Finance
How To Calculate My Minimum Payment On Loan
Published: February 26, 2024
Learn how to calculate your minimum payment on a loan with our finance guide. Understand the factors that affect your repayment amount. Start managing your finances today!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When you take out a loan, whether it's for a car, a home, or any other major purchase, understanding how to calculate the minimum payment is crucial for managing your finances. The minimum payment represents the lowest amount you are required to pay each month to keep your loan in good standing. It typically includes a portion of the principal amount borrowed, the accrued interest, and any applicable fees. By grasping the factors that influence this essential figure, you can gain insight into your financial obligations and make informed decisions regarding your loan repayment strategy.
Understanding the intricacies of minimum payments on loans empowers you to budget effectively and avoid potential financial strain. This article will delve into the key components of loan terms, interest rates, and principal amounts, providing a comprehensive guide to calculating your minimum payment. Additionally, we will explore a practical example to illustrate the application of the minimum payment formula and discuss the various factors that can impact this vital aspect of loan management. Furthermore, we will offer valuable tips for effectively managing minimum payments to help you navigate the complexities of loan repayment with confidence.
By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of how minimum payments are calculated, enabling you to approach your loan obligations with clarity and financial acumen. Whether you are a first-time borrower or seeking to refine your financial management skills, mastering the calculation of minimum payments is an essential step toward achieving long-term financial stability. Let's embark on this enlightening journey to demystify the process of determining your minimum loan payment.
Understanding the Loan Terms
Before delving into the intricacies of calculating your minimum loan payment, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental terms associated with the loan agreement. When you secure a loan, whether it’s a personal loan, a mortgage, or a student loan, you enter into a contractual arrangement with a lender. This agreement outlines the specific terms and conditions governing the loan, including the principal amount, interest rate, and repayment schedule.
The principal amount refers to the initial sum of money borrowed. This forms the basis for calculating interest and determining the minimum payment. Understanding the principal amount is crucial, as it directly influences the total cost of the loan and the duration of the repayment period.
The interest rate is the percentage of the principal amount charged by the lender as compensation for the use of their funds. It plays a significant role in determining the total amount of interest accrued over the life of the loan. Additionally, the interest rate directly impacts the minimum payment, as a higher rate results in increased interest charges, thereby affecting the overall repayment obligation.
The repayment schedule outlines the frequency and amount of payments required to satisfy the loan. It is essential to review this schedule carefully, as it dictates the minimum payment amount and the total duration of the repayment period. Whether the payments are due monthly, bi-weekly, or according to another schedule, understanding the repayment timeline is crucial for effective financial planning.
By familiarizing yourself with these key loan terms, you lay the groundwork for comprehending how the minimum payment is calculated. The next step is to delve into the factors that influence the interest rate, as well as the process of determining the principal amount, which collectively contribute to the formula for calculating the minimum payment on your loan.
Determining the Interest Rate
The interest rate on a loan is a critical factor that significantly impacts the total cost of borrowing and, consequently, the calculation of the minimum payment. Lenders consider various elements when determining the interest rate for a loan, and understanding these factors can provide insight into the overall repayment obligation.
Credit Score: One of the primary determinants of the interest rate you receive is your credit score. This numerical representation of your creditworthiness is based on factors such as payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, and types of credit accounts. A higher credit score often translates to a lower interest rate, as it signifies a lower risk for the lender.
Market Conditions: The prevailing economic environment and market conditions play a significant role in shaping interest rates. Lenders adjust their rates in response to changes in the broader economy, including fluctuations in the prime lending rate set by the central bank. Monitoring market conditions can provide insight into potential shifts in interest rates, enabling borrowers to make informed decisions.
Loan Term: The duration of the loan, commonly referred to as the loan term, can influence the interest rate. Shorter-term loans often carry lower interest rates compared to longer-term loans, as they present less risk for the lender. Understanding the relationship between the loan term and the interest rate is crucial for evaluating the overall cost of borrowing and its impact on the minimum payment.
By gaining a deeper understanding of the factors that determine the interest rate, borrowers can assess the potential impact on their minimum payment obligations. Additionally, staying informed about market trends and maintaining a strong credit profile can contribute to securing favorable interest rates, ultimately facilitating more manageable loan repayment terms.
Calculating the Principal Amount
Before delving into the specifics of calculating the minimum payment on a loan, it is essential to understand the concept of the principal amount. The principal amount represents the initial sum of money borrowed from a lender, forming the basis for the total loan amount. When determining the minimum payment, it is crucial to consider the impact of the principal amount on the overall repayment obligation.
Loan Origination Fees: In some cases, lenders may charge loan origination fees, which are upfront costs associated with processing the loan. These fees are typically calculated as a percentage of the total loan amount and are deducted from the principal before the funds are disbursed to the borrower. Understanding the implications of loan origination fees is essential for accurately assessing the principal amount and its influence on the minimum payment.
Additional Principal Payments: Borrowers may have the option to make additional payments toward the principal amount, thereby reducing the overall balance of the loan. By strategically allocating extra funds to the principal, borrowers can potentially shorten the repayment period and decrease the total interest paid over the life of the loan. Understanding the impact of additional principal payments is crucial for proactive loan management and long-term interest savings.
Amortization Schedule: The amortization schedule outlines the breakdown of each loan payment, specifying the allocation of funds toward the principal and interest. As the loan progresses, the proportion of each payment attributed to the principal amount gradually increases, while the portion designated for interest decreases. Familiarizing oneself with the amortization schedule is essential for gaining insight into the gradual reduction of the principal balance over time.
By comprehending the nuances of the principal amount, including potential fees, the option for additional principal payments, and the structure of the amortization schedule, borrowers can make informed decisions regarding their minimum payment obligations. The principal amount forms a foundational element in the calculation of the minimum payment, and a clear understanding of its dynamics is integral to effective loan management.
Finding the Minimum Payment Formula
Calculating the minimum payment on a loan involves a formula that takes into account the principal amount, the interest rate, and the repayment schedule. By understanding the components of this formula, borrowers can gain insight into the factors influencing their minimum payment obligations and make informed financial decisions.
The minimum payment formula typically incorporates the following elements:
- Principal Amount: The initial sum of money borrowed, which forms the basis for the loan.
- Interest Rate: The percentage charged by the lender for the use of their funds, influencing the total cost of borrowing.
- Repayment Schedule: The frequency and amount of payments required to satisfy the loan, impacting the duration of the repayment period.
While the specific formula may vary depending on the type of loan and the lender’s policies, a common approach to calculating the minimum payment involves considering the accrued interest and a portion of the principal amount. This ensures that the borrower gradually reduces the outstanding balance over the course of the loan term.
It’s important to note that some loans, particularly those with variable interest rates or specific repayment structures, may have more complex formulas for determining the minimum payment. In such cases, borrowers should carefully review the loan agreement and seek clarification from the lender to fully understand the calculation methodology.
By familiarizing themselves with the minimum payment formula and seeking clarity on its application to their specific loan, borrowers can proactively manage their repayment obligations and budget effectively. Understanding how the minimum payment is derived empowers borrowers to make strategic financial decisions and gain control over their loan repayment journey.
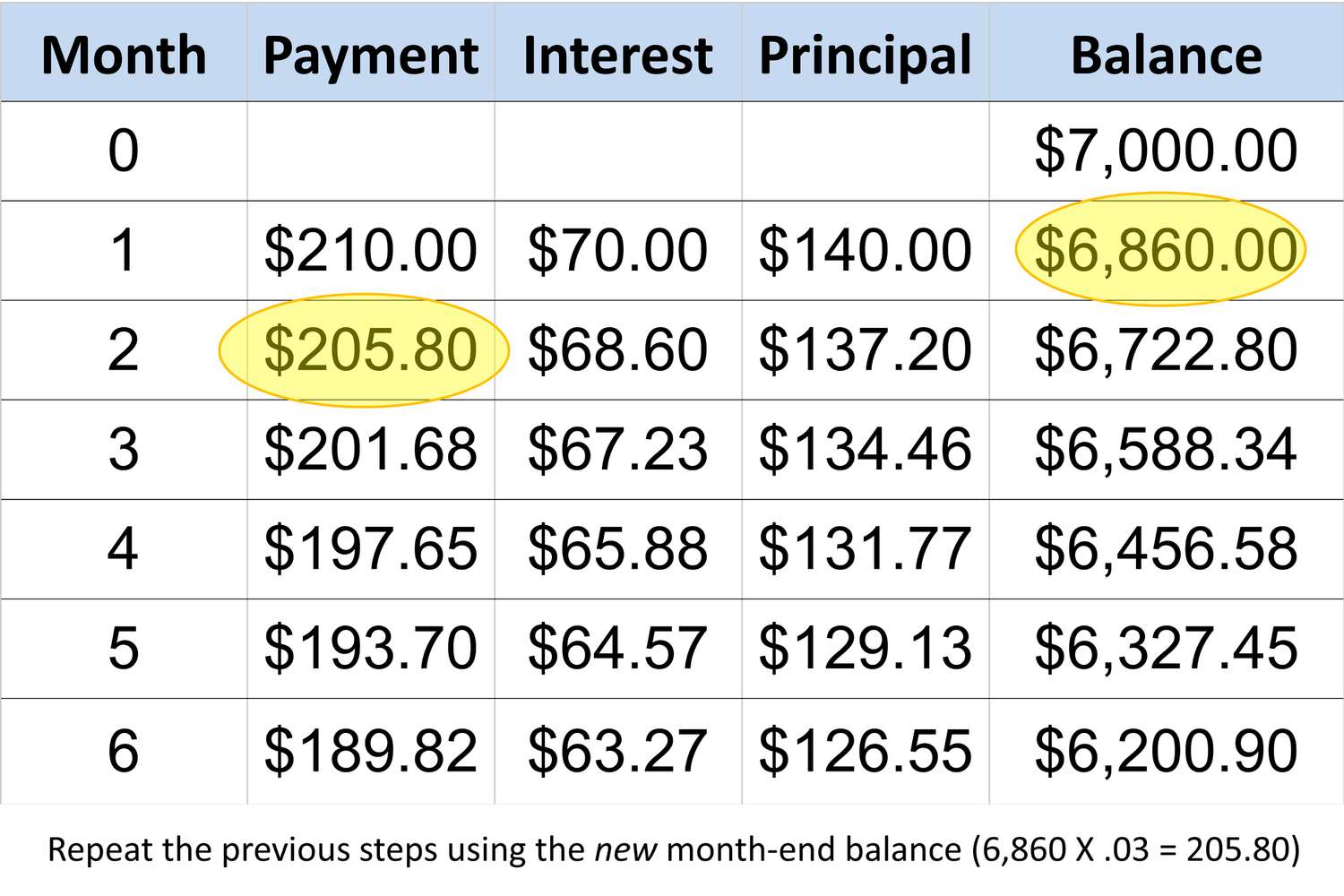
Example Calculation
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario to illustrate the calculation of the minimum payment on a loan. Suppose you have taken out a personal loan with the following details:
- Principal Amount: $10,000
- Interest Rate: 8% annually
- Repayment Schedule: Monthly payments over a 3-year term
To calculate the minimum payment for the first month, you can follow these steps:
- Calculate Monthly Interest: Divide the annual interest rate by 12 to obtain the monthly interest rate. In this case, 8% annually translates to approximately 0.67% monthly (8% / 12).
- Determine Accrued Interest: Multiply the monthly interest rate by the outstanding principal amount. For the first month, the accrued interest would be $10,000 * 0.0067, resulting in $67.
- Add Portion of Principal: Subtract the accrued interest from the total monthly payment to determine the portion allocated to reducing the principal amount. If the minimum payment is $250, the portion allocated to the principal would be $250 – $67, equaling $183.
As the loan progresses, the allocation between interest and principal in each payment gradually shifts, leading to a reduction in the outstanding balance. This gradual reduction reflects the amortization process, wherein a larger proportion of each payment goes toward the principal over time.
By understanding this example calculation, borrowers can gain clarity on the factors influencing their minimum payment and the gradual reduction of the principal amount over the course of the loan term. This insight enables borrowers to approach their loan obligations with informed decision-making and a strategic outlook toward managing their financial responsibilities.
Factors Affecting Minimum Payment
Several key factors influence the determination of the minimum payment on a loan, impacting the amount due each month and the overall repayment obligation. Understanding these factors is essential for borrowers seeking to manage their loan effectively and make informed financial decisions.
Principal Amount: The initial sum borrowed directly affects the minimum payment, as a higher principal amount typically results in larger minimum payment obligations. Borrowers should carefully evaluate the principal amount and its implications for the total cost of borrowing.
Interest Rate: The interest rate charged by the lender significantly influences the minimum payment. A higher interest rate leads to increased interest charges, thereby contributing to a larger minimum payment. Borrowers should be mindful of the impact of the interest rate on their repayment obligations and explore opportunities to secure favorable rates.
Loan Term: The duration of the loan plays a crucial role in determining the minimum payment. Shorter loan terms often result in higher monthly payments but lower total interest costs, while longer terms may yield lower monthly payments but higher overall interest expenses. Understanding the relationship between the loan term and the minimum payment is essential for effective financial planning.
Loan Type: Different types of loans, such as fixed-rate loans, adjustable-rate loans, and interest-only loans, have varying structures that can affect the minimum payment. Borrowers should familiarize themselves with the specific terms of their loan type and how these terms impact their minimum payment obligations.
Additional Fees: Some loans may entail additional fees, such as origination fees, late payment fees, or prepayment penalties. These fees can impact the minimum payment amount and should be carefully considered when evaluating the total cost of borrowing.
By considering these factors, borrowers can gain a comprehensive understanding of the elements influencing their minimum payment obligations. This awareness empowers borrowers to navigate their loan repayment journey with foresight and financial acumen, ultimately fostering effective management of their financial responsibilities.
Tips for Managing Minimum Payments
Effectively managing minimum payments on loans is crucial for maintaining financial stability and minimizing the long-term cost of borrowing. By implementing strategic approaches to handle minimum payments, borrowers can navigate their loan obligations with confidence and proactive financial management. Here are some valuable tips for managing minimum payments:
- Budget Wisely: Prioritize your minimum loan payments within your overall budget. Allocate sufficient funds to cover these obligations each month, ensuring timely payments to avoid potential penalties and negative impacts on your credit score.
- Pay More Than the Minimum: Whenever possible, consider paying more than the minimum required amount. By allocating additional funds toward your loan payments, you can accelerate the reduction of the principal amount and minimize the total interest paid over the life of the loan.
- Monitor Interest Rates: Stay informed about prevailing interest rates and explore opportunities to refinance your loan if favorable rates become available. Lowering your interest rate can lead to reduced minimum payments and overall interest costs.
- Understand Loan Terms: Familiarize yourself with the specific terms of your loan, including any potential fees, prepayment options, and the structure of the repayment schedule. Clarity on these terms enables you to make informed decisions regarding your minimum payment obligations.
- Build an Emergency Fund: Establishing an emergency fund can provide a safety net for unexpected financial challenges. Having reserves set aside can help prevent missed loan payments during difficult times, safeguarding your financial well-being.
- Seek Financial Guidance: If you encounter difficulties in managing your minimum payments, don’t hesitate to seek guidance from financial advisors or credit counseling services. These professionals can offer tailored strategies to help you effectively handle your loan obligations and improve your overall financial situation.
By incorporating these tips into your approach to managing minimum payments, you can proactively navigate the complexities of loan repayment and work toward achieving financial security. Strategic financial planning and informed decision-making are essential for effectively managing minimum payments and progressing toward long-term financial stability.
Conclusion
Understanding how to calculate and manage minimum payments on loans is a fundamental aspect of effective financial management. By comprehending the key components influencing minimum payments, including the principal amount, interest rate, and loan terms, borrowers can approach their loan obligations with clarity and strategic foresight.
Through the example calculation and exploration of factors impacting minimum payments, borrowers have gained valuable insight into the dynamics of loan repayment. The ability to budget wisely, consider additional payments, monitor interest rates, and seek financial guidance empowers individuals to navigate their loan obligations with confidence and proactive financial acumen.
By implementing the tips for managing minimum payments, borrowers can proactively address their financial responsibilities and work toward minimizing the long-term cost of borrowing. Building a solid understanding of loan terms, exploring opportunities for refinancing, and establishing financial safeguards contribute to a well-rounded approach to managing minimum payments effectively.
In conclusion, mastering the calculation and management of minimum payments on loans is a pivotal step toward achieving financial stability and long-term prosperity. By leveraging the insights and strategies outlined in this guide, borrowers can approach their loan obligations with confidence, informed decision-making, and a proactive mindset, ultimately fostering a path toward financial well-being and security.