Home>Finance>How To Public Pension Funds Invest Their Money?


Finance
How To Public Pension Funds Invest Their Money?
Published: January 23, 2024
Learn how public pension funds strategically invest their money in various financial instruments to secure long-term returns. Explore the finance strategies and considerations behind pension fund investments.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Understanding the Investment Strategies of Public Pension Funds
Public pension funds play a pivotal role in ensuring the financial security of retired individuals, as they are responsible for managing the assets that will provide pension benefits in the future. These funds are typically established and managed by government entities at the federal, state, or local levels. Understanding how public pension funds invest their money is crucial, as it impacts the long-term financial well-being of countless retirees.
Public pension funds are entrusted with the responsibility of prudently investing the contributions made by employees and employers. The ultimate goal is to generate returns that will sustain pension payments over the long term. Given the significant impact of their investment decisions, it is essential to delve into the various aspects of how these funds operate and allocate their resources.
In this article, we will explore the intricate world of public pension fund investments, shedding light on the diverse types of public pension funds, their investment strategies, asset allocation practices, risk management approaches, performance evaluation methods, as well as the challenges and considerations that shape their investment decisions. By gaining insight into these crucial elements, readers will develop a deeper understanding of the complex and impactful nature of public pension fund investments.
Types of Public Pension Funds
Public pension funds come in various forms, each tailored to the specific needs and structures of the organizations they serve. Understanding the different types of public pension funds is essential for comprehending the nuances of their investment strategies and operations. Here are the primary categories of public pension funds:
- Defined Benefit Plans: These funds guarantee a specified monthly benefit upon retirement, based on a pre-determined formula that considers factors such as salary history and years of service. The responsibility for investment management and the associated risks lies with the pension fund.
- Defined Contribution Plans: In contrast to defined benefit plans, defined contribution plans specify the contributions made by employers and employees, with the eventual benefits dependent on the performance of the investment portfolio. Individual accounts are maintained for each participant, offering more flexibility and portability.
- Hybrid Plans: These plans combine elements of both defined benefit and defined contribution structures, providing a mix of guaranteed benefits and individual account options. Hybrid plans aim to offer the security of defined benefits while incorporating the flexibility of defined contributions.
Each type of public pension fund comes with its own set of challenges and considerations, influencing the investment approaches adopted to secure the financial future of retirees. By recognizing the distinctions between these fund types, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the diverse strategies employed in managing pension assets.
Investment Strategies
Public pension funds employ various investment strategies to achieve their long-term financial objectives while managing risks and meeting the future pension obligations of beneficiaries. These strategies are designed to generate returns that outpace inflation and sustain the fund’s ability to fulfill its commitments. Here are some common investment strategies utilized by public pension funds:
- Diversification: Pension funds diversify their investment portfolios across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and alternative investments, to spread risk and optimize returns. Diversification helps mitigate the impact of market fluctuations on the overall portfolio.
- Long-Term Focus: Public pension funds adopt a long-term investment horizon, allowing them to capitalize on market opportunities and withstand short-term volatility. This approach aligns with the extended time horizon of pension liabilities.
- Active and Passive Management: Pension funds utilize a combination of active and passive management strategies. While active management aims to outperform the market through strategic buying and selling of assets, passive management seeks to replicate the performance of a specific market index.
- Risk Management: Effective risk management strategies are integral to pension fund investments. This involves identifying and mitigating various types of risk, including market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, and operational risk, among others.
- Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Integration: Many public pension funds integrate ESG factors into their investment decision-making processes, considering environmental and social impacts, as well as corporate governance practices, to align with responsible investing principles.
By implementing these strategies, public pension funds aim to achieve a balance between risk and return, ensuring the sustainability of pension benefits while prudently managing the assets entrusted to them.
Asset Allocation
Asset allocation is a critical component of public pension fund management, encompassing the distribution of investments across various asset classes to optimize risk-adjusted returns and align with the fund’s long-term objectives. The strategic allocation of assets plays a pivotal role in shaping the overall risk-return profile of the investment portfolio. Here are key aspects of asset allocation for public pension funds:
- Strategic Asset Allocation: Pension funds establish a strategic asset allocation framework based on their long-term investment goals, risk tolerance, and market expectations. This involves setting target allocations for different asset classes, such as equities, fixed income, real estate, and alternative investments, to achieve the desired risk-return balance.
- Tactical Asset Allocation: In response to short-term market dynamics and opportunities, pension funds may engage in tactical asset allocation to capitalize on market inefficiencies or adjust the portfolio’s exposure to specific asset classes. Tactical allocation decisions are often based on market outlook and valuation metrics.
- Asset Class Diversification: Diversifying across asset classes is fundamental to asset allocation, as it helps mitigate concentration risk and enhances the potential for consistent returns. Pension funds carefully assess the correlation and performance characteristics of various asset classes to construct a well-diversified portfolio.
- Rebalancing: Regular portfolio rebalancing is essential to maintain the intended asset allocation. Pension funds periodically reallocate assets to align with target percentages, ensuring that market movements do not significantly skew the portfolio’s risk profile.
- Alternative Investments: Many pension funds incorporate alternative investments, such as private equity, hedge funds, and infrastructure, into their asset allocation strategies to access additional sources of return and diversification beyond traditional asset classes.
Effective asset allocation enables public pension funds to optimize risk-adjusted returns, manage volatility, and navigate changing market conditions while upholding their fiduciary responsibilities to pension beneficiaries.
Risk Management
Risk management is a fundamental aspect of public pension fund operations, encompassing the identification, assessment, and mitigation of various risks that could impact the fund’s ability to meet its long-term obligations. Given the significance of pension assets in securing retirees’ financial well-being, effective risk management strategies are crucial for safeguarding the stability and sustainability of these funds. Here are key elements of risk management in the context of public pension fund investments:
- Market Risk: Pension funds are exposed to market risk stemming from fluctuations in asset prices, interest rates, and currency exchange rates. Mitigating market risk involves diversifying the investment portfolio, employing hedging strategies, and maintaining a long-term perspective to withstand short-term market volatility.
- Credit Risk: The risk of issuer default or credit deterioration in fixed income and other debt instruments poses a threat to pension fund investments. Rigorous credit analysis, diversification across issuers and credit ratings, and ongoing monitoring are essential for managing credit risk.
- Liquidity Risk: Ensuring adequate liquidity to meet pension benefit payments and unexpected cash flow needs is paramount. Pension funds must balance the pursuit of higher returns with maintaining sufficient liquidity through prudent cash management and asset allocation strategies.
- Operational Risk: Operational risks encompass a range of potential disruptions, including errors, fraud, technology failures, and legal and compliance issues. Robust internal controls, governance structures, and operational due diligence are critical for mitigating operational risk.
- Regulatory and Compliance Risk: Public pension funds operate within a complex regulatory environment, and non-compliance can lead to legal and financial repercussions. Compliance risk management involves staying abreast of regulatory changes, maintaining transparency, and adhering to fiduciary responsibilities.
By proactively addressing these risks and implementing robust risk management frameworks, public pension funds can enhance their resilience, protect the interests of pension beneficiaries, and uphold their fiduciary duties to effectively steward the assets under their care.
Performance Evaluation
Performance evaluation is a critical process through which public pension funds assess the effectiveness of their investment strategies, asset allocation decisions, and overall portfolio management. By systematically evaluating performance, pension funds can gauge their ability to meet long-term objectives, identify areas for improvement, and demonstrate accountability to stakeholders. Here are key aspects of performance evaluation in the context of public pension fund investments:
- Investment Return Analysis: Pension funds analyze investment returns across various asset classes and investment managers to assess their contribution to overall portfolio performance. This involves comparing actual returns against benchmarks and peer groups to evaluate relative performance.
- Risk-Adjusted Returns: Evaluating risk-adjusted returns provides insights into the level of risk taken to achieve investment performance. Metrics such as the Sharpe ratio and the Information Ratio help pension funds assess whether returns adequately compensate for the risks undertaken.
- Attribution Analysis: Attribution analysis dissects the sources of portfolio returns, identifying the impact of asset allocation decisions, security selection, and other factors on investment performance. This analysis aids in understanding the drivers of portfolio returns.
- Peer Comparison: Benchmarking against peer pension funds and industry standards allows for meaningful comparisons of investment performance, asset allocation practices, and risk management approaches. Peer comparison provides valuable context for assessing relative strengths and weaknesses.
- Transparency and Reporting: Transparent reporting of investment performance, fees, and portfolio holdings fosters accountability and trust. Public pension funds often provide regular performance reports to stakeholders, offering insights into investment activities and outcomes.
By conducting thorough performance evaluations, public pension funds can make informed decisions to enhance investment outcomes, refine asset allocation strategies, and uphold their fiduciary duties to pension beneficiaries and the broader community.
Challenges and Considerations
Managing public pension fund investments presents a myriad of challenges and considerations that necessitate careful navigation to ensure the long-term financial security of pension beneficiaries. Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial for fostering effective investment stewardship and mitigating potential risks. Here are key challenges and considerations faced by public pension funds:
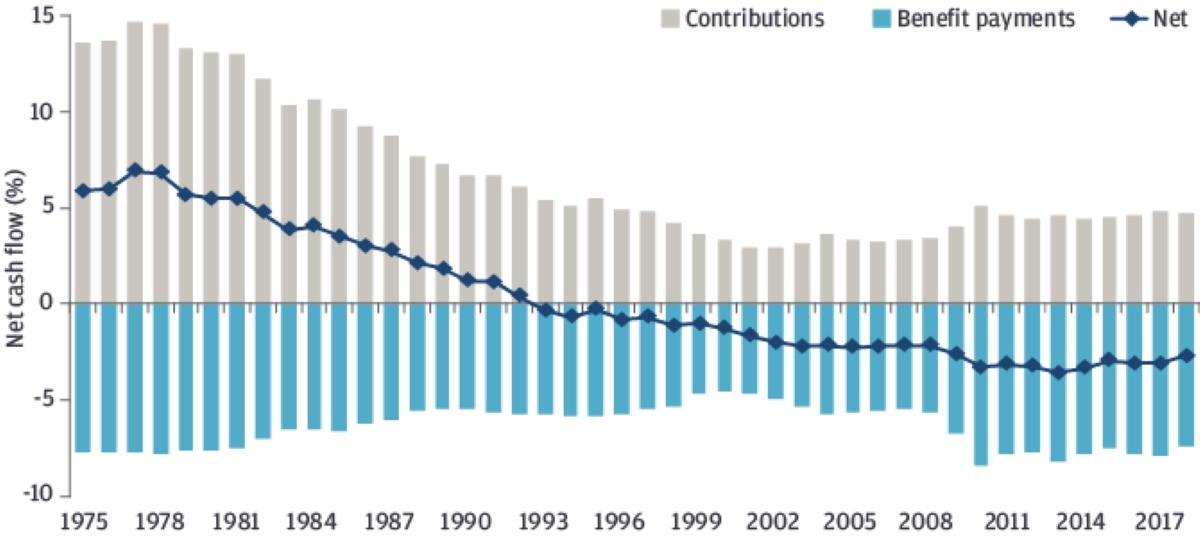
- Long-Term Liabilities: Pension funds must contend with the long-term nature of their liabilities, as they are obligated to provide pension benefits to retirees over extended time horizons. Balancing the investment portfolio to meet these future obligations while generating sufficient returns poses a significant challenge.
- Market Volatility: Fluctuations in financial markets can impact the value of pension fund assets, potentially affecting the fund’s ability to meet its obligations. Managing market volatility requires robust risk management strategies and a long-term investment perspective.
- Funding Adequacy: Ensuring that pension funds are adequately funded to meet future benefit payments is a critical consideration. Demographic shifts, economic conditions, and contribution levels all influence the fund’s ability to maintain solvency and fulfill pension commitments.
- Regulatory Compliance: Public pension funds operate within a complex regulatory framework, requiring compliance with fiduciary responsibilities, investment guidelines, reporting standards, and legal requirements. Staying abreast of regulatory changes and fulfilling compliance obligations is essential.
- Sustainable Investing: Integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into investment decisions while pursuing sustainable and responsible investing practices presents both opportunities and challenges for pension funds. Balancing financial objectives with ESG considerations is a key consideration.
- Cost Management: Managing investment costs, including fees paid to external managers and administrative expenses, is vital for optimizing returns and preserving the fund’s assets. Cost-effective investment strategies and fee transparency are essential considerations.
Addressing these challenges and considerations requires a holistic approach that encompasses prudent investment strategies, robust risk management frameworks, diligent oversight, and a commitment to fulfilling fiduciary duties to pension beneficiaries. By navigating these challenges effectively, public pension funds can strive to fulfill their crucial role in safeguarding the financial well-being of retirees.
Conclusion
Public pension funds play a vital role in securing the financial future of retirees, as they are entrusted with the responsibility of prudently managing pension assets to meet long-term obligations. Understanding the intricate investment strategies, asset allocation practices, risk management approaches, and performance evaluation methods employed by these funds is essential for stakeholders and the broader community.
By delving into the diverse types of public pension funds, including defined benefit plans, defined contribution plans, and hybrid plans, stakeholders gain insight into the unique structures and challenges that shape pension fund operations. Moreover, the adoption of various investment strategies, such as diversification, long-term focus, and ESG integration, underscores the multifaceted approaches employed to generate sustainable returns while managing risks.
Asset allocation emerges as a critical component, with strategic and tactical allocation decisions shaping the risk-return profile of pension fund portfolios. Effective asset allocation enables funds to optimize returns, diversify risk, and navigate changing market conditions. Furthermore, robust risk management practices, encompassing market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, and operational risk, are vital for safeguarding pension assets and ensuring the stability of fund operations.
Performance evaluation serves as a mechanism for assessing investment outcomes, identifying areas for improvement, and demonstrating accountability to stakeholders. By conducting thorough evaluations, pension funds can refine their strategies, enhance investment outcomes, and uphold their fiduciary responsibilities.
Amidst the challenges and considerations posed by long-term liabilities, market volatility, funding adequacy, regulatory compliance, sustainable investing, and cost management, public pension funds must navigate complex landscapes to fulfill their crucial role in securing retirees’ financial well-being.
In conclusion, the effective management of public pension fund investments requires a comprehensive understanding of the multifaceted strategies, considerations, and challenges that shape these funds. By upholding prudent stewardship, embracing innovation, and navigating complexities with diligence, public pension funds can strive to fulfill their pivotal mission of safeguarding the financial security of retirees.