Finance
How Many Credit Hours For Associate Degree
Published: January 11, 2024
Learn how many credit hours are required to earn an associate degree in finance and start your career in the financial industry.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Obtaining an associate degree is a significant milestone in one’s educational journey. It serves as a stepping stone to higher education and opens up opportunities for entry-level jobs. One of the key considerations when pursuing an associate degree is the credit hour requirements.
Credit hours are a measure of the time and effort a student needs to invest in their studies to earn a degree. They represent the quantity of coursework completed, with each credit hour typically translating to around 45 hours of total student work, including lectures, assignments, and studying. Understanding credit hour requirements is essential for students to plan their academic journey effectively.
The number of credit hours required for an associate degree can vary depending on several factors, including the field of study, the institution’s academic policies, and individual program requirements. While the specifics may differ, most associate degree programs typically require anywhere from 60 to 70 credit hours to complete.
In this article, we will explore the various factors that affect credit hour requirements for associate degrees, common credit hour requirements in different fields of study, the transfer of credit hours, and the importance of credit hours for associate degree completion. By understanding these aspects, students can make informed decisions and optimize their academic experience.
Understanding Credit Hours
Credit hours are a fundamental unit of measurement in higher education that represent the time and effort students spend on completing a course. They provide a standard way to quantify and compare the workload required for different courses or degree programs.
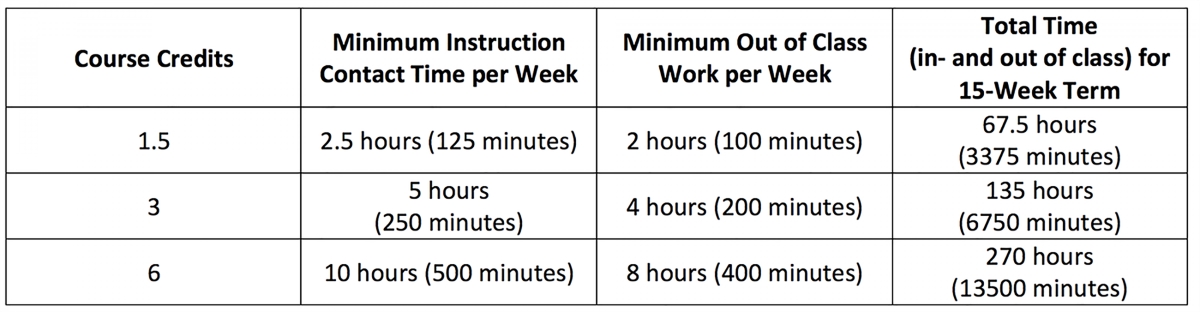
Typically, credit hours are awarded based on the number of instructional hours per week, with each credit hour representing one hour of classroom instruction per week over a semester or quarter. For example, a three-credit course would generally involve three hours of classroom instruction per week for a 15-week semester.
However, credit hours also encompass additional student work outside of the classroom, such as studying, completing assignments, and conducting research. As a general guideline, it is estimated that for every credit hour, students should expect to invest two to three hours of additional work outside of class per week. This additional work includes reading, writing papers, studying for exams, and participating in group projects.
Furthermore, credit hours can vary in their value based on the content and complexity of the course. For instance, a laboratory or studio-based course may require more hours of work than a lecture-based course due to the hands-on nature of the activities involved. Therefore, it is crucial for students to consider both the number of credit hours and the nature of the course when planning their academic workload.
It is important to note that credit hours are not solely determined by the amount of time spent on a course. They also take into account the learning outcomes and the level of mastery expected from students. Higher-level courses that demand more in-depth analysis and critical thinking skills may carry more credits than introductory courses.
Overall, understanding credit hours is essential for students to effectively navigate their academic journey. By being aware of the time commitment and workload associated with each credit hour, students can better manage their time, plan their course schedules, and ensure they are on track to meet the credit hour requirements for their chosen degree program.
Credit Hour Requirements for Associate Degree Programs
The credit hour requirements for associate degree programs can vary depending on the field of study, the specific program, and the institution’s academic policies. However, most associate degree programs typically require students to complete between 60 and 70 credit hours.
These credit hours are usually divided among general education courses and major-specific courses. General education courses provide a well-rounded foundation of knowledge in subjects such as English, mathematics, natural sciences, social sciences, and humanities. They aim to develop critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving skills that are essential for success in any field.
Major-specific courses, on the other hand, focus on the knowledge and skills needed for a particular area of study. These courses delve deeper into the subject matter and equip students with specialized knowledge and competencies. The number of credit hours allocated to major-specific courses can vary depending on the breadth and depth of the program.
In addition to general education and major-specific courses, associate degree programs often include elective courses, which give students the flexibility to explore other areas of interest or supplement their major with additional coursework. Elective courses allow students to customize their degree to some extent, depending on their career goals and personal interests.
It’s important to note that credit hour requirements can differ between associate of arts (AA) and associate of science (AS) degrees. AA degrees typically require more credit hours in humanities, social sciences, and fine arts, while AS degrees focus on natural sciences, mathematics, and technology-related courses.
Furthermore, some associate degree programs may have additional requirements such as internships, capstone projects, or experiential learning opportunities. These components provide hands-on experience in the field and help students apply the knowledge and skills they have acquired throughout their coursework.
It’s crucial for students to be aware of the credit hour requirements for their specific associate degree program. By understanding these requirements from the outset, students can plan their course schedule effectively, ensure they meet all the necessary prerequisites, and stay on track towards degree completion.
Factors Affecting Credit Hour Requirements
Several factors can influence the credit hour requirements for associate degree programs. These factors can vary among colleges, universities, and specific degree programs. Understanding these factors can help students better comprehend the curriculum and optimize their academic journey.
1. Program of Study: The field of study chosen for an associate degree greatly impacts the credit hour requirements. Some programs, such as healthcare or engineering, may have more extensive coursework and a higher number of credit hours due to the technical and specialized knowledge required. On the other hand, programs like general studies or liberal arts may have more flexibility in course selection, potentially resulting in lower credit hour requirements.
2. Institution’s Policies: Different educational institutions have their own policies regarding credit hour requirements. While the guidelines for associate degree programs may be similar across institutions, there can be variations in the number of electives, general education courses, or major-specific requirements. It is important for students to review the specific policies of the institution they are attending to ensure they meet all the necessary credit hour requirements.
3. Accreditation Standards: Accreditation bodies, such as regional accrediting agencies, often set standards and guidelines for credit hour requirements. Institutions must adhere to these standards to ensure the quality and consistency of education. These accreditation standards can influence the credit hour requirements for associate degree programs, ensuring that a certain level of rigor and academic depth is maintained.
4. Transfer Credits: Students who transfer from one institution to another may have previously earned credit hours that can be applied towards their associate degree. The acceptance of transfer credits can reduce the overall credit hour requirements, allowing students to progress more quickly towards degree completion. However, the transferability of credits depends on factors such as the similarity of coursework, accreditation of the sending institution, and the receiving institution’s transfer credit policies.
5. Academic Performance and Course Load: The academic performance of students and the number of courses they take per semester or quarter can also impact credit hour requirements. Students who excel academically, meet prerequisites, or have the ability to handle a heavier course load may have the opportunity to complete their degree requirements in a shorter time frame.
It is important for students to consult with academic advisors, review program requirements, and understand these factors that influence credit hour requirements. By doing so, students can tailor their academic plan, stay on track for timely degree completion, and make the most of their associate degree program.
Common Credit Hour Requirements in Different Fields of Study
The credit hour requirements for associate degree programs can vary significantly based on the field of study. Below are some common credit hour requirements for different fields of study:
- Business Administration: Associate degree programs in business administration typically require around 60-65 credit hours. These programs include courses in accounting, economics, management, marketing, and business communications.
- Health Sciences: Health science associate degree programs often have higher credit hour requirements, averaging between 65-70 credit hours. These programs include coursework in anatomy and physiology, medical terminology, pharmacology, and specialized courses in areas like nursing or medical assisting.
- Information Technology: Associate degree programs in information technology typically require around 60-65 credit hours. These programs cover subjects like computer programming, networking, database management, cybersecurity, and system analysis.
- Education: Education-related associate degree programs usually require around 60-65 credit hours. These programs include coursework in educational psychology, teaching methods, child development, and field experiences in classroom settings.
- Criminal Justice: Associate degree programs in criminal justice often require around 60-65 credit hours. These programs cover topics such as criminal law, criminology, forensic science, ethics, and corrections.
- Liberal Arts: Associate degree programs in liberal arts offer a broad range of course options. The credit hour requirements can vary but typically range from 60-65 credit hours. These programs include coursework in humanities, social sciences, mathematics, natural sciences, and fine arts.
It is essential to note that these credit hour requirements are just general guidelines, and the actual requirements may vary among institutions and specific degree programs. Additionally, there may be variations within each field of study based on the institution’s curriculum and academic policies.
Students interested in a particular field of study should consult with academic advisors or review program requirements to get a more accurate understanding of the credit hour requirements for their desired associate degree program. By doing so, students can plan their academic journey effectively and ensure timely completion of their degree.
Transfer of Credit Hours
One of the factors that can impact the credit hour requirements for an associate degree is the transfer of credit hours from previous coursework. Transferring credit hours can be beneficial for students who have completed coursework at another institution and want to apply those credits toward their current degree program.
The transferability of credit hours depends on several factors, including the accreditation of the sending and receiving institutions, the similarity of coursework, and the policies of the receiving institution. Many colleges and universities have established transfer credit guidelines to assess the appropriateness and applicability of credits earned elsewhere.
Here are some key aspects to consider regarding the transfer of credit hours for associate degrees:
- Transferring from a Community College to a Four-Year Institution: Many students begin their academic journey at a community college and then transfer to a four-year institution to complete their associate degree. In these cases, the receiving institution may have established articulation agreements or transfer pathways to facilitate the transfer of credits from the community college to the four-year institution.
- General Education Transfers: General education courses, such as English composition, mathematics, and social sciences, often have higher transferability rates. These courses typically fulfill foundational requirements and are more likely to align with the general education requirements of other institutions.
- Course Equivalency and Acceptance: When transferring credits, institutions may assess course equivalency to determine if the content and level of rigor match their own courses. If the courses are deemed equivalent, the credit hours may be accepted. In some cases, credits may be accepted as elective credits if there is no direct equivalent.
- Maximum Transferable Credits: Some institutions have limits on the maximum number of transferable credit hours, regardless of how many credits the student has earned. It is essential for students to understand these limits and ensure they do not exceed them during the transfer process.
- Transferring to a Different Degree Program: If a student decides to change their field of study or pursue a different associate degree program, the transferability of credit hours may vary. Some credits earned for the previous program may still fulfill general education requirements, while others may only count as elective credits.
Students who plan to transfer credit hours should work closely with academic advisors at both the sending and receiving institutions to understand transfer credit policies, ensure a smooth credit transfer process, and make the most of their prior coursework.
Importance of Credit Hours for Associate Degree Completion
Credit hours play a crucial role in the successful completion of an associate degree. Understanding the importance of credit hours can help students effectively plan their academic journey and ensure a timely graduation.
Mapping Progress and Degree Requirements: Credit hours provide a clear framework for tracking academic progress. Each course completed and the corresponding credit hours earned contribute to the total required for degree completion. By keeping track of credit hours, students can monitor their progress and ensure they are meeting the requirements of their associate degree program.
Time Management and Course Planning: Credit hours guide students in managing their time and planning their course schedules. Each credit hour corresponds to a certain amount of time and effort required for coursework and study. Understanding this can help students make informed decisions about the number of courses to take each semester or quarter, balancing their workload with other responsibilities and commitments.
Staying on Schedule: Credit hour requirements serve as a roadmap for students to stay on track and graduate within a specific timeframe. By following the recommended credit hour requirements, students can ensure they are taking the necessary steps to complete their degree within the designated time period. Falling behind on credit hours may lead to delays in degree completion, additional time and financial resources needed.
Transferability and Articulation Agreements: Credit hours are essential when considering transferring to another institution or pursuing further education. Many colleges and universities have articulation agreements and transfer credit policies that consider the number of credit hours earned. The transferability of credit hours can impact a student’s ability to seamlessly transition to another institution or program and avoid unnecessary duplication of coursework.
Financial Considerations: Credit hours can also have financial implications. Tuition and fees are often calculated based on the number of credit hours enrolled. By efficiently managing credit hours and completing the required courses within the stipulated credit hour requirements, students can optimize their investment in their education.
Meeting Program and Institution Requirements: Credit hour requirements are set by educational institutions based on industry standards, accreditation guidelines, and program-specific outcomes. Meeting these requirements ensures that students have acquired the necessary knowledge and skills for their chosen field of study. It also ensures that the institution maintains academic standards and quality in its associate degree programs.
Overall, credit hours are an integral part of the associate degree journey. By understanding their importance, students can navigate their academic path effectively, stay on track for timely graduation, and maximize their educational and career opportunities.
Conclusion
Credit hours are a vital component in the pursuit of an associate degree. They serve as a measure of the time and effort students invest in their coursework and provide a roadmap for degree completion. Understanding credit hour requirements is crucial for effective academic planning, timely graduation, and maximizing educational opportunities.
Throughout this article, we have explored the various aspects of credit hours for associate degrees. We have learned about the definition and calculation of credit hours, including the additional work required outside of the classroom. We have also examined the common credit hour requirements for different fields of study, the factors that can influence credit hour requirements, and the importance of credit hours in completing an associate degree.
By understanding credit hour requirements, students can make informed decisions when selecting courses, balancing their workload, and planning their academic schedule. They can ensure they are meeting the necessary prerequisites and progressing towards their degree goals in a timely manner.
Additionally, the transferability of credit hours allows students to leverage their prior coursework and seamlessly transition between institutions or programs. Understanding the transfer process and articulation agreements can help students avoid unnecessary duplication of coursework and expedite their progress towards degree completion.
Ultimately, credit hour requirements provide structure and accountability in the pursuit of an associate degree. They ensure that students not only acquire the essential knowledge and skills in their chosen field of study but also meet the requirements set by educational institutions and accrediting bodies.
As students embark on their associate degree journey, they should consult with academic advisors, review program requirements, and stay mindful of credit hour calculations. By doing so, they can navigate their academic path effectively, stay on track for graduation, and set themselves up for success in their future endeavors.