
Finance
What Is Personal Cash Flow
Published: December 20, 2023
Discover the importance of personal cash flow in managing your finances. Learn how to analyze and improve your financial situation with expert tips and strategies.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Personal Cash Flow
- Importance of Personal Cash Flow Management
- Components of Personal Cash Flow
- Tracking Personal Cash Flow
- Benefits of Maintaining a Positive Cash Flow
- Strategies to Improve Personal Cash Flow
- Common Cash Flow Challenges
- Tips for Effective Cash Flow Management
- Conclusion
Introduction
Managing our personal finances is an essential aspect of our lives. It helps us achieve our financial goals, build wealth, and attain financial security. While budgeting, saving, and investing are commonly discussed topics when it comes to personal finance, one crucial aspect that often gets overlooked is personal cash flow.
Personal cash flow refers to the movement of money in and out of an individual’s pocket on a regular basis. It involves tracking and managing the inflows and outflows of cash to ensure a healthy financial situation. Understanding and managing personal cash flow is vital because it provides a clear picture of how money moves in our lives and helps us make informed financial decisions.
This article will delve into the concept of personal cash flow, its importance, and strategies to improve it. We will explore the components of personal cash flow, the challenges people commonly face, and practical tips for effective cash flow management. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of personal cash flow and be equipped with the tools to optimize it.
Definition of Personal Cash Flow
Personal cash flow is the movement of money in and out of an individual’s finances. It represents the inflow and outflow of cash from various sources, such as income, expenses, investments, and savings. Personal cash flow allows individuals to understand how much money they are earning, how much they are spending, and where their money is going.
Essentially, personal cash flow is a measurement of an individual’s financial health. It provides insight into how effectively someone manages their money and whether they have positive or negative cash flow. Positive cash flow occurs when an individual’s income exceeds their expenses, allowing them to save and invest. Negative cash flow, on the other hand, happens when expenses exceed income, often leading to financial stress and debt accumulation.
Tracking personal cash flow involves recording and categorizing all sources of income and expenses, including fixed monthly bills, variable expenses, debt repayments, investments, savings, and any other financial transactions. By analyzing personal cash flow, individuals can evaluate their spending habits, identify areas where they can reduce expenses, and allocate their income more effectively.
Furthermore, personal cash flow goes beyond simply tracking income and expenses. It also takes into account the timing of cash flows. For example, a person might receive a paycheck once a month but make multiple payments throughout the month. Understanding the timing of cash inflows and outflows is crucial for managing financial obligations and avoiding cash flow gaps or liquidity issues.
In summary, personal cash flow is a comprehensive analysis of an individual’s financial position, considering the movement of money in and out of their finances. It is a valuable tool for understanding spending patterns, identifying areas for improvement, and making informed financial decisions to achieve long-term financial stability.
Importance of Personal Cash Flow Management
Effective management of personal cash flow is vital for achieving financial stability and success. Here are several reasons why it is essential to prioritize personal cash flow management:
- Financial Awareness: Tracking and managing personal cash flow allows individuals to gain a clear understanding of their income, expenses, and overall financial situation. It provides a realistic view of where money is being spent and helps identify areas where spending can be reduced or optimized.
- Budgeting and Planning: Personal cash flow management is the foundation of creating a budget and financial plan. By accurately tracking income and expenses, individuals can set realistic financial goals, allocate funds for savings and investments, and plan for future expenses such as emergencies, education, or retirement.
- Debt Management: Personal cash flow management plays a crucial role in managing debt. By analyzing cash inflows and outflows, individuals can prioritize debt repayments and structure monthly budgets accordingly. This helps in reducing interest expenses and improving overall financial health.
- Goal Achievement: Efficient cash flow management enables individuals to allocate funds toward achieving their financial goals. Whether it is saving for a down payment on a house, funding a dream vacation, or building an emergency fund, understanding personal cash flow allows for effective goal planning and progress tracking.
- Financial Decision-Making: Personal cash flow management provides valuable insights for making informed financial decisions. It helps individuals evaluate the affordability of major purchases, assess the feasibility of taking on additional debt, and determine the impact of income changes on their overall financial position.
- Stress Reduction: By consistently managing personal cash flow, individuals can reduce financial stress and gain peace of mind. Having control over income and expenses enables individuals to be prepared for unexpected expenses, live within their means, and avoid the burden of excessive debt.
In summary, personal cash flow management is crucial for gaining financial awareness, budgeting effectively, managing debt, achieving financial goals, making informed decisions, and reducing financial stress. By actively tracking and optimizing personal cash flow, individuals can improve their financial well-being and build a solid foundation for long-term financial success.
Components of Personal Cash Flow
Personal cash flow consists of various components that contribute to the movement of money in and out of an individual’s finances. Understanding these components is essential for effectively managing personal cash flow. Here are the key components:
- Income: Income is the primary component of personal cash flow. It includes wages, salaries, commissions, bonuses, rental income, dividends, and any other sources of money earned. Tracking and recording all sources of income is crucial for evaluating cash flow and planning expenses.
- Expenses: Expenses encompass all the costs incurred to maintain one’s lifestyle. They include fixed expenses, such as rent or mortgage payments, utility bills, insurance premiums, as well as variable expenses like groceries, transportation, entertainment, and discretionary spending. Categorizing and monitoring expenses helps identify areas where spending can be reduced or optimized.
- Savings and Investments: Saving and investing play a significant role in personal cash flow management. Allocating a portion of income towards savings and investments is crucial for building an emergency fund, achieving financial goals, and securing future financial stability. By analyzing the amount saved and invested, individuals can assess their long-term financial growth prospects.
- Debt Payments: Debt payments are an essential consideration in personal cash flow management. This includes credit card payments, loans, mortgages, and any other outstanding debts. Tracking and managing debt payments helps individuals allocate funds effectively and avoid unnecessary interest expenses.
- Irregular Inflows and Outflows: Personal cash flow also includes irregular inflows and outflows of money. This may include tax refunds, bonuses, unexpected expenses, or one-time income sources. It is important to account for these irregular cash flows to ensure an accurate representation of overall cash flow and to plan for future expenses.
- Cash Flow Surplus/Deficit: The cash flow surplus or deficit is the result of comparing total income to total expenses. A cash flow surplus occurs when income exceeds expenses, providing room for saving and investing. Conversely, a cash flow deficit happens when expenses exceed income, leading to financial stress and potential debt accumulation. Monitoring and managing cash flow surplus/deficit is crucial for maintaining financial stability.
In summary, the components of personal cash flow include income, expenses, savings and investments, debt payments, irregular inflows and outflows, and the overall cash flow surplus/deficit. By understanding and effectively managing these components, individuals can gain control over their finances, make informed decisions, and achieve long-term financial goals.
Tracking Personal Cash Flow
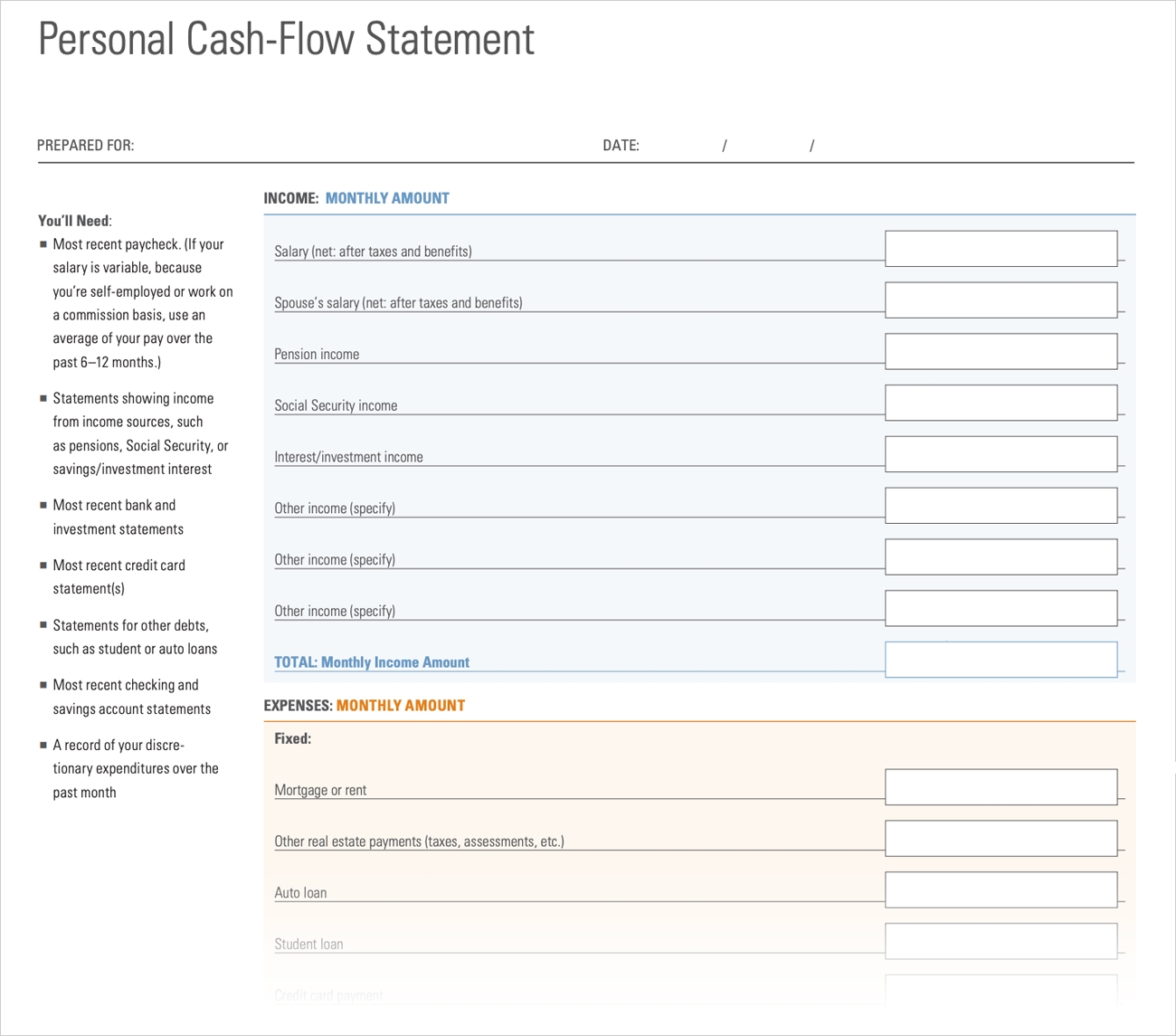
Tracking personal cash flow is a fundamental step in effectively managing one’s finances. It allows individuals to monitor their income, expenses, savings, and investments, providing valuable insights into their financial well-being. Here are some key steps to track personal cash flow:
- Gather Financial Documents: Begin by gathering all relevant financial documents, such as bank statements, credit card statements, bills, and receipts. These documents will serve as a reference for tracking income and expenses.
- Create Categories: Establish clear categories to organize and track income and expenses. Common categories include housing, transportation, groceries, utilities, entertainment, debt payments, savings, and investments. Categorization helps identify spending patterns and areas where adjustments can be made.
- Record Income: Record all sources of income, including salaries, wages, bonuses, rental income, and any other earnings. Ensure that each income source is assigned to the appropriate category.
- Track Expenses: Document all expenses, both fixed and variable. Include bills, loan payments, groceries, dining out, entertainment, transportation, and any other expenses. Use receipts, online banking statements, expenditure tracking apps, or expense tracking spreadsheets for accuracy.
- Monitor Daily Transactions: Keep track of daily transactions by reviewing bank and credit card statements regularly. Check for any discrepancies or unauthorized charges that may affect cash flow.
- Review and Analyze: Periodically review and analyze cash flow data. Look for trends, identify areas of overspending, and evaluate savings and investment contributions. This analysis will help make necessary adjustments to achieve a healthy cash flow.
- Automate Payments and Savings: Consider automating bill payments and savings contributions. This ensures that payments are made on time and that money is consistently set aside for savings and investments.
- Use Technology: Leverage technology to simplify the tracking process. Numerous personal finance apps and software programs are available that can automatically sync with bank accounts and credit cards, categorize expenses, and generate reports for easy analysis.
- Review and Adjust: Regularly review cash flow tracking methods and make adjustments as needed. As financial circumstances change, such as a change in income or major life events, reassessing and modifying the tracking process will provide a more accurate representation of personal cash flow.
Tracking personal cash flow is an ongoing process. By consistently monitoring and analyzing cash flow data, individuals can gain insights into their financial habits, make informed decisions, and optimize their cash flow to achieve their financial goals.
Benefits of Maintaining a Positive Cash Flow
Maintaining a positive cash flow is crucial for achieving financial stability and long-term success. Here are several key benefits of consistently managing and improving your personal cash flow:
- Financial Stability: A positive cash flow indicates that your income exceeds your expenses. This financial stability allows you to meet your financial obligations, cover unexpected expenses, and avoid accumulating excessive debt.
- Debt Reduction: With a positive cash flow, you have the ability to allocate extra funds towards debt payments. This allows you to pay off debts faster, save on interest charges, and ultimately become debt-free sooner.
- Opportunity for Savings: Positive cash flow provides the opportunity to save for short-term and long-term financial goals. Whether it’s an emergency fund, a down payment on a home, or retirement savings, maintaining a positive cash flow enables you to allocate funds for saving and investing.
- Improved Credit Score: Consistently managing a positive cash flow allows you to make timely debt payments, thereby improving your credit score. A higher credit score opens doors to better interest rates on loans and greater financial opportunities in the future.
- Reduced Financial Stress: Having a positive cash flow reduces financial stress and provides peace of mind. It allows you to live within your means, cover bills without worry, and handle unforeseen expenses without experiencing significant financial strain.
- Financial Flexibility: A positive cash flow provides you with the flexibility to make financial decisions. It allows you to comfortably pursue opportunities such as career changes, investments, or starting a business, as you have the necessary funds to support these endeavors.
- Ability to Seize Opportunities: With a positive cash flow, you are in a better position to take advantage of opportunities that arise. Whether it’s investing in stocks, purchasing property, or funding education, positive cash flow provides the means to capitalize on these opportunities.
- Long-Term Wealth Building: Maintaining a positive cash flow and effectively managing your finances lays the foundation for long-term wealth building. As you consistently save, invest, and make wise financial decisions, you increase your overall net worth and improve your financial security.
In summary, maintaining a positive cash flow offers a plethora of benefits, including financial stability, debt reduction, the opportunity for savings and investments, an improved credit score, reduced financial stress, financial flexibility, the ability to seize opportunities, and long-term wealth building. By prioritizing cash flow management, individuals can build a solid financial foundation and achieve their financial goals.
Strategies to Improve Personal Cash Flow
Improving personal cash flow involves implementing strategies to increase income and reduce expenses. By effectively managing cash flow, individuals can achieve a healthier financial position and work toward their financial goals. Here are several strategies to improve personal cash flow:
- Enhance Income: Consider exploring opportunities to increase your income. This can be achieved through side hustles, freelance work, or taking on additional responsibilities at your current job. Increasing your income provides more financial flexibility and boosts your overall cash flow.
- Reduce Discretionary Spending: Identify and reduce unnecessary discretionary spending. Cut back on non-essential expenses such as dining out, entertainment, and impulse purchases. By being mindful of your spending habits, you can free up cash that can be allocated towards debt payments or savings.
- Lower Fixed Expenses: Evaluate your fixed expenses such as rent, mortgage payments, and utility bills. Consider options like downsizing your living arrangement, refinancing your mortgage, or renegotiating service contracts to reduce these fixed costs and improve your cash flow.
- Consolidate and Refinance Debt: If you have multiple debts with high-interest rates, explore options to consolidate or refinance them into a single loan with a lower interest rate. This can help reduce monthly payments and free up cash flow for other financial priorities.
- Negotiate Bills and Expenses: Take the time to negotiate bills and expenses to potentially lower their costs. This can include negotiating lower rates for insurance policies, cable and internet bills, or even your cell phone plan. Saving on these monthly expenses can significantly improve your cash flow over time.
- Automate Savings: Set up automatic transfers to your savings and investment accounts. By automating your savings, you ensure that a portion of your income is consistently allocated towards long-term financial goals. This helps prioritize saving and promotes disciplined saving habits.
- Review and Adjust Budget: Regularly review your budget to identify areas where you can make adjustments. Analyze your spending patterns and identify expenses that can be reduced or eliminated. By making conscious choices and aligning your spending with your priorities, you can improve your cash flow.
- Invest Wisely: Seek opportunities to invest your money strategically. Explore investment options that align with your risk tolerance and financial goals. Investing wisely can provide additional income streams and contribute to long-term wealth accumulation.
- Continuously Educate Yourself: Stay updated on personal finance strategies and best practices. By continuously learning about financial management, you can discover new techniques to improve your cash flow and make more informed financial decisions.
Implementing these strategies can gradually improve your personal cash flow and lead to financial stability and growth. Remember that consistency and discipline are key to effectively managing your cash flow and achieving your financial goals.
Common Cash Flow Challenges
Managing personal cash flow can present various challenges for individuals. Recognizing these common challenges is crucial for developing effective strategies to overcome them. Here are some of the most common cash flow challenges:
- Irregular Income: For individuals with irregular income, such as freelancers or self-employed individuals, cash flow management can be particularly challenging. Fluctuating income makes it difficult to establish a consistent budget and may require more careful tracking and planning.
- High Expenses: High expenses relative to income can significantly impact personal cash flow. This can occur due to various reasons such as excessive debt payments, high living costs, or unexpected expenses. When expenses outweigh income, it can lead to negative cash flow and financial stress.
- Emergency Expenses: Unforeseen emergency expenses can throw off a carefully managed budget and disrupt cash flow. Without adequate emergency savings, individuals may resort to borrowing or using credit cards, leading to increased debt and potential financial strain.
- Debt Burden: Debt payments can consume a significant portion of income, making it challenging to maintain positive cash flow. High-interest rates and multiple debt obligations can make it difficult to allocate funds for other financial priorities.
- Inconsistent Expense Tracking: Failing to consistently track expenses can hinder effective cash flow management. Incomplete or inaccurate records may lead to difficulty in identifying spending patterns or areas where adjustments can be made.
- Lack of Financial Discipline: A lack of financial discipline can make it challenging to stick to a budget and prioritize savings. Without disciplined spending habits, individuals may struggle to maintain positive cash flow and make progress towards their financial goals.
- Managing Multiple Income Streams: Individuals with multiple income streams may find it complex to track and manage cash flow effectively. Coordinating various sources of income and aligning them with expenses and savings can be a challenge without proper organization and planning.
- Unexpected Income Changes: Significant changes in income, such as job loss or salary reductions, can put a strain on personal cash flow. Adjusting expenses and finding alternative income sources may be necessary to adapt to these changes and maintain positive cash flow.
- Living Beyond Means: Living beyond one’s means, or spending more than what is earned, is a common challenge that leads to negative cash flow. Over-reliance on credit cards and excessive borrowing can exacerbate the issue and result in long-term financial difficulties.
Addressing these common cash flow challenges requires a proactive approach. Implementing strategies such as budgeting, expense tracking, reducing debt, building emergency savings, and cultivating financial discipline can help overcome these challenges and improve personal cash flow management.
Tips for Effective Cash Flow Management
Effective cash flow management is essential for maintaining financial stability and achieving financial goals. By implementing smart money management strategies, individuals can optimize their cash flow and improve their overall financial well-being. Here are some tips to help you effectively manage your cash flow:
- Create a Realistic Budget: Develop a comprehensive budget that accurately reflects your income, expenses, and financial goals. Consider both fixed and variable expenses and allocate a portion of your income towards savings and investments.
- Track and Categorize Expenses: Keep a detailed record of all your expenses and categorize them accordingly. This will help you identify spending patterns, monitor where your money is going, and make necessary adjustments to optimize your cash flow.
- Prioritize Debt Repayments: If you have outstanding debts, prioritize debt repayments to reduce interest costs and free up cash flow. Consider the debt avalanche or debt snowball method to systematically pay off debts.
- Build an Emergency Fund: Establish an emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses and financial setbacks. Aim to save three to six months’ worth of living expenses in case of job loss, medical emergencies, or other unforeseen circumstances.
- Automate Savings and Bill Payments: Set up automatic transfers for savings and automate bill payments to ensure they are paid on time. This will help you stay on track with your savings goals and minimize the risk of late payments or missed bills.
- Reduce Discretionary Spending: Identify areas where you can reduce discretionary spending. Cut back on unnecessary expenses such as entertainment, dining out, and luxury purchases. Redirect those funds towards debt repayment or savings.
- Negotiate Bills and Expenses: Regularly review your bills and negotiate to get better deals. Contact service providers, insurance companies, and utility providers to negotiate lower rates or explore alternative options to reduce your ongoing expenses.
- Explore Additional Income Opportunities: Consider taking on a side job or freelancing to increase your income. Explore opportunities to monetize your skills or hobbies that can supplement your primary source of income.
- Review and Adjust Regularly: Regularly review your cash flow, budget, and financial goals. Life circumstances and financial situations can change, so it’s important to adjust your strategies accordingly and align them with your evolving needs.
- Seek Professional Advice: If you feel overwhelmed or uncertain about managing your cash flow, consider consulting with a financial advisor. They can provide tailored advice, help you create a personalized financial plan, and guide you towards effective cash flow management.
By following these tips and implementing effective cash flow management strategies, you can take control of your finances, optimize your cash flow, and work towards achieving your financial objectives.
Conclusion
Managing personal cash flow is a critical aspect of achieving financial stability and success. By understanding and effectively managing the movement of money in and out of our finances, we can make informed financial decisions, reduce debt, save for the future, and work towards our financial goals.
In this article, we explored the concept of personal cash flow and its importance in our financial lives. We discussed the components of personal cash flow, including income, expenses, savings, and debt payments. Additionally, we explored common challenges that individuals face when managing their cash flow and provided strategies to overcome those challenges.
We highlighted the benefits of maintaining a positive cash flow, such as financial stability, reduced debt, improved credit score, and the ability to save and invest. Moreover, we offered practical tips to effectively manage personal cash flow, including creating a budget, tracking expenses, prioritizing debt repayments, building an emergency fund, and seeking additional income opportunities.
Remember, effective cash flow management requires consistency, discipline, and adaptability. Regularly reviewing and adjusting your financial strategies will help you stay on track and make necessary changes as your financial circumstances evolve.
By implementing the strategies and tips outlined in this article, you can take control of your personal cash flow, optimize your financial situation, and pave the way for a healthier and more secure financial future.