Finance
How Does An Eviction Affect Your Credit
Published: January 11, 2024
An eviction can have a significant impact on your credit, affecting your ability to secure future finances and loans. Learn more about the consequences of eviction on your credit.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Evictions are unfortunate circumstances that can arise due to various reasons, such as failure to pay rent, violation of rental agreement terms, or other lease infractions. They can be stressful and disruptive to both tenants and landlords alike. However, aside from the immediate implications of losing your home, an eviction can also have a long-lasting impact on your financial well-being, particularly on your credit.
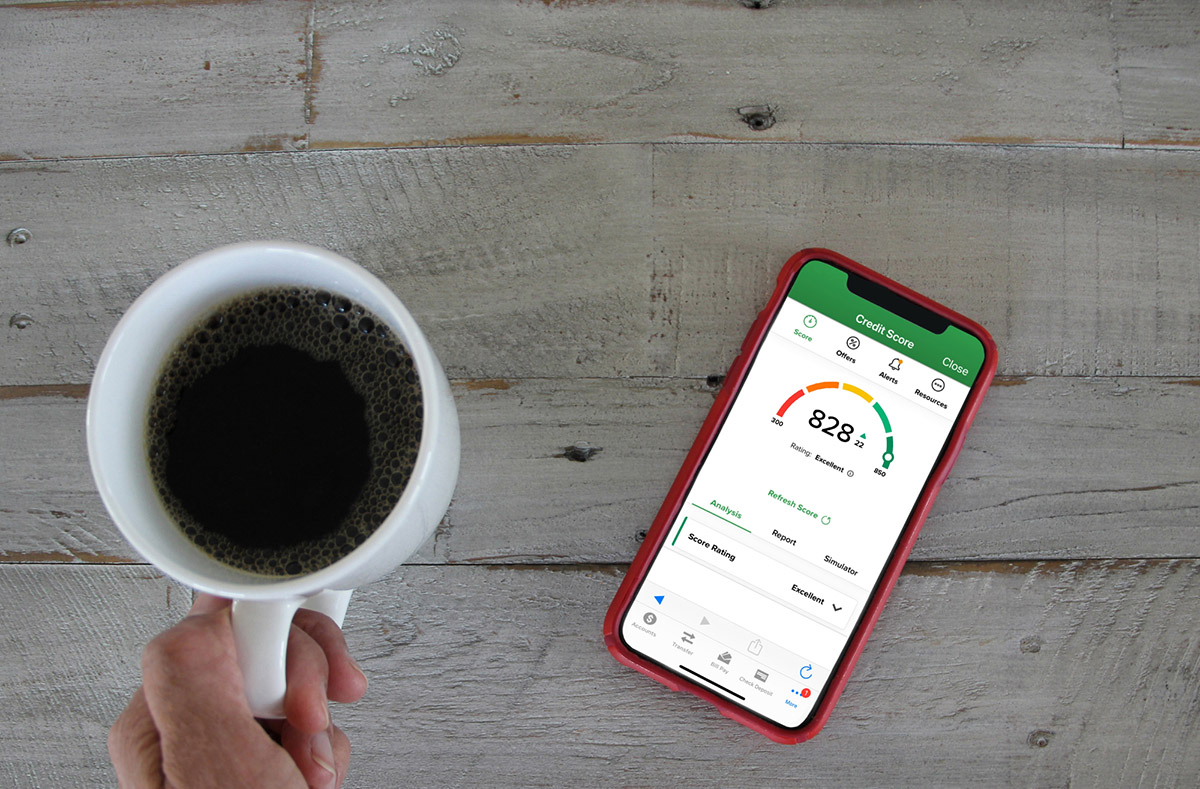
Your credit score is a crucial piece of financial information that lenders, landlords, and even potential employers may use to assess your financial responsibility and reliability. It is a reflection of your creditworthiness and can significantly influence your ability to secure loans, rental agreements, and favorable interest rates.
In this article, we will delve into the relationship between evictions and credit scores, exploring the immediate and long-term effects, as well as discussing strategies for rebuilding credit after an eviction. Understanding the impact of an eviction on your credit can help you make informed decisions and take proactive steps to protect and improve your financial standing.
What is an eviction?
An eviction is a legal process that occurs when a landlord forcibly removes a tenant from their rented property. It is typically initiated when the tenant violates the terms of their lease agreement, fails to pay rent, or engages in illegal activities on the premises. Evictions can be a complex and stressful experience for both parties involved, as they involve legal proceedings that vary depending on local laws and regulations.
Evictions are generally seen as a last resort when other measures, such as negotiation, mediation, or warnings, have failed to resolve the underlying issues. Landlords must follow specific legal procedures to evict a tenant, including providing proper notice and filing the necessary paperwork with the appropriate court. Tenants have the right to contest an eviction and present their case if they believe it is unjust or if their rights have been violated.
It is important to note that evictions are not limited to residential properties. Commercial tenants can also face eviction if they breach agreements or fail to meet their obligations. The process, however, may differ slightly from residential evictions.
Evictions can have serious consequences for both tenants and landlords. For tenants, it means the loss of their home and potential difficulties in finding alternative housing. Landlords, on the other hand, may face financial losses and be burdened with the task of finding new tenants to replace those who have been evicted.
Understanding the eviction process and the reasons behind it is essential for tenants to protect their rights and for landlords to uphold their responsibilities. By familiarizing yourself with local laws and regulations, you can navigate these situations more effectively and minimize the negative impact they may have on your credit and financial stability.
Understanding credit scores
A credit score is a numerical representation of an individual’s creditworthiness and financial history. It provides lenders, landlords, and other organizations with a quick assessment of an individual’s likelihood to repay debts and manage financial obligations responsibly. Credit scores are calculated based on a variety of factors, including payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, types of credit, and new credit applications.
The most commonly used scoring model is the FICO credit score, which ranges from 300 to 850. Generally, a higher credit score signifies a lower level of risk for lenders, making it easier for individuals to secure loans, rental agreements, and favorable interest rates. Conversely, a lower credit score can make it more challenging to access credit, resulting in higher interest rates or even being denied credit altogether.
While there are several credit scoring models available, the key factors considered by most scoring systems are payment history and credit utilization. Payment history accounts for the largest portion of your credit score, reflecting your ability to make timely payments on loans, credit cards, and other financial obligations. Credit utilization measures the amount of available credit you are using, with lower utilization rates generally indicating responsible credit management.
It is important to monitor your credit score regularly and take steps to improve it if necessary. This includes paying bills on time, keeping credit card balances low, and only applying for new credit when necessary. Understanding how credit scores are calculated and what factors influence them can empower individuals to make informed financial decisions and maintain a healthy credit profile.
In the following sections, we will explore how an eviction can impact your credit score and the steps you can take to mitigate the negative effects and rebuild your credit.
How does an eviction affect your credit?
An eviction can have a significant impact on your credit score and overall creditworthiness. When you are evicted, it indicates to potential lenders and landlords that you have failed to fulfill your financial obligations and may be a high-risk borrower or tenant.
Immediate impact on credit score
Once an eviction is filed against you, it becomes a matter of public record. This means that it will be visible on your credit report, which can negatively impact your credit score. A public record, such as an eviction, can stay on your credit report for up to seven years, and its presence can lower your credit score by a significant amount.
It is important to note that even if an eviction does not appear on your credit report immediately, it can still affect your creditworthiness. Landlords and property management companies often rely on screening services that include eviction records when assessing rental applications. If an eviction appears during this process, your application may be denied or you may be required to pay a higher security deposit.
Long-term impact on credit score
The long-term impact of an eviction on your credit score depends on various factors, including your overall credit history and whether you have any other negative items on your credit report. For individuals with an otherwise strong credit history, the impact of an eviction may be mitigated over time. However, if you have a history of late payments, delinquencies, or other negative marks, the addition of an eviction can further damage your credit score and make it more challenging to access credit in the future.
Rebuilding credit after an eviction
While an eviction can have a detrimental effect on your credit, it is not the end of the road. Rebuilding your credit is possible with consistent effort and responsible financial management. Here are some steps to consider:
- Pay all bills on time: Consistently making on-time payments is crucial for improving your creditworthiness.
- Reduce credit card balances: Aim to keep your credit card balances low to improve your credit utilization ratio.
- Open a secured credit card: A secured credit card can be a useful tool for rebuilding credit. These cards require a security deposit, but they can help demonstrate your ability to manage credit responsibly.
- Consider credit counseling: Credit counseling can provide guidance and strategies for managing your debts and improving your credit score.
- Work towards positive credit history: Over time, positive credit history can outweigh the negative impact of an eviction. Focus on responsible credit management and building a solid financial track record.
Protecting your credit during an eviction
While it may be challenging to avoid the negative impact of an eviction on your credit, there are steps you can take to protect your credit during the process:
- Communicate with your landlord: If you are facing difficulties that may lead to an eviction, it is essential to communicate with your landlord and explore possible solutions.
- Seek legal advice: Consult an attorney who specializes in tenant rights to understand your legal options and navigate the eviction process.
- Document all communications: Keep written records of your interactions with your landlord, including any agreements, payments made, and requests for repairs.
- Continue paying rent: Even if an eviction is imminent, continuing to pay your rent can demonstrate your willingness to fulfill your financial obligations.
While an eviction can have a negative impact on your credit, it is important to remember that it is not the end of your financial journey. By taking proactive steps to rebuild your credit and protecting your credit during the eviction process, you can minimize the long-term effects and work towards a brighter financial future.
Immediate impact on credit score
When an eviction is filed against you, it can have an immediate and significant impact on your credit score. Once the eviction becomes a matter of public record, it will be visible on your credit report and can lower your credit score by a considerable amount. This negative impact stems from the fact that an eviction suggests to lenders and landlords that you have failed to meet your financial obligations.
A public record, such as an eviction, can stay on your credit report for up to seven years. During this time, it can be accessed by potential lenders, landlords, and even employers, affecting your ability to secure loans, rental agreements, or job opportunities.
In addition to appearing on your credit report, an eviction can also influence the outcome of future rental applications. Many landlords and property management companies conduct background checks that include eviction records. If an eviction appears during this screening process, it can be a red flag for potential landlords, leading to either a denial of your application or the requirement of a higher security deposit.
It is important to note that even if an eviction does not immediately appear on your credit report, it can still impact your creditworthiness. Some credit reporting agencies may update their records periodically, meaning that the eviction may show up on your report at a later date. As a result, it is crucial to address the issue and seek solutions as soon as possible to minimize the negative consequences.
While the immediate impact of an eviction on your credit score can be substantial, it is important to remember that it is not permanent. Over time, responsible financial management and positive credit behavior can help rebuild your credit and mitigate the negative effects of the eviction.
In the next section, we will discuss the long-term impact of an eviction on your credit score and explore strategies for rebuilding your credit after experiencing an eviction.
Long-term impact on credit score
An eviction can have a long-lasting impact on your credit score and overall creditworthiness. The extent of this impact depends on a variety of factors, including your overall credit history and the presence of other negative marks on your credit report.
When an eviction appears on your credit report, it signals to lenders and creditors that you have not fulfilled your financial obligations and may be a risky borrower. This can result in a decrease in your credit score, making it more difficult to obtain credit, secure loans, or even sign a lease for a new rental property.
In addition, an eviction can compound the negative effects of other negative items on your credit report, such as late payments, collections, or bankruptcies. If you already have a less-than-stellar credit history, the addition of an eviction can further lower your credit score and make it challenging to access favorable interest rates or credit opportunities.
The impact of an eviction on your credit score can vary in duration. Generally, an eviction can remain on your credit report for up to seven years, depending on local laws and regulations. However, its influence on your creditworthiness may diminish over time if you actively work towards rebuilding your credit and maintaining a positive credit history.
To mitigate the long-term impact of an eviction on your credit score, consider the following strategies:
- Focus on positive credit behavior: Make all future payments on time, pay off outstanding debts, and keep credit card balances low. Consistent positive credit behavior can help offset the negative impact of an eviction.
- Build a solid credit history: In addition to timely payments, focus on building a diverse credit history. This can be done by responsibly using different types of credit, such as credit cards, loans, or lines of credit.
- Monitor your credit report: Regularly check your credit report for errors or inaccuracies related to the eviction. If you find any, dispute them with the credit reporting agencies to have them corrected or removed.
- Consider credit counseling: Seeking guidance from a credit counseling agency can provide you with tools and strategies to manage your debts and improve your credit score.
- Patience and perseverance: Rebuilding your credit takes time and effort. Be patient, stay committed to responsible financial habits, and keep working towards improving your creditworthiness.
While an eviction can have a significant and long-term impact on your credit score, it does not mean that you are forever destined to have poor credit. By taking proactive steps and demonstrating responsible financial behavior, you can gradually rebuild your credit and improve your overall financial standing.
In the next section, we will explore strategies for rebuilding your credit after experiencing an eviction.
Rebuilding credit after an eviction
Recovering from the negative impact of an eviction on your credit score requires consistent effort and responsible financial management. While it may take time to rebuild your credit, it is not an impossible task. Here are some strategies to consider:
- 1. Pay bills on time: Consistently making on-time payments for all your bills, including rent, utilities, and credit cards, is crucial for rebuilding your credit. Payment history is a significant factor in credit scoring models, and establishing a track record of timely payments demonstrates financial responsibility.
- 2. Reduce credit card balances: Aim to keep your credit card balances low, ideally below 30% of your credit limit. High credit card utilization can negatively impact your credit score. Focus on paying down your balances and keeping them as low as possible to improve your credit utilization ratio.
- 3. Open a secured credit card: A secured credit card can be a helpful tool for rebuilding credit. With a secured card, you provide a cash deposit as collateral, and the credit limit is usually equal to the deposit amount. By using the card responsibly and making timely payments, you can demonstrate creditworthiness and establish a positive credit history.
- 4. Consider credit counseling: Seeking assistance from a reputable credit counseling agency can provide you with personalized guidance and strategies for managing your debts and improving your credit. Credit counselors can help you create a budget, negotiate with creditors, and develop a plan to rebuild your credit.
- 5. Monitor your credit report: Regularly check your credit report to ensure its accuracy and to identify any potential errors or discrepancies related to the eviction. If you find any inaccuracies, file a dispute with the credit reporting agencies to have them corrected or removed.
- 6. Use different types of credit: Having a mix of credit accounts, such as credit cards and installment loans, can demonstrate your ability to manage different types of credit responsibly. Consider diversifying your credit portfolio over time, while being cautious not to take on too much new credit at once.
- 7. Be patient and persistent: Rebuilding credit after an eviction takes time and consistent effort. Be patient with the process and avoid becoming discouraged. Stay committed to responsible financial habits, and over time, you will see improvements in your creditworthiness.
Remember, the key is to avoid repeating past mistakes and to establish a track record of responsible financial management. By implementing these strategies and maintaining good financial habits, you can gradually rebuild your credit and open doors to better financial opportunities in the future.
In the next section, we will discuss ways to protect your credit during an eviction to minimize the potential negative impact.
Protecting your credit during an eviction
Going through an eviction can be a challenging and stressful experience, but it is important to take steps to protect your credit during this time. While an eviction can have a negative impact on your credit score, there are measures you can take to minimize the potential damage. Here are some tips for protecting your credit during an eviction:
- 1. Communicate with your landlord: If you are facing difficulties that may lead to an eviction, open up a line of communication with your landlord. Explain your situation, discuss possible solutions, and try to negotiate a resolution that works for both parties. By demonstrating your willingness to address the issue and find a solution, you may be able to avoid an eviction altogether.
- 2. Seek legal advice: If you believe the eviction is unjust or if you feel your rights as a tenant have been violated, consult with an attorney who specializes in tenant rights. They can guide you through the legal process, help you understand your rights, and advise you on the best course of action to protect your interests.
- 3. Document all communications: Keep a record of all communications with your landlord, including emails, letters, or any documentation related to your rental agreement. This documentation can serve as evidence in case of any disputes or inaccuracies that may arise during or after the eviction process.
- 4. Continue paying rent: Even if an eviction seems imminent, it is important to continue paying your rent. This demonstrates your commitment to fulfilling your financial obligations and can potentially mitigate the impact on your credit score. It may also provide you with leverage to negotiate alternative solutions with your landlord.
- 5. Explore assistance programs: Depending on your circumstances, there may be government or community-based assistance programs available to help with rental payments or other financial support. Research and inquire about these programs to see if you qualify for any assistance.
- 6. Be proactive: Take proactive steps to find alternative housing before the eviction process is complete. This can help minimize the disruption and prevent a gap in your rental history, which can impact your creditworthiness when applying for future rental agreements.
It’s important to remember that while an eviction can be a challenging process, it is not the end of your credit journey. By communicating, seeking legal advice, and being proactive, you can protect your credit and financial well-being during an eviction. Maintaining a positive attitude and working towards a resolution can also help you navigate this difficult time and lay the foundation for a better financial future.
In the next section, we will conclude our discussion on how an eviction affects your credit and provide some final thoughts.
Conclusion
An eviction can have a significant impact on your credit, affecting your financial standing and future opportunities. Understanding how an eviction affects your credit is crucial for making informed decisions and taking proactive steps to mitigate the negative consequences. While the immediate and long-term impact of an eviction on your credit score can be substantial, it is important to remember that it is not insurmountable.
An eviction becomes a matter of public record and can stay on your credit report for up to seven years, damaging your creditworthiness. It can affect your ability to secure loans, rental agreements, and favorable interest rates. However, with patience, persistence, and responsible financial management, you can rebuild your credit over time.
Rebuilding credit after an eviction involves paying bills on time, reducing credit card balances, diversifying your credit, and seeking credit counseling if needed. It requires consistent effort and a commitment to positive financial habits. Additionally, protecting your credit during the eviction process by maintaining open communication with your landlord and seeking legal advice can help minimize the impact on your credit score.
Remember, an eviction does not define your financial future. By focusing on rebuilding your credit, being proactive, and demonstrating financial responsibility, you can overcome the challenges posed by an eviction and move towards a brighter financial future.
While the journey may not be easy, taking control of your financial situation and working towards improving your creditworthiness can open doors to better opportunities and stability. Use the knowledge gained from understanding how an eviction affects your credit to empower yourself and make confident choices for your financial well-being.
By staying informed, taking action, and seeking support when needed, you can regain control of your credit and pave a path towards a stronger financial foundation.