Home>Finance>Cumulative Preferred Stock: Definition, How It Works, And Example


Finance
Cumulative Preferred Stock: Definition, How It Works, And Example
Published: November 6, 2023
Looking for a comprehensive guide to cumulative preferred stock? Learn the definition, working mechanism, and get an example in the field of finance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Welcome to the World of Cumulative Preferred Stock!
When it comes to investing, there are various options available in the market. One such option is cumulative preferred stock, a unique type of equity investment that offers investors steady returns and certain benefits.
Key Takeaways:
- Cumulative preferred stock provides investors with fixed dividends and a priority claim on company assets in the event of bankruptcy.
- It is a type of stock that carries a higher yield than common stock but lower potential for capital appreciation.
Now, you might be wondering, what exactly is cumulative preferred stock? How does it work? And why should you consider investing in it? Let’s dive deeper and find out.
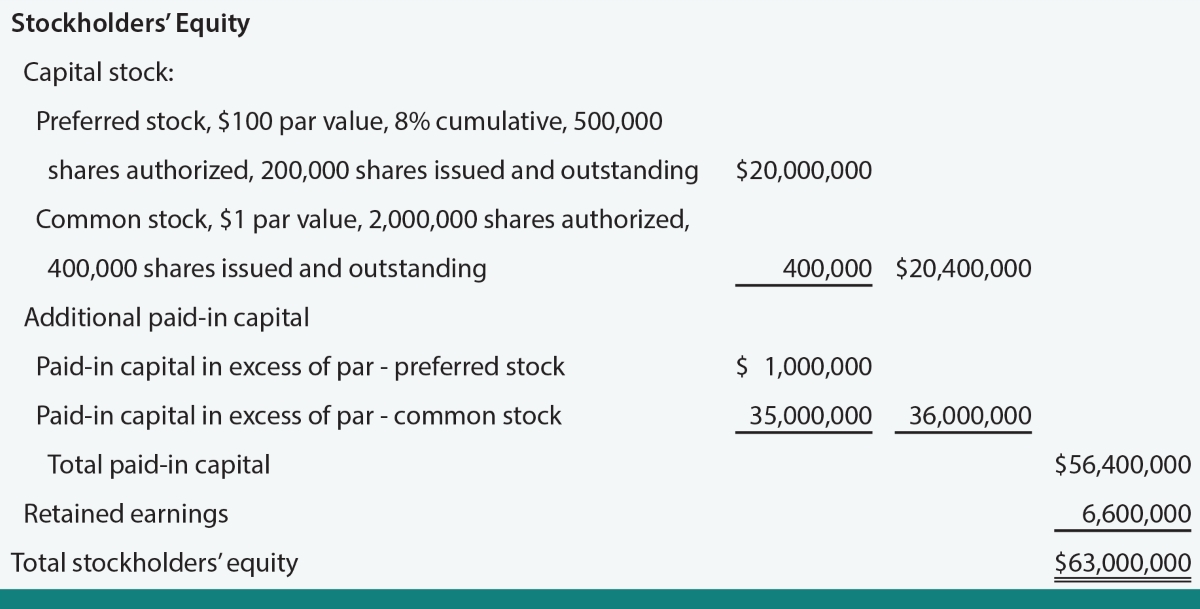
Definition: Cumulative preferred stock represents ownership in a corporation and carries a fixed dividend that accumulates over time. Unlike common stock, which offers voting rights and the potential for capital appreciation, cumulative preferred stock provides a guaranteed dividend payment at a specified rate.
Here’s how it works. When a company issues cumulative preferred stock, the shareholders who own this type of stock have a right to receive their dividends before any dividends are distributed to common stockholders. These dividends are “cumulative,” meaning that if the company skips paying dividends in a particular year, the unpaid amount accumulates and must be paid before any dividends can be distributed to common stockholders.
Let’s say, for example, that XYZ Corporation issues cumulative preferred stock with an annual dividend rate of 5%. If the company fails to pay dividends in the first year, the unpaid dividend amount will accumulate to the next year. In the second year, the company will need to pay not only the current year’s dividend but also the accumulated unpaid dividend from the previous year.
Now, you might be wondering, why would anyone invest in cumulative preferred stock when it offers a fixed dividend and limited potential for capital appreciation?
Here are a few reasons why investors consider cumulative preferred stock:
- Steady Income: Cumulative preferred stock provides investors with a predictable and regular income stream. The fixed dividends ensure a stable return on investment, making it an attractive option for income-oriented investors.
- Priority Claim: In the event that a company goes bankrupt, cumulative preferred stockholders have a higher claim on the company’s assets compared to common stockholders. This priority position provides an added layer of security to investors.
Now that you understand the basics of cumulative preferred stock, it’s important to assess your investment goals and risk tolerance before diving into this type of investment. If you’re seeking a steady income stream with some degree of safety, cumulative preferred stock might be the right choice for you.
Remember, it’s always a good idea to consult with a financial advisor or do thorough research before making any investment decisions.
So, if you’re looking for an investment option that offers fixed dividends and a priority claim on company assets, don’t overlook cumulative preferred stock. It could be the perfect addition to your investment portfolio!