
Finance
How To Calculate The Minimum Payment On A Loan
Published: February 25, 2024
Learn how to calculate the minimum payment on a loan and manage your finances effectively with this comprehensive guide. Understand the key factors that influence minimum payments and take control of your financial situation today.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Understanding the Importance of Calculating the Minimum Payment on a Loan
Introduction
When you take out a loan, whether it's for a car, a home, or any other significant purchase, it's crucial to understand how the minimum payment is calculated. The minimum payment represents the least amount you are required to pay each month to keep your loan in good standing. Understanding how this amount is determined can help you manage your finances more effectively and avoid potential pitfalls.
Knowing how to calculate the minimum payment on a loan is an essential aspect of financial literacy. It enables borrowers to plan their budgets effectively and stay on top of their financial obligations. Moreover, comprehending the factors that influence the minimum payment empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their borrowing and repayment strategies.
As we delve into the intricacies of minimum payments, it's important to recognize that this calculation can vary depending on the type of loan and the terms set by the lender. Whether you're dealing with a fixed-rate mortgage, a revolving credit account, or a student loan, understanding the minimum payment calculation is key to managing your financial responsibilities and avoiding potential financial strain.
In the following sections, we will explore the key components of loan minimum payments, including the factors that influence their calculation and the importance of making these payments in a timely manner. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of this fundamental aspect of borrowing, you will be better equipped to navigate the world of personal finance and make informed decisions about your financial well-being.
Understanding the Loan Terms
Before delving into the calculation of the minimum payment on a loan, it’s essential to grasp the key terminologies associated with borrowing. When you take out a loan, you enter into a financial agreement with a lender, and this agreement is governed by specific terms and conditions. Here are some crucial terms to understand:
- Principal: This refers to the initial amount of money borrowed. It is the base amount upon which interest is calculated.
- Interest Rate: The interest rate determines the cost of borrowing and is usually expressed as a percentage of the principal amount.
- Loan Term: This is the period over which the loan is to be repaid. It can vary from a few months to several decades, depending on the type of loan.
- Minimum Payment: The minimum amount that must be paid each month to keep the loan in good standing.
- Amortization Schedule: This is a table that details each loan payment’s allocation between principal and interest over the loan term.
Understanding these terms is vital for comprehending how the minimum payment is calculated and how it impacts the overall repayment of the loan. The interplay between the principal, interest rate, and loan term significantly influences the minimum payment amount. Moreover, being aware of these terms enables borrowers to make informed decisions about their borrowing and repayment strategies.
When borrowers have a clear understanding of these loan terms, they are better equipped to manage their financial obligations effectively. This knowledge empowers individuals to assess the implications of taking on a loan and to plan for its repayment in a way that aligns with their financial goals and capabilities.
As we move forward, we will explore how these loan terms interrelate in the calculation of the minimum payment, shedding light on the factors that borrowers should consider when managing their loan obligations.
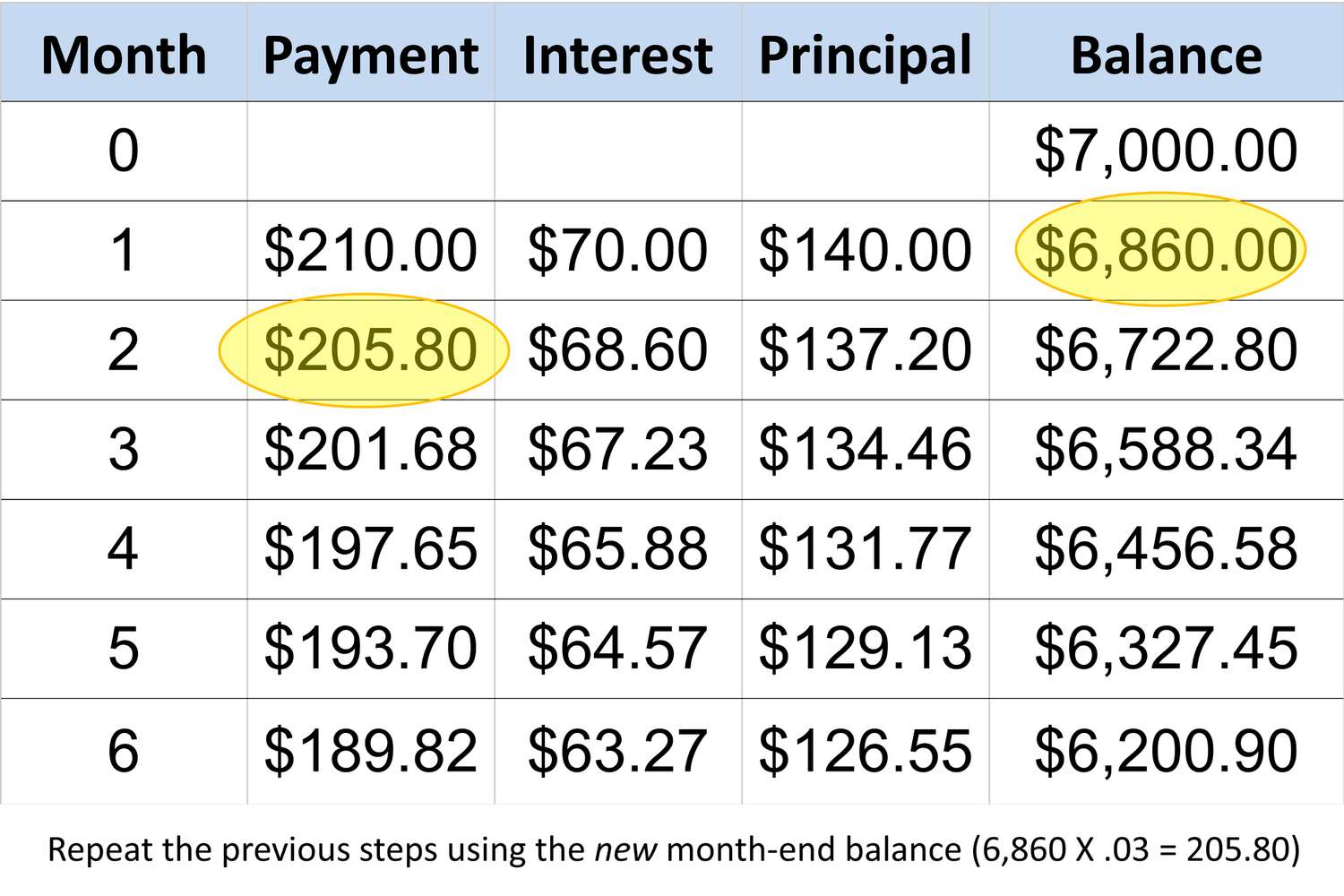
Calculating the Minimum Payment
Calculating the minimum payment on a loan involves several factors, including the loan amount, interest rate, and loan term. The minimum payment is typically designed to cover the interest accrued for that period, a portion of the principal amount, and any applicable fees. While the specific calculation method can vary depending on the loan type and lender, the following general formula is commonly used to determine the minimum payment:
Minimum Payment = (Principal x Monthly Interest Rate) / (1 – (1 + Monthly Interest Rate)^(-Number of Months))
Where:
- Principal: The initial amount borrowed
- Monthly Interest Rate: The annual interest rate divided by 12 to obtain the monthly rate
- Number of Months: The total number of months over which the loan will be repaid
It’s important to note that this formula provides a simplified overview of the minimum payment calculation and may not encompass additional factors such as fees or changes in the interest rate over time. For loans with variable interest rates, the minimum payment calculation can become more complex due to fluctuations in the interest rate.
Understanding the minimum payment calculation empowers borrowers to anticipate their monthly financial obligations and plan their budgets accordingly. By knowing how much is required to keep the loan in good standing, individuals can align their repayment strategy with their overall financial situation and goals.
As we delve deeper into the factors influencing the minimum payment, it becomes evident that a comprehensive understanding of the calculation process is essential for effective financial planning and debt management. By gaining insight into this aspect of borrowing, individuals can make informed decisions about their loan obligations and work towards achieving financial stability.
Factors Affecting the Minimum Payment
Several key factors influence the minimum payment on a loan, impacting the amount borrowers are required to pay each month. Understanding these factors is crucial for borrowers seeking to manage their financial obligations effectively. Here are the primary elements that can affect the minimum payment:
- Principal Amount: The initial amount borrowed, known as the principal, directly influences the minimum payment. A higher principal typically results in a higher minimum payment, assuming other factors remain constant.
- Interest Rate: The annual interest rate on the loan significantly affects the minimum payment amount. A higher interest rate leads to a greater portion of the minimum payment going towards interest rather than the principal, potentially increasing the total payment amount.
- Loan Term: The duration of the loan impacts the minimum payment. Shorter loan terms often result in higher monthly payments, while longer terms may yield lower minimum payments but lead to higher overall interest costs.
- Loan Type: Different types of loans, such as fixed-rate mortgages, adjustable-rate mortgages, and revolving credit accounts, have varying minimum payment calculation methods. The specific terms and conditions of each loan type can influence the minimum payment amount.
- Additional Fees: Some loans may entail additional fees, such as origination fees or late payment penalties, which can affect the minimum payment amount. It’s essential for borrowers to be aware of any extra charges that could impact their monthly obligations.
By considering these factors, borrowers can gain insight into the dynamics of minimum payment calculations and make informed decisions about their borrowing and repayment strategies. Additionally, understanding how these elements interrelate empowers individuals to plan their finances effectively and navigate the complexities of loan repayment.
As we explore the significance of making minimum payments, it becomes evident that a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing these payments is essential for borrowers to manage their financial responsibilities and work towards achieving their long-term financial goals.
Importance of Making Minimum Payments
Making minimum payments on a loan is a fundamental aspect of maintaining good financial standing and managing debt responsibly. While it may be tempting to pay only the minimum required amount, doing so can have significant implications for borrowers. Here are several reasons highlighting the importance of making minimum payments:
- Preserving Credit Score: Timely minimum payments contribute to a positive credit history, which is crucial for maintaining a healthy credit score. A good credit score can facilitate future borrowing at favorable terms and conditions.
- Avoiding Late Fees: Failing to make the minimum payment on time can result in late fees and penalties, adding to the overall cost of the loan. By making timely minimum payments, borrowers can avoid these additional charges.
- Preventing Default: Consistently making at least the minimum payment ensures that the loan remains in good standing, reducing the risk of default and potential legal consequences.
- Managing Interest Costs: While paying only the minimum may extend the overall repayment period, it helps manage short-term financial obligations and prevents the accumulation of excessive interest charges.
- Building Financial Discipline: Meeting minimum payment requirements instills financial discipline and responsibility, fostering healthy financial habits that can benefit borrowers in the long run.
Understanding the importance of making minimum payments empowers borrowers to prioritize their financial commitments and navigate the challenges of loan repayment effectively. By recognizing the broader implications of these payments, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their debt and work towards achieving their financial goals.
As we explore strategies for managing loan payments, it becomes evident that the significance of making minimum payments extends beyond mere compliance with loan terms. It is a cornerstone of responsible financial management, contributing to long-term financial well-being and stability.
Tips for Managing Loan Payments
Effectively managing loan payments is essential for maintaining financial stability and achieving long-term financial goals. Here are some valuable tips to help borrowers navigate the process of loan repayment:
- Create a Budget: Develop a comprehensive budget that allocates funds for loan payments while accounting for other essential expenses and financial goals. This ensures that loan obligations are integrated into your overall financial plan.
- Pay More Than the Minimum: Whenever possible, consider paying more than the minimum required amount. Doing so can help reduce the total interest paid over the life of the loan and expedite the repayment process.
- Automate Payments: Set up automatic payments for the minimum amount or more to ensure timely payments and avoid the risk of missing due dates. This can also streamline your financial management process.
- Communicate with Lenders: If you encounter financial challenges that may affect your ability to make minimum payments, communicate with your lenders proactively. They may offer assistance or alternative payment arrangements to help you manage your obligations.
- Monitor Interest Rates: For loans with variable interest rates, stay informed about any rate changes that may impact your minimum payments. Understanding these fluctuations can help you prepare for potential adjustments in your financial plan.
- Consider Refinancing or Consolidation: Explore options for refinancing or consolidating loans to potentially secure more favorable terms, lower interest rates, or extended repayment periods that align with your financial circumstances.
- Seek Financial Guidance: If you are facing challenges in managing loan payments or navigating complex financial situations, consider seeking advice from financial professionals who can provide personalized guidance and strategies.
By implementing these tips, borrowers can take proactive steps to manage their loan payments effectively and work towards achieving financial stability. Navigating the complexities of loan repayment requires careful planning, disciplined financial management, and a proactive approach to addressing potential challenges.
Understanding the nuances of managing loan payments empowers individuals to take control of their financial well-being and make informed decisions that align with their long-term financial goals. By prioritizing effective loan management, borrowers can pave the way for a more secure financial future.














