Finance
Futures Market Definition
Modified: December 30, 2023
Discover the definition and importance of futures market in finance. Learn how futures contracts allow investors to buy or sell assets at a predetermined price, enabling them to manage risk and speculate on market movements.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Understanding Futures Market Definition: A Guide to Financial Futures
Have you ever wondered what the term “futures market” actually means? If you are interested in finance and have come across this term before, you may have found it somewhat complex or confusing. Don’t worry; you’re not alone! In this blog post, we will demystify the futures market definition and explain it in a way that everyone can understand. So, let’s dive in!
Key Takeaways:
- The futures market is a financial marketplace where individuals and institutions trade contracts to buy or sell assets at a predetermined price and date in the future.
- It provides an opportunity for investors to speculate on the future price movement of commodities, currencies, stocks, and other financial instruments.
What is a Futures Market?
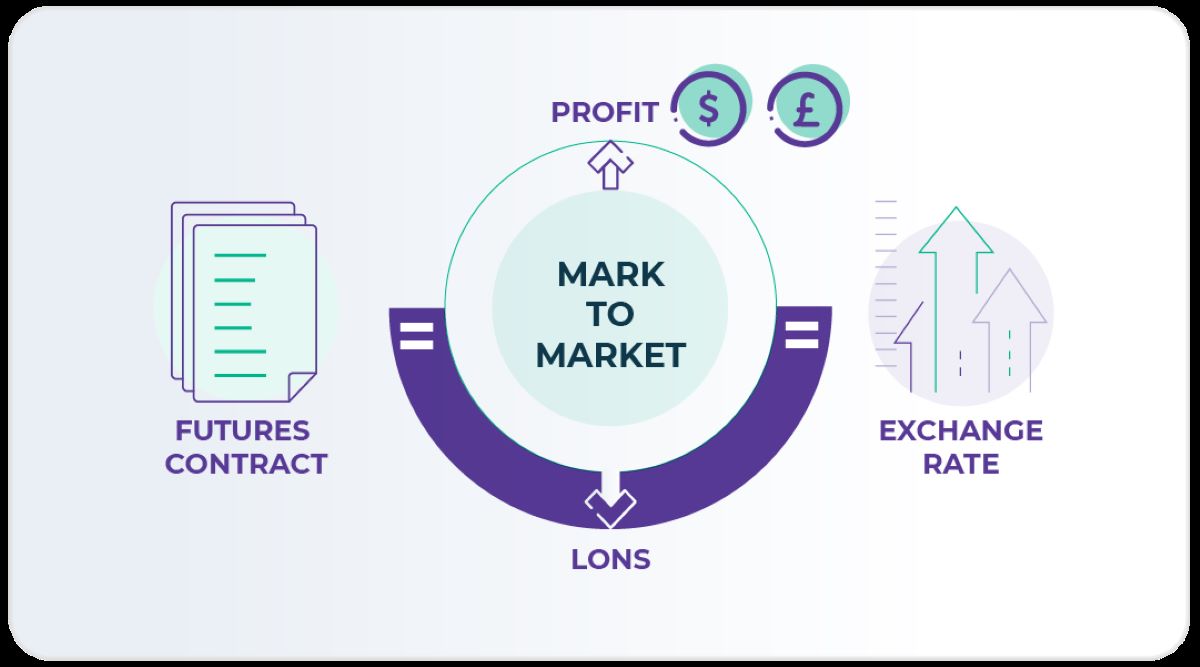
At its core, a futures market is a financial marketplace where individuals and institutions can trade contracts that obligate them to buy or sell assets (known as the underlying assets) at a predetermined price and date in the future. These assets can range from commodities like gold and oil to financial instruments such as currencies, stocks, and bonds. The contracts traded in the futures market are known as futures contracts.
The futures market serves several important purposes in the financial world. Firstly, it provides a platform for producers and consumers of commodities to hedge against price fluctuations. For example, an oil producer may want to lock in a favorable price for their oil several months in advance, while an airline company may want to secure a fixed price for jet fuel. By entering into a futures contract, both parties can protect themselves from potential price volatility.
Secondly, the futures market offers investors an opportunity to speculate on the future price movement of various assets. Unlike the stock market, where investors buy and sell shares of a company, the futures market allows investors to trade contracts based on their expectations of future price movements. This speculative aspect of futures trading can provide opportunities for profit but also carries inherent risks.
How Does the Futures Market Work?
The mechanics of the futures market are relatively straightforward. Buyers and sellers enter into a futures contract, which outlines the terms of the trade, including the asset being traded, the quantity, the price, and the delivery date. While the specifics vary depending on the type of futures contract and the exchange where it is traded, the basic principles remain consistent.
Here is a simplified breakdown of how the futures market works:
- Contract Creation: Buyers and sellers enter into agreements by creating a futures contract. The contract is standardized and traded on regulated exchanges.
- Trading: The futures contract is then traded on an exchange, where buyers and sellers can enter and exit positions based on their expectations of future price movements.
- Margin Requirements: To participate in futures trading, traders must deposit a margin, which serves as collateral for potential losses. This margin requirement ensures that the parties involved have sufficient funds to fulfill their obligations.
- Contract Settlement: At the end of the futures contract’s life, settlement occurs. Depending on the type of futures contract, settlement can be cash-based or physically delivered. Cash settlement involves the transfer of cash, while physical settlement involves the physical delivery of the underlying asset.
The Pros and Cons of Futures Trading
As with any investment strategy, futures trading has its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these pros and cons can help investors make informed decisions about entering the futures market:
Pros:
- Potential for significant profits due to leverage.
- Ability to hedge against price fluctuations in commodities.
- Liquidity and easy access to markets.
Cons:
- High volatility and potential for substantial losses.
- Requires in-depth knowledge and research to make informed decisions.
- Requires initial capital as margin requirements.
Overall, the futures market plays a crucial role in the world of finance, allowing businesses to manage risk and investors to speculate on price movements. While the concept may initially seem complex, understanding the futures market definition and how it functions can empower you to make sound financial decisions.
If you are interested in exploring the futures market further, it is essential to educate yourself and seek advice from experienced professionals. By doing so, you can leverage the potential opportunities while minimizing risks.
Disclaimer: This blog post aims to provide a general understanding of the futures market definition. It is not financial or investment advice. Please consult a financial advisor or professional for personalized guidance.