Finance
How Do I Report A Tenant To The Credit Bureau
Published: March 3, 2024
Learn how to report a tenant to the credit bureau and understand the financial implications. Get expert advice on handling tenant credit issues.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
**
Introduction
**
Reporting a tenant to the credit bureau is a serious matter that requires careful consideration and adherence to legal guidelines. As a landlord or property manager, you may encounter situations where a tenant's failure to pay rent or other financial obligations necessitates reporting their delinquency to the credit bureau. This action can have significant implications for the tenant's credit score and financial standing. Therefore, it's crucial to understand the reporting process, gather necessary information, and follow the appropriate steps when reporting a tenant to the credit bureau.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of reporting a tenant to the credit bureau, providing valuable insights into the process and the essential steps to take. By understanding the nuances of this procedure, landlords and property managers can navigate the reporting process with confidence and ensure compliance with legal requirements. Additionally, we will explore the potential repercussions for tenants and the importance of following up on the reported information. Let's embark on this informative journey to gain a comprehensive understanding of how to report a tenant to the credit bureau effectively and responsibly.
Understanding the Reporting Process
Before delving into the process of reporting a tenant to the credit bureau, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental aspects of credit reporting. The credit bureau, also known as a consumer reporting agency, plays a pivotal role in collecting and maintaining individuals’ credit information. When a tenant applies for a lease, the landlord or property manager may conduct a credit check through one of the major credit bureaus, such as Equifax, Experian, or TransUnion, to assess the tenant’s financial history and creditworthiness.
When a tenant fails to meet their financial obligations, such as rent payments, the landlord or property manager may consider reporting the delinquency to the credit bureau. This reporting process involves providing accurate and verifiable information about the tenant’s payment history and outstanding debts. It’s important to note that reporting delinquent payments to the credit bureau can significantly impact the tenant’s credit score and financial reputation.
Landlords and property managers must adhere to the guidelines outlined in the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) when reporting tenant information to the credit bureau. This federal law regulates how consumer credit information is collected, used, and shared, ensuring fairness, accuracy, and privacy in the credit reporting system. Understanding the legal framework and requirements is paramount to avoid potential legal repercussions and uphold ethical reporting practices.
Moreover, it’s crucial to recognize that the reported information can influence a tenant’s ability to secure future housing and obtain credit. Therefore, the decision to report a tenant to the credit bureau should be approached thoughtfully and judiciously. By comprehending the intricacies of the reporting process and its implications, landlords and property managers can make informed decisions aligned with legal and ethical standards.
Gathering Necessary Information
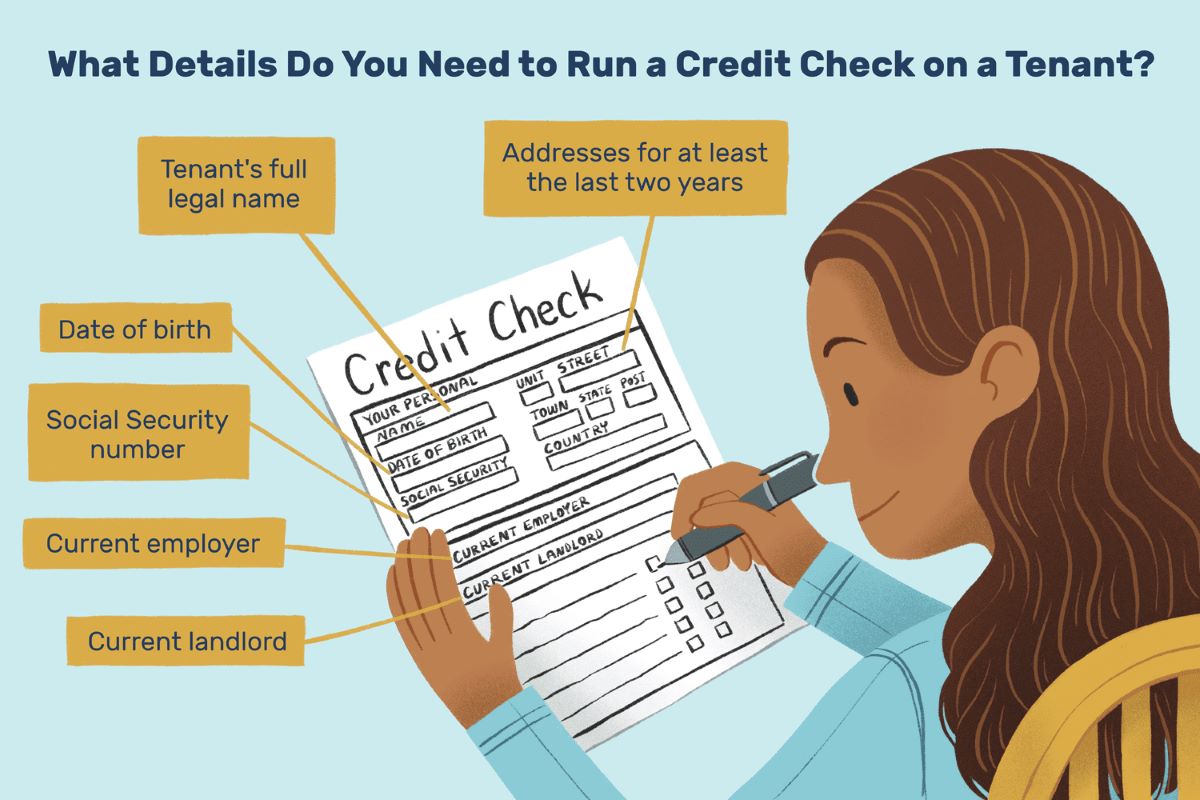
Before initiating the process of reporting a tenant to the credit bureau, it is imperative to gather comprehensive and accurate information pertaining to the tenant’s delinquent payments or financial obligations. This step is crucial in ensuring that the reported information is precise, verifiable, and compliant with the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA).
Initially, landlords and property managers should meticulously document the tenant’s payment history, specifically focusing on any outstanding rent payments or unresolved financial obligations. This documentation should include details such as the dates of missed payments, the amount owed, and any relevant correspondence or notices sent to the tenant regarding the delinquency. Maintaining a thorough record of these critical details will serve as essential evidence when reporting the tenant to the credit bureau.
Furthermore, it is essential to gather specific information about the lease agreement, including the terms and conditions related to rent payments, late fees, and any clauses pertaining to the consequences of non-payment. Understanding the contractual obligations and the remedies available within the lease agreement is vital in substantiating the grounds for reporting the tenant’s delinquency to the credit bureau.
Additionally, gathering the tenant’s contact information, such as their current address and phone number, is essential for communication purposes during the reporting process. In some cases, landlords or property managers may need to reach out to the tenant to provide notification regarding the impending credit reporting or to facilitate resolution of the outstanding financial matters.
By diligently collecting and organizing the necessary information, landlords and property managers can ensure that the reported data is accurate, complete, and compliant with legal requirements. This proactive approach not only strengthens the credibility of the reported information but also demonstrates a commitment to ethical and responsible credit reporting practices.
Contacting the Credit Bureau
Once the pertinent information regarding the tenant’s delinquency has been meticulously gathered and documented, the next step in the process of reporting a tenant to the credit bureau involves initiating contact with the relevant credit bureau. Landlords and property managers must identify which credit bureau they intend to report the tenant’s delinquency to, as well as ensure compliance with the FCRA and any applicable state regulations.
Prior to contacting the credit bureau, it is advisable to review the specific procedures and requirements outlined by the bureau for reporting delinquent tenant information. Each credit bureau may have distinct protocols and forms for submitting such reports, and it is essential to adhere to their guidelines to facilitate a smooth and accurate reporting process.
When reaching out to the credit bureau, landlords and property managers should be prepared to provide comprehensive details regarding the tenant’s delinquency, including the dates and amounts of missed payments, relevant lease agreement clauses, and any supporting documentation. Clear and concise communication with the credit bureau is crucial to ensure that the reported information is accurately documented and attributed to the correct tenant.
It is important to note that the FCRA mandates the fair and accurate reporting of consumer credit information. Therefore, landlords and property managers must exercise diligence in verifying the accuracy of the information being reported and should refrain from reporting false or misleading data, as it could lead to legal ramifications.
Furthermore, it is advisable to maintain a record of all communications with the credit bureau, including the date and time of contact, the details provided, and any reference numbers or confirmation of the reported information. This documentation can serve as valuable evidence in the event of any discrepancies or inquiries regarding the reported tenant delinquency.
By proactively and responsibly engaging with the credit bureau, landlords and property managers can navigate the reporting process with integrity and ensure that the reported information adheres to legal and ethical standards.
Reporting the Tenant
When reporting a tenant to the credit bureau, it is essential to ensure that the process is conducted in a meticulous and compliant manner. Once all necessary information has been gathered and the contact with the credit bureau has been established, landlords and property managers can proceed with reporting the tenant’s delinquency.
The reporting should accurately reflect the tenant’s payment history, specifically highlighting the instances of non-payment or default on financial obligations. It is imperative to provide the credit bureau with precise details, including the dates of missed payments, the outstanding amounts, and any pertinent clauses from the lease agreement that substantiate the reported delinquency.
It is crucial to exercise transparency and integrity throughout the reporting process. Providing verifiable evidence and maintaining accurate records of the reported information are essential components of responsible credit reporting. Landlords and property managers should refrain from embellishing or misrepresenting the tenant’s delinquency, as such actions can contravene the FCRA and ethical reporting practices.
Furthermore, it is advisable to confirm with the credit bureau that the reported information has been accurately received and processed. This confirmation can help mitigate any potential errors or discrepancies in the reporting, ensuring that the tenant’s credit file reflects the reported delinquency appropriately.
Throughout the reporting process, it is essential to uphold professionalism and compliance with legal requirements. By adhering to the established guidelines and maintaining accuracy and transparency in the reported information, landlords and property managers can fulfill their obligations while upholding ethical standards in credit reporting.
Following Up
After reporting a tenant to the credit bureau for delinquent payments, it is prudent for landlords and property managers to engage in appropriate follow-up measures to ensure that the reported information is accurately reflected in the tenant’s credit file. Following up on the reporting process can help address any potential discrepancies or oversights, ultimately contributing to the integrity and fairness of the credit reporting system.
One crucial step in the follow-up process is to monitor the tenant’s credit report to verify that the reported delinquency has been duly documented. This proactive approach enables landlords and property managers to confirm that the reported information aligns with the tenant’s credit history and accurately reflects the reported delinquency.
If any discrepancies or inaccuracies are identified in the reported information, landlords and property managers should promptly communicate with the credit bureau to rectify the errors. This may involve providing additional documentation or evidence to support the accurate reporting of the tenant’s delinquency, ensuring that the credit bureau’s records are updated accordingly.
Additionally, maintaining open communication with the tenant regarding the reported delinquency is essential. In some cases, tenants may take steps to address the outstanding financial obligations, potentially leading to the resolution of the reported delinquency. Keeping the lines of communication open can facilitate transparency and cooperation between landlords, property managers, and tenants in resolving financial matters.
Furthermore, landlords and property managers should remain vigilant for any inquiries or disputes related to the reported delinquency. Addressing any inquiries from the credit bureau or the tenant in a timely and professional manner can help mitigate potential misunderstandings and uphold the accuracy of the reported information.
By actively following up on the reporting process and addressing any discrepancies or inquiries that may arise, landlords and property managers demonstrate a commitment to ethical and responsible credit reporting practices, contributing to the integrity and fairness of the credit reporting system.
Conclusion
Reporting a tenant to the credit bureau is a consequential process that necessitates a thorough understanding of the legal and ethical considerations involved. Landlords and property managers must approach this undertaking with diligence, transparency, and adherence to the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) to ensure the accuracy and fairness of the reported information.
By comprehensively understanding the reporting process and gathering necessary information, landlords and property managers can lay a solid foundation for responsibly reporting a tenant’s delinquency to the credit bureau. This entails meticulous documentation of the tenant’s payment history, lease agreement details, and communication with the credit bureau to facilitate an accurate and compliant reporting process.
Throughout this process, it is imperative to uphold the principles of transparency, accuracy, and ethical conduct. Reporting the tenant’s delinquency should be rooted in verifiable evidence and should refrain from misrepresentation or embellishment. By maintaining integrity and professionalism, landlords and property managers can navigate the reporting process with due diligence and respect for the tenant’s financial reputation.
Furthermore, engaging in thorough follow-up measures, including monitoring the reported information and addressing any discrepancies or inquiries, is essential in ensuring the accuracy and fairness of the reported delinquency. Open communication with the tenant and proactive resolution of outstanding financial matters can contribute to a constructive and cooperative approach to credit reporting.
In conclusion, the process of reporting a tenant to the credit bureau demands a balanced approach that prioritizes legal compliance, ethical conduct, and fairness. By adhering to these principles and maintaining meticulous attention to detail, landlords and property managers can fulfill their responsibilities while upholding the integrity of the credit reporting system. Ultimately, responsible credit reporting serves to promote transparency, accuracy, and fairness in assessing individuals’ financial history and creditworthiness.