Home>Finance>Adjustable-Rate Preferred Stock (ARPS) Definition


Finance
Adjustable-Rate Preferred Stock (ARPS) Definition
Published: October 1, 2023
Learn about Adjustable-Rate Preferred Stock (ARPS) in finance. Understand the definition and its importance in the financial market.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Understanding Adjustable-Rate Preferred Stock (ARPS)
When it comes to investing, there are numerous options available to individuals looking to grow their wealth. In the world of finance, one often comes across terms like stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, but have you ever heard of Adjustable-Rate Preferred Stock (ARPS)? If not, you’re in the right place! In this blog post, we will explore the definition and key aspects of ARPS, an investment instrument that combines the benefits of both stocks and preferred stock.
Key Takeaways:
- ARPS are a type of preferred stock that have a variable dividend rate based on an underlying benchmark.
- They have a predetermined dividend reset date, where the rate is adjusted based on the performance of the benchmark.
What is Adjustable-Rate Preferred Stock (ARPS)?
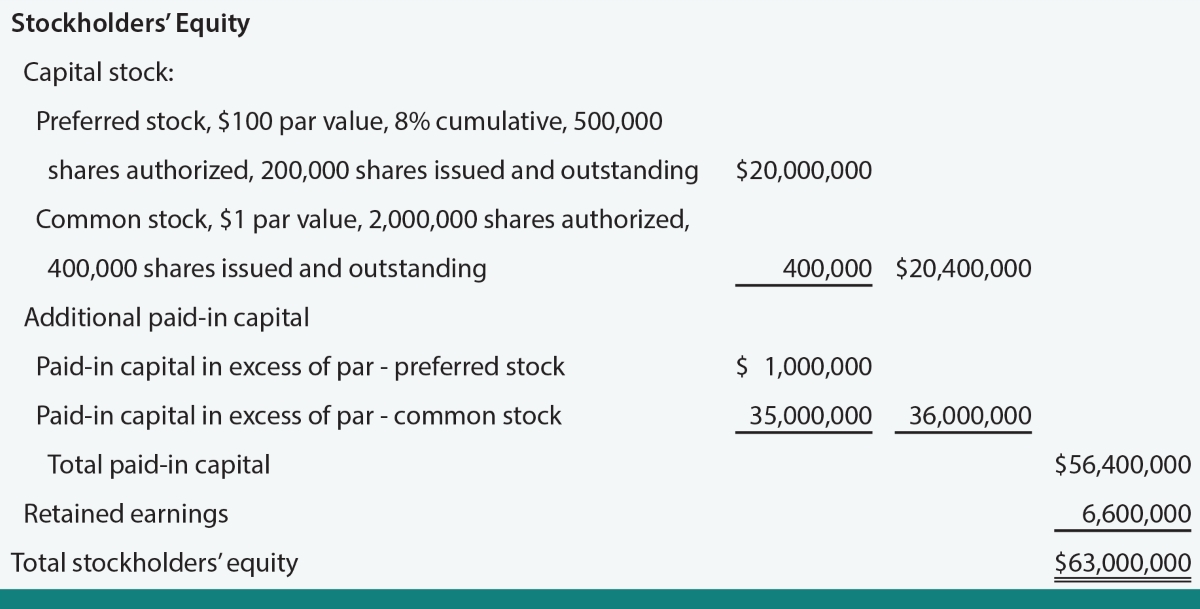
Adjustable-Rate Preferred Stock (ARPS) is a type of preferred stock that differs from traditional fixed-rate preferred stocks. Unlike regular preferred stocks, which have a fixed dividend rate, ARPS have a variable dividend rate that is tied to an underlying benchmark, such as the prime rate or the London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR). The dividend rate is generally set at a spread above the benchmark rate, providing investors with the potential for higher returns. However, it is important to note that the dividend rate can also go down if the benchmark rate decreases.
How do Adjustable-Rate Preferred Stocks work?
Adjustable-Rate Preferred Stocks have a predetermined dividend reset date. On this date, the dividend rate is adjusted based on the performance of the underlying benchmark. If the benchmark rate increases, the dividend rate of the ARPS also increases. Conversely, if the benchmark rate decreases, the dividend rate of the ARPS may decrease as well. This feature of ARPS allows investors to benefit from potential increases in interest rates, while still enjoying the relative stability and priority of preferred stock. It is essential for investors to keep an eye on the benchmark rates, as they play a crucial role in determining the returns on ARPS.
Advantages of Adjustable-Rate Preferred Stocks
- Potential for Higher Returns: ARPS offer the potential for higher dividend payments if the benchmark rate increases, making them an attractive investment option for individuals seeking higher yields.
- Stability and Priority: Preferred stocks, including ARPS, generally have a higher priority than common stocks when it comes to receiving dividends. This provides investors with a greater degree of stability and income relative to common stockholders.
- Diversification: Investing in ARPS can help diversify an investment portfolio, as they offer a different risk-return profile compared to other traditional investment options, such as stocks or bonds.
Conclusion
Adjustable-Rate Preferred Stock (ARPS) is a unique investment instrument that combines the benefits of preferred stock with a variable dividend rate tied to an underlying benchmark. While they may not be suitable for all investors, ARPS offer the potential for higher returns and can provide stability and income in an investment portfolio. As with any investment, it is important to conduct thorough research and consider your financial goals and risk tolerance before investing in ARPS.