Finance
How To Use Life Insurance As A Bank
Published: October 15, 2023
Learn how to leverage life insurance as a powerful financial tool to secure your financial future and maximize your wealth. Discover the benefits of using life insurance as a bank and how it can help you achieve your financial goals.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of finance where innovative strategies are constantly evolving to help individuals manage and grow their wealth. One such strategy gaining popularity is the use of life insurance as a bank. It may sound unusual at first, but it offers a unique way to leverage life insurance as a financial tool.
Traditionally, life insurance is seen as a means to protect your loved ones financially in the event of your untimely demise. However, it can serve a dual purpose by providing additional benefits while you are alive. This article will explore how you can utilize life insurance as a bank and the advantages it can offer.
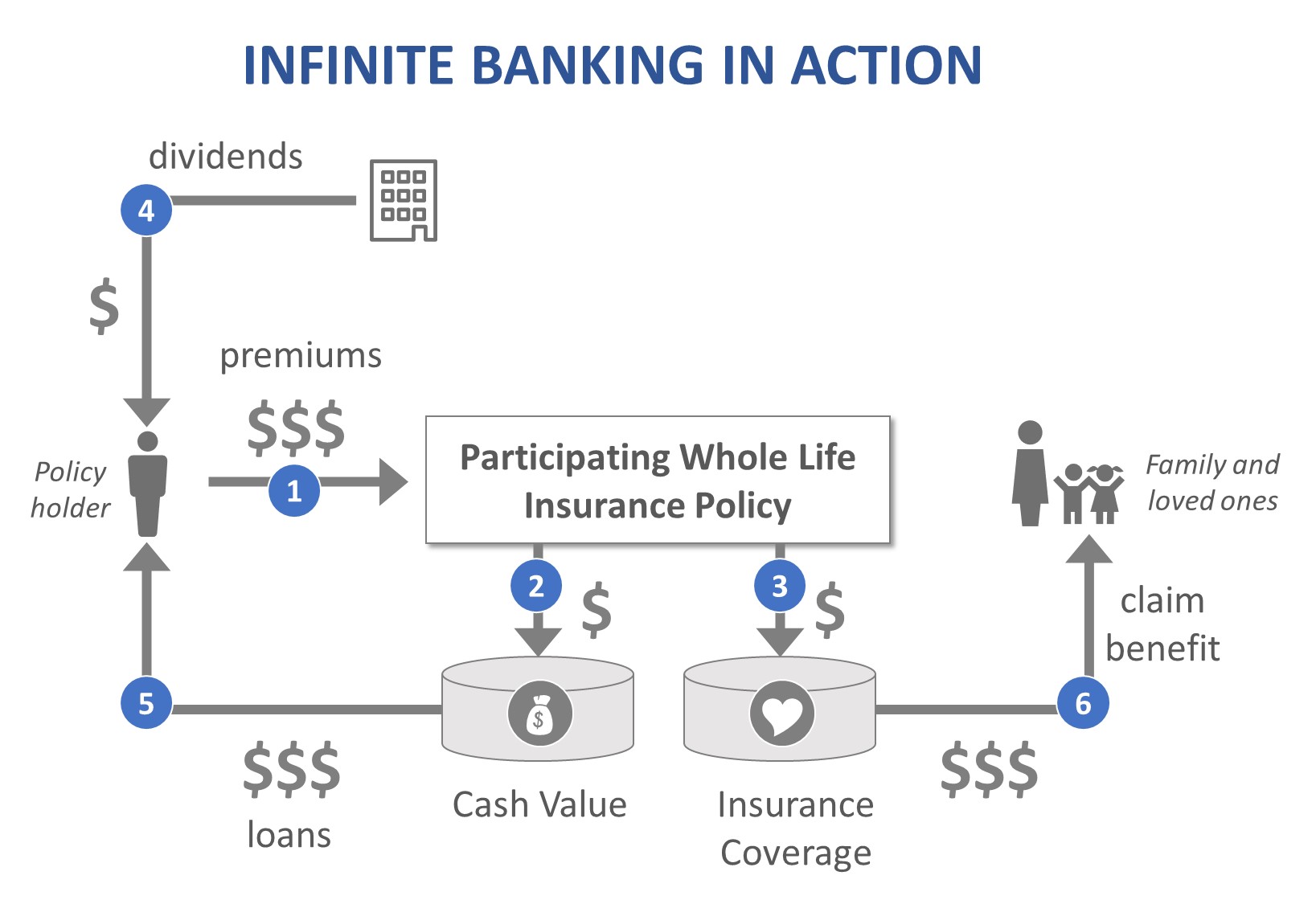
Using life insurance as a bank involves growing cash value within a permanent life insurance policy, such as whole life or universal life. These policies accrue cash value over time, creating a pool of funds that can be accessed and used for various purposes. It essentially allows you to have a “bank” within your life insurance policy.
Understanding Life Insurance as a Bank
When using life insurance as a bank, it’s important to understand the basic principle behind it. Instead of solely using a traditional bank or financial institution, you can leverage the cash value component of a permanent life insurance policy to fulfill your financial needs.
Permanent life insurance policies offer death benefit coverage as well as a cash value component. The cash value grows over time as you pay premiums, and it can be accessed and used for various purposes, similar to a savings account or a line of credit.
By utilizing life insurance as a bank, you can potentially enjoy benefits such as tax-deferred growth, asset protection, and the ability to access funds quickly and easily.
It’s important to note that using life insurance as a bank is not for everyone. It requires a long-term commitment and the ability to maintain premium payments. Additionally, it’s crucial to consult with a financial advisor or insurance professional to determine if this strategy aligns with your specific financial goals and circumstances.
Benefits of Using Life Insurance as a Bank
Using life insurance as a bank comes with several noteworthy benefits that can help you manage and grow your wealth. Let’s explore some of these benefits below:
1. Tax advantages: One of the key advantages of using life insurance as a bank is the potential tax benefits. The cash value in a permanent life insurance policy grows on a tax-deferred basis, meaning you don’t have to pay taxes on the growth as long as the funds remain within the policy. Additionally, policyholders can potentially access the cash value through loans or withdrawals on a tax-free basis, depending on certain criteria.
2. Asset protection: Life insurance policies typically offer a level of asset protection from creditors. In the event of financial difficulties, the cash value in your life insurance policy may be protected from creditors and legal claims, providing a safeguard for your accumulated wealth.
3. Flexibility: Another advantage of utilizing life insurance as a bank is the flexibility it offers. Unlike traditional bank loans, the process of accessing funds from the cash value in a life insurance policy is typically straightforward and hassle-free. This can be particularly beneficial during times of financial need or when opportunities arise that require quick access to funds.
4. Stable and guaranteed growth: Permanent life insurance policies guarantee a minimum rate of return on the cash value component. This means that you can rely on the growth of your policy’s cash value, providing stability and ensuring that your funds are working for you over the long term.
5. Death benefit protection: Using life insurance as a bank does not mean sacrificing the primary purpose of life insurance, which is to provide a death benefit to your beneficiaries. Even while utilizing the cash value, the death benefit component of the policy remains intact, providing financial protection to your loved ones in the event of your passing.
These are just a few of the benefits that come with using life insurance as a bank. It’s important to carefully assess your financial goals and consider working with a knowledgeable professional to determine if this strategy aligns with your specific circumstances.
Building Cash Value in a Life Insurance Policy
Building cash value in a life insurance policy is a key aspect of utilizing life insurance as a bank. The cash value serves as a savings component within the policy, offering the potential for growth over time. Here are some ways in which cash value is built within a life insurance policy:
1. Premium Payments: Cash value is primarily built through the regular premium payments made towards the life insurance policy. When you pay your premiums, a portion of the payment goes towards covering the cost of insurance, while another portion is allocated towards the cash value. Over time, these accumulated contributions help grow the cash value.
2. Interest and Dividends: Cash value in some permanent life insurance policies may also grow through interest or dividends. The insurance company may credit the policy’s cash value with a fixed interest rate or provide dividends based on the insurance company’s financial performance. These additional earnings can further enhance the growth of the cash value.
3. No Lapse Guaranteed Riders: Some insurance policies offer no lapse guaranteed riders. These riders can help ensure that the policy remains in force even if the cash value falls below the required amount to cover the premiums. This ensures that the cash value continues to grow without interruption, providing a more stable accumulation of funds.
It’s important to understand that the cash value within a life insurance policy accumulates gradually, and it may take several years before it becomes significant. However, the advantage is that the cash value has the potential to grow on a tax-deferred basis, allowing for potentially greater accumulation over time.
It’s essential to review the terms and conditions of the policy, including the rate of return on the cash value, any associated fees, and the impact of withdrawals or loans on the growth of the cash value. Consulting with a financial advisor or insurance professional is highly recommended to ensure that you have a clear understanding of how the cash value will build within your specific policy.
Accessing Cash Value for Loans or Withdrawals
One of the significant advantages of using life insurance as a bank is the ability to access the cash value within the policy through loans or withdrawals. This flexibility allows policyholders to tap into their accumulated funds when needed. Here’s how you can access cash value in a life insurance policy:
1. Policy Loans: Many life insurance policies allow policyholders to borrow against the cash value of the policy. These loans typically have lower interest rates compared to traditional bank loans. When you take out a policy loan, the cash value serves as collateral, and the loan is repaid with interest. It’s important to note that policy loans can impact the growth of the cash value and the death benefit, and if not repaid, they can reduce the amount available to your beneficiaries.
2. Withdrawals: Depending on the terms of the life insurance policy, you may be able to make partial withdrawals from the cash value without taking out a loan. Withdrawals are typically tax-free up to the amount of premiums paid, and any excess is subject to taxation. It’s crucial to review the policy guidelines regarding withdrawals, as excessive or early withdrawals can deplete the cash value and potentially impact the policy’s sustainability.
3. Collateral Assignment: In certain situations, policyholders may use the cash value as collateral for securing a loan from an external financial institution. The policy is assigned as collateral, providing security to the lender. This option allows you to leverage the cash value in your life insurance policy to secure financing for other purposes, such as starting a business or making a large purchase.
It’s important to carefully consider the impact of loans or withdrawals on your life insurance policy. Any outstanding loans, if not repaid, will reduce the death benefit payable to your beneficiaries. Additionally, loans and withdrawals may affect the cash value growth and overall policy performance.
Consulting with a financial advisor or insurance professional is highly recommended to fully understand the implications of accessing cash value through loans or withdrawals. They can help you navigate the process and determine the most appropriate strategy based on your financial goals and circumstances.
Managing Premium Payments
When using life insurance as a bank, it’s crucial to manage your premium payments effectively to ensure the long-term sustainability of your policy and the growth of your cash value. Here are some key factors to consider when managing premium payments:
1. Budgeting: Budgeting plays a vital role in managing your premium payments. It’s important to allocate sufficient funds to cover your life insurance premiums without impacting your overall financial well-being. Analyze your income and expenses to determine a realistic premium payment that you can comfortably afford without straining your finances.
2. Premium Flexibility: Depending on the type of life insurance policy you have, there may be flexibility in premium payment options. Some policies offer the ability to pay premiums monthly, quarterly, semi-annually, or annually. Explore the options available to you and choose a frequency that aligns with your cash flow and financial goals.
3. Automatic Premium Payments: Many insurance companies offer automatic premium payment options, where the premium amount is automatically debited from your bank account. Setting up automatic payments ensures that your premiums are paid on time, eliminating the risk of missed payments that could result in policy lapse or other penalties.
4. Premium Financing: In situations where cash flow is a concern, premium financing may be an option to consider. Premium financing involves borrowing funds to pay the life insurance premiums, with the life insurance policy serving as collateral. It’s important to carefully evaluate the terms and interest rates associated with premium financing before proceeding, as it may affect the overall cost of the policy.
5. Policy Review: Regular policy reviews with your financial advisor or insurance professional are essential to ensure that your premium payment strategy aligns with your financial goals. Changes in your financial situation or life circumstances may necessitate adjustments to your premiums or policy structure. A policy review can help identify any necessary modifications to optimize your policy’s performance.
Remember, consistent and timely premium payments are crucial to maintaining the benefits of using life insurance as a bank, such as the growth of cash value and the protection of the death benefit. Keeping a close eye on premium management will help ensure the long-term success of your life insurance policy as a financial tool.
Tax Implications of Using Life Insurance as a Bank
Understanding the tax implications of using life insurance as a bank is essential for maximizing the benefits and avoiding any unforeseen tax liabilities. Here are some key considerations regarding the tax treatment of using life insurance as a financial tool:
1. Tax-Deferred Growth: One of the primary advantages of using life insurance as a bank is the potential for tax-deferred growth. The cash value within a life insurance policy grows on a tax-deferred basis, meaning you do not have to pay taxes on the growth as long as the funds remain within the policy. This allows for potentially greater accumulation over time.
2. Tax-Free Loans and Withdrawals: Policyholders may be able to access the cash value through policy loans or withdrawals on a tax-free basis, depending on certain criteria. Generally, policy loans are not subject to income tax, as they are considered borrowed funds rather than taxable income. However, it’s important to repay policy loans in a timely manner to avoid any potential tax consequences.
3. Taxable Events: While policy loans and withdrawals are generally tax-free, certain events can trigger tax implications. If the policy lapses or is surrendered, any outstanding loans may be subject to income tax. Additionally, if withdrawals exceed the amount of premiums paid into the policy, the excess may be considered taxable income.
4. Gift and Estate Taxes: Life insurance policies can play a role in estate planning and wealth transfer strategies. Generally, life insurance proceeds are not subject to income tax for beneficiaries. However, the policy death benefit may be included in the insured individual’s estate for estate tax purposes. Consulting with an estate planning professional can help you explore strategies to minimize potential estate tax implications.
5. Keep Up with Tax Law Changes: Tax laws can change over time, impacting the tax treatment of life insurance policies. It’s crucial to stay updated on any changes in tax regulations and consult with a tax advisor or insurance professional to ensure compliance with current laws and maximize tax benefits.
It’s important to note that tax implications can vary depending on the type and structure of the life insurance policy, as well as individual circumstances. Consulting with a financial advisor or tax professional is strongly recommended to fully understand the tax implications of using life insurance as a bank and to devise a strategy that aligns with your specific financial goals.
Risks and Considerations
While using life insurance as a bank offers numerous benefits, it’s important to be aware of the risks and considerations associated with this financial strategy. Here are some key factors to keep in mind:
1. Long-Term Commitment: Utilizing life insurance as a bank requires a long-term commitment. It’s essential to maintain premium payments over an extended period to ensure the continued growth of the cash value and the sustainability of the policy. If premium payments are missed or the policy lapses, it can impact the policy’s benefits and potentially result in financial losses.
2. Insurance Costs: Permanent life insurance policies, such as whole life or universal life, tend to have higher premiums compared to term life insurance. It’s important to understand the cost structure of the policy and ensure that the premiums are affordable and align with your financial capabilities.
3. Policy Performance: The growth of cash value within a life insurance policy is influenced by multiple factors, including interest rates, policy fees, and insurance company performance. It’s crucial to review the policy illustrations and consult with an insurance professional to evaluate the expected performance of the policy and understand the potential risks of policy underperformance.
4. Opportunity Cost: When allocating funds towards a life insurance policy, it’s essential to consider the opportunity cost of not investing those funds in other potentially higher yielding investment vehicles. While life insurance as a bank offers stability and certain tax advantages, it may not provide the same rate of return as other investment options.
5. Withdrawal Impact: Taking policy loans or withdrawals can reduce the cash value and death benefit of the life insurance policy. It’s important to carefully consider the impact of accessing funds from the policy and how it may affect the long-term growth and the coverage provided to your beneficiaries.
Every individual’s financial situation is unique, and what works for one person may not be suitable for another. It’s crucial to conduct a thorough assessment of your financial goals, risk tolerance, and overall financial plan when considering the use of life insurance as a bank. Consulting with a financial advisor or insurance professional can provide valuable insights and guidance to help you make informed decisions.
Conclusion
Using life insurance as a bank can be a powerful financial strategy, offering unique benefits and opportunities for individuals looking to manage and grow their wealth. By leveraging the cash value component of a permanent life insurance policy, policyholders can enjoy tax advantages, asset protection, and flexibility in accessing funds when needed.
However, it’s important to approach this strategy with careful consideration and a thorough understanding of the associated risks. The long-term commitment, insurance costs, policy performance, opportunity cost, and withdrawal impact are crucial factors to evaluate when using life insurance as a bank.
Consulting with a financial advisor or insurance professional is highly recommended to navigate the complexities of this strategy and ensure that it aligns with your specific financial goals and circumstances. They can provide personalized guidance, help you analyze the potential benefits and risks, and devise a strategy that suits your needs.
Ultimately, using life insurance as a bank can offer tax advantages, stable growth, and asset protection. It can be a valuable tool to complement your overall financial plan and provide additional financial security for yourself and your loved ones.
Remember, every financial decision should be made after careful consideration and in alignment with your unique circumstances. By staying informed, seeking expert advice, and regularly reviewing your strategy, you can make the most of life insurance as a bank and achieve your financial objectives.