Home>Finance>Common Size Income Statement Definition And Example


Finance
Common Size Income Statement Definition And Example
Modified: December 30, 2023
Learn about the common size income statement in finance with definition and example. Understand how it helps analyze financial performance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Understanding the Common Size Income Statement: Definition and Example
Welcome to our “Finance” category blog post! Today, we will delve into a fundamental financial statement known as the common size income statement. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting to explore the world of finance, understanding this statement is crucial for analyzing a company’s financial health. Let’s take a closer look at what a common size income statement is and its importance in assessing a company’s financial performance.
Key Takeaways:
- A common size income statement is a financial statement that presents each line item as a percentage of a company’s total revenue or sales.
- It allows investors and analysts to compare the financial performance of different companies, or the same company over multiple periods, more easily.
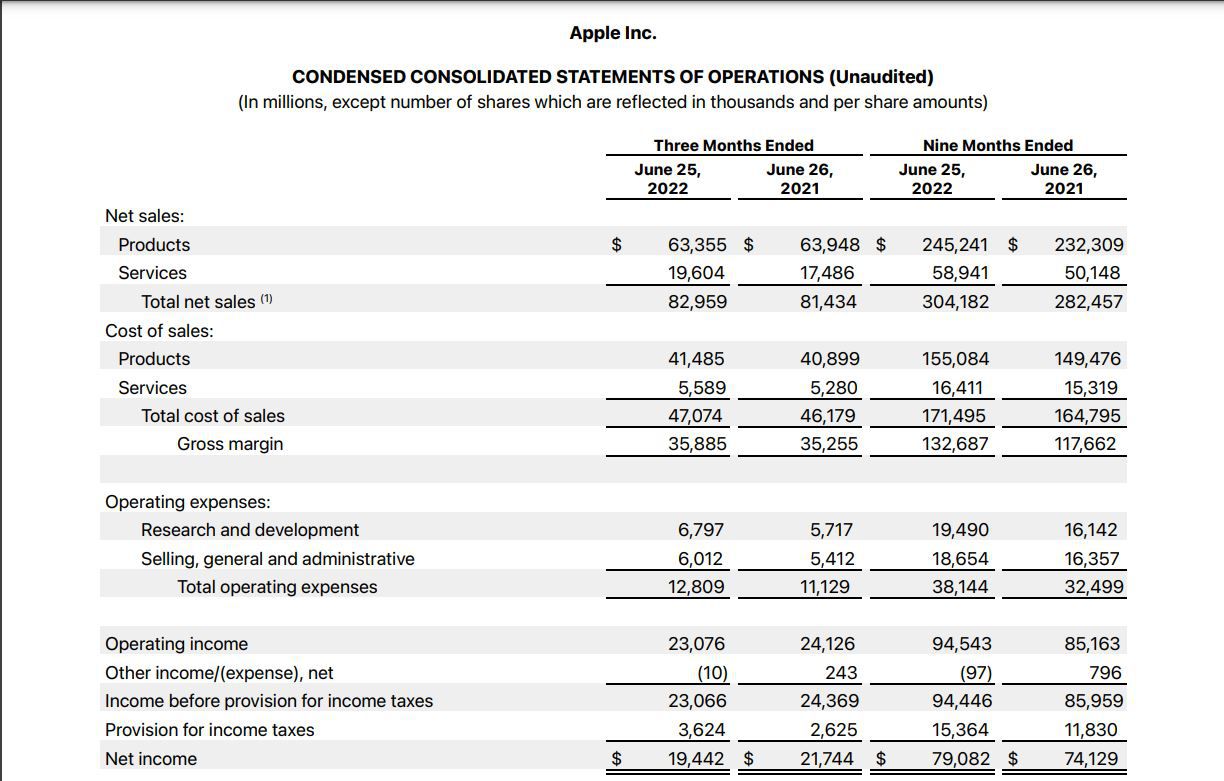
So, what exactly is a common size income statement? In simple terms, it is a financial statement that presents each line item as a percentage of a company’s total revenue or sales, rather than using the actual dollar amount. This presentation format allows investors, analysts, and managers to gain insights into the relative importance of different aspects of a company’s financial statements.
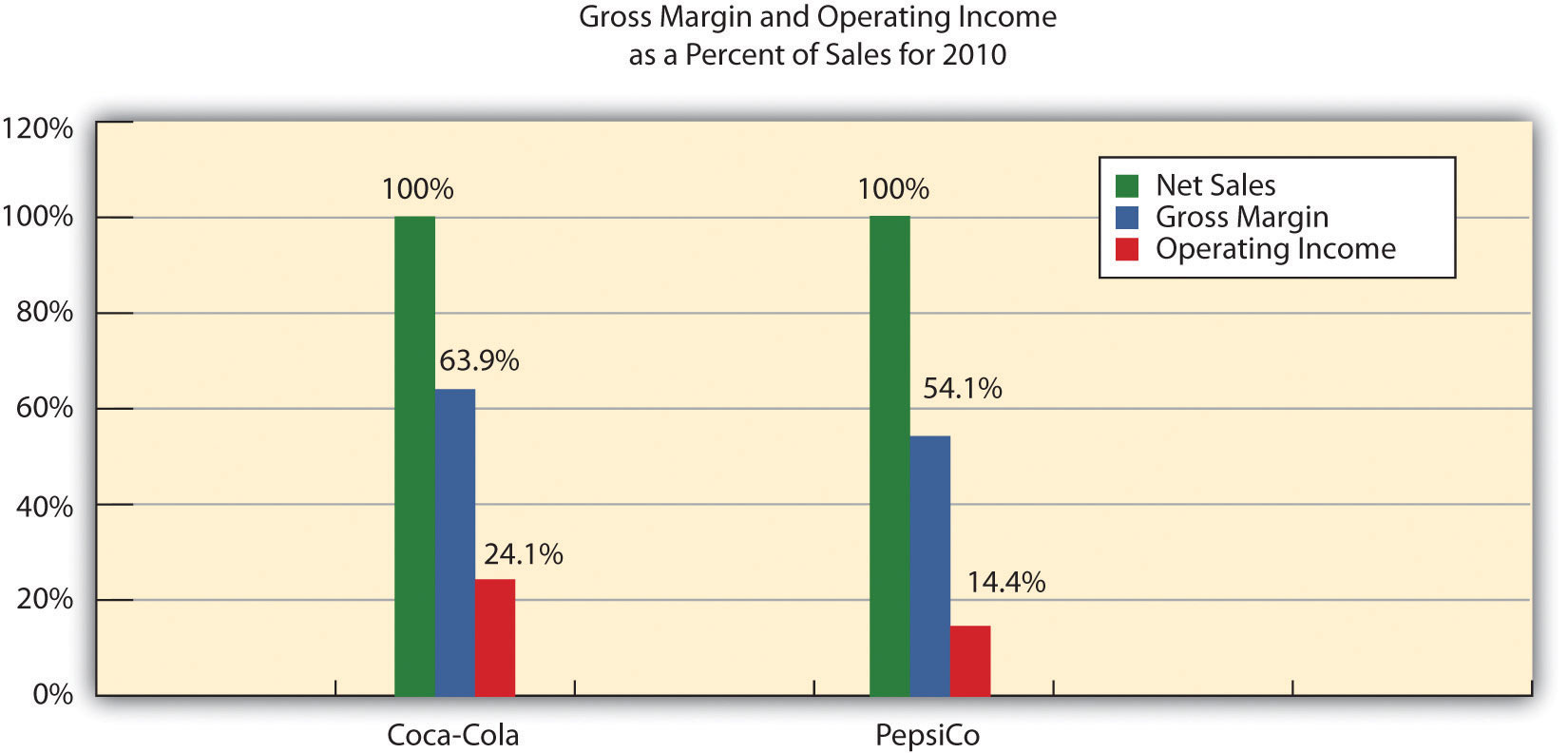
Here’s an example to illustrate how a common size income statement works. Let’s say we have a company called ABC Corporation, and their total revenue for the year is $1,000,000. On their common size income statement, each line item is expressed as a percentage of that total revenue.
For instance, if ABC Corporation’s cost of goods sold (COGS) is $600,000, it would be displayed as 60% (600,000/1,000,000) on the common size income statement. Similarly, if their operating expenses amount to $200,000, it would be represented as 20% (200,000/1,000,000).
The primary advantage of using a common size income statement is that it allows for easier comparison between companies or the same company over multiple periods. By normalizing the financial data, investors and analysts can identify trends, highlight potential issues, and make more informed investment decisions.
Now that we have a basic understanding of the common size income statement, let’s go over a few key takeaways:
- Increased Comparability: The use of percentages instead of dollar amounts makes it easier to compare financial performance between companies of different sizes or industries, as well as track a company’s progress over time.
- Identifying Trends and Focus Areas: By analyzing the proportion of various line items, investors and analysts can identify trends, such as increasing or decreasing costs, and spot areas where a company might be heavily investing or struggling.
In conclusion, understanding the common size income statement is essential for anyone involved in finance. By representing financial data as percentages of total revenue, this statement offers a way to compare companies and analyze trends in a more standardized manner. So, next time you come across a company’s financial statements, remember to take a look at the common size income statement and unlock valuable insights.