Home>Finance>Comprehensive Income: Statement, Purpose, And Definition


Finance
Comprehensive Income: Statement, Purpose, And Definition
Modified: December 30, 2023
Learn the definition and purpose of comprehensive income in finance with our comprehensive guide. Understand how this statement impacts financial reporting and analysis.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Comprehensive Income: Statement, Purpose, and Definition
When it comes to managing your finances, understanding key financial statements is crucial. One often overlooked but important financial statement is the comprehensive income statement. In this blog post, we will explore what comprehensive income is, its purpose, and its definition. So, grab a cup of coffee and let’s delve into the world of comprehensive income!
Key Takeaways
- Comprehensive income includes all changes in equity during a period, excluding transactions with owners.
- The purpose of the comprehensive income statement is to provide a complete picture of a company’s financial performance, including non-operating income and expenses.
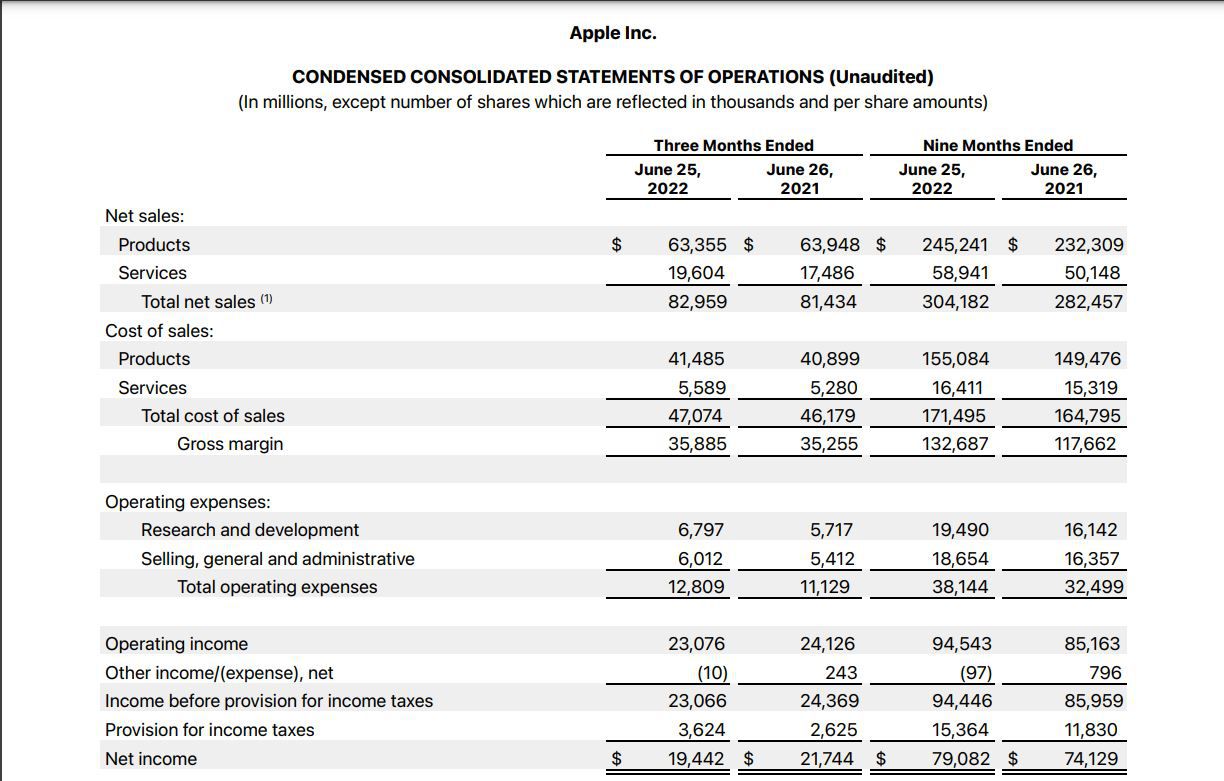
What is Comprehensive Income?
Comprehensive income can be defined as all changes in equity during a specific period, excluding transactions with owners (such as dividends or share issuance). It goes beyond the traditional net income figure by including other comprehensive income items, such as unrealized gains or losses on investments, foreign currency translation adjustments, and changes in the fair value of certain financial instruments.
In simpler terms, comprehensive income measures not only the regular operating activities but also factors in other income or expenses that may impact a company’s financial position. It provides a more comprehensive view of a company’s overall profitability and financial health.
Purpose of the Comprehensive Income Statement
The comprehensive income statement serves a vital purpose in financial reporting. It provides a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial performance by including all relevant income and expenses, both operating and non-operating.
By including these additional elements, the comprehensive income statement offers a more transparent view of a company’s financial position to stakeholders, such as investors, creditors, and analysts. They can gain insights into factors that impact a company’s financial standing beyond just the regular operations. This allows for better decision-making based on a more complete financial picture.
Defining the Components of Comprehensive Income
Comprehensive income is comprised of two key components:
- Net Income – This is the traditional measure of a company’s profitability, calculated by subtracting all expenses, including taxes, from revenues during a specific period.
- Other Comprehensive Income (OCI) – This includes gains or losses that bypass the income statement under Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). It encompasses items such as unrealized gains or losses on investments, foreign currency translation adjustments, pension plan adjustments, and more.
Combining these components gives us the comprehensive income figure, providing a more accurate and complete reflection of a company’s financial performance.
In conclusion, understanding comprehensive income is crucial for anyone looking to gain a deeper understanding of a company’s financial health. By including all relevant income and expenses, the comprehensive income statement offers a more accurate and comprehensive view of a company’s financial position. So, the next time you come across a comprehensive income statement, you’ll have a better understanding of its purpose and meaning!
Key Takeaways:
- Comprehensive income includes all changes in equity during a period, excluding transactions with owners.
- The purpose of the comprehensive income statement is to provide a complete picture of a company’s financial performance, including non-operating income and expenses.