Home>Finance>Top-Down Investing: Definition, Example, Vs. Bottom-Up


Finance
Top-Down Investing: Definition, Example, Vs. Bottom-Up
Published: February 9, 2024
Learn the definition and example of top-down investing in finance. Understand the differences between top-down and bottom-up approaches to make informed investment decisions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Top-Down Investing: Definition, Example, Vs. Bottom-Up
Welcome to the FINANCE category of our blog! In this post, we will delve into the fascinating world of top-down investing. What exactly is top-down investing, and how does it differ from bottom-up investing? Join us as we explore this investment approach, provide examples, and highlight the key differences. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of top-down investing and why it matters in the world of finance.
Key Takeaways
- Top-down investing focuses on analyzing broader economic and market trends before selecting individual investments.
- This approach helps investors identify opportunities and mitigate risks based on a macroeconomic perspective.
Understanding Top-Down Investing
In the world of investing, there are two primary strategies: top-down and bottom-up. While both approaches aim to create wealth, they differ in their methodologies and perspectives. Top-down investing is a macroeconomic approach that focuses on analyzing the overall economic landscape, including market trends, industry sectors, and global influences. The goal is to identify potential investment opportunities and make informed decisions based on these broader factors.
Let’s break down the top-down investing process into three key steps:
- Economic Analysis: At the heart of top-down investing is a thorough examination of the overall economic landscape. This includes assessing factors such as GDP growth, inflation rates, interest rates, and unemployment levels. By understanding the big picture, investors can gauge the direction of the market and identify sectors that are likely to thrive or struggle.
- Market Analysis: Armed with the knowledge gained from the economic analysis, investors move on to assess the market’s performance. This involves scrutinizing stock market indices, sector-specific indices, and trend indicators. By analyzing the overall market trends, investors can identify potential investment opportunities or risks.
- Investment Selection: Based on the economic and market analysis, investors select specific investments that align with the identified trends. This could involve investing in sectors that are expected to outperform or avoiding industries that are expected to face challenges. Through a top-down approach, investors aim to optimize their portfolios to navigate the ever-changing financial landscape.
To illustrate how top-down investing works, let’s consider an example. Suppose an investor conducts extensive economic and market analysis, and as a result, identifies that renewable energy is a fast-growing industry with considerable potential. They might then decide to invest in renewable energy companies, such as solar panel manufacturers or wind energy developers. By taking a top-down approach, this investor is leveraging their understanding of the overall economic and market trends to make informed investment choices.
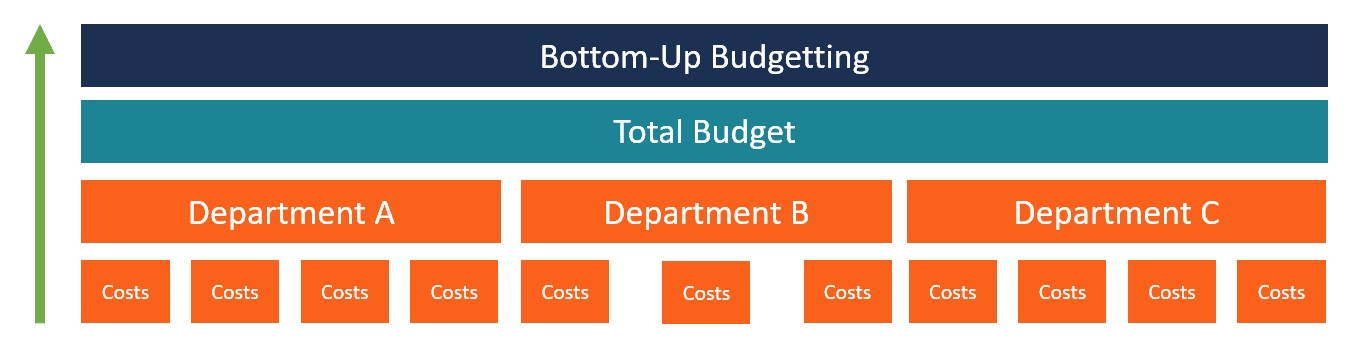
Top-Down Vs. Bottom-Up Investing
Now that we have explored top-down investing, it’s important to understand how it differs from bottom-up investing. While both strategies aim to achieve investment success, they approach it from different angles.
Top-Down Investing:
- Starts with the broader economic landscape and market trends
- Identifies sectors or industries likely to perform well based on macroeconomic analysis
- Selects specific investments within those sectors
Bottom-Up Investing:
- Focuses on individual companies and their financial health
- Analyzes a company’s fundamentals, such as earnings growth, competitive advantages, and management
- Builds a portfolio based on the strength and potential of individual companies
While top-down investors take a macroeconomic view, bottom-up investors dig deep into the specifics of individual companies. Both approaches have their merits, and some investors may even combine elements of both in their investment strategies.
In conclusion, top-down investing is a macroeconomic approach that allows investors to make informed decisions based on economic and market analysis. By understanding the broader economic landscape and identifying trends, investors can allocate their capital strategically. It’s important to note, however, that no approach guarantees success, and investors should always conduct thorough research and seek professional advice before making any investment decisions.
Thank you for joining us on this financial exploration into top-down investing! We hope this article has provided clarity and insight into this investment strategy.