Home>Finance>Which Should Be Entered On A Cash Flow Budgeting Tool?


Finance
Which Should Be Entered On A Cash Flow Budgeting Tool?
Modified: December 29, 2023
Discover the perfect cash flow budgeting tool for your finance needs. Maximize your financial management with our comprehensive solution.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Cash Flow Budgeting
- Importance of Cash Flow Budgeting
- Key Features of a Cash Flow Budgeting Tool
- Essential Components to Enter on a Cash Flow Budgeting Tool
- Cash Inflows
- Cash Outflows
- Account Receivables
- Account Payables
- Loan Payments
- Investments
- Contingency Funds
- Profit and Loss Data
- Historical Cash Flow Data
- Tracking and Reporting Features
- Customization Options
- Integration with Accounting Software
- Conclusion
Introduction
Cash flow budgeting is a crucial aspect of financial planning for individuals and businesses alike. It involves managing and tracking the cash inflows and outflows to ensure that there is enough liquidity to cover expenses and achieve financial goals.
Having a comprehensive understanding of cash flow budgeting can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions, monitor their financial health, and avoid cash crunches. To streamline this process, many people turn to cash flow budgeting tools that provide a convenient and efficient way to manage their finances.
In this article, we will explore the key components that should be entered on a cash flow budgeting tool to maximize its effectiveness. We will delve into the essential features that such a tool should possess and discuss why each component is crucial in creating an accurate and reliable cash flow budget.
By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of the vital aspects to include when utilizing a cash flow budgeting tool, enabling you to optimize your financial planning and make more informed decisions.
Understanding Cash Flow Budgeting
Cash flow budgeting is the process of forecasting and managing the cash inflows and outflows of an individual or organization. It provides a comprehensive overview of the financial health and liquidity position by tracking the flow of cash over a specific period of time, such as a month, quarter, or year.
The primary objective of cash flow budgeting is to ensure that there is enough cash available to cover expenses, repay debts, invest in growth opportunities, and maintain sufficient reserves for emergencies. By keeping a close eye on cash flow, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions, identify potential cash shortfalls, and take proactive measures to mitigate financial risks.
One of the key benefits of cash flow budgeting is its ability to highlight the timing of cash inflows and outflows. It enables individuals and businesses to anticipate when they will receive cash from various sources, such as income, loans, investments, or accounts receivables, and plan their expenses accordingly. By aligning the timing of cash flows, individuals and businesses can avoid running out of cash and ensure that funds are available when needed.
Cash flow budgeting also helps in identifying areas where expenses can be reduced or managed more efficiently. By analyzing the cash outflows, individuals and businesses can identify any unnecessary expenditures, negotiate better deals with suppliers, or find ways to optimize their operational costs. This can ultimately contribute to cost savings and improve the overall financial performance.
Additionally, cash flow budgeting provides a platform for financial goal setting and tracking. It allows individuals and businesses to set realistic targets and monitor progress towards achieving them. By regularly reviewing the cash flow budget, adjustments can be made to align with changing circumstances, ensuring that financial goals remain achievable and realistic.
In summary, cash flow budgeting is a fundamental aspect of financial management that helps individuals and businesses maintain a healthy financial position. By accurately forecasting cash inflows and outflows, it allows for better decision making, risk management, and goal tracking. Utilizing a cash flow budgeting tool can greatly simplify and enhance this process.
Importance of Cash Flow Budgeting
Cash flow budgeting plays a crucial role in the overall financial health and success of individuals and businesses. It provides a clear picture of the available cash resources and helps in managing expenses, meeting financial obligations, and achieving long-term goals. Here are some key reasons why cash flow budgeting is essential:
1. Ensures Financial Stability: Cash flow budgeting allows individuals and businesses to anticipate and prepare for any upcoming cash shortfalls. By tracking cash inflows and outflows, it helps identify potential gaps and enables proactive measures to be taken, such as securing short-term loans or implementing cost-cutting strategies. This ensures financial stability and reduces the risk of liquidity issues.
2. Enables Effective Decision Making: A well-prepared cash flow budget provides valuable insights into the financial standing of an individual or business. It helps in making informed decisions about investments, expenditures, and financial strategies. With a clear understanding of cash flow patterns, individuals and businesses can prioritize spending, allocate resources efficiently, and seize opportunities for growth.
3. Supports Debt Management: Cash flow budgeting is essential for managing debt obligations. By accurately forecasting cash inflows and outflows, it allows individuals and businesses to plan loan repayments and avoid defaults. It helps identify opportunities for debt restructuring or refinancing, reducing interest costs and improving overall financial health.
4. Facilitates Goal Setting and Tracking: Cash flow budgeting helps individuals and businesses set realistic financial goals and track progress towards achieving them. It provides a clear understanding of cash availability, enabling proper allocation of funds to various goals, such as savings, investments, or expansion plans. Regularly monitoring cash flow against budgeted goals allows for adjustments and ensures that financial objectives remain on track.
5. Enhances Creditworthiness: Cash flow management is crucial in building and maintaining a good credit profile. Lenders and investors often assess cash flow budgets to evaluate the ability of individuals and businesses to meet financial obligations. A well-maintained cash flow budget showcases financial discipline and responsibility, improving creditworthiness and increasing access to favorable loan terms and investment opportunities.
Overall, cash flow budgeting is a vital aspect of financial planning. It provides the foundation for making informed decisions, managing finances effectively, and achieving long-term financial goals. By utilizing cash flow budgeting tools and regularly monitoring and updating budgets, individuals and businesses can optimize their financial management practices and set themselves up for success.
Key Features of a Cash Flow Budgeting Tool
A cash flow budgeting tool is a powerful resource that helps individuals and businesses effectively manage their finances. It provides a centralized platform to monitor cash inflows and outflows, track expenses, and make informed financial decisions. Here are some key features and functionalities to look for in a cash flow budgeting tool:
1. User-Friendly Interface: A cash flow budgeting tool should have an intuitive and user-friendly interface. The tool should be easy to navigate, with clear and concise instructions, making it accessible for individuals with varying levels of financial expertise. A well-designed interface enhances user experience and ensures efficient budget management.
2. Cash Inflow and Outflow Tracking: The tool should allow users to easily record and track their cash inflows and outflows. It should provide the flexibility to categorize and subcategorize expenses, making it easier to analyze and identify spending patterns. Additionally, it should support the inclusion of multiple sources of income, such as salary, rental income, or investment returns.
3. Forecasting and Projection Capabilities: A robust cash flow budgeting tool should have built-in forecasting and projection features. This allows users to anticipate future cash flows based on historical data and predefined assumptions. With accurate projections, users can plan ahead, identify potential cash gaps, and make informed financial decisions.
4. Expense Management: The tool should provide comprehensive expense management capabilities. Users should be able to easily track and categorize their expenses, set spending limits, and receive alerts when they approach or exceed budgeted amounts. The inclusion of features like expense analysis, visualization, and trend tracking can greatly assist in identifying areas for cost optimization.
5. Goal Setting and Tracking: A cash flow budgeting tool should allow users to set financial goals and track their progress. It should enable users to define specific objectives, allocate funds towards them, and monitor their achievement. Visual representations, such as progress bars or charts, can provide motivating feedback on goal attainment.
6. Reporting and Analytics: The tool should have robust reporting capabilities, allowing users to generate customized reports and analyze their financial performance. It should provide key metrics, such as net cash flow, cash flow ratios, and budget variances. Additionally, the ability to export reports to commonly used formats, such as CSV or PDF, can facilitate further analysis or sharing with financial advisors.
7. Integration with Financial Accounts: A valuable feature of a cash flow budgeting tool is integration with financial accounts, such as bank accounts, credit cards, or investment portfolios. This enables automatic synchronization of transactions, reducing manual data entry and ensuring accurate and up-to-date cash flow analysis.
8. Mobile Accessibility: In today’s mobile-driven world, having access to financial information on the go is crucial. A cash flow budgeting tool with a mobile application or responsive web design allows users to manage their budgets anytime, anywhere, from their smartphones or tablets.
9. Security and Data Privacy: Given the sensitive nature of financial data, a cash flow budgeting tool should prioritize security and data privacy. Look for tools that utilize encryption, have secure authentication protocols, and adhere to industry-standard security practices to protect user information.
When selecting a cash flow budgeting tool, consider your specific needs and preferences. Pay attention to the features and functionalities that align with your financial goals and management style. By choosing the right tool, you can streamline your cash flow management and gain greater control over your finances.
Essential Components to Enter on a Cash Flow Budgeting Tool
When using a cash flow budgeting tool, it is important to enter accurate and comprehensive data to ensure the effectiveness of the budgeting process. Here are some essential components that should be entered on a cash flow budgeting tool:
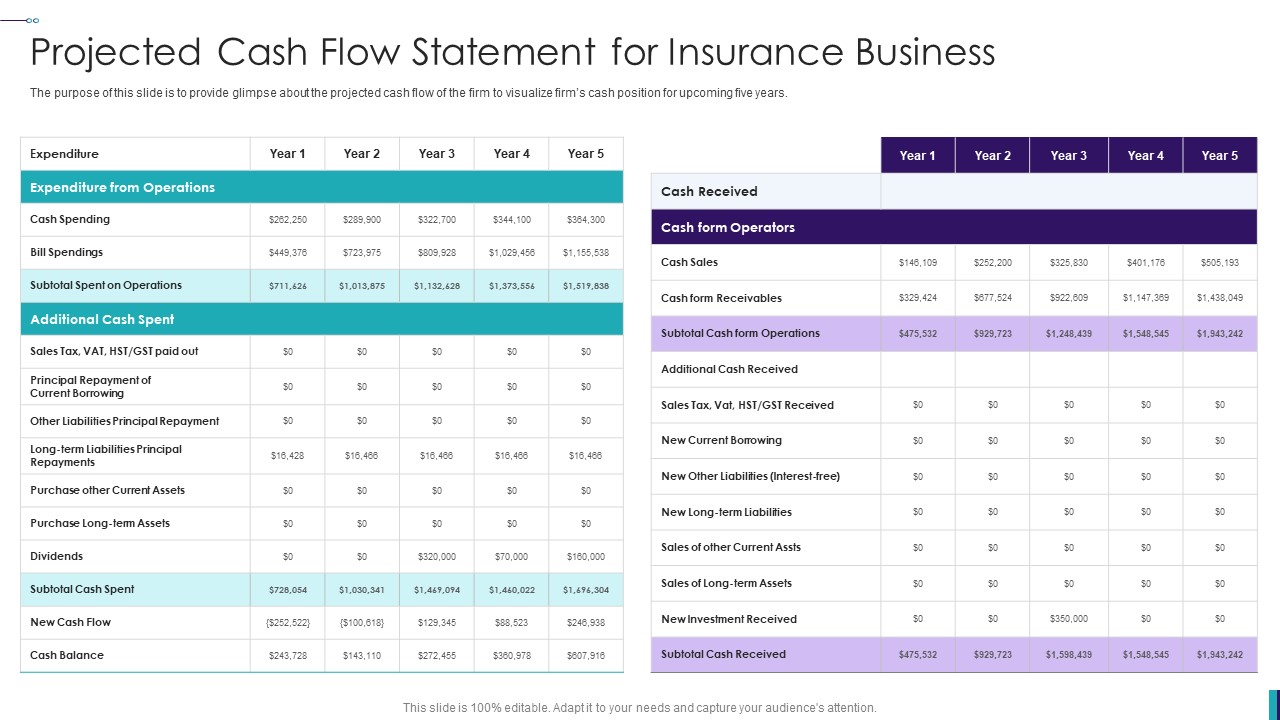
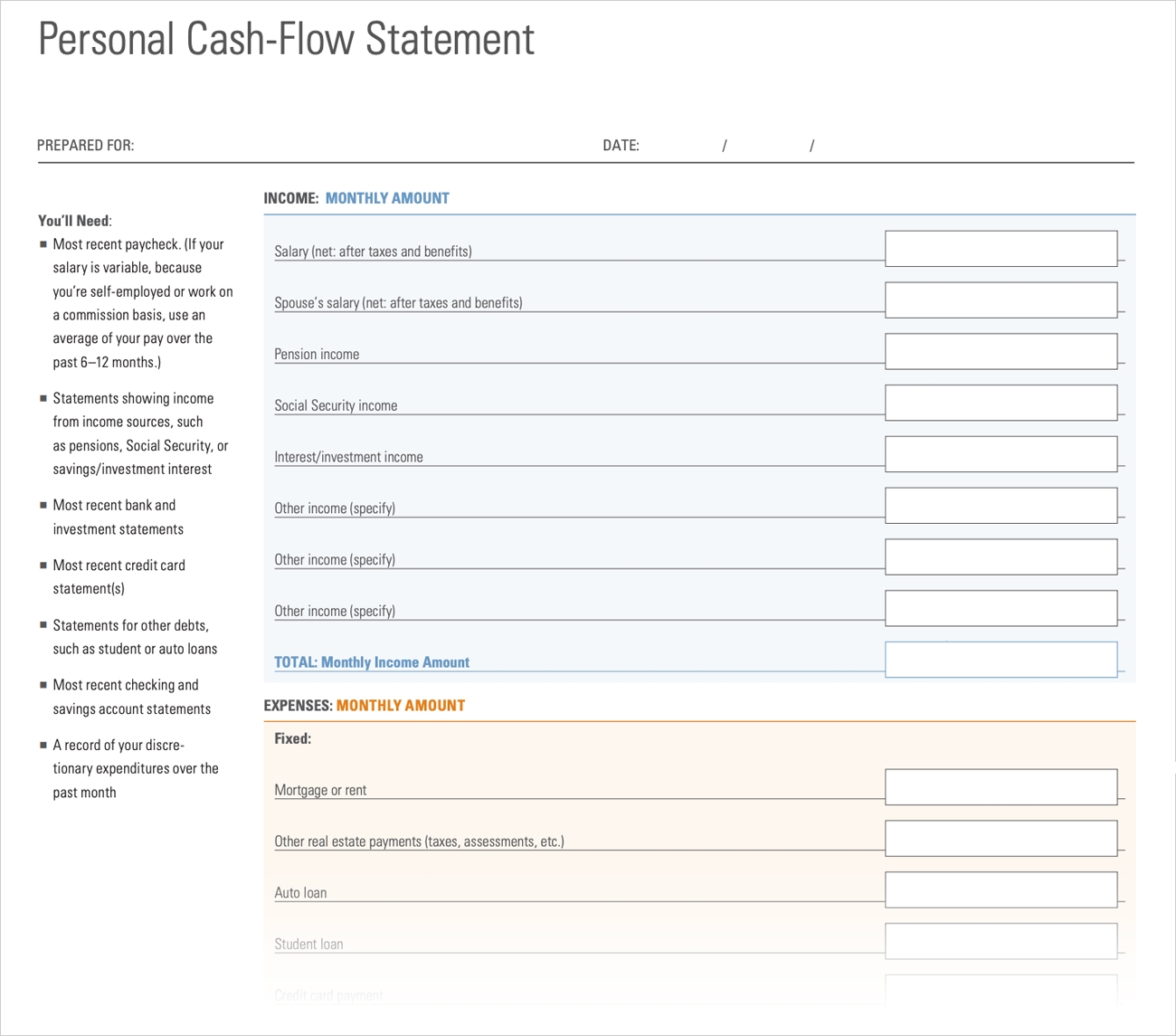
1. Cash Inflows: Enter all sources of income, such as wages, salaries, tips, rental income, or business revenue. Specify the frequency and amount of each inflow to accurately forecast and track your cash flow.
2. Cash Outflows: Record all your expenses, including fixed expenses like rent or mortgage payments, utilities, insurance, and loan payments, as well as variable expenses like groceries, transportation, entertainment, and discretionary spending. Categorize each expense to gain visibility into different areas of spending.
3. Accounts Receivables: If you have a business that sells goods or services on credit, it is essential to enter your accounts receivables. This helps in tracking the expected cash inflow from customers who haven’t yet paid, allowing you to anticipate and manage cash flow fluctuations.
4. Accounts Payables: In addition to tracking cash inflows, it is crucial to keep track of your accounts payables. Enter the amounts and due dates of your bills, invoices, loans, and credit card payments. This data helps you plan your cash outflows and avoid late payment penalties or cash shortages.
5. Loan Payments: If you have any outstanding loans, it is necessary to include the monthly or periodic loan payments in your cash flow budgeting tool. By doing so, you can accurately forecast your future cash outflows and ensure that you have sufficient funds to meet your obligations.
6. Investments: If you have investments, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate, enter the income or dividends you receive from these investments in your cash flow budgeting tool. This allows you to factor in these cash inflows when assessing your overall financial position.
7. Contingency Funds: It is essential to set aside funds for contingency or emergency expenses. Enter a monthly or periodic amount to allocate to a contingency fund. This ensures that you are prepared for unexpected costs or financial setbacks.
8. Profit and Loss Data: If you are using the cash flow budgeting tool for a business, it is important to include profit and loss data. Enter your revenue, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and taxes. This allows you to assess the profitability of your business and make informed financial decisions.
9. Historical Cash Flow Data: If you have historical cash flow data, input it into the cash flow budgeting tool. This helps to establish trends, identify seasonal patterns, and make more accurate projections for future cash flows.
10. Tracking and Reporting Features: Utilize the tracking and reporting features of your cash flow budgeting tool to assess your progress. Monitor your actual cash flow against your budgeted cash flow and analyze any deviations. Reporting features can also provide insights and highlight areas for improvements or adjustments in your financial management.
By entering these essential components into your cash flow budgeting tool, you can accurately track and manage your cash inflows and outflows. This will enable you to make informed financial decisions, prioritize your spending, and achieve your financial goals.
Cash Inflows
Cash inflows refer to the money that comes into your accounts from various sources. Tracking and accurately entering your cash inflows in a cash flow budgeting tool is crucial for understanding your financial position and managing your funds effectively. Here are some important types of cash inflows to consider:
1. Employment Income: If you are employed, enter your regular salary or wages as a cash inflow. Ensure that you include any additional income components such as bonuses, commissions, or overtime pay. Inputting these details allows you to track your primary income source.
2. Self-Employment or Business Income: If you are self-employed or have a business, include the income you generate from your business activities. This can include revenue from sales, services, or consulting fees. Tracking your business income separately helps you assess the profitability and cash flow of your business.
3. Rental Income: If you own rental properties or receive rental income from assets, enter these funds as cash inflows. Consider both residential and commercial rental income. By tracking your rental income, you can assess the return on your investment properties and identify any potential cash flow gaps.
4. Investment Income: If you have investments, such as stocks, bonds, or mutual funds, enter the income generated from these investments. This can include dividends, interest payments, or capital gains. Tracking your investment income provides a clear picture of your overall cash inflows and allows you to evaluate the performance of your investments.
5. Royalties or Licensing Fees: If you receive royalties or licensing fees for intellectual property, patents, or copyrighted materials, enter these payments as cash inflows. This category is relevant for authors, musicians, inventors, and other creatives who receive income from their intellectual assets.
6. Government Benefits or Assistance: If you receive any type of government benefits or assistance, such as unemployment benefits, social security payments, or disability income, include these inflows in your cash flow budgeting tool. This helps you track all sources of income and ensures accurate financial planning.
7. Other Sources of Income: Consider any additional sources of income, such as side jobs, freelance work, or part-time gigs. Include these amounts in your cash inflows section. By tracking all of your income sources, you can gain a holistic view of your financial situation.
It’s important to record the frequency and expected amount of each cash inflow accurately. This allows the cash flow budgeting tool to provide accurate projections and assist in effective decision making. Review and update your cash inflow data regularly to reflect any changes in income or new sources of revenue.
By diligently entering and tracking your cash inflows, you gain better visibility into your overall financial health. This information helps you in budgeting, managing expenses, and making informed financial decisions. Ultimately, it allows you to align your cash inflows with your financial goals and achieve greater financial stability.
Cash Outflows
Cash outflows refer to the money that is spent or disbursed from your accounts to cover various expenses. Accurately tracking and entering your cash outflows in a cash flow budgeting tool is critical for understanding your spending patterns, managing your budget, and maintaining financial stability. Here are some key categories of cash outflows to consider:
1. Fixed Expenses: Fixed expenses are recurring costs that generally remain stable from month to month. Examples include rent or mortgage payments, utility bills, insurance premiums, and subscription fees. Enter these expenses with their corresponding amounts and due dates to ensure you have an accurate representation of your fixed cash outflows.
2. Variable Expenses: Variable expenses are costs that fluctuate from month to month and are more discretionary in nature. These can include groceries, dining out, entertainment, shopping, and other personal expenses. It is important to track these expenses by categorizing them accordingly in your cash flow budgeting tool, allowing you to identify areas where you can potentially reduce or optimize your spending.
3. Debt Payments: If you have any outstanding debts, such as credit card balances, student loans, or car loans, include the monthly principal and interest payments in your cash outflows. Tracking your debt payments helps you stay on top of your financial obligations and monitor progress towards debt reduction.
4. Insurance Premiums: If you have insurance policies, such as health insurance, life insurance, or automobile insurance, include the corresponding premiums as cash outflows. Keeping track of insurance payments ensures that you are adequately covered and that these expenses are accounted for in your budget.
5. Taxes: Taxes are a significant category of cash outflows for individuals and businesses. Enter your estimated tax payments, including income tax, property tax, and any other applicable taxes. This helps you plan for the financial impact of tax obligations and avoids any surprises when it comes time to pay your taxes.
6. Savings and Investments: Allocating funds towards savings and investments is essential for long-term financial security and growth. Include contributions to retirement accounts, emergency funds, and other savings or investment vehicles as cash outflows. Tracking these allocations encourages consistent saving habits and helps you pursue your financial goals.
7. Subscriptions and Memberships: If you have any ongoing subscriptions, memberships, or service fees, enter these as cash outflows. This can include gym memberships, streaming services, software subscriptions, and other recurrent fees. Tracking these expenses allows you to assess their value and make informed decisions about which subscriptions are essential and which ones you can consider canceling.
8. Miscellaneous Expenses: It is important to allocate a category for miscellaneous or unexpected expenses in your cash flow budgeting tool. This can cover unforeseen costs, repairs, or any other unpredictable expenses that may arise. Having a contingency category ensures that you have some buffer for unexpected cash outflows.
Regularly review and update your cash outflows in your cash flow budgeting tool to reflect any changes in expenses or new financial obligations. This allows for accurate budgeting and helps you make informed decisions about your spending habits.
By diligently tracking and entering your cash outflows, you can gain a better understanding of your overall spending patterns. This insight enables you to identify areas where you can potentially cut back or reallocate funds, ensuring that your budget aligns with your financial goals and helps you maintain financial stability.
Account Receivables
Account receivables refer to the money that is owed to you or your business by customers or clients for goods or services provided on credit. Including account receivables in your cash flow budgeting tool is crucial for effectively managing your cash flow and anticipating future inflows. Here is why tracking account receivables is important and how to handle them in your budgeting process:
1. Anticipating Cash Inflows: By including account receivables in your cash flow budgeting tool, you can track and estimate the expected cash inflows from customers who have not yet paid their invoices. This allows you to have a more accurate view of your overall cash flow and plan your budget accordingly.
2. Identifying Outstanding Invoices: Tracking account receivables helps you stay on top of outstanding invoices and follow up with customers who have not made their payments. This is crucial for timely collections, reducing the risk of delayed cash inflows, and maintaining a healthy cash flow position.
3. Assessing Credit Policies: Account receivables data also provides insights into the effectiveness of your credit policies. It allows you to evaluate the average time it takes for customers to pay their invoices, identify slow-paying customers, and make informed decisions about extending credit to specific individuals or businesses.
4. Cash Flow Forecasting: Including account receivables in your cash flow budgeting tool enables you to make more accurate cash flow projections. By estimating the timing of these inflows and factoring them into your budget, you can better anticipate cash availability, plan for expenses, and avoid potential cash flow shortages.
5. Managing Late or Non-Payments: Tracking account receivables helps you identify customers who consistently pay late or fail to make payments altogether. This allows you to take appropriate measures, such as implementing stricter credit terms, offering incentives for early payments, or pursuing collection activities if necessary.
6. Communicating with Customers: Having a clear view of your account receivables also facilitates effective communication with your customers. It enables you to provide timely payment reminders, clarify any billing inquiries, or negotiate payment terms, ensuring a smooth and transparent customer experience.
7. Analyzing Cash Conversion Cycle: Account receivables play a vital role in the cash conversion cycle, which measures the time it takes for capital invested in inventory or services to be converted into cash inflows. By integrating account receivables into your cash flow budgeting tool, you can analyze and optimize this cycle, ultimately improving your overall cash flow efficiency.
When entering account receivables in your cash flow budgeting tool, include the expected payment amounts, due dates, and the age of the outstanding invoices. This allows you to track and monitor the aging of receivables, assess the impact on your cash flow, and take appropriate actions to ensure timely collections.
By effectively managing your account receivables and integrating them into your cash flow budgeting tool, you can maintain a healthy cash flow position, minimize cash flow gaps, and ensure timely collections from your customers.
Account Payables
Account payables represent the money you owe to suppliers, vendors, service providers, or creditors for goods or services received on credit. Including account payables in your cash flow budgeting tool is essential for managing your cash outflows and ensuring timely payments. Here’s why tracking account payables is important and how to handle them in your budgeting process:
1. Managing Cash Outflows: By including account payables in your cash flow budgeting tool, you can effectively track and plan for your upcoming expenses. This allows you to forecast your cash outflows with accuracy and ensures that you have enough funds available to meet payment obligations.
2. Maintaining Supplier Relationships: Tracking account payables enables you to stay on top of your payment commitments and maintain healthy relationships with your suppliers or vendors. Timely payments can improve your credibility, strengthen partnerships, and potentially lead to better terms or discounts in the future.
3. Avoiding Late Payment Penalties: Including account payables in your budgeting process ensures that you are aware of payment due dates and that you avoid late payment penalties or interest charges. This helps you stay in good financial standing with your creditors and minimizes unnecessary expenses.
4. Assessing Cash Flow Availability: Monitoring account payables allows you to assess your cash flow availability accurately. By knowing when payments are due, you can align your cash flow projections and plan for any potential cash flow gaps or shortfalls in advance.
5. Negotiating Payment Terms: Understanding your account payables position provides you with valuable information for negotiating payment terms with your suppliers or vendors. It enables you to have informed discussions about payment schedules, credit terms, or even early payment discounts, allowing you to optimize your cash flow and potentially save money.
6. Tracking Debt Obligations: Account payables include any outstanding debts or obligations, such as credit card payments, loans, or lease payments. Applying these obligations in your budgeting tool ensures that you have a holistic view of your financial responsibilities and helps you manage your debt effectively.
7. Budgeting for Growth: Monitoring account payables allows you to allocate resources towards growth initiatives. By understanding your upcoming payment obligations, you can make informed decisions about investing in new projects, capital expenditures, or expanding your business while considering your cash flow availability.
When entering account payables in your cash flow budgeting tool, include the payment amounts, due dates, and any additional terms or conditions that may affect the payment schedule. This ensures that you accurately track and monitor your payment obligations.
By effectively managing your account payables and incorporating them into your cash flow budgeting tool, you can maintain good relationships with your suppliers and vendors, optimize your cash flow, avoid unnecessary penalties, and ensure the timely payments of your financial obligations.
Loan Payments
Loan payments are an important component to consider when managing your cash flow budgeting. Whether you have a mortgage, car loan, student loan, or any other type of borrowing, tracking and planning for your loan payments is crucial for financial stability. Here’s why loan payments are significant and how to handle them in your budgeting process:
1. Timely Repayment: One of the most important reasons to include loan payments in your cash flow budgeting is to ensure timely repayment. By tracking your loan payments, you can allocate the necessary funds to meet your obligations, avoiding late payment fees and potential damage to your credit score.
2. Cash Flow Projection: Including loan payments in your budgeting tool helps you accurately project your cash flow. By knowing when payments are due, you can ensure that you have sufficient funds available to cover your loan repayments without jeopardizing other essential expenses.
3. Interest Accruals: Loan payments include both principal and interest. Tracking these payments allows you to monitor the interest that accrues on your loan and understand its impact on your overall cash flow. This knowledge can help you strategize on optimizing your loan repayment.
4. Prepayment Considerations: If you have the ability to make prepayments on your loan, it’s essential to factor these into your cash flow budgeting as well. Consider the impact of prepayments on the remaining loan term and interest savings, and update your budget accordingly to reflect any changes in loan payment amounts or frequency.
5. Adjusting for Rate Changes: If you have a floating interest rate loan, such as an adjustable-rate mortgage or variable interest rate loan, it’s important to consider potential rate changes in your cash flow budgeting. Anticipating rate adjustments helps you plan for potential increases in your loan payments and adjust your budget accordingly.
6. Loan Amortization: Understanding the amortization schedule of your loan is key to accurately tracking your loan payments. Incorporate the principal and interest breakdown according to the specific terms of your loan agreement. This allows you to visualize how your payments reduce your outstanding balance over time.
7. Budgeting for New Loans: If you’re considering taking on additional debt, such as a new loan for a home purchase or business expansion, include the estimated loan payments for these potential loans in your cash flow budgeting. This helps you assess the feasibility of taking on new debt and ensures that you can comfortably manage the additional financial obligations.
Make sure to enter your loan payments accurately, including the payment amount, due date, and any specific terms or terms. This ensures that your cash flow budgeting tool provides an accurate representation of your loan repayment obligations.
By effectively managing your loan payments through your cash flow budgeting, you can stay on track with your financial goals, avoid any potential financial strain, and maintain a healthy cash flow position.
Investments
When managing your cash flow budgeting, it’s important to consider any investments you have and their impact on your overall financial picture. Investments can play a significant role in your financial planning, and properly tracking them in your budgeting process is essential. Here’s why investments are important and how to handle them in your cash flow budgeting:
1. Income Generation: Investments, such as stocks, bonds, or rental properties, can generate income in the form of dividends, interest, or rental payments. Including these investment income streams in your cash flow budgeting helps you accurately assess your total cash inflows and plan your budget accordingly.
2. Capital Gains or Losses: Investments are subject to fluctuations in value, leading to potential capital gains or losses when sold or realized. If you engage in buy-and-sell activities, it’s important to consider gains or losses as they impact your overall cash flow and tax obligations. Tracking these transactions in your budgeting allows you to assess their impact on your financial position.
3. Retirement Contributions: If you contribute to retirement accounts such as 401(k)s or IRAs, including these contributions in your cash flow budgeting is crucial. These contributions not only reduce your taxable income but also have long-term benefits in building a nest egg for your retirement. Accurately tracking these investments ensures you are on track with your retirement savings goals.
4. Rebalancing Strategies: If you actively manage your investment portfolio, periodic rebalancing may be necessary to maintain desired asset allocation. Consider the costs associated with rebalancing activities in your cash flow budgeting, such as transaction fees or tax implications. Tracking these expenses helps ensure you have sufficient funds allocated to rebalance your portfolio as needed.
5. Tax Implications: Investments can have tax implications, such as taxable interest income or gains subject to capital gains tax. Incorporating these tax obligations into your cash flow budgeting allows you to accurately assess your overall tax liability and properly allocate funds to meet your tax obligations.
6. Diversification Strategies: Diversifying your investment portfolio is important for managing risk and potentially optimizing returns. If you plan on making additional investments to diversify your portfolio, consider the cash outflows associated with acquiring new investments. This helps you evaluate the impact on your cash flow and plan your budget accordingly.
7. Planning for Major Expenses: Investments can also serve as a source of funds for major expenses such as education expenses, home renovations, or starting a business. In your cash flow budgeting, consider the potential liquidation of investments to fund these expenses. Properly tracking and planning for these potential cash inflows allows you to ensure that you have the necessary resources to cover major financial goals.
When entering investments in your cash flow budgeting, include the specific investment instruments, contribution or withdrawal amounts, and the associated timing. This ensures that you have an accurate representation of the cash inflows and outflows associated with your investments.
By effectively managing your investments in your cash flow budgeting, you can assess their impact on your overall cash flow, make informed investment decisions, and align your budget with your long-term financial goals.
Contingency Funds
Contingency funds, also known as emergency funds or rainy-day funds, are essential financial resources set aside to handle unexpected expenses or financial emergencies. Including contingency funds in your cash flow budgeting is crucial for maintaining financial stability and being prepared for unforeseen circumstances. Here’s why contingency funds are important and how to handle them in your budgeting process:
1. Financial Security: Contingency funds provide a safety net that safeguards your financial well-being. Having a designated fund for emergencies ensures that you can cover unexpected expenses without resorting to high-interest loans, credit card debt, or liquidating long-term assets. This promotes overall financial security and peace of mind.
2. Unexpected Expenses: Life is filled with unexpected events or expenditures, such as medical emergencies, home repairs, or car breakdowns. By setting aside funds in a contingency fund, you have a dedicated resource to handle these unforeseen expenses, reducing financial stress and avoiding disrupting your regular cash flow budget.
3. Job Loss or Income Interruptions: In the event of a job loss or income interruption, a contingency fund acts as a financial cushion. It provides a temporary source of income to cover essential expenses, such as food, rent, or utility bills, until alternative income or employment is secured.
4. Peace of Mind: Having an emergency fund brings peace of mind and reduces financial anxiety. Knowing that you have a financial safety net in place helps alleviate stress associated with unexpected events or financial setbacks, allowing you to focus on other areas of your life and long-term financial goals.
5. Avoiding Debt: A well-funded contingency fund helps you avoid taking on unnecessary debt. By having the financial resources to handle emergencies, you can avoid relying on credit cards or loans to cover unexpected expenses. This ensures that you can maintain your financial stability and minimize interest payments or fees on borrowed funds.
6. Funding Opportunities: Contingency funds can also serve as a source of funding for new opportunities that may arise. In certain cases, unexpected circumstances can create opportunities for investment, business ventures, or education. Having a dedicated contingency fund allows you to seize such opportunities without jeopardizing your regular cash flow or long-term financial goals.
7. Setting Financial Goals: Building a contingency fund is often the first step towards achieving other financial goals. Once you have established a solid emergency fund, you can redirect your savings towards long-term goals, such as retirement, homeownership, or travel, without worrying about unexpected expenses derailing your plans.
When incorporating contingency funds into your cash flow budgeting, set a specific savings goal and allocate a certain amount each month or paycheck towards building your emergency fund. Aim to save three to six months’ worth of living expenses as a general guideline, but adjust the target based on your personal circumstances and risk tolerance.
By effectively managing your contingency funds in your cash flow budgeting, you can ensure financial stability, mitigate the impact of unexpected events, and maintain control over your long-term financial well-being.
Profit and Loss Data
Profit and loss data, also known as income statements or P&L statements, provide valuable insights into the financial performance of a business or individual. Including profit and loss data in your cash flow budgeting allows you to evaluate your income sources, understand your expenses, and make informed financial decisions. Here’s why profit and loss data is important and how to handle it in your budgeting process:
1. Assessing Financial Performance: Profit and loss data provides a snapshot of your financial performance, allowing you to assess how your income compares to your expenses. This data helps you identify periods of profitability, losses, or potential areas for improvement in your budget management.
2. Tracking Revenue Sources: Profit and loss data allows you to track and analyze your various sources of income. It helps you understand which income streams contribute the most to your overall revenue and identify opportunities for diversifying your income sources.
3. Monitoring Expenses: Profit and loss data helps you track and categorize your expenses, providing visibility into where your money is being spent. By identifying major expense categories, you can evaluate cost-saving opportunities, optimize your spending, and make informed decisions about budget reallocation.
4. Identifying Cost Overruns: Analyzing your profit and loss data allows you to identify any cost overruns or areas of excessive spending. By comparing your actual expenses to your budgeted amounts, you can pinpoint potential areas of inefficiency and take corrective measures to better manage your cash flow.
5. Evaluating Profitability: Profit and loss data helps you assess the profitability of your business or specific income-generating activities. By comparing your revenue against your expenses, you can determine your net profit or loss and make informed decisions about the viability or potential growth of your business endeavors.
6. Decision Making and Planning: Profit and loss data plays a crucial role in making informed financial decisions and planning for the future. By analyzing your financial performance, you can adjust your budget, allocate resources more effectively, and better align your spending with your financial goals.
7. Tax Planning: Profit and loss data is invaluable for tax planning purposes. It provides the necessary information to accurately calculate your taxable income, allowing you to estimate your tax liability and plan ahead for tax obligations. This helps you avoid surprises when it comes to filing your taxes.
When incorporating profit and loss data into your cash flow budgeting, review your income and expense records regularly to ensure accurate and up-to-date information. Use historical data to identify trends, forecast future revenue and expenses, and make adjustments to your budget accordingly.
By effectively managing profit and loss data in your cash flow budgeting, you can gain valuable insights into your financial performance, make informed decisions about your income and expenses, and work towards achieving your financial goals.
Historical Cash Flow Data
Historical cash flow data provides a valuable record of your past cash inflows and outflows over a specific period of time. Incorporating historical cash flow data in your cash flow budgeting allows you to analyze trends, patterns, and fluctuations in your cash flow, providing insights that can inform your financial decision-making. Here’s why historical cash flow data is important and how to use it in your budgeting process:
1. Identifying Seasonal Trends: Historical cash flow data helps identify seasonal trends in your cash inflows and outflows. By analyzing your historical data, you can anticipate periods of high or low cash flow, plan for seasonal variations, and adjust your budget and spending accordingly.
2. Forecasting Future Cash Flow: Past cash flow patterns can serve as a useful guide for forecasting and projecting future cash flow. By analyzing historical data, you can identify trends, seasonality, and growth patterns that can guide your future budgeting decisions and help you establish realistic expectations for your cash flow.
3. Evaluating Budget Accuracy: Comparing historical cash flow data to your budgeted amounts allows you to assess the accuracy of your budgeting process. By analyzing the variances between your budgeted figures and the actual cash inflows and outflows, you can make informed adjustments to future budgets to improve their accuracy and reliability.
4. Assessing Financial Stability: Historical cash flow data helps you assess your financial stability over time. By examining your past cash flow, you can evaluate your ability to cover expenses, manage debt obligations, and build a sufficient cash reserve. This assessment provides insights into your financial health and can guide your future financial planning.
5. Identifying Cash Flow Gaps: Historical cash flow data can reveal periods where your cash inflows were insufficient to cover your outflows. By analyzing these gaps, you can identify potential cash flow challenges and take proactive measures to avoid liquidity issues in the future. It helps you plan for contingencies and build appropriate reserves.
6. Supporting Strategic Decision-Making: Historical cash flow data provides valuable information for strategic decision-making. By analyzing past cash flow patterns, you can evaluate the financial impact of previous decisions and make more informed choices for future investments, expansion plans, or cost-saving opportunities.
When incorporating historical cash flow data in your budgeting process, review multiple periods of historical cash flow data to capture enough variations and identify consistent patterns. Consider using software or spreadsheets to organize and analyze the data effectively, allowing you to draw meaningful insights for your budgeting process.
By effectively utilizing historical cash flow data in your cash flow budgeting, you can gain a deeper understanding of your financial trends, improve the accuracy of your budgeting process, make informed decisions, and strengthen your overall financial management.
Tracking and Reporting Features
Tracking and reporting features are essential components of a cash flow budgeting tool. These features enable you to monitor and analyze your financial performance, track your progress towards your financial goals, and generate comprehensive reports for better decision-making. Here’s why tracking and reporting features are important and how they enhance your cash flow budgeting process:
1. Real-Time Monitoring: Tracking features allow you to monitor your cash flow in real-time. You can track your income, expenses, and cash flow position, enabling you to make timely adjustments and stay on top of your financial situation. Real-time monitoring helps you identify potential cash flow gaps or surpluses and take immediate action to optimize your financial management.
2. Category-based Tracking: Tracking features enable you to categorize your income and expenses based on specific categories or subcategories. This allows for a more detailed analysis of your cash flow, empowering you to identify trends, understand your spending patterns, and make informed decisions about budget reallocation or cost-cutting measures.
3. Visualization Tools: Effective tracking features often incorporate visualization tools, such as charts or graphs, to present your cash flow data in a visually appealing and easily understandable format. These visual representations allow you to quickly grasp your financial performance, spot trends, and identify areas for improvement at a glance.
4. Budget vs. Actual Comparisons: Tracking features enable you to compare your actual cash flow against your budgeted amounts. This allows you to assess the accuracy of your budget and identify any variances or deviations. Budget vs. actual comparisons help you identify areas where you are overspending or underspending, allowing for course correction to align your financial habits with your budgeting goals.
5. Goal Tracking: Many cash flow budgeting tools offer goal tracking features. These features allow you to set financial goals, such as saving a certain amount or paying off debt, and track your progress towards achieving them. By monitoring your goal attainment, you can stay motivated and adjust your budgeting strategies to ensure successful goal completion.
6. Report Generation: Reporting features allow you to generate comprehensive reports summarizing your cash flow, income, expenses, and financial performance. These reports can be customized to display the specific information you need, enabling you to analyze your financial data, measure your progress, and identify trends or areas for improvement. Reports can be generated on a regular basis or as needed for financial reviews or presentations.
7. Data Exporting and Integration: Some tracking and reporting features allow you to export your cash flow data to other software or integrate it with accounting systems. This integration streamlines your financial management processes and ensures that your cash flow data is seamlessly integrated into your overall financial reporting and analysis.
When selecting a cash flow budgeting tool, consider the tracking and reporting features it offers. Look for tools that provide flexibility, customization options, and user-friendly interfaces. These features will empower you to effectively track your cash flow, analyze your financial position, and make well-informed decisions.
By utilizing tracking and reporting features in your cash flow budgeting, you gain greater visibility into your financial performance, make data-driven decisions, and optimize your financial management practices for long-term success.
Customization Options
Customization options are an important aspect to consider when selecting a cash flow budgeting tool. These options allow you to personalize the tool to fit your unique financial needs and preferences. Here’s why customization options are significant and how they enhance your cash flow budgeting process:
1. Budget Categories: Customization options enable you to create and tailor budget categories based on your specific income sources and expense types. This customization ensures that your budget aligns with your financial situation and captures the relevant details of your cash inflows and outflows.
2. Subcategories and Tags: Customizing subcategories and tags allows for more detailed expense tracking. By creating subcategories within your budget categories, you can capture specific expenses and categorize them accordingly. Additionally, using tags allows for further customization and organization of expenses based on different criteria, such as projects, locations, or priorities.
3. Variable Expense Allocation: Customization options enable you to allocate funds specifically for variable expenses. This flexibility allows you to adjust and allocate different amounts to different categories or subcategories based on your spending priorities or anticipated needs for each period.
4. Frequency and Duration: Customization options allow you to set the frequency and duration of your budgeting periods. Whether you prefer a weekly, monthly, or yearly budgeting approach, customization ensures that the tool adapts to your preferred timeframes and matches your financial planning needs.
5. Income and Expense Projections: Customization options enable you to set up individual income and expense projections based on your unique circumstances. This customization allows you to factor in changes in income sources or expenses over time, improving the accuracy of your cash flow predictions.
6. Reporting Templates: Customization options extend to reporting templates, allowing you to generate reports that suit your specific reporting requirements. Customizable reporting templates enable you to display the data and metrics that are most relevant and meaningful to your financial analysis and decision-making process.
7. User Interface and Display: Customization options also encompass the user interface and display preferences of the cash flow budgeting tool. Whether you prefer a simplistic or more detailed interface, customization allows you to personalize the tool’s appearance to enhance usability and align with your visual preferences during budgeting activities.
When selecting a cash flow budgeting tool, prioritize the customization options that align with your financial needs and provide the flexibility to adapt as your circumstances change over time. Look for tools that offer a wide range of customization features, and consider your specific requirements to ensure the tool meets your expectations.
By utilizing customization options in your cash flow budgeting, you can create a personalized financial management tool that suits your unique financial situation, enabling you to track your cash flow with precision and make informed decisions about your spending and savings.
Integration with Accounting Software
Integration with accounting software is a valuable feature to have in a cash flow budgeting tool. This integration allows for seamless and efficient transfer of financial data between the two systems, streamlining your financial management processes. Here’s why integrating with accounting software is important and how it enhances your cash flow budgeting:
1. Streamlined Data Entry: Integrating your cash flow budgeting tool with accounting software eliminates the need for manual data entry. Your financial transactions, income, and expenses are automatically synced between the systems, saving you time and reducing the risk of data entry errors.
2. Enhanced Accuracy: By integrating with accounting software, you can ensure the accuracy and consistency of your financial data. Any changes or updates made in your accounting software, such as recording sales or expenses, are reflected in your cash flow budgeting tool instantly, providing you with up-to-date and reliable information for budgeting and decision-making.
3. Real-Time Financial Insights: Integration with accounting software allows for real-time financial insights. You can view your financial data, including cash inflows and outflows, profit and loss statements, and balance sheets, directly within your cash flow budgeting tool. This access to real-time data enables you to make informed decisions based on the most current information.
4. Reduction in Duplicate Work: Integration eliminates the need for duplicate work across multiple systems. With data flowing seamlessly between your cash flow budgeting tool and accounting software, you can avoid the time-consuming task of manually entering and reconciling financial data in multiple places, reducing the risk of errors and improving overall efficiency.
5. Comprehensive Financial Analysis: Integration allows for comprehensive financial analysis by consolidating your financial data from various sources. You can analyze your cash flow, income, and expenses holistically, enabling you to gain a deeper understanding of your financial performance and identify areas for improvement or cost optimization.
6. Simplified Tax Reporting: Integrating your cash flow budgeting tool with accounting software makes tax reporting more efficient. Your financial data is readily available in one place, making it easier to generate accurate tax reports, calculate your tax liability, and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
7. Scalability and Growth: Integration with accounting software accommodates scalability and growth. As your business or financial needs expand, your cash flow budgeting tool can seamlessly integrate with more advanced accounting systems, allowing for comprehensive financial management and analysis as your requirements evolve.
When selecting a cash flow budgeting tool, consider its compatibility and integration capabilities with popular accounting software platforms. Ensure that the integration is seamless and works well with your existing or preferred accounting software.
By seamlessly integrating your cash flow budgeting tool with your accounting software, you can streamline your financial management processes, improve data accuracy, gain real-time financial insights, and enhance your ability to make informed decisions based on comprehensive and up-to-date financial information.
Conclusion
Cash flow budgeting is a critical aspect of financial management for individuals and businesses. It helps ensure financial stability, effective decision-making, and the achievement of long-term financial goals. Incorporating the right components in a cash flow budgeting tool is essential to optimize the budgeting process and gain valuable insights into your financial health. By including components such as cash inflows, cash outflows, account receivables, account payables, loan payments, investments, contingency funds, profit and loss data, historical cash flow data, and utilizing tracking and reporting features, you can enhance your budgeting process significantly.
Accurate tracking of cash inflows and outflows allows for a comprehensive view of your financial position and enables better decision-making based on real-time information. Including account receivables and payables ensures that you stay on top of outstanding invoices and manage your financial obligations effectively. By accounting for loan payments, you can plan and allocate funds to meet your debt obligations without any financial strain. Monitoring your investments helps you assess their impact on your overall cash flow and align them with your financial goals.
Contingency funds are essential to prepare for unexpected expenses and maintain financial security. Incorporating profit and loss data and historical cash flow data enhances your financial analysis, allowing you to identify trends, track performance, and make informed decisions. Tracking and reporting features provide real-time monitoring, visualization, and goal tracking capabilities that empower you to stay on track and assess your progress.
Customization options and integration with accounting software further enhance the effectiveness of cash flow budgeting. Customizing budget categories and subcategories allows for a personalized approach to fit your specific financial needs. Integration with accounting software streamlines data entry, ensures accuracy, and provides real-time financial insights for informed decision-making.
In conclusion, utilizing a comprehensive cash flow budgeting tool with the right components and features allows you to optimize your financial planning and management. It enhances your ability to track and analyze your cash inflows and outflows, maintain financial stability, achieve your financial goals, and make sound financial decisions. By embracing cash flow budgeting and utilizing the appropriate tools, you can pave the way for a healthier financial future.