Home>Finance>How Much Taxable College Grant Or Scholarship Aid Did You Report To The IRS As Income?

Finance
How Much Taxable College Grant Or Scholarship Aid Did You Report To The IRS As Income?
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn about reporting taxable college grant or scholarship aid as income to the IRS. Gain valuable insights into managing your finances and maximizing deductions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding College Grant and Scholarship Aid
- Taxability of College Grant and Scholarship Aid
- Reporting College Grant and Scholarship Aid as Income to the IRS
- Determining if Your College Grant or Scholarship Aid is Taxable
- Steps to Report College Grant or Scholarship Aid to the IRS
- Exceptions and Exclusions for Taxable College Grant or Scholarship Aid
- Common Questions and Answers about Reporting College Grant or Scholarship Aid to the IRS
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of college grants and scholarships! College can be an expensive endeavor, and these types of financial aid can make a significant impact on the affordability of higher education. However, as a recipient of college grant or scholarship aid, it’s important to understand the potential tax implications that may come along with it.
In this article, we will delve into the topic of taxable college grant or scholarship aid and provide you with the necessary information to navigate the complexities of reporting it to the IRS. We will explore the various factors that determine whether or not your grant or scholarship aid is taxable, as well as the steps you need to take to accurately report it.
Whether you’re a student who just received a generous scholarship, or a parent supporting a child through college, understanding the tax implications of grant or scholarship aid is crucial for effective financial planning. By being aware of the rules and regulations surrounding taxable aid, you can avoid potential surprises come tax season and ensure compliance with the IRS.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on how to handle taxable college grant or scholarship aid, including the exceptions and exclusions that may apply. So, let’s dive in and demystify the world of reporting college grant or scholarship aid to the IRS!
Understanding College Grant and Scholarship Aid
Before delving into the taxability of college grant and scholarship aid, it’s important to have a clear understanding of what these forms of financial assistance entail.
College grants and scholarships are funds provided to students to help cover the costs associated with higher education, such as tuition, fees, books, and living expenses. These funds can come from a variety of sources, including federal and state governments, colleges and universities, private organizations, and foundations.
Grants and scholarships can be need-based or merit-based. Need-based aid is awarded to students who demonstrate financial need, typically determined by a family’s income and assets. Merit-based aid, on the other hand, is awarded based on academic or extracurricular achievements, such as high grades, test scores, or athletic prowess.
One of the key advantages of receiving grants and scholarships is that they don’t need to be repaid like student loans. This makes them highly desirable for students seeking to minimize their student loan debt.
It’s essential to note that not all college grant and scholarship aid is taxable. The taxability depends on various factors, such as the purpose of the funds and the specific rules set by the IRS.
Now that we have a basic understanding of college grant and scholarship aid, let’s explore the tax implications associated with these forms of financial assistance.
Taxability of College Grant and Scholarship Aid
When it comes to the taxability of college grant and scholarship aid, the general rule is that if the funds are used for qualified education expenses, they are not considered taxable income. Qualified education expenses include tuition, fees, books, and required supplies for enrollment or attendance at an eligible educational institution.
However, if any portion of the grant or scholarship aid is used for non-qualified expenses, such as room and board, travel, or personal expenses, that portion may be subject to taxation. Additionally, if the aid exceeds the total qualified expenses, the excess amount may also be taxable.
The IRS considers these funds as part of your overall income, and depending on your total income and filing status, it could push you into a higher tax bracket or impact the eligibility for certain tax credits or deductions.
It’s important to note that even if your grant or scholarship aid is taxable, it doesn’t necessarily mean that you will owe a significant amount of tax. The tax liability will depend on your individual circumstances, such as your income level and the amount of taxable aid received.
Next, let’s explore how to determine if your college grant or scholarship aid is taxable.
Reporting College Grant and Scholarship Aid as Income to the IRS
When it comes to reporting college grant or scholarship aid as income to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), it’s important to understand the guidelines and ensure accurate reporting on your tax return. Failure to report taxable income can lead to penalties and potential audits.
The first step in reporting your grant or scholarship aid is determining if it is taxable. As mentioned earlier, if the funds were used for qualified education expenses, they are generally not considered taxable income. However, if any portion of the aid was used for non-qualified expenses, that portion may be subject to taxation.
If your grant or scholarship aid is indeed taxable, you must include it as income on your tax return, regardless of whether you received a Form W-2 or 1099 from the educational institution or organization that granted the funds.
In most cases, you will report the taxable grant or scholarship aid as part of your total income on Form 1040 or 1040A. The specific section where you report the income may vary depending on your filing status and any other sources of income you may have.
It’s important to accurately calculate and report the taxable amount of your grant or scholarship aid. If you’re unsure about the taxability or how to calculate the taxable portion, seeking professional tax advice or using tax software can help ensure accurate reporting.
Remember, it’s better to be proactive and report the income correctly rather than face potential consequences in the form of audits or penalties for underreporting.
Now that we’ve covered the basics of reporting college grant or scholarship aid as income, let’s move on to understanding how to determine if your aid is taxable in the first place.
Determining if Your College Grant or Scholarship Aid is Taxable
When it comes to determining the taxability of your college grant or scholarship aid, there are a few key factors to consider:
- Purpose of the funds: If the grant or scholarship aid is used for qualified education expenses, such as tuition, fees, books, and required supplies, it is generally not considered taxable income. However, if the funds are used for non-qualified expenses like room and board, travel, or personal expenses, those portions may be subject to taxation.
- Type of grant or scholarship: Different types of grants and scholarships may have different tax implications. For example, need-based grants are generally not taxable if used for qualified education expenses. However, merit-based scholarships may have different rules, so it’s essential to understand the specific terms and conditions of the grant or scholarship you received.
- Enrollment status: Your enrollment status as a full-time or part-time student can also impact the taxability of your grant or scholarship aid. In some cases, grants and scholarships may be prorated based on the number of credit hours you are enrolled in, with only the portion used for qualified education expenses being non-taxable.
- Filing status: The taxability of your grant or scholarship aid may be influenced by your filing status. For example, if you are married and file jointly, your combined income and the income thresholds for tax brackets and deductions may affect the taxability of your aid.
It’s important to review the terms and documentation provided by the grantor or scholarship provider to understand any specific requirements or restrictions regarding the taxability of the funds. If you’re unsure about whether your grant or scholarship aid is taxable, consulting a tax professional can provide you with the necessary guidance to navigate this complex area.
Now that you have a better understanding of how to determine the taxability of your college grant or scholarship aid, let’s move on to the steps involved in reporting it to the IRS.
Steps to Report College Grant or Scholarship Aid to the IRS
Reporting your college grant or scholarship aid to the IRS may seem daunting, but by following these steps, you can ensure accurate and timely reporting:
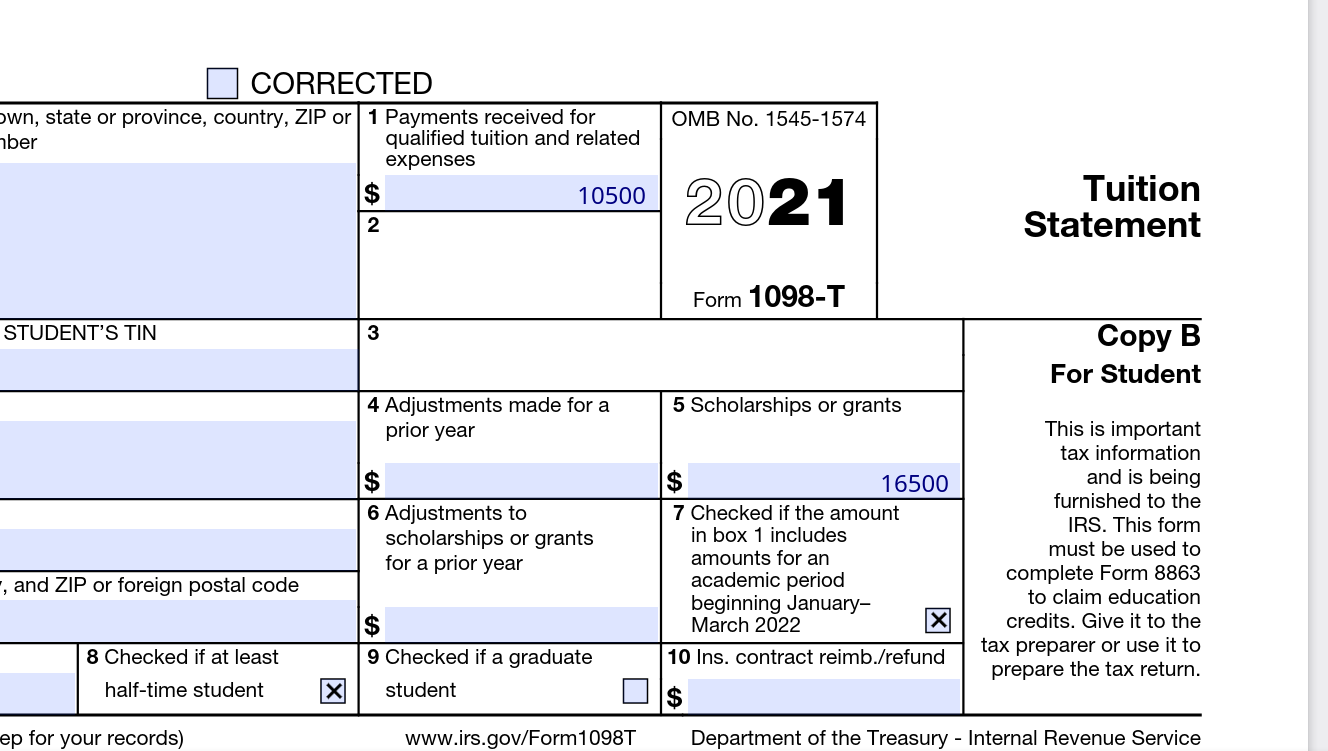
- Gather necessary documentation: Collect all the relevant documentation related to your grant or scholarship aid. This may include Form W-2 or 1099 from the educational institution or organization that granted the funds.
- Determine the taxability: Review the purpose of the funds and determine if any portion of your grant or scholarship aid is taxable. Calculate the taxable amount by subtracting the portion used for qualified education expenses from the total aid received.
- Complete your tax return: Choose the appropriate tax form (such as Form 1040 or 1040A) and accurately report your grant or scholarship aid as income. Look for the specific section on the form where you report additional income not listed on your W-2 or 1099 forms.
- Use tax software or seek professional help: If you’re unsure about how to report your grant or scholarship aid or calculate the taxable amount, consider using tax software or consulting a tax professional. They can guide you through the process and help ensure accurate reporting.
- File your tax return: Once you have completed all the necessary sections of your tax return and reported your grant or scholarship aid as income, file your tax return by the deadline specified by the IRS. Keep copies of all the relevant documents for your records.
Remember, accuracy is key when reporting your grant or scholarship aid to the IRS. Double-check your calculations and make sure you report the correct amount of taxable income. Failing to accurately report your taxable aid can result in penalties or potential audits.
By following these steps and taking the time to properly report your college grant or scholarship aid to the IRS, you can ensure compliance with tax regulations and maintain peace of mind come tax season.
Now, let’s explore the exceptions and exclusions that may apply to taxable college grant or scholarship aid.
Exceptions and Exclusions for Taxable College Grant or Scholarship Aid
While most taxable college grant or scholarship aid needs to be reported as income to the IRS, there are certain exceptions and exclusions that may apply. These exceptions and exclusions can help reduce or eliminate the amount of taxable income, providing some relief for recipients. Here are a few key exceptions and exclusions to be aware of:
- Qualified tuition reductions: If you receive a grant or scholarship that is a qualified tuition reduction, the amount used to pay for qualified education expenses may be tax-free. Qualified tuition reductions are benefits provided by an educational institution to its employees or their dependents for education below the graduate level. Certain criteria must be met for this exclusion to apply.
- Fellowships and grants for research or teaching: Fellowships or grants received by individuals pursuing research or teaching may be excluded from taxable income under certain circumstances. These grants must be designated for research or teaching and must be used to pay for qualified education expenses.
- Veterans’ and military aid: Certain types of financial assistance provided to veterans and members of the military may be exempt from taxation. This includes benefits such as the GI Bill and tuition assistance programs offered by the military.
- Employer-provided educational assistance: If your employer provides educational assistance as part of a benefits package, up to a certain amount per year may be excluded from taxable income. There are criteria that the educational assistance must meet, such as it being limited to job-related courses.
- Scholarships for non-degree-seeking students: Scholarships or grants received for non-degree-seeking programs, such as vocational or technical training, may be exempt from taxation if they meet certain requirements.
It’s crucial to carefully review the specific criteria and guidelines for each exception and exclusion to determine if you qualify. In some cases, you may need to meet specific educational requirements or provide documentation to support your eligibility for the exclusion.
When reporting your taxable college grant or scholarship aid to the IRS, be sure to take advantage of any applicable exceptions or exclusions. This can help reduce your overall tax liability and ensure that you’re not paying more taxes than necessary.
Now that we’ve explored the exceptions and exclusions for taxable grant or scholarship aid, let’s address some common questions and provide answers to help clarify any remaining doubts.
Common Questions and Answers about Reporting College Grant or Scholarship Aid to the IRS
Reporting college grant or scholarship aid to the IRS can raise a number of questions. To help clarify any confusion, here are answers to some commonly asked questions:
- Do I need to report my grant or scholarship aid as income?
- What forms do I need to report my grant or scholarship aid?
- How do I calculate the taxable amount of my grant or scholarship aid?
- Can I claim any deductions or credits for my education expenses?
- What if my grant or scholarship aid exceeds my qualified expenses?
- Will reporting grant or scholarship aid as income affect my financial aid eligibility?
Generally, if your grant or scholarship aid is used for qualified education expenses, it is not considered taxable income. However, if any portion of the aid is used for non-qualified expenses or if the aid exceeds your total qualified expenses, that portion may be subject to taxation.
You may receive Form W-2 or 1099 from the educational institution or organization that granted the funds. However, even if you don’t receive these forms, you are still responsible for reporting your grant or scholarship aid as income on your tax return.
To determine the taxable amount, subtract the portion of the aid used for qualified education expenses from the total aid received. Non-qualified expenses, such as room and board, should be accounted for when calculating the taxable portion.
Depending on your eligibility and circumstances, you may be able to claim deductions or credits for education expenses. The most common ones are the American Opportunity Credit and the Lifetime Learning Credit. Consult a tax professional or use tax software to determine if you qualify for these benefits.
If the aid you receive exceeds your qualified education expenses, you may need to report the excess amount as taxable income. It’s important to keep track of your expenses and report the correct taxable amount on your tax return.
Reporting grant or scholarship aid as income on your tax return may impact your financial aid eligibility for future years. It’s important to consult with your college’s financial aid office to understand any potential implications for your specific situation.
These are just a few common questions related to reporting college grant or scholarship aid to the IRS. It’s essential to stay informed and seek professional advice if you have specific queries or concerns related to your unique circumstances.
Now, as we wrap up this article, let’s recap the key points we’ve covered.
Conclusion
Navigating the taxability and reporting of college grant or scholarship aid to the IRS may seem daunting, but with the right information, you can confidently handle this aspect of your financial journey. By understanding the rules and regulations surrounding taxable aid, you can ensure accurate reporting and avoid potential penalties or audits.
Remember, not all college grant or scholarship aid is taxable. If the funds are used for qualified education expenses, they are generally not considered taxable income. However, if any portion of the aid is used for non-qualified expenses, such as room and board, that portion may be subject to taxation.
When reporting your grant or scholarship aid as income, gather all the necessary documentation, accurately calculate the taxable amount, and select the appropriate section on your tax return to report the income. Utilizing tax software or seeking professional help can provide additional guidance and ensure accurate reporting.
It’s important to take note of exceptions and exclusions that may apply, such as qualified tuition reductions or certain types of veteran or military aid, which may exempt a portion of your aid from taxation. Understanding and utilizing these exceptions and exclusions can help reduce your overall tax liability.
As with any tax-related matters, it’s crucial to stay informed and seek professional advice if needed. Consult with a tax professional or utilize resources provided by the IRS to ensure compliance with tax regulations and make the most of any applicable deductions or credits for education expenses.
In conclusion, by being aware of the taxability of your college grant or scholarship aid and accurately reporting it to the IRS, you can navigate the complexities of taxation while focusing on your educational journey. Maximize the benefits of financial aid, make informed decisions, and set yourself up for financial success as you pursue your college dreams.