
Finance
What Is Spread In Forex Trading
Published: December 22, 2023
Learn the basics of spread in forex trading with our comprehensive finance guide. Understand how this key concept impacts your trades and profitability.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of forex trading, where currencies are bought and sold on the global market. As a savvy investor or trader, it’s important to understand the various factors that can affect your profitability in this highly volatile market. One such factor is the concept of “spread,” which plays a crucial role in forex trading.
In simple terms, spread refers to the difference between the buying price (bid) and the selling price (ask) of a currency pair. It is essentially the cost of executing a trade in the forex market. Understanding the concept of spread and how it works is essential to making informed trading decisions and maximizing your profits.
The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, and sees trillions of dollars being exchanged daily. Spread is a fundamental aspect of this market, as it represents the compensation that brokers receive for facilitating your trades. It is important to note that different currencies have different spreads, which can be influenced by multiple factors such as liquidity, market conditions, and the broker’s fee structure.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the concept of spread and explore how it works in forex trading. We will also discuss the various types of spreads, factors that affect spread, and why spread is an important consideration for traders. Additionally, we will provide strategies to help you minimize spread costs and optimize your trading experience.
So, whether you are a beginner exploring the world of forex trading or an experienced trader looking to enhance your understanding, read on to gain insights into the fascinating world of spread in forex trading.
Understanding Forex Trading
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is the act of buying and selling currencies with the aim of profiting from the fluctuations in their exchange rates. It is a decentralized market where participants trade currencies directly or through intermediaries, such as brokers.
The forex market operates in pairs, with the value of one currency relative to another. For example, the popular currency pair EUR/USD represents the value of the euro compared to the US dollar. Traders speculate on whether a currency will rise or fall relative to another, aiming to profit from these price movements.
One of the key benefits of forex trading is its high liquidity. The market is enormous, with trillions of dollars being traded daily, making it highly attractive to investors and traders alike. Additionally, forex trading offers the opportunity for leverage, allowing traders to control larger positions with a smaller initial investment.
To participate in forex trading, you’ll need a trading account with a reputable broker. The broker serves as the intermediary between you and the market, executing your trades and providing you with access to trading platforms, charts, and analysis tools.
Forex trading involves various strategies and techniques, including technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and risk management. Technical analysis involves studying historical price data and using indicators to predict future price movements. Fundamental analysis, on the other hand, focuses on analyzing economic and political factors that can impact a currency’s value. Effective risk management is crucial in forex trading, as it helps to protect your capital and minimize losses.
It is important to note that forex trading carries a certain level of risk. Due to the high volatility of the market, it is possible to experience substantial gains, but also significant losses. It is essential to have a solid understanding of the market, continuously educate yourself, and develop a disciplined trading plan.
Now that we have a basic understanding of forex trading, let’s delve into the concept of spread and its significance in this exciting market.
What is Spread?
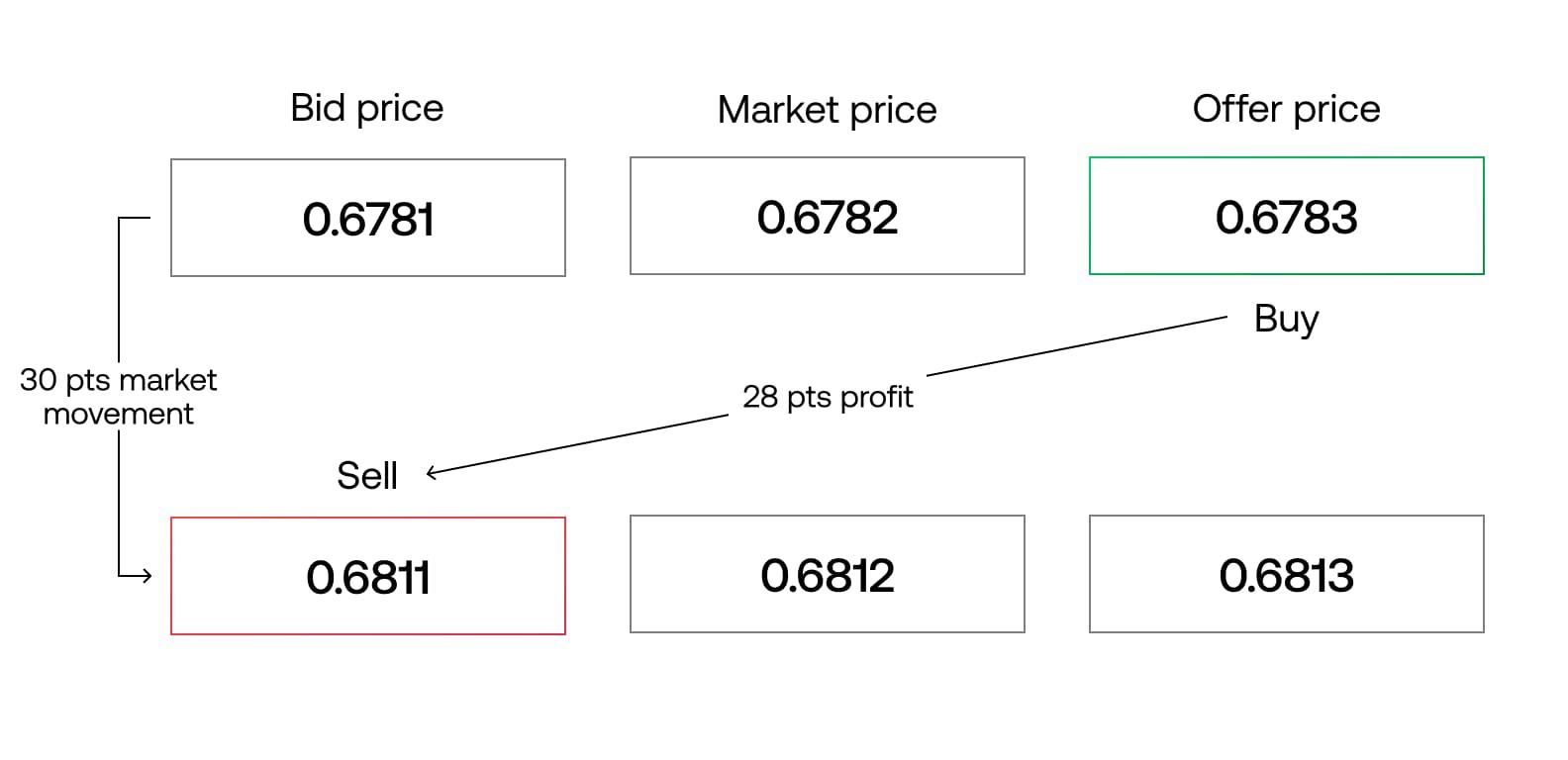
In forex trading, spread refers to the difference between the bid (buying) price and the ask (selling) price of a currency pair. It is typically measured in pips, which is the smallest unit of price movement in the forex market. The spread is the cost that traders incur for executing a trade.
Let’s take an example to understand. Suppose you are looking to buy the EUR/USD currency pair, and the current bid price is 1.2000, while the ask price is 1.2002. In this case, the spread is 2 pips.
Spread exists due to the various players in the forex market, such as banks, financial institutions, and brokers, who facilitate the buying and selling of currencies. These market participants earn a profit by offering bid and ask prices, with the difference between the two representing their compensation.
Spread is an essential concept in forex trading as it directly impacts the profitability of a trade. It is important to note that spreads can vary across different currency pairs and brokers. Major currency pairs, such as EUR/USD and GBP/USD, generally have tighter spreads due to their high liquidity and trading volume. On the other hand, exotic currency pairs may have wider spreads due to lower trading activity.
Understanding the spread is crucial when entering and exiting trades, as it affects the breakeven point and potential profits. For example, if the spread on a currency pair is wide, the price must move significantly in your favor to cover the cost and start making a profit. On the other hand, a narrow spread allows for quicker and easier profit realization.
Next, let’s explore how the spread works in forex trading and its impact on your trades.
How Does Spread Work in Forex Trading?
The spread in forex trading works by incorporating the broker’s fee into the bid and ask prices of a currency pair. When you place a trade, you are essentially buying at the ask price and selling at the bid price. The difference between the two prices is the spread, which compensates the broker for their services.
Brokers can offer two types of spreads: fixed spreads and variable spreads. A fixed spread remains constant regardless of market conditions, while a variable spread can fluctuate based on factors such as liquidity, volatility, and market demand.
Let’s understand the mechanism behind the spread with an example. Suppose the bid price for the EUR/USD currency pair is 1.2000 and the ask price is 1.2002. In this case, the spread would be 2 pips. If you were to buy the currency pair, your trade would execute at the ask price of 1.2002. Conversely, if you were to sell the currency pair, your trade would execute at the bid price of 1.2000.
The difference between the execution price and the market price represents the cost of the spread. For example, if you bought the currency pair and it immediately moved in your favor by 2 pips, the market price would need to rise by 2 pips for you to break even. This is because you would need to cover the spread cost before making a profit.
It is important to note that while the spread represents the broker’s compensation, it does not directly impact the market’s movements or the currency pair’s value. The spread simply reflects the difference between the buy and sell price at a particular time.
The size of the spread can vary among brokers based on their fee structure. Some brokers may offer tighter spreads by charging a commission on each trade, while others may generate revenue solely through the spread. It is essential to consider the spread and other trading costs when choosing a broker, as tighter spreads can significantly affect your overall profitability.
Now that we understand how the spread works, let’s explore the different types of spreads you may encounter in forex trading.
Types of Spreads
In forex trading, there are three common types of spreads: fixed spreads, variable spreads, and floating spreads. Let’s explore each type in more detail:
1. Fixed Spreads: As the name suggests, fixed spreads remain constant regardless of market conditions. This means that the difference between the bid and ask prices remains the same, providing traders with certainty about the cost of executing a trade. Fixed spreads are typically higher than variable spreads but can be advantageous during times of high market volatility when variable spreads tend to widen.
2. Variable Spreads: Variable spreads, also known as dynamic spreads, fluctuate based on market conditions. During periods of high liquidity and low volatility, the spread tends to be tighter, meaning the difference between the bid and ask prices is smaller. However, during times of low liquidity or significant market events, the spread can widen, reflecting increased uncertainty and potentially higher trading costs.
3. Floating Spreads: Floating spreads are similar to variable spreads, but they can widen or tighten beyond the typical range depending on market conditions. Brokers offering floating spreads adjust the spread based on various factors such as liquidity, volatility, and order flow. This type of spread can provide traders with the opportunity to benefit from favorable market conditions with tighter spreads, but it also carries the risk of widening spreads during less favorable market conditions.
The choice between fixed, variable, or floating spreads depends on your trading style and preferences. Fixed spreads provide transparency and consistent trading costs, which can be suitable for traders who prefer stability. Variable spreads may be preferred by those who seek the potential for lower costs during times of tight spreads but are willing to accept wider spreads when market conditions are less favorable. Floating spreads offer a combination of flexibility and potential cost optimization but come with the risk of wider spreads during volatile periods.
It is important to note that the spread is just one aspect to consider when choosing a broker. Other factors, such as the broker’s reputation, regulatory compliance, trading platform, customer support, and additional trading fees, should also be taken into account when making a decision.
Now that we have discussed the types of spreads, let’s explore the factors that can influence the size of spreads in forex trading.
Fixed Spread vs. Variable Spread
When it comes to forex trading, there are two main types of spreads to consider: fixed spreads and variable spreads. Understanding the differences between these two types can help you make informed decisions about your trading strategy. Let’s explore the characteristics of each:
Fixed Spreads: A fixed spread remains constant regardless of market conditions. It is predetermined by the broker and does not change, providing traders with consistency and predictability in terms of trading costs. Fixed spreads are typically higher than variable spreads but can be advantageous during times of high market volatility when variable spreads tend to widen. Traders who prefer stable trading costs and want to know their expenses upfront may opt for fixed spreads.
Variable Spreads: Unlike fixed spreads, variable spreads fluctuate based on market conditions. They are influenced by factors such as liquidity, volatility, and order flow. During periods of high liquidity and low volatility, variable spreads tend to be tighter, meaning the difference between the bid and ask prices is smaller. This can result in potentially lower trading costs for traders. However, during times of low liquidity or significant market events, variable spreads can widen, reflecting increased uncertainty and potentially higher trading costs.
The choice between fixed and variable spreads depends on various factors, including your trading style, market conditions, and risk tolerance. Here are some key considerations:
- Cost: Fixed spreads generally have higher trading costs compared to variable spreads. However, variable spreads can significantly widen during volatile market conditions, potentially increasing trading costs.
- Stability: Fixed spreads provide stability and predictability in terms of trading costs. Traders who want to know their expenses upfront may find this beneficial.
- Flexibility: Variable spreads can offer flexibility, especially during times of tight spreads. This can be advantageous for traders who seek potential cost optimization and are willing to accept wider spreads during less favorable market conditions.
- Market Conditions: If you primarily trade during high volatility periods, a fixed spread might not be the most cost-effective option. Variable spreads tend to reflect market conditions more accurately during such times.
It’s important to note that different brokers may offer different spreads, even within the same category. Additionally, some brokers may provide the option to switch between fixed and variable spreads, allowing traders to adapt their trading strategy to changing market conditions.
When choosing between fixed and variable spreads, it’s crucial to consider your trading goals, risk tolerance, and the specific market conditions you expect to encounter. A thorough evaluation of your trading needs and careful consideration of the pros and cons of each type of spread will help you make an informed decision.
Now that we have explored fixed spreads and variable spreads, let’s discuss the factors that can influence the size of spreads in forex trading.
Factors that Affect Spread
The size of the spread in forex trading is influenced by various factors that can vary from one currency pair to another and from one broker to another. Understanding these factors can help you better comprehend why spreads fluctuate and how they can impact your trading. Here are some key factors that affect spread:
1. Liquidity: Liquidity refers to the ease with which a currency pair can be bought or sold without significantly impacting its price. Highly liquid currency pairs, such as EUR/USD and USD/JPY, tend to have tighter spreads due to the large number of buyers and sellers in the market. On the other hand, less liquid currency pairs may have wider spreads due to the lower trading activity and fewer market participants.
2. Volatility: Volatility represents the magnitude of price fluctuations in the market. When there is increased volatility, spreads can widen to reflect the higher level of risk and uncertainty. This is especially true during significant market events such as economic announcements, political developments, or unexpected news that can impact currency prices.
3. Market Conditions: Market conditions play a significant role in determining spreads. During times of normal market conditions, spreads tend to be relatively stable. However, during periods of high volatility, low liquidity, or market uncertainty, spreads can widen as brokers adjust their pricing to reflect the increased risk and potential costs associated with executing trades.
4. Broker’s Fee Structure: Different brokers have varying fee structures, which can impact the spreads they offer. Some brokers may charge a fixed commission per trade, while others generate their revenue solely through the spread. Brokers offering tighter spreads may charge higher commissions or have different account types with varying spreads, so it’s important to consider the overall trading costs when evaluating different brokers.
5. Trading Session: Spreads can vary depending on the trading session. The forex market operates 24 hours a day, and each major trading session (Asian, European, and North American) has its own characteristics. For example, during the overlap of the European and North American sessions, there tends to be higher trading activity and liquidity, resulting in tighter spreads compared to other sessions.
6. Currency Pair: Different currency pairs have different levels of liquidity and trading volume, which can influence the spread. Major currency pairs, such as EUR/USD and GBP/USD, typically have tighter spreads due to their high liquidity. Exotic currency pairs, which involve less commonly traded currencies, may have wider spreads due to lower trading activity.
Understanding these factors can help you anticipate potential spread fluctuations and adjust your trading strategy accordingly. Keep in mind that spreads may vary between brokers, so it’s advisable to compare spreads, along with other important factors, when choosing a broker for your forex trading.
Now that we have explored the factors that affect spreads, let’s delve into the importance of spread consideration in forex trading.
Importance of Spread in Forex Trading
The spread plays a crucial role in forex trading and has significant implications for traders. Understanding the importance of spread consideration can help you make informed trading decisions and maximize your profitability. Here are some key reasons why spread is important:
1. Trading Costs: The spread represents the cost of executing a trade in the forex market. It is essentially the difference between the buying price (bid) and selling price (ask). By considering the spread, traders can accurately calculate their trading costs and determine the potential profitability of a trade. Tighter spreads allow for lower trading costs, enabling traders to achieve breakeven and profit targets more quickly.
2. Impact on Profitability: The size of the spread is directly correlated to the breakeven point and potential profits. A wider spread requires the currency pair to move in a favorable direction by a larger number of pips to cover the spread cost and generate a profit. Tighter spreads provide traders with an advantage as they require smaller price movements to achieve profitability. Therefore, minimizing spread costs can significantly impact overall trading profitability.
3. Trade Entry and Exit: The spread affects the entry and exit points of trades. When entering a trade, the ask price is considered, while the bid price is relevant when exiting the trade. Considering the spread allows traders to choose optimal entry and exit points, ensuring that they are not immediately in a losing position due to spread costs. This is particularly important for day traders and scalpers who aim to capitalize on short-term price movements.
4. Risk Management: Managing risk is crucial in forex trading, and understanding the spread is an integral part of it. Spread costs directly impact the risk-reward ratio of a trade. By factoring in the spread when determining stop-loss and take-profit levels, traders can establish appropriate risk management strategies. This helps to protect their capital, limit potential losses, and maintain a favorable risk-reward balance.
5. Broker Selection: The spread differs among brokers, and selecting the right broker can have a significant impact on your trading success. Comparing spreads from different brokers is essential to ensure you are getting competitive pricing and minimizing trading costs. Consider other factors such as regulatory compliance, trading platform features, customer support, and additional fees when choosing a broker.
It is important to note that spread consideration should be balanced with other factors such as execution quality, slippage, and reliable trade execution. While tight spreads are desirable, it is also crucial to choose a reputable and reliable broker to ensure a smooth trading experience.
In summary, the spread is a fundamental aspect of forex trading that directly influences trading costs, profitability, risk management, and broker selection. By understanding and considering the spread, traders can make informed decisions and optimize their trading strategies to achieve their financial goals.
Now, let’s explore some strategies to minimize spread costs and enhance your forex trading experience.
Strategies to Minimize Spread Costs
Minimizing spread costs is a priority for forex traders, as it directly impacts profitability. While traders cannot control the size of the spread set by the broker, there are strategies they can employ to minimize spread costs and optimize their trading experience. Here are some effective strategies:
1. Choose a Broker with Competitive Spreads: Research and compare brokers to find the one that offers tight spreads. Consider not only the size of the spread but also the overall trading conditions, execution quality, and the broker’s reputation. A broker with competitive spreads can significantly reduce your trading costs over time.
2. Trade During High Liquidity Periods: Liquidity affects the spread size. During periods of high liquidity, spreads tend to be narrower due to the increased number of buyers and sellers in the market. Trading during major trading sessions or overlapping sessions can help you benefit from tighter spreads and lower trading costs.
3. Avoid Trading During News Releases: Economic reports and other major news releases can cause significant volatility in the forex market, leading to wider spreads. It’s advisable to avoid trading during these periods or use appropriate risk management techniques to account for the potential impact on spreads and ensure you are adequately protected.
4. Utilize Limit Orders: Limit orders allow you to specify the desired entry or exit price in advance. By using limit orders, you can attempt to execute trades at a specific price or better when the market reaches your desired level. This can help you avoid unfavorable spreads and minimize slippage.
5. Consider Commission-Based Accounts: Some brokers offer commission-based accounts where the spread is narrower, but traders pay a separate commission per trade. This can be beneficial for high-volume traders as it reduces overall trading costs. Evaluate the trading volume and frequency of your trades to determine if a commission-based account may be more cost-effective for you.
6. Use Tight Stop-Loss Orders: While risk management is crucial, using tight stop-loss orders can help you minimize potential losses related to spread costs. Placing stop-loss orders closer to your entry point reduces the required price movement to achieve breakeven and can help protect capital. However, it is important to ensure your stop-loss is still wide enough to withstand market fluctuations and avoid premature stopouts.
7. Monitor Spread Fluctuations: Spreads can vary, especially during volatile market conditions. Regularly monitor spread fluctuations and be aware of the average spread for the currency pairs you trade. By keeping an eye on these changes, you can time your trades to take advantage of tighter spreads and avoid executing trades during periods of wider spreads.
Implementing these strategies can help you minimize spread costs and improve your trading performance. However, it is important to balance spread considerations with other factors such as trade execution quality, slippage, and the overall trading experience provided by your chosen broker.
Now that we have explored strategies to minimize spread costs, let’s wrap up the article.
Conclusion
In conclusion, spread is a fundamental concept in forex trading, representing the difference between the bid and ask prices of a currency pair. It is the cost incurred by traders when executing trades and directly impacts their profitability. Understanding the importance of spread consideration and implementing strategies to minimize spread costs is vital for successful trading.
By choosing a broker with competitive spreads, trading during high liquidity periods, avoiding news releases, utilizing limit orders, considering commission-based accounts, using tight stop-loss orders, and monitoring spread fluctuations, traders can optimize their trading experience and reduce trading costs.
Additionally, being aware of the factors that affect spread, such as liquidity, volatility, and market conditions, allows traders to better anticipate spread fluctuations. This knowledge empowers them to make informed trading decisions and adjust their strategies accordingly.
It is important to note that while minimizing spread costs is essential, traders should also consider other factors such as trade execution quality, slippage, and overall trading conditions provided by their chosen broker. A comprehensive evaluation of these factors ensures a well-rounded and successful trading experience.
Whether you are a beginner exploring the world of forex trading or an experienced trader looking to refine your strategies, understanding spread and its significance is essential. By incorporating spread considerations into your trading plan, you can enhance your profitability, manage risk effectively, and navigate the dynamic forex market with confidence.
Now that you have gained insights into the concept of spread in forex trading, it is time to apply this knowledge and embark on your trading journey armed with a solid understanding of this crucial aspect of the forex market.