consolidation can impact your credit score. When you apply for a new credit card or loan for refinancing, it may result in a temporary dip in your score due to the hard inquiry. However, if you manage the new credit effectively, your score can improve in the long run. Debt consolidation can also have an impact on your credit score, as it involves closing existing credit card accounts and obtaining a new loan. However, if you make timely payments on the consolidation loan, it can positively impact your credit score over time.
These key differences highlight the various aspects to consider when deciding between credit card refinancing and debt consolidation. It’s important to evaluate your financial goals, creditworthiness, and personal circumstances before choosing the most suitable option for your debt management strategy.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Credit Card Refinancing and Debt Consolidation
Choosing between credit card refinancing and debt consolidation requires careful consideration of various factors. Your financial situation, goals, and preferences will play a significant role in determining which option is best suited for you. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Interest rates: Compare the interest rates on your current credit cards with those offered through credit card refinancing or debt consolidation options. Determine if the potential interest savings justify the costs and fees associated with each option.
- Monthly payments: Evaluate the impact on your monthly cash flow. Credit card refinancing can result in lower monthly payments, especially during promotional periods. Debt consolidation loans may offer longer repayment terms, which can also reduce your monthly payments. Consider your budget and determine which option aligns best with your ability to make consistent payments.
- Length of repayment: Consider how quickly you want to pay off your debt. Credit card refinancing may offer shorter repayment durations due to promotional periods or personal loan terms. Debt consolidation loans often come with longer repayment terms, which can result in lower monthly payments but a longer time to becoming debt-free.
- Collateral: Assess your comfort level with using collateral, such as your home or other valuable assets, when considering debt consolidation. If you’re not comfortable putting your assets at risk, credit card refinancing may be a more suitable option.
- Credit score: Understand the potential impact on your credit score with both options. Credit card refinancing may result in a temporary dip in your score due to the hard inquiry and new credit accounts. Debt consolidation may also impact your score, but if you consistently make payments on time, it can have a positive effect over time.
- Financial goals and preferences: Consider your long-term financial goals and personal preferences. Are you looking to become debt-free as quickly as possible, even if it means higher monthly payments? Or do you prefer the flexibility of lower monthly payments and a longer repayment term? Determine which option aligns with your financial goals and preferences.
Ultimately, the right choice between credit card refinancing and debt consolidation depends on your unique financial situation and objectives. It may be beneficial to consult with a financial advisor or credit counselor who can provide personalized guidance based on your specific circumstances.
Remember, the decision you make should be based on a comprehensive analysis of your financial needs, affordability, and risk tolerance. By carefully considering these factors, you can determine the best approach to manage your debt and pave the way towards a healthier financial future.
Pros and Cons of Credit Card Refinancing
Credit card refinancing offers several potential advantages and disadvantages that you should consider before deciding to pursue this debt management strategy. Understanding the pros and cons can help you make an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals. Let’s explore these pros and cons:
Pros of Credit Card Refinancing:
- Lower interest rates: One of the primary benefits of credit card refinancing is the opportunity to secure a lower interest rate. By transferring your credit card balances to a new card with a lower rate or obtaining a personal loan with a favorable rate, you can save money on interest charges and potentially pay off your debt faster.
- Opportunity for promotional periods: Many credit card refinancing options offer promotional periods with low or 0% interest rates for balance transfers. This gives you a specific timeframe to focus on paying down your debt without accruing additional interest charges.
- Simplified payments: By consolidating your credit card balances onto a single card or loan, you can streamline your payments. This can make it easier to manage your debts and ensure that you stay organized with your finances.
- Potential credit score improvement: Making timely payments on your new credit card or personal loan can help improve your credit score over time. As you reduce your outstanding balances and demonstrate responsible credit behavior, your creditworthiness may improve.
Cons of Credit Card Refinancing:
- Balance transfer fees: Some credit card refinancing options come with balance transfer fees, which can offset the potential savings from the lower interest rate. It’s important to factor in any fees associated with the transfer when evaluating the cost-effectiveness of credit card refinancing.
- Risk of higher interest rates: If you are unable to pay off your credit card balance within the promotional period, you may face a higher interest rate once the promotional rate expires. It’s essential to consider your ability to repay the debt within the designated timeframe to avoid incurring additional interest charges.
- Qualification requirements: To take advantage of credit card refinancing options, you need to meet certain qualification requirements. This may include having a good credit score, a stable income, and a low debt-to-income ratio. If your financial situation does not meet the eligibility criteria, you may not be able to secure favorable refinancing options.
- Potential for increased debt: Credit card refinancing may provide lower interest rates, but it can also tempt individuals to accumulate more debt. If you continue to use your credit cards without addressing the underlying spending habits and financial discipline, you may find yourself in a worse financial situation in the long run.
When considering credit card refinancing, carefully weigh these pros and cons in the context of your financial circumstances. It may be beneficial to consult with a financial advisor to assess whether this strategy is the right fit for your specific needs and goals. Remember, consistent, and responsible management of your credit is key to successfully leveraging credit card refinancing for debt relief.
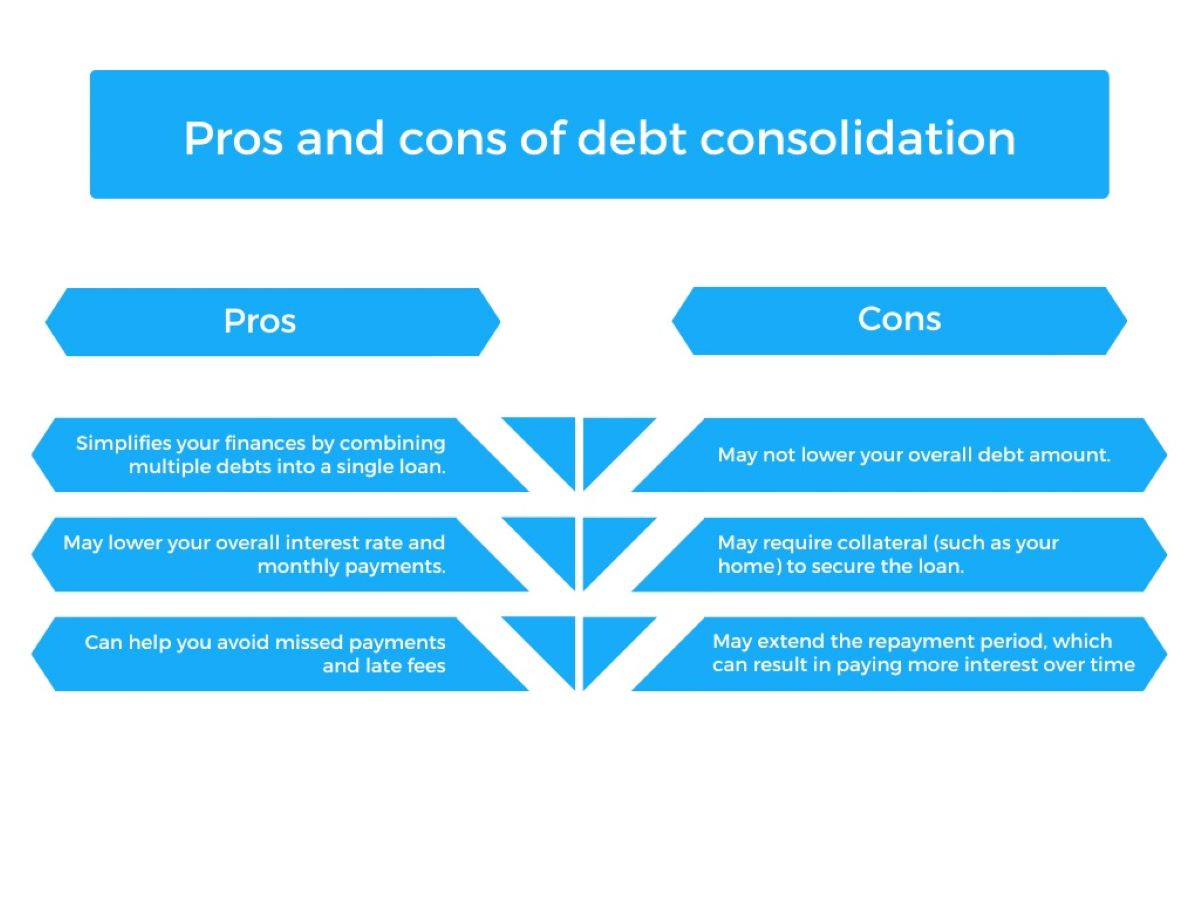
Pros and Cons of Debt Consolidation
Debt consolidation offers several potential advantages and disadvantages that you should consider before deciding to pursue this debt management strategy. Understanding the pros and cons can help you make an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals. Let’s explore the pros and cons of debt consolidation:
Pros of Debt Consolidation:
- Simplified payments: One of the main benefits of debt consolidation is the consolidation of multiple debts into a single loan or payment plan. This simplifies your financial obligations, as you only need to make one monthly payment instead of managing multiple payments to different creditors.
- Potentially lower interest rates: Debt consolidation loans often come with lower interest rates compared to credit cards, which can help reduce the amount of interest you pay over time. By consolidating your debts, you may be able to secure a single loan with a more favorable interest rate, potentially saving you money.
- Extended repayment terms: Debt consolidation loans can provide you with longer repayment terms, which can result in lower monthly payments. This can ease the financial burden and make it more manageable to meet your payment obligations.
- Improvement of credit score: Consistently making timely payments on your debt consolidation loan can positively impact your credit score. By responsibly managing your consolidated debt, you demonstrate your ability to handle your financial obligations, which can improve your creditworthiness over time.
Cons of Debt Consolidation:
- Collateral requirement: Depending on the type of debt consolidation, such as a home equity loan or HELOC, it may require collateral such as your home. This puts your property at risk if you are unable to make the required payments.
- Extended repayment period: While extended repayment terms can lower your monthly payments, it also means that you may be in debt for a longer period of time. This could result in paying more interest over the life of the consolidation loan compared to your original debts.
- Potential for higher overall cost: If you opt for a debt consolidation loan with a lower monthly payment and longer repayment term, you may end up paying more in interest charges over time. It’s important to calculate the total cost of the loan, including interest, and compare it to your existing debts to ensure that debt consolidation is cost-effective for your situation.
- Qualification requirements: Similar to credit card refinancing, debt consolidation loans have qualification requirements, such as a good credit score and stable income. If you do not meet the necessary criteria, you may have difficulty securing favorable consolidation loan terms.
Before pursuing debt consolidation, carefully evaluate these pros and cons in relation to your financial circumstances. It is advisable to speak with a financial advisor or credit counselor who can provide personalized guidance based on your specific needs. Remember, debt consolidation is a tool to help manage your debts effectively, but it requires discipline and responsible financial management to achieve the desired results.
Conclusion
When faced with the challenge of managing credit card debt, credit card refinancing and debt consolidation are two viable options to consider. Understanding the key differences and evaluating the pros and cons of each strategy is crucial in making an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals and circumstances.
Credit card refinancing offers the opportunity to transfer your credit card balances to a new card or obtain a personal loan with a lower interest rate. This can save you money on interest payments and simplify your payments. However, it’s important to be mindful of balance transfer fees, potential higher interest rates after promotional periods, and qualification requirements.
Debt consolidation, on the other hand, allows you to combine multiple debts into a single loan with potentially lower interest rates and extended repayment terms. This can streamline your payments and make it more manageable to meet your financial obligations. However, collateral may be required, and a longer repayment period may result in higher overall costs.
Ultimately, the decision between credit card refinancing and debt consolidation depends on your individual financial situation and goals. Consider factors such as interest rates, monthly payments, repayment terms, collateral requirements, credit score impact, and your long-term financial objectives. Consulting with a financial advisor or credit counselor can provide valuable insights and guidance specific to your circumstances.
Regardless of the approach you choose, it’s important to develop responsible financial habits, such as budgeting, tracking expenses, and avoiding unnecessary debt. Remember that debt management is a journey, and it requires discipline, commitment, and a well-considered strategy to achieve financial freedom.
By taking the time to assess your options and making an informed decision, you can take proactive steps towards effectively managing your credit card debt and improving your overall financial well-being.