
Finance
What Are Hard Commodities
Published: October 27, 2023
Discover the world of hard commodities in finance and learn about their importance in investment portfolios. Explore various types of hard commodities and their potential for growth and diversification.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for LiveWell, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Hard commodities play a crucial role in the global economy and financial markets. These tangible assets, such as precious metals, industrial metals, energy commodities, and agricultural commodities, are essential for various industries and everyday life. Understanding the nature of hard commodities, their types, and the factors that affect their prices is crucial for investors and traders looking to capitalize on these valuable assets.
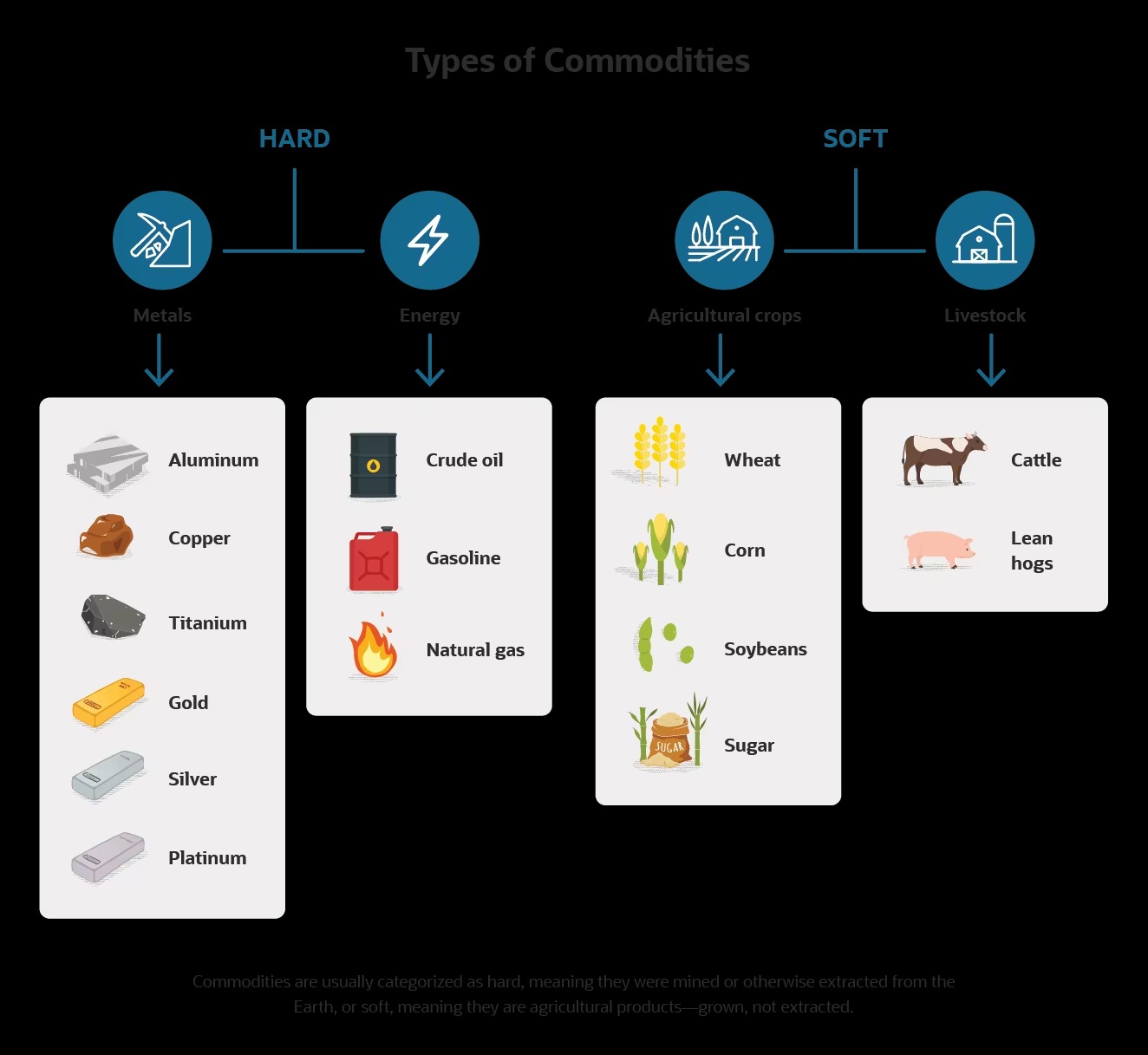
Commodities, in general, are defined as raw materials or primary agricultural products that can be bought and sold. While soft commodities refer to agricultural products like coffee, sugar, and wheat, hard commodities encompass non-perishable goods that are mined or extracted.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the world of hard commodities, exploring their definition, different types, and factors influencing their prices. We will also discuss investment opportunities and strategies for those interested in tapping into the potential of hard commodities.
So, whether you are a seasoned investor or someone looking to broaden your knowledge of the financial world, read on to discover the fascinating world of hard commodities and their impact on global markets.
Definition of Hard Commodities
Hard commodities, sometimes referred to as non-perishable goods, are natural resources that are extracted from the earth and have tangible value. These commodities are typically used for industrial purposes, manufacturing, and energy production.
What sets hard commodities apart from other types of commodities is their physical nature and finite supply. Unlike soft commodities, such as agricultural products, hard commodities cannot be reproduced or grown. Instead, they must be extracted from the earth through various processes like mining, drilling, or harvesting.
The value of hard commodities is derived from their scarcity and the demand for them in the global market. Due to their limited supply, these commodities can hold significant value and are often subject to price fluctuations based on factors such as geopolitical events, economic conditions, and supply and demand dynamics.
Hard commodities can be further categorized into several types, including precious metals, industrial metals, energy commodities, and agricultural commodities. Each type has its unique characteristics and uses in different sectors of the economy.
Overall, the definition of hard commodities encompasses those tangible resources that are extracted from the earth and are essential for various industries and everyday life.
Types of Hard Commodities
Hard commodities can be classified into several categories based on their characteristics and uses. These categories include precious metals, industrial metals, energy commodities, and agricultural commodities.
1. Precious Metals:
Precious metals are highly valued for their rarity and aesthetic properties. The most well-known precious metals are gold, silver, platinum, and palladium. These metals have been used as a store of value and a medium of exchange for centuries. Besides their traditional use in jewelry, precious metals also play a vital role in various industries such as electronics, dentistry, and investment. Their relatively limited supply and global demand contribute to their high market value.
2. Industrial Metals:
Industrial metals are essential for manufacturing and construction. Aluminum, copper, zinc, nickel, and lead are some examples of industrial metals. These metals are characterized by their strength, durability, and conductivity. They are utilized in various industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and infrastructure. The demand for industrial metals is influenced by economic growth, technological advancements, and global infrastructure development.
3. Energy Commodities:
Energy commodities consist of resources that are used for energy production. Crude oil, natural gas, coal, and uranium are the primary energy commodities. These resources are crucial for generating electricity, fueling vehicles, and powering industries. Energy commodities are heavily influenced by geopolitical events, global energy consumption patterns, and government policies. Their prices can be volatile and subject to supply disruptions and changes in global energy demand.
4. Agricultural Commodities:
Agricultural commodities are derived from the cultivation of crops or the rearing of livestock. Wheat, corn, soybeans, cotton, sugar, and coffee are examples of agricultural commodities. These commodities are essential for the food industry and are also used in the production of various consumer goods. Agricultural commodity prices are influenced by factors such as weather conditions, global demand for food, government policies, and economic factors affecting the agricultural sector.
These are the primary types of hard commodities. Each type has its unique characteristics and factors affecting its value. Understanding these different categories is crucial for investors and traders looking to navigate the world of hard commodities.
Precious Metals
Precious metals, including gold, silver, platinum, and palladium, hold a special place in the world of hard commodities due to their rarity, beauty, and exceptional value. These metals have been treasured for centuries and have a wide range of uses in industry, investment, and jewelry.
1. Gold:
Gold is perhaps the most well-known precious metal and has been used as a form of currency and a store of value for thousands of years. It is valued for its lustrous appearance, scarcity, and resistance to corrosion. Gold is widely used in the jewelry industry, but it also has industrial applications in electronics, aerospace, and dentistry. Additionally, gold is sought after as an investment and a hedge against inflation and currency fluctuations.
2. Silver:
Silver is another popular precious metal with a long history of use in jewelry, coins, and decorative art. It is known for its brilliant white luster and excellent conductivity, making it a valuable component in various industries, including electronics, photography, and solar energy. Silver is also an investment asset and is often seen as a more affordable alternative to gold.
3. Platinum:
Platinum is a dense, silver-white metal that is highly regarded for its durability and resistance to corrosion. Its most significant use is in catalytic converters for vehicles, helping reduce harmful emissions. Platinum is also used in the jewelry industry and has investment potential due to its limited supply and high demand in industrial applications.
4. Palladium:
Palladium is a lesser-known precious metal, but its importance is rapidly growing, particularly in the automotive industry. It is widely used in catalytic converters to reduce harmful emissions from vehicles. Palladium is also used in electronics, dentistry, and jewelry. Like platinum, palladium’s limited supply and increasing demand make it an attractive investment option.
The prices of precious metals are influenced by a variety of factors, including economic conditions, geopolitical events, inflation, and market sentiment. Investors can choose to invest in these metals directly through physical ownership or indirectly through exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and mining company stocks.
Overall, precious metals are highly sought after for their aesthetic appeal, industrial utility, and value as a store of wealth. They offer investors a unique opportunity to diversify their portfolios and protect against economic uncertainty.
Industrial Metals
Industrial metals are a crucial category of hard commodities that serve as the backbone of global manufacturing and construction industries. These metals are valued for their strength, durability, conductivity, and various other properties that make them essential for a wide range of applications.
1. Aluminum:
Aluminum is a lightweight and corrosion-resistant metal that is extensively used in the aerospace, automotive, and construction industries. It is valued for its high strength-to-weight ratio, making it an ideal choice for applications where lightness and strength are important, such as aircraft frames, vehicle parts, and building facades.
2. Copper:
Copper is a highly conductive metal that is widely used in electrical wiring, plumbing, and electronics. Its excellent conductivity makes it invaluable for transmitting electricity and heat efficiently. Copper is also sought after for its antimicrobial properties, making it ideal for healthcare applications such as hospitals and water purification systems.
3. Zinc:
Zinc is primarily used as a protective coating for steel and iron to prevent corrosion, a process known as galvanization. It is widely used in construction, automotive manufacturing, and infrastructure projects. Zinc is also an essential component of batteries, making it vital for energy storage systems and electric vehicles.
4. Nickel:
Nickel is valued for its resistance to corrosion, high melting point, and conductivity. It is commonly used in the production of stainless steel, which is used in various applications, including cutlery, kitchen appliances, and construction materials. Nickel is also an important component in batteries, particularly in rechargeable batteries used in electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems.
5. Lead:
Lead has a long history of use in batteries, especially in automotive batteries. It is also used in the construction industry for roofing materials, pipes, and radiation shielding. However, due to its toxicity, lead usage is strictly regulated to protect human health and the environment.
Industrial metals play a critical role in driving economic growth and technological advancements. Investments in industrial metals can be made through futures contracts, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), or mining company stocks, enabling investors to capitalize on the demand for these metals driven by industrial and infrastructure developments.
In summary, industrial metals are the building blocks of modern society, supporting industries ranging from construction and manufacturing to electronics and renewable energy. Their versatility and durability make them indispensable for a wide array of applications, ensuring the continued demand for these hard commodities in the global marketplace.
Energy Commodities
Energy commodities are a vital category of hard commodities that power industries, transportation, and everyday life. These commodities are necessary for energy production and play a significant role in shaping global economies and energy markets.
1. Crude Oil:
Crude oil is the most widely traded energy commodity, serving as a major source of fuel for transportation, heating, and electricity generation. It is refined into various products such as gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, and lubricants. The price of crude oil is influenced by factors such as geopolitical events, supply and demand dynamics, and OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries) policies.
2. Natural Gas:
Natural gas is a versatile energy commodity used for heating, electricity generation, and as a feedstock in various industrial processes, including the production of fertilizers and chemicals. It is considered a cleaner alternative to coal and oil, leading to its increased use in power generation. The price of natural gas is affected by factors such as weather patterns, supply and demand dynamics, and geopolitical factors.
3. Coal:
Coal has been traditionally used as a fuel for electricity generation and industrial processes. However, its usage has declined in recent years due to environmental concerns over greenhouse gas emissions. Despite this decline, coal still plays a significant role in some regions and industries, particularly in countries with abundant coal reserves.
4. Uranium:
Uranium is a key energy commodity used in nuclear power generation. It is a highly efficient source of energy with low carbon emissions. Nuclear power plants generate electricity by harnessing the energy released through nuclear fission. The price of uranium is influenced by factors such as geopolitical events, nuclear energy policies, and the demand for clean energy sources.
Investing in energy commodities can be done through various instruments, including futures contracts, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and energy company stocks. It is important to consider factors such as geopolitical stability, supply and demand trends, and government regulations when making investment decisions in the energy commodity markets.
Energy commodities are essential drivers of economic growth and are subject to price volatility due to factors like global energy demand, geopolitical tensions, and advancements in renewable energy technologies. Understanding the dynamics of energy markets is crucial for investors looking to capitalize on opportunities in this sector.
Agricultural Commodities
Agricultural commodities are a vital category of hard commodities that consist of crops and livestock products. These commodities are essential for the food industry, providing sustenance and raw materials for various consumer goods. They are influenced by factors such as weather conditions, global demand for food, economic factors, and government policies.
1. Wheat:
Wheat is one of the most widely consumed grains globally and a staple food for many cultures. It is used in various forms, such as bread, pasta, and pastries. The price of wheat is often influenced by factors such as global weather patterns, production levels, and export/import policies of major wheat-producing countries.
2. Corn:
Corn, also known as maize, is a primary cereal crop used in animal feed, ethanol production, and food products. It has a wide range of applications, from snack foods to sweeteners and biofuels. The corn market is influenced by factors such as weather conditions, global demand for animal feed, and government policies supporting biofuel production.
3. Soybeans:
Soybeans are a versatile legume used for various purposes like animal feed, vegetable oil, and food products. They are a significant source of protein in many diets around the world. The soybean market is influenced by factors such as weather conditions, global demand for animal protein, and trade policies.
4. Cotton:
Cotton is a soft fiber used in the textile industry to produce clothing, bedding, and other textile products. The cotton market is influenced by factors such as weather conditions, global demand for textiles, and government policies related to subsidies and trade restrictions.
5. Sugar:
Sugar is a sweetener, widely used in culinary applications and the food and beverage industry. It can be derived from sugarcane or sugar beets. The sugar market is influenced by factors such as weather conditions, production levels, global demand, and government policies related to trade and subsidies.
Agricultural commodities provide investment opportunities through futures contracts, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and commodity indices. Investing in agricultural commodities allows investors to diversify their portfolios and gain exposure to the global agriculture industry.
Understanding the supply and demand dynamics, weather patterns, and government policies impacting agricultural commodities is crucial for investors and traders looking to participate in this market and navigate the various opportunities and risks it presents.
Factors Influencing Hard Commodities Prices
Several factors can significantly impact the prices of hard commodities. Understanding these factors is essential for investors and traders looking to analyze and predict price movements in the commodities market. Here are some key factors that influence hard commodities prices:
1. Supply and Demand:
The fundamental principle of supply and demand plays a vital role in determining commodity prices. When the demand for a commodity outweighs its supply, prices tend to rise. Conversely, when supply exceeds demand, prices tend to decline. Factors such as population growth, economic development, weather conditions, and geopolitical events can affect supply and demand dynamics in the commodities market.
2. Economic Conditions:
Economic conditions, both globally and domestically, have a significant impact on commodities prices. When the economy is growing robustly, the demand for commodities, particularly industrial metals and energy resources, tends to increase, driving prices higher. Conversely, during economic downturns, the demand for commodities may decline, leading to lower prices.
3. Geopolitical Events:
Geopolitical events, such as conflicts, wars, and political instability, can disrupt the production, transportation, and supply of hard commodities. These events can lead to supply disruptions, driving up commodity prices. For example, political tensions in major oil-producing countries can cause disruptions in oil supplies and result in higher crude oil prices.
4. Currency Movements:
The value of currencies relative to commodities can impact their prices. A weaker currency can make commodities more expensive for countries that import them, leading to a decrease in demand and potential price declines. Conversely, a stronger currency can make commodities more affordable, bolstering demand and potentially pushing prices higher.
5. Weather Conditions:
Weather conditions, such as droughts, floods, hurricanes, and other natural disasters, can significantly impact the production of agricultural commodities. Crop failures or reduced yields due to adverse weather conditions can lead to supply shortages and subsequent price increases in agricultural commodities like wheat, corn, and soybeans.
6. Government Policies:
Government policies, including trade tariffs, subsidies, regulations, and taxation, can have a substantial impact on commodity prices. For instance, import or export restrictions can affect the flow of commodities, influencing their prices. Similarly, subsidies or incentives provided by governments can impact the production and consumption of certain commodities.
It is important to note that these factors do not operate in isolation but often interact with and influence each other. Monitoring and analyzing these factors can help investors make more informed decisions when participating in the commodities market.
Investing in Hard Commodities
Investing in hard commodities can offer investors an opportunity to diversify their portfolios and potentially profit from the global demand for these essential resources. Here are some ways in which investors can participate in the commodities market:
1. Direct Ownership:
One way to invest in hard commodities is through direct ownership. Investors can physically own commodities such as gold or silver bullion, which can be stored securely. However, direct ownership requires careful consideration of storage and security arrangements.
2. Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs):
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) provide investors with a convenient way to gain exposure to a diversified portfolio of hard commodities. These ETFs are traded on stock exchanges and aim to track the price movements of specific commodities or commodity indices. ETFs offer liquidity, flexibility, and ease of trading compared to direct ownership.
3. Commodity Futures Contracts:
Commodity futures contracts allow investors to speculate on the future price of a specific commodity. Investors enter into a contract to buy or sell a specified quantity of the commodity at a predetermined price and date in the future. Futures contracts involve leverage and are commonly used by active traders and speculators seeking short-term price movements.
4. Commodity-Linked Stocks:
Investing in companies involved in the production, exploration, or distribution of hard commodities is another way to gain exposure to the commodities market. These companies’ stock prices are influenced by the price movements of the commodities they deal in. Investors can analyze and select individual stocks or invest in commodity-focused mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that hold a diversified portfolio of commodity-related stocks.
5. Commodity Index Funds:
Commodity index funds enable investors to gain exposure to a broad basket of commodities or a specific commodity sector. These funds aim to track the performance of a specific commodity index. Investing in index funds can provide diversification across different commodities and reduce the risk associated with investing in individual commodities.
When investing in hard commodities, it is crucial to conduct thorough research, monitor global trends, and stay informed about geopolitical events and economic factors that can influence commodity prices. Additionally, investors should consider their risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon before making investment decisions in the commodities market.
It is important to note that investing in commodities, like any investment, comes with risks. Commodity prices can be volatile and subject to supply and demand imbalances, geopolitical events, and economic fluctuations. Therefore, it is advisable for investors to seek professional advice and diversify their portfolios to mitigate the risks associated with investing in hard commodities.
Conclusion
Hard commodities play a significant role in the global economy, serving as essential resources for various industries and everyday life. Understanding the nature of hard commodities, their types, and the factors that influence their prices is crucial for investors and traders looking to capitalize on these valuable assets.
Precious metals, such as gold, silver, platinum, and palladium, hold a special place in the world of hard commodities. They are valued for their rarity, beauty, and utility in various industries. Industrial metals, including aluminum, copper, zinc, nickel, and lead, are essential for manufacturing and construction. Energy commodities such as crude oil, natural gas, coal, and uranium power industries and transportation. Agricultural commodities, such as wheat, corn, soybeans, cotton, sugar, and coffee, fuel the food industry and provide raw materials for consumer goods.
The prices of hard commodities are influenced by various factors, including supply and demand dynamics, economic conditions, geopolitical events, currency movements, weather conditions, and government policies. Understanding these factors is crucial for investors to analyze and predict price movements in the commodities market.
Investing in hard commodities can be done through direct ownership, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), commodity futures contracts, commodity-linked stocks, and commodity index funds. Each method offers its advantages and considerations, and investors should evaluate their risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon before making investment decisions in the commodities market.
While investing in hard commodities can provide diversification and potentially profitable opportunities, it is important to recognize the inherent risks associated with commodity investments. Commodity prices can be volatile, subject to supply and demand imbalances, geopolitical events, and economic fluctuations. Therefore, investors should conduct thorough research, seek professional advice, and diversify their portfolios to manage risks effectively.
In conclusion, hard commodities play a critical role in the global economy and offer investment opportunities for those looking to diversify their portfolios and potentially profit from the growing demand for these essential resources. By understanding the types of hard commodities, factors influencing their prices, and different investment avenues, investors can navigate the commodities market with greater confidence and enhance their overall investment strategy.